- +91 9884350006
- +1-972-502-9262
- [email protected]


Why is it important to do a literature review in research?
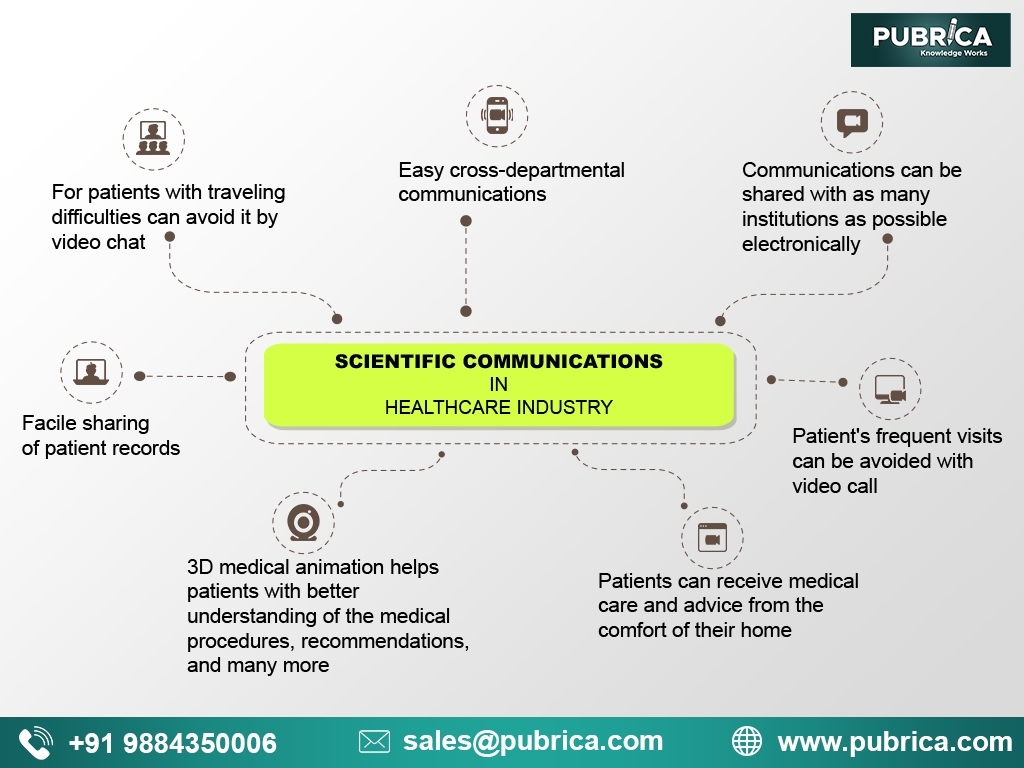
The importance of scientific communication in the healthcare industry
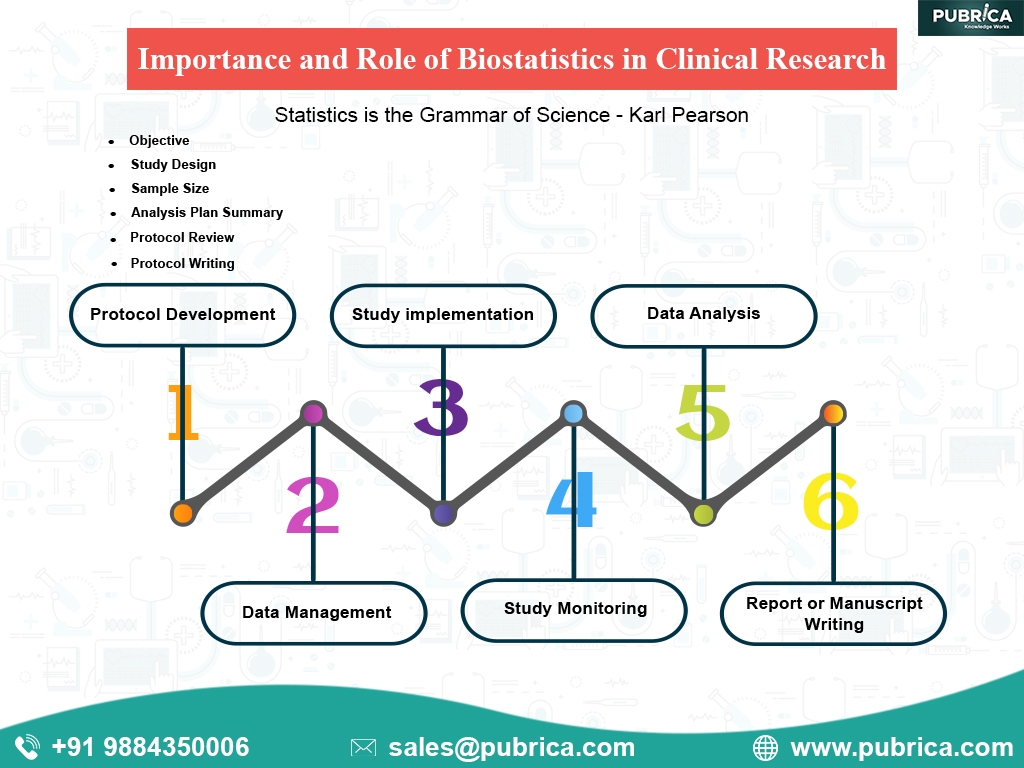
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
“A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research”. Boote and Baile 2005
Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review. Since it is one of the basic needs for researches at any level, they have to be done vigilantly. Only then the reader will know that the basics of research have not been neglected.
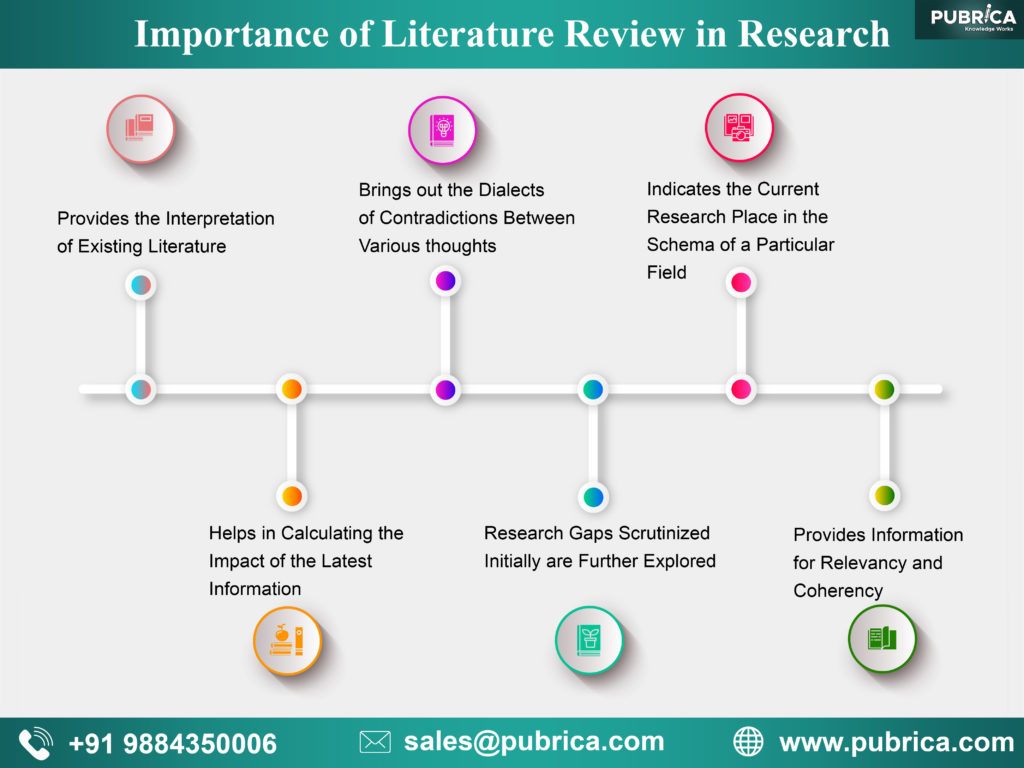
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research. It is possible only with profound knowledge of what is wrong in the existing findings in detail to overpower them. For other researches, the literature review gives the direction to be headed for its success.
The common perception of literature review and reality:
As per the common belief, literature reviews are only a summary of the sources related to the research. And many authors of scientific manuscripts believe that they are only surveys of what are the researches are done on the chosen topic. But on the contrary, it uses published information from pertinent and relevant sources like
- Scholarly books
- Scientific papers
- Latest studies in the field
- Established school of thoughts
- Relevant articles from renowned scientific journals
and many more for a field of study or theory or a particular problem to do the following:
- Summarize into a brief account of all information
- Synthesize the information by restructuring and reorganizing
- Critical evaluation of a concept or a school of thought or ideas
- Familiarize the authors to the extent of knowledge in the particular field
- Encapsulate
- Compare & contrast
By doing the above on the relevant information, it provides the reader of the scientific manuscript with the following for a better understanding of it:
- It establishes the authors’ in-depth understanding and knowledge of their field subject
- It gives the background of the research
- Portrays the scientific manuscript plan of examining the research result
- Illuminates on how the knowledge has changed within the field
- Highlights what has already been done in a particular field
- Information of the generally accepted facts, emerging and current state of the topic of research
- Identifies the research gap that is still unexplored or under-researched fields
- Demonstrates how the research fits within a larger field of study
- Provides an overview of the sources explored during the research of a particular topic
Importance of literature review in research:
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevancy of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gaps scrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherency to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point of any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing it with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more the reference of relevant sources of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not to repeat other’s original idea
- By preventing plagiarism , it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense and synthesize gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of the existing other researches
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately for allowing any new methodology of research than the existing ones
- Enables the readers of the manuscript to answer the following questions of its readers for its better chances for publication
- What do the researchers know?
- What do they not know?
- Is the scientific manuscript reliable and trustworthy?
- What are the knowledge gaps of the researcher?
22. It helps the readers to identify the following for further reading of the scientific manuscript:
- What has been already established, discredited and accepted in the particular field of research
- Areas of controversy and conflicts among different schools of thought
- Unsolved problems and issues in the connected field of research
- The emerging trends and approaches
- How the research extends, builds upon and leaves behind from the previous research
A profound literature review with many relevant sources of reference will enhance the chances of the scientific manuscript publication in renowned and reputed scientific journals .
References:
http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/phd6.pdf
journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific communication services
Related Topics:
Meta Analysis
Scientific Research Paper Writing
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Communication in healthcare
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Systematically Reviewing the Literature: Building the Evidence for Health Care Quality
Suzanne austin boren , phd, david moxley , mlis.
- Author information
- Copyright and License information
Contact: [email protected]
Corresponding author.
There are important research and non-research reasons to systematically review the literature. This article describes a step-by-step process to systematically review the literature along with links to key resources. An example of a graduate program using systematic literature reviews to link research and quality improvement practices is also provided.
Introduction
Systematic reviews that summarize the available information on a topic are an important part of evidence-based health care. There are both research and non-research reasons for undertaking a literature review. It is important to systematically review the literature when one would like to justify the need for a study, to update personal knowledge and practice, to evaluate current practices, to develop and update guidelines for practice, and to develop work related policies. 1 A systematic review draws upon the best health services research principles and methods to address: What is the state of the evidence on the selected topic? The systematic process enables others to reproduce the methods and to make a rational determination of whether to accept the results of the review. An abundance of articles on systematic reviews exist focusing on different aspects of systematic reviews. 2 – 9 The purpose of this article is to describe a step by step process of systematically reviewing the health care literature and provide links to key resources.
Systematic Review Process: Six Key Steps
Six key steps to systematically review the literature are outlined in Table 1 and discussed here.
Systematic Review Steps
1. Formulate the Question and Refine the Topic
When preparing a topic to conduct a systematic review, it is important to ask at the outset, “What exactly am I looking for?” Hopefully it seems like an obvious step, but explicitly writing a one or two sentence statement of the topic before you begin to search is often overlooked. It is important for several reasons; in particular because, although we usually think we know what we are searching for, in truth our mental image of a topic is often quite fuzzy. The act of writing something concise and intelligible to a reader, even if you are the only one who will read it, clarifies your thoughts and can inspire you to ask key questions. In addition, in subsequent steps of the review process, when you begin to develop a strategy for searching the literature, your topic statement is the ready raw material from which you can extract the key concepts and terminology for your strategies. The medical and related health literature is massive, so the more precise and specific your understanding of your information need, the better your results will be when you search.
2. Search, Retrieve, and Select Relevant Articles
The retrieval tools chosen to search the literature should be determined by the purpose of the search. Questions to ask include: For what and by whom will the information be used? A topical expert or a novice? Am I looking for a simple fact? A comprehensive overview on the topic? Exploration of a new topic? A systematic review? For the purpose of a systematic review of journal research in the area of health care, PubMed or Medline is the most appropriate retrieval tool to start with, however other databases may be useful ( Table 2 ). In particular, Google Scholar allows one to search the same set of articles as PubMed/MEDLINE, in addition to some from other disciplines, but it lacks a number of key advanced search features that a skilled searcher can exploit in PubMed/MEDLINE.
Examples of Electronic Bibliographic Databases Specific to Health Care
Note: These databases may be available through university or hospital library systems.
An effective way to search the literature is to break the topic into different “building blocks.” The building blocks approach is the most systematic and works the best in periodical databases such as PubMed/MEDLINE. The “blocks” in a “building blocks” strategy consist of the key concepts in the search topic. For example, let’s say we are interested in researching about mobile phone-based interventions for monitoring of patient status or disease management. We could break the topic into the following concepts or blocks: 1. Mobile phones, 2. patient monitoring, and 3. Disease management. Gather synonyms and related terms to represent each concept and match to available subject headings in databases that offer them. Organize the resulting concepts into individual queries. Run the queries and examine your results to find relevant items and suggest query modifications to improve your results. Revise and re-run your strategy based on your observations. Repeat this process until you are satisfied or further modifications produce no improvements. For example in Medline, these terms would be used in this search and combined as follows: cellular phone AND (ambulatory monitoring OR disease management), where each of the key word phrases is an official subject heading in the MEDLINE vocabulary. Keep detailed notes on the literature search, as it will need to be reported in the methods section of the systematic review paper. Careful noting of search strategies also allows you to revisit a topic in the future and confidently replicate the same results, with the addition of those subsequently published on your topic.
3. Assess Quality
There is no consensus on the best way to assess study quality. Many quality assessment tools include issues such as: appropriateness of study design to the research objective, risk of bias, generalizability, statistical issues, quality of the intervention, and quality of reporting. Reporting guidelines for most literature types are available at the EQUATOR Network website ( http://www.equator-network.org/ ). These guidelines are a useful starting point; however they should not be used for assessing study quality.
4. Extract Data and Information
Extract information from each eligible article into a standardized format to permit the findings to be summarized. This will involve building one or more tables. When making tables each row should represent an article and each column a variable. Not all of the information that is extracted into the tables will end up in the paper. All of the information that is extracted from the eligible articles will help you obtain an overview of the topic, however you will want to reserve the use of tables in the literature review paper for the more complex information. All tables should be introduced and discussed in the narrative of the literature review. An example of an evidence summary table is presented in Table 3 .
Example of an evidence summary table
Notes: BP = blood pressure, HbA1c = Hemoglobin A1c, Hypo = hypoglycemic, I = Internet, NS = not significant, PDA = personal digital assistant, QOL = quality of life, SMBG = self-monitored blood glucose, SMS = short message service, V = voice
5. Analyze and Synthesize Data and information
The findings from individual studies are analyzed and synthesized so that the overall effectiveness of the intervention can be determined. It should also be observed at this time if the effect of an intervention is comparable in different studies, participants, and settings.
6. Write the Systematic Review
The PRISMA 12 and ENTREQ 13 checklists can be useful resources when writing a systematic review. These uniform reporting tools focus on how to write coherent and comprehensive reviews that facilitate readers and reviewers in evaluating the relative strengths and weaknesses. A systematic literature review has the same structure as an original research article:
TITLE : The systematic review title should indicate the content. The title should reflect the research question, however it should be a statement and not a question. The research question and the title should have similar key words.
STRUCTURED ABSTRACT: The structured abstract recaps the background, methods, results and conclusion in usually 250 words or less.
INTRODUCTION: The introduction summarizes the topic or problem and specifies the practical significance for the systematic review. The first paragraph or two of the paper should capture the attention of the reader. It might be dramatic, statistical, or descriptive, but above all, it should be interesting and very relevant to the research question. The topic or problem is linked with earlier research through previous attempts to solve the problem. Gaps in the literature regarding research and practice should also be noted. The final sentence of the introduction should clearly state the purpose of the systematic review.
METHODS: The methods provide a specification of the study protocol with enough information so that others can reproduce the results. It is important to include information on the:
Eligibility criteria for studies: Who are the patients or subjects? What are the study characteristics, interventions, and outcomes? Were there language restrictions?
Literature search: What databases were searched? Which key search terms were used? Which years were searched?
Study selection: What was the study selection method? Was the title screened first, followed by the abstract, and finally the full text of the article?
Data extraction: What data and information will be extracted from the articles?
Data analysis: What are the statistical methods for handling any quantitative data?
RESULTS: The results should also be well-organized. One way to approach the results is to include information on the:
Search results: What are the numbers of articles identified, excluded, and ultimately eligible?
Study characteristics: What are the type and number of subjects? What are the methodological features of the studies?
Study quality score: What is the overall quality of included studies? Does the quality of the included studies affect the outcome of the results?
Results of the study: What are the overall results and outcomes? Could the literature be divided into themes or categories?
DISCUSSION: The discussion begins with a nonnumeric summary of the results. Next, gaps in the literature as well as limitations of the included articles are discussed with respect to the impact that they have on the reliability of the results. The final paragraph provides conclusions as well as implications for future research and current practice. For example, questions for future research on this topic are revealed, as well as whether or not practice should change as a result of the review.
REFERENCES: A complete bibliographical list of all journal articles, reports, books, and other media referred to in the systematic review should be included at the end of the paper. Referencing software can facilitate the compilation of citations and is useful in terms of ensuring the reference list is accurate and complete.
The following resources may be helpful when writing a systematic review:
CEBM: Centre for Evidence-based Medicine. Dedicated to the practice, teaching and dissemination of high quality evidence based medicine to improve health care Available at: http://www.cebm.net/ .
CITING MEDICINE: The National Library of Medicine Style Guide for Authors, Editors, and Publishers. This resource provides guidance in compiling, revising, formatting, and setting reference standards. Available at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7265/ .
EQUATOR NETWORK: Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research. The EQUATOR Network promotes the transparent and accurate reporting of research studies. Available at: http://www.equator-network.org/ .
ICMJE RECOMMENDATIONS: International Committee of Medical Journal Editors Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals. The ICJME recommendations are followed by a large number of journals. Available at: http://www.icmje.org/about-icmje/faqs/icmje-recommendations/ .
PRISMA STATEMENT: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Authors can utilize the PRISMA Statement checklist to improve the reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Available at: http://prisma-statement.org .
THE COCHRANE COLLABORATION: A reliable source for making evidence generated through research useful for informing decisions about health. Available at: http://www.cochrane.org/ .
Examples of Systematic Reviews To Link Research and Quality Improvement
Over the past 17 years more than 300 learners, including physicians, nurses, and health administrators have completed a course as part of a Master of Health Administration or a Master of Science in Health Informatics degree at the University of Missouri. An objective of the course is to educate health informatics and health administration professionals about how to utilize a systematic, scientific, and evidence-based approach to literature searching, appraisal, and synthesis. Learners in the course conduct a systematic review of the literature on a health care topic of their choosing that could suggest quality improvement in their organization. Students select topics that make sense in terms of their core educational competencies and are related to their work. The categories of topics include public health, leadership, information management, health information technology, electronic medical records, telehealth, patient/clinician safety, treatment/screening evaluation cost/finance, human resources, planning and marketing, supply chain, education/training, policies and regulations, access, and satisfaction. Some learners have published their systematic literature reviews 14 – 15 . Qualitative comments from the students indicate that the course is well received and the skills learned in the course are applicable to a variety of health care settings.
Undertaking a literature review includes identification of a topic of interest, searching and retrieving the appropriate literature, assessing quality, extracting data and information, analyzing and synthesizing the findings, and writing a report. A structured step-by-step approach facilitates the development of a complete and informed literature review.
Suzanne Austin Boren, PhD, MHA, (above) is Associate Professor and Director of Academic Programs, and David Moxley, MLIS, is Clinical Instructor and Associate Director of Executive Programs. Both are in the Department of Health Management and Informatics at the University of Missouri School of Medicine.

None reported.
- 1. Polit DF, Beck CT. Nursing Research: principles and methods. 9th edition. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Bruce J, Mollison J. Reviewing the literature: adopting a systematic approach. Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care. 2004;30(1) doi: 10.1783/147118904322701901. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Cronin P, Ryan F, Coughlin M. Undertaking a literature review: A step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008;17(1):38–43. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2008.17.1.28059. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Crowther DM. A clinician’s guide to systematic reviews. Nutr Clin Pract. 2013;28:459–462. doi: 10.1177/0884533613490742. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Hasse SC. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127:955–966. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318200afa9. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Mandrekar JN, Mandreker SJ. Systematic reviews and meta analysis of published studies: An over view and best practices. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6(8):1301–1303. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31822461b0. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Ng KH, Peh WC. Writing a systematic review. Singapore Med J. 2010 May;51(5):362–6. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Price B. Guidance on conducting a literature search reviewing mixed literature. Nursing Standard. 2009;23(24):43–49. doi: 10.7748/ns2009.02.23.24.43.c6829. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Engberg S. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis: Studies of studies. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2008;35(3):258–265. doi: 10.1097/01.WON.0000319122.76112.23. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Benhamou PY, Melki V, Boizel R, et al. One-year efficacy and safety of Web-based follow-up using cellular phone in type 1 diabetic patients under insulin pump therapy: the PumpNet study. Diabetes & Metabolism. 2007;33(3):220–6. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2007.01.002. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Marquez Contreras E, de la Figuera von Wichmann M, Gil Guillen V, Ylla-Catala A, Figueras M, Balana M, Naval J. Effective news of an inter vention to provide information to patients with hypertension as short text messages and reminder sent to their mobile phone [Spanish] Aten Primaria. 2004;34(8):399–405. doi: 10.1016/S0212-6567(04)78922-2. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–269. W64. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012;12(1):181. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-181. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Hart MD. Informatics competency and development within the US nursing population workforce. CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing. 2008;26(6):320–329. doi: 10.1097/01.NCN.0000336462.94939.4c. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Bryan C, Boren SA. The use and effectiveness of electronic clinical decision support tools in the ambulatory, primary care setting: A systematic review of the literature. Informatics in Primary Care. 2008 Jun;16(2):79–91. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v16i2.679. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- PDF (510.6 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help

YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral

Literature Review - what is a Literature Review, why it is important and how it is done
What are literature reviews, goals of literature reviews, types of literature reviews, about this guide/licence.
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
- Useful Resources
Help is Just a Click Away
Search our FAQ Knowledge base, ask a question, chat, send comments...
Go to LibAnswers
What is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries. " - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d) "The literature review: A few tips on conducting it"
Source NC State University Libraries. This video is published under a Creative Commons 3.0 BY-NC-SA US license.
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what have been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed a new light into these body of scholarship.
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature reviews look at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic have change through time.
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
- Narrative Review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : This is a type of review that focus on a small set of research books on a particular topic " to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches" in the field. - LARR
- Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L.K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . San Diego, CA: Plural Publishing.
- Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M.C. & Ilardi, S.S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Malden, MA: Blackwell Pub.
- Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). "Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts," Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53(3), 311-318.
Guide adapted from "Literature Review" , a guide developed by Marisol Ramos used under CC BY 4.0 /modified from original.
- Next: Strategies to Find Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/Literature-Review
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Service update: Some parts of the Library’s website will be down for maintenance on August 11.
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: why do a literature review, why do a literature review.
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed.
You identify:
- core research in the field
- experts in the subject area
- methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
- gaps in knowledge -- or where your research would fit in
It Also Helps You:
- Publish and share your findings
- Justify requests for grants and other funding
- Identify best practices to inform practice
- Set wider context for a program evaluation
- Compile information to support community organizing
Great brief overview, from NCSU
Want To Know More?
- Next: How To Find "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research.
To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address; To develop your theoretical framework and methodology; To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic; Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
By integrating findings and perspectives from many empirical findings, a literature review can address research questions with a power that no single study has. It can also help to provide an overview of areas in which the research is disparate and interdisciplinary.
There are important research and non-research reasons to systematically review the literature. This article describes a step-by-step process to systematically review the literature along with links to key resources.
A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas. Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
What is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are.
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are.
Conducting a literature review is essential for developing a research idea, to consolidate what is already known about a subject and to enable you to identify any knowledge gaps and how your research could contribute to further understanding.
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed. You identify: core research in the field. experts in the subject area. methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Helps focus your own research questions or problems. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas. Suggests unexplored ideas or populations.