
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

9 Closing a Speech: End with Power and Let Them Know It is Time to Clap

Open Your Speech With a Bang Close It With a Slam-Dunk Westside Toastmasters
“Great is the art of beginning, but greater is the art of ending,” according to poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow. The first few words of your speech make the audience want to listen and the last few sentences help them decide what they feel about you and your topic. In this chapter, I will explain the function of a conclusion, the format of a conclusion, and I will give you numerous examples of ways to end your speech. Most of this chapter is dedicated to showing you good examples of different types of speech closings. Let’s get started by talking about the purpose of the closing.
A Strong Closing Does Many Things
- Summarizes the points. By restating your points your audience is more likely to remember them.
- Tells the audience when to clap. Let’s face it, it is so awkward when you are done with your speech, and no one claps. Being clear the end is near, relieves the audience of the pressure of wondering if they are clapping at the right time.
- Provides resolution. Your speech should give the audience a sense of resolve or a sense of being challenged.
The Formula for Closing Most Speeches
- Transition statement to ending.
- Review the main points–repeat the thesis.
- If it is a persuasive speech, tell the audience what you want them to do or think.
- Provide a closing statement.
Restate the Thesis
Tell them what you are going to say, say it, tell them what you have said. This speech pattern is useful in most types of speeches because it helps the speaker to remember your key points. As you build your closing, make sure you restate the thesis. A good rule of thumb is to write it in such a way that if the audience were asked to restate the main points, their answer would match closely with your thesis.
EXAMPLE Watch as Stella Young gives her thesis and then restates her thesis at the end of the speech as she wraps up. The thesis of the talk in the introduction: We’ve been sold the lie that disability is a Bad Thing, capital B, capital T. It’s a bad thing, and to live with a disability makes you exceptional. It’s not a bad thing, and it doesn’t make you exceptional. Restates the thesis of the talk at the closing: Disability doesn’t make you exceptional but questioning what you think you know about it does.
Stella Young, I’m not your inspiration, thank you very much. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GtPGrLoU5Uk
This next example is from a student’s speech. It is easy to pull out one sentence that clearly summarizes the main points of her speech. Following her summary, she winds the speech down into a thoughtful conclusion and ends with three powerful words.
Now is the time to separate the war on drugs from the war on addiction. T oday you’ve heard the problems, impacts, and solutions of criminalizing addictions. Bruce Callis is 50 years old now. And he is still struggling with his addiction. while you all are sitting out there listening to this, I’m living with it. Bruce Callis is my father and for my entire life, I have watched our misguided system destroy him. The irony here is that we live in a society where we are told to recycle. We recycle paper, aluminum, and electronics. But why don’t we ever consider recycling them most precision think on Earth– the human life. Student Tunnette Powell, Winner of the 2012 Interstate Oratorical Association Contest.
Closing Phrases
After you restate your thesis, you should carefully deliver your closing phrases. Your closing should provide a resolution to your speech and/or it should challenge the audience. Frantically Speaking writer Hrideep Barot suggests “a conclusion is like tying a bow or ribbon to a box of your key ideas that your audience will be taking along with them.”
A speech closing is not just about the words you say, but it is also the way you say it. Change the pace near the end of your speech. Let your tone alone should signal the end is near. It is about deliberate voice control, don’t let your voice weakly away.
In the next section, I will cover these ways to end your speech:
End with powerful words End with a quote End with a graphic End with parallel construction End on a positive note End with a challenge End with a question End with inspiration End with well-wishing End with humor End with a call to action End with a feeling of resolve End with a prop
The best way to teach you about advanced closings is to show not tell. For this section, I will briefly explain each type of closing and then provide a video. Each video is queued so you can play the video and watch the closing statement. I included a transcript under each video if you want to follow along. It will be most beneficial for you to watch the clip and not just read the text. By watching, you will have a chance to hear the subtle changes in the speaker’s voice as they deliver their closing statements.
End with Powerful Words
As you design your closing, look at the last three to five words and examine them to see if they are strong words. Oftentimes, you can rearrange a sentence to end with a powerful word. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Watch this clip for how BJ Miller ends with a powerful thought and a powerful word.
Parts of me died early on, and that’s something we can all say one way or another. I got to redesign my life around this fact, and I tell you it has been a liberation to realize you can always find a shock of beauty or meaning in what life you have left, like that snowball lasting for a perfect moment, all the while melting away. If we love such moments ferociously, then maybe we can learn to live well — not in spite of death, but because of it. Let death be what takes us, not lack of imagination. BJ Miller, What Really Matters at the End of Life
End by Circling Back to the Opening
Another type of ending is to circle back to what you said in the beginning. You can revisit a quote, share the end to an illustration that was begun in the beginning, or you can put away a prop you got out in the beginning.
Watch this clip for how Zubing Zhang begins and ends with the same quote to circle back around to the main idea.
She starts by telling a story of bungee jumping off the world’s highest platform and how she saw a sign with a quote that says, “Life begins at the edge of your comfort zone.” After telling her own story about pushing her emotional limits, she circles back around at the end by saying, “As the words said high on the bungee platform, “Life begins at the edge of your comfort zone.”
Yubing Zhang, Life Begins at the End of Your Comfort Zone.
End With Quote
If you end your speech with a quote, attend to the following.
- Always say the author of the quote before the quote for example, “I want to leave you with a leadership quote ‘What you do has far greater impact than what you say,’ Steven Covey.” The problem with this ending is that “Stephen Covey” are the last two words of the speech and that is boring. Consider instead this ending. “I think Robin Sharma said it best ‘Leadership is not about a title or a designation. It’s about impact, influence, and inspiration.'” In this arrangement, the last three words are powerful–influence and inspiration.
- Provided context for the quote before or after. Make sure the quote is meaningful and not just an easy way to end.
Watch this clip for how Sir Ken Robinson ends with a quote. Notice how he says the author and then the quote.
Also, notice how he then ties his speech to the quote with a final few sentences and ends with the powerful word–“revolution” and how he uses a strong vocal emphasis as he says his last word. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
There’s a wonderful quote from Benjamin Franklin. “There are three sorts of people in the world: Those who are immovable, people who don’t get it, or don’t want to do anything about it; there are people who are movable, people who see the need for change and are prepared to listen to it; and there are people who move, people who make things happen.” And if we can encourage more people, that will be a movement. And if the movement is strong enough, that’s, in the best sense of the word, a revolution. And that’s what we need.
Sir Ken Robinson, How to Escape Education’s Death Valley.
End with a Graphic
You might want to use a visual to make your final point. Bringing in a picture, graphic, or object, reengages the audience to pay attention to your final ideas.
Watch this clip for how Barry Schartz uses the magic words “so to conclude” and then he creatively uses a picture of a fishbowl to narrow in on his point. Notice how his final word is spoken with urgency as he says “disaster.” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
So, to conclude. (He shows a picture of fish in a fishbowl) He says, “You can be anything you want to be — no limits.” You’re supposed to read this cartoon and, being a sophisticated person, say, “Ah! What does this fish know? Nothing is possible in this fishbowl.” Impoverished imagination, a myopic view of the world –that’s the way I read it at first. The more I thought about it, however, the more I came to the view that this fish knows something. Because the truth of the matter is, if you shatter the fishbowl so that everything is possible, you don’t have freedom. You have paralysis. If you shatter this fishbowl so that everything is possible, you decrease satisfaction. You increase paralysis, and you decrease satisfaction. Everybody needs a fishbowl. This one is almost certainly too limited –perhaps even for the fish, certainly for us. But the absence of some metaphorical fishbowl is a recipe for misery and, I suspect, disaster. Barry Schwartz, The Paradox of Choice
End with Parallel Construction
Parallel construction is a series of repeated phrases. It can be a powerful tool to use in a persuasive speech as it creates a feeling of importance.
Watch this clip for how Malala Yousafzai ends with a series of parallel statements to build momentum. Notice how her pace perfectly matches her words and you feel her strength when she ends with “education first.” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Dear brothers and sisters, we must not forget that millions of people are suffering from poverty, injustice, and ignorance. We must not forget that millions of children are out of schools. We must not forget that our sisters and brothers are waiting for a bright peaceful future. So let us wage a global struggle against illiteracy, poverty, and terrorism, and let us pick up our books and pens. They are our most powerful weapons. One child, one teacher, one pen, and one book can change the world. Education is the only solution. Education First.
Malala Yousafzai, United Nations Youth Assembly
End on a Positive Note
Audiences are constantly evaluating a speaker to determine their attitude and motivation. As you consider your speech closing, ask yourself what type of impression do you want to leave? Do you want to leave them with depression or hope? Sadness or promise? Most of the time, audiences will receive messages that end positively better than speeches that end negatively.
In this speech sample, Hans Rosling showed the audience some hard statistics and he even pointed fingers at the audience as part of the problem. To help them hear his main point, he wisely ends on a positive note.
Watch this clip for how Hans Rosling ends this thought-provoking talk on a positive note. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Now, when thinking about where all this leaves us, I have just one little humble advice for you, besides everything else, look at the data. Look at the facts about the world and you will see where we are today and how we can move forwards with all these billions on our wonderful planet. The challenge of extreme poverty has been greatly reduced and it’s for the first time in history within our power to end it for good. The challenge of population growth is, in fact, already being solved, the number of children has stopped growing. And for the challenge for climate change, we can still avoid the worst, but that requires the richest, as soon as possible, find a way to use their set their use of resources and energy at a level that, step by step, can be shared by 10 billion or 11 billion by the end of this century. I’ve never called myself an optimist, but I do say I’m a possibilist and I also say the world is much better than many of you think.
Hans Rosling, Facts about the Population.
End with a Challenge
Leave the audience with a doable personal challenge. Help them mentally make sense of all the information that you shared by helping them know how to file it away and how to use it.
Watch this clip for how Melissa Butler ends with a challenge. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
So, I challenge each of you, when you go home today, look at yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all of your greatness that you embody, accept it, and love it. And finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn’t look like you . Melissa Butler, Why You Think You’re Ugly.
Watch this clip as Darren LaCroix literally falls face down to anchor the point that when we fall, we “fall forward.” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Darren LaCroix talks about taking risks and falling down and getting back up, he literally and purposefully falls down during his speech and ends this way: What’s your next step… take it. I didn’t want to look back at my life and say you know I never did try that comedy thing, but I died debt-free. All of us are headed toward that goal we are going to teach a point where we get stuck and our feet are like in cement and we can’t move but we’re so afraid of that ouch but we forget that if we lean forward and take a risk–(He falls face down) and we fall on our face. When we get up, notice, you still made progress. So please, with me, go ahead and fall. But fall forward. Darren LaCroiz, Winning Speech delivered at National Speech Association
End with a Question
Asking a question at the end is one way to reengage the audience. It helps them think about what your topic might mean for them.
Watch this clip for how David Eagleman reminds us about why his topic is important and then ends with a question. Notice how he pauses before his final question and how he changes the pace of his speech for the final sentence. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
So I think there’s really no end to the possibilities on the horizon for human expansion. Just imagine an astronaut being able to feel the overall health of the International Space Station, or, for that matter, having you feel the invisible states of your own health, like your blood sugar and the state of your microbiome, or having 360-degree vision or seeing in infrared or ultraviolet. So the key is this: As we move into the future, we’re going to increasingly be able to choose our own peripheral devices. We no longer have to wait for Mother Nature’s sensory gifts on her timescales, but instead, like any good parent, she’s given us the tools that we need to go out and define our own trajectory. So the question now is, how do you want to go out and experience your universe?
David Eagleman, Can We Create New Senses for Humans?
Watch this clip for how Lera Boroditsky ends with a personal note and a powerful final question. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
I want to leave you with this final thought. I’ve told you about how speakers of different languages think differently, but of course, that’s not about how people elsewhere think. It’s about how you think. It’s how the language that you speak shapes the way that you think. And that gives you the opportunity to ask, “Why do I think the way that I do?” “How could I think differently?” And also, “What thoughts do I wish to create?” Lera Boroditsky, How Language Shapes the Way We Think
End with Inspiration
“Inspiring your audience is all about helping them see their own vision, not yours.”
You may want to end your speech with inspiring and encouraging words. Pick words that resonate with most of your audience and deliver them in such a way that your audience feels your lift in emotion.
Watch this clip for how Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie ends with an inspiring final note and a powerful last few words “regain a kind of paradise” (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
Stories matter. Many stories matter. Stories have been used to dispossess and to malign, but stories can also be used to empower and humanize. Stories can break the dignity of a people, but stories can also repair that broken dignity.
I would like to end with this thought: That when we reject the single-story, when we realize that there is never a single story about any place, we regain a kind of paradise.
Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie, The Danger of a Single Story
Watch this clip for how Dan Pink ends with an inspiring final note. (I have the video cued to play just the closing) Let me wrap up. There is a mismatch between what science knows and what business does. Here is what science knows. One: Those 20th century rewards, those motivators we think are a natural part of business, do work, but only in a surprisingly narrow band of circumstances. Two: Those if-then rewards often destroy creativity. Three: The secret to high performance isn’t rewards and punishments, but that unseen intrinsic drive– the drive to do things for their own sake. The drive to do things cause they matter.
And here’s the best part. We already know this. The science confirms what we know in our hearts. So, if we repair this mismatch between what science knows and what business does, if we bring our motivation, notions of motivation into the 21st century, if we get past this lazy, dangerous, ideology of carrots and sticks, we can strengthen our businesses, we can solve a lot of those candle problems, and maybe, maybe — we can change the world. I rest my case. Dan Pink, The Puzzle of Motivation
End with Well Wishing
There are several types of closings where the speaker wished the audience well.
The Benediction Close: M ay God bless and keep you…. The Presidential Close: God bless you and may God bless the USA The Congratulatory Close: I congratulate you on your accomplishment and wish you continued success.
End with Humor
You can end on a fun lighthearted note. It is important to always run your humor by a variety of people to make sure you are funny, and your humor is appropriate.
Watch this clip for how Andrew Dunham uses humor throughout his speech and ends with a funny one-liner. (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
I wish you all the best as we begin this journey on our paths and I sincerely hope and pray that your time and success have proven to be as memorable and spiritually rewarding as mine. If not, there’s always summer school.
Andrew Dunham, Valedictorian Comes Out As Autistic During Speech
End with a Call to Action
If you are delivering a persuasive speech, let the audience know exactly what you want them to do.
End with a Feeling of Resolve
Paul Harvey made famous the line “And now you know…the rest of the story.” Your closing should allow us to know the rest of the story or to know how a situation was resolved.
Watch this clip for how Lucy Hone ends this tough but inspiring talk with a feeling of resolve (I have the video cued to play just the closing)
https://youtu.be/9-5SMpg7Q0k?t=913 If you ever find yourself in a situation where you think there’s no way I’m coming back from this, I urge you to lean into these strategies and think again. I won’t pretend that thinking this way is easy and it doesn’t remove all the pain. But if I’ve learned anything over the last five years, it is that thinking this way really does help. More than anything it has shown me that it is possible to live and grieve at the same time. And for that I will be always grateful. Lucy Hone, The Three Secrets of Resilient People
End with a Prop
Nancy Duarte says you should give your audience, SOMETHING THEY will ALWAYS REMEMBER–S.T.A.R. One way to do that is with an action or statement that will have the audience talking about it for a long time. President Obama did it with a mic drop.
Memorize Your Conclusion
End on time.
Do not diminish the effect of a great speech with a bloated, aimless conclusion. Dan Rothwell.
“Times about up.”
Don’t end with any references to time. It is like a giant stop sign saying, “stop listening.” Don’t highlight that you ran over time or that it is almost time for lunch. You want them to think about your speech, not the clock.
“Any Questions?”
You want them to feel a sense of closure for your speech. End with something powerful and let them applaud. After the applause, you can offer to answer questions. Similarly, projecting your last slide with the words, “Any Questions” is a weak ending.
“Let Me Add This Point I Missed”
If you forget something in the body of your speech, it is usually best to leave it out. Most of the time you are the only one who will miss it.
“Thank You to the Team”
There is a time to thank the organizers and those who helped you but it is not at the end of your speech. Your focus should be on your audience and what they need and what they need to hear is your idea. Send a thank you letter to the team if you want them to feel your appreciation.
“I’m Sorry”
“Sorry again for the technology issue,” “I apologize for going over time, ” “I regret I have no answer to this.” These are all negative phrases. Keep to your topic that is what they need to hear and stay focused.
“I’ll Close with this Video”
No, you should close with talking about the big idea.
If you don’t have a plan at the end, you will ramble. “Steer clear of meandering endings they kill a story,” according to the Moth Storytelling website. “Your last line should be clear in your head before you start. Yes, bring the audience along with you as you contemplate what transpires in your story, but remember, you are driving the story, and must know the final destination. Keep your hands on the wheel!”
To Thank or Not to Thank, That is the Question
There is a debate amongst speech professionals, speech teachers, and speech coaches about whether or not you should thank the audience. Here are their main arguments.
Why You Should Not Say Thank You
- You want to end with powerful words. “Thank you” are not strong words.
- The recency effect suggests they will remember the last words you spoke. You want them to remember more than just “thank you.”
- It is not a very creative way to end.
- It can be a sign of a lazy speaker, “I have no idea how to end this, I’ve run out of good things to say so I’ll say ‘Thank you’ so you will clap now.”
Why You Should Say Thank You
- It has come to be the expected ending in many settings. Violating their expectations can cause them to have a negative reaction.
- It clearly signals you are finished so the audience knows when to clap. The relieves the pressure from both you and the audience.
- It expresses gratitude.
I will leave it up to you to decide what works for you. As for me, I plan on trying to find more creative ways to end other than just saying “thank you.”
Maximizing the Primacy Recency Effect
If I were to read you a list of thirty things on my grocery list and then asked you to list all that you can remember, chances are you would remember the first times on the list and the last items on the list ( and any ones you found interesting from the middle). When people engage in listening, they tend to remember the first and last things they hear, it is called the primacy-recency effect. T his is just one more reason that your introduction and conclusion should be so well planned out. It is those first words and last words that the audience is going to remember.
The primacy recency effect influences, not only what people pay attention to in a speech, but also which speech we pay the most attention to in a series of speeches. For example, if there is a lineup of six speakers, the first and last speakers tend to get the most attention.
As a speaker, you can use this information to your advantage by volunteering to go first or last. If you are giving a long presentation, you can break it up by allowing the audience to move around or talk to a neighbor. When you come back from break, you have re-engaged that primacy effect and moved them back to a high state of attention.
Do You Have Everything You Need for a Strong Closing?
- Have I signaled my speech is coming to an end with my words or my voice?
- Have I restated my main points?
- If I am persuading my audience, do they know what I want them to do or think?
- Have I written the last three to five words in such a way that I end with powerful words?
- Have I memorized my closing?
Getting Off the Platform is Part of Your Closing
Plan on making a strong exit. Whether you are stepping off a stage or simply going to your seat, you should consider that the audience is watching you.
I have had students who finished their speech and then walked over to the trashcan and in a large, exaggerated movement, they threw their notecards in the trash. In our minds, we threw their message away with those cards. I’ve seen speakers, sit in their chairs and then announce, “I can’t believe my hands were shaking so much.” I’ve sat there and thought, “I didn’t notice.” I then realized that the comments they made influenced my perception of them and my perception of their topic.
You said your last word and the audience is applauding, now what? Look at your audience and smile and nod in appreciation before walking off the stage. If you will be answering questions, wait until after the applause stops to begin your question and answering period.
When practicing your speech, it is a good idea to start from your chair, walk up to a spot and then give your speech, and then walk back to your chair and sit down. Your “speech” impression begins and ends from your chair.
Key Takeaways
Remember This!
- A speech closing should include a review of the main points and a purposeful closing sentence.
- Persuasive speech endings should tell the audience specifically what they should do or think about.
- The recency effect suggests that people remember the most recent things they have heard which is one reason the closing is so important.
- Chance the pace of your speech and the tone of your voice to signal the end of the speech.
Please share your feedback, suggestions, corrections, and ideas.
I want to hear from you.
Do you have an activity to include? Did you notice a typo that I should correct? Are you planning to use this as a resource and do you want me to know about it? Do you want to tell me something that really helped you?
Click here to share your feedback.
Adichie, C.N. (2009). The danger of a single story. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D9Ihs241zeg Standard YouTube License.
Anderson, C. (2016). TED talks: The official TED guide to public speaking. Mariner Books.
Barot, H. Fifteen powerful speech ending lines (and tips to create your own). Frantically Speaking. https://franticallyspeaking.com/15-powerful-speech-ending-lines-and-tips-to-create-your-own/
Boroditsky, L. (2017). How language shapes the way we think. https://www.ted.com/talks/lera_boroditsky_how_language_shapes_the_way_we_think Standard Youtube License.
Butler, M. (2018). Why you think you’re ugly. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=imCBztvKgus Standard YouTube License.
Dunham. A. (2019). Valedictorian comes out as autistic during speech. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GtPGrLoU5Uk Standard Youtube License.
Eagleman, D. (2015). Can we create new senses for humans?[Video]. YouTube https://youtu.be/4c1lqFXHvqI Standard YouTube License.
Hone, L. (2019). The three secrets of resilient people. [Video]. YouTube https://youtu.be/NWH8N-BvhAw Standard YouTube License.
Jeff, P. (2009). Ten ways to end your speech with a bang. http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/10-ways-to-end-your-speech
Jobs, S. (2005). You’ve got to find what you love. https://news.stanford.edu/2005/06/14/jobs-061505/
Khanna, P. (2016). Let the head of TED show you how to end your speech with power. https://www.fastcompany.com/3059459/let-the-head-of-ted-show-you-how-to-end-your-speech-with-p
Karia, A. (2013). How to open and close a TED talk (or any other speech or presentation). https://akashkaria.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/HowtoOpenandCloseaTEDTalk.pdf
LaCroix, D. (2001). World champion of public speaking. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FUDCzbmLV-0 Standard YouTube License.
Mandela, N. (2011). Speech from the dock in the Rivonia trial.[Video]. YouTube https://www.nelsonmandela.org/news/entry/i-am-prepared-to-die Standard YouTube License.
Mandela, N. (1994). Presidential Inaugural Speech. [Video]. YouTube https://www.americanrhetoric.com/speeches/nelsonmandelainauguralspeech.htm Standard YouTube License.
Miller, B.J. (2015). What really matters at the end of life. [Video]. YouTube https://www.ted.com/talks/bj_miller_what_really_matters_at_the_end_of_life?language=en Standard YouTube License.
Moth. (2021). Storytelling tips and tricks: How to tell a successful story. https://themoth.org/share-your-story/storytelling-tips-tricks
Obama, B. (2016). White House correspondents dinner. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NxFkEj7KPC0 Standard YouTube License.
Pink, D. (2009). The puzzle of motivation. [Video]. YouTube https://www.ted.com/talks/dan_pink_the_puzzle_of_motivation Standard YouTube License.
Rothwell, D. (2014). Practically Speaking. Oxford University Press.Robinson, K. (2013). How to escape education’s death valley. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wX78iKhInsc Standard YouTube License.
Rosling, H. (2014). Don’t Panic-Hans Rosling showing the facts about population.[Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FACK2knC08E Standard YouTube License.
Schwartz, B. (2005). The paradox of choice. [Video]. YouTube https://www.ted.com/talks/barry_schwartz_the_paradox_of_choice Standard YouTube License.
Toastmasters International. (2016). Concluding your Speech. https://www.toastmasters.org/Resources/Concluding-Your-Speech
Young, S. (2014). I’m not your inspiration, thank you very much. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GtPGrLoU5Uk Standard YouTube License.
Yousafzai, M. (2013). Malala Yousafzai addresses United Nations Youth Assembly. [Video]. YouTube https://youtu.be/3rNhZu3ttIU Standard YouTube License.
Zhang, Y. (2015). Life begins at the end of your comfort zone. [Video]. YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cmN4xOGkxGo Standard YouTube License.
Media Attributions
- Audience clapping © Alex Motoc is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- jose-aragones-81QkOoPGahY-unsplash © Jose Aragones is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
Advanced Public Speaking Copyright © 2021 by Lynn Meade is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- Blogging Aloud
- About me/contact
- How to end a speech effectively
How to end a speech memorably
3 ways to close a speech effectively.
By: Susan Dugdale
Knowing how, and when, to end a speech is just as important as knowing how to begin. Truly.
What's on this page:
- why closing well is important
- 3 effective speech conclusions with examples and audio
- 7 common ways people end their speeches badly - what happens when you fail to plan to end a speech memorably
- How to end a Maid Honor speech: 20 examples
- links to research showing the benefits of finishing a speech strongly

Why ending a speech well is important
Research * tells us people most commonly remember the first and last thing they hear when listening to a speech, seminar or lecture.
Therefore if you want the audience's attention and, your speech to create a lasting impression sliding out with: "Well, that's all I've got say. My time's up anyway. Yeah - so thanks for listening, I guess.", isn't going to do it.
So what will?
* See the foot of the page for links to studies and articles on what and how people remember : primacy and recency.
Three effective speech conclusions
Here are three of the best ways to end a speech. Each ensures your speech finishes strongly rather than limping sadly off to sure oblivion.
You'll need a summary of your most important key points followed by the ending of your choice:
- a powerful quotation
- a challenge
- a call back
To work out which of these to use, ask yourself what you want audience members to do or feel as a result of listening to your speech. For instance;
- Do you want to motivate them to work harder?
- Do you want them to join the cause you are promoting?
- Do you want them to remember a person and their unique qualities?
What you choose to do with your last words should support the overall purpose of your speech.
Let's look at three different scenarios showing each of these ways to end a speech.
To really get a feel for how they work try each of them out loud yourself and listen to the recordings.
1. How to end a speech with a powerful quotation

Your speech purpose is to inspire people to join your cause. Specifically you want their signatures on a petition lobbying for change and you have everything ready to enable them to sign as soon as you have stopped talking.
You've summarized the main points and want a closing statement at the end of your speech to propel the audience into action.
Borrowing words from a revered and respected leader aligns your cause with those they fought for, powerfully blending the past with the present.
For example:
"Martin Luther King, Jr said 'The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy.'
Now is the time to decide. Now is the time to act.
Here's the petition. Here's the pen. And here's the space for your signature.
Now, where do you stand?"
Try it out loud and listen to the audio
Try saying this out loud for yourself. Listen for the cumulative impact of: an inspirational quote, plus the rhythm and repetition (two lots of 'Now is the time to...', three of 'Here's the...', three repeats of the word 'now') along with a rhetorical question to finish.
Click the link to hear a recording of it: sample speech ending with a powerful quotation .
2. How to end a speech with a challenge

Your speech purpose is to motivate your sales force.
You've covered the main points in the body of it, including introducing an incentive: a holiday as a reward for the best sales figures over the next three weeks.
You've summarized the important points and have reached the end of your speech. The final words are a challenge, made even stronger by the use of those two extremely effective techniques: repetition and rhetorical questions.
"You have three weeks from the time you leave this hall to make that dream family holiday in New Zealand yours.
Can you do it?
Will you do it?
The kids will love it.
Your wife, or your husband, or your partner, will love it.
Do it now!"
Click the link to listen to a recording of it: sample speech ending with a challenge . And do give it a go yourself.
3. How to end a speech with a call back

Your speech purpose is to honor the memory of a dear friend who has passed away.
You've briefly revisited the main points of your speech and wish in your closing words to leave the members of the audience with a happy and comforting take-home message or image to dwell on.
Earlier in the speech you told a poignant short story. It's that you return to, or call back.
Here's an example of what you could say:
"Remember that idyllic picnic I told you about?
Every blue sky summer's day I'll see Amy in my mind.
Her red picnic rug will be spread on green grass under the shade of an old oak tree. There'll be food, friends and laughter.
I'll see her smile, her pleasure at sharing the simple good things of life, and I know what she'd say too. I can hear her.
"Come on, try a piece of pie. My passing is not the end of the world you know."
Click the link to hear a recording of it: sample speech ending with a call back . Try it out for yourself too. (For some reason, this one is a wee bit crackly. Apologies for that!)
When you don't plan how to end a speech...
That old cliché 'failing to plan is planning to fail' can bite and its teeth are sharp.
The 'Wing It' Department * delivers lessons learned the hard way. I know from personal experience and remember the pain!
How many of these traps have caught you?
- having no conclusion and whimpering out on a shrug of the shoulders followed by a weak, 'Yeah, well, that's all, I guess.', type of line.
- not practicing while timing yourself and running out of it long before getting to your prepared conclusion. (If you're in Toastmasters where speeches are timed you'll know when your allotted time is up, that means, finish. Stop talking now, and sit down. A few seconds over time can be the difference between winning and losing a speech competition.)
- ending with an apology undermining your credibility. For example: 'Sorry for going on so long. I know it can be a bit boring listening to someone like me.'
- adding new material just as you finish which confuses your audience. The introduction of information belongs in the body of your speech.
- making the ending too long in comparison to the rest of your speech.
- using a different style or tone that doesn't fit with what went before it which puzzles listeners.
- ending abruptly without preparing the audience for the conclusion. Without a transition, signal or indication you're coming to the end of your talk they're left waiting for more.
* Re The 'Wing It' Department
One of the most galling parts of ending a speech weakly is knowing it's avoidable. Ninety nine percent of the time it didn't have to happen that way. But that's the consequence of 'winging it', trying to do something without putting the necessary thought and effort in.
It's such a sod when there's no one to blame for the poor conclusion of your speech but yourself! ☺
How to end a Maid of Honor speech: 20 examples
More endings! These are for Maid of Honor speeches. There's twenty examples of varying types: funny, ones using Biblical and other quotations... Go to: how to end a Maid of Honor speech

How to write a speech introduction
Now that you know how to end a speech effectively, find out how to open one well. Discover the right hook to use to captivate your audience.
Find out more: How to write a speech introduction: 12 of the very best ways to open a speech .

More speech writing help

You do not need to flail around not knowing what to do, or where to start.
Visit this page to find out about structuring and writing a speech .
You'll find information on writing the body, opening and conclusion as well as those all important transitions. There's also links to pages to help you with preparing a speech outline, cue cards, rehearsal, and more.
Research on what, and how, people remember: primacy and recency
McLeod, S. A. (2008). Serial position effect . (Primacy and recency, first and last) Simply Psychology.
Hopper, Elizabeth. "What Is the Recency Effect in Psychology?" ThoughtCo, Feb. 29, 2020.
ScienceDirect: Recency Effect - an overview of articles from academic Journals & Books covering the topic.
- Back to top of how to end a speech page
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
- Personal Development
- Sales Training
- Business Training
- Time Management
- Leadership Training
- Book Writing
- Public Speaking
- Live Speaker Training With Brian
- See Brian Speak
- Coaching Programs
- Become a Coach
- Personal Success
- Sales Success
- Business Success
- Leadership Success
- How to End a Speech: What You Need for a Bang
A good talk or public speech is like a good play, movie, or song.
It opens by arresting the listener’s attention, develops point by point, and then ends strongly, ensuring that the audience’s attention is maintained throughout.
The truth is, if you don’t know how to end a speech, the overall message won’t be persuasive and your key points may get lost.
The words you say at the beginning, and especially at the end of your talk, are usually the most persuasive parts of the speech and will be remembered longer than almost any other part of your speech. It’s crucial to leave a lasting impression with a powerful conclusion.
Some of the great speeches in history and some of the most memorable Ted talks have ended with powerful, stirring words that live on in memory.
How do you end a speech and get the standing ovation that you deserve?
Keep reading to discover how…
Here are 9 tips and examples for concluding a speech.
To ensure that your conclusion is as powerful as it can be, you must plan it word for word, including a strong closing statement.
Ask yourself, “What is the purpose of this talk?”
Your answer should involve the actions that you want your listeners to take after hearing you speak on this subject.
When you are clear about the end result you desire, it becomes much easier to design a conclusion that asks your listeners to take that action. It is also crucial to restate a key idea to reinforce your message and leave a lasting impression.
The best strategy for ending with a BANG is to plan your close before you plan the rest of your speech.
You then go back and design your opening so that it sets the stage for your conclusion.
The body of your talk is where you present your ideas and make your case for what you want the audience to think, remember, and do after hearing you speak.
2) Always End A Speech With A Call To Action
It is especially important to tell the audience what you want it to do as a result of hearing you speak.
A call to action is the best way to wrap up your talk with strength and power. Reinforce your key points by summarizing the main message, ensuring it leaves a lasting impression. Closing the speech effectively can evoke emotions and make a significant impact on the audience.
Here’s a Speech Call To Action Example
“We have great challenges and great opportunities, and with your help, we will meet them and make this next year the best year in our history!”
Consider ending with a thought-provoking question to challenge the audience to think differently and inspire them to take action.
Whatever you say, imagine an exclamation point at the end. As you approach the conclusion, pick up your energy and tempo. This is even more important if the presentation you are giving is virtual .
Speak with strength and emphasis.
Drive the final point home.
Regardless of whether the audience participants agree with you or are willing to do what you ask, it should be perfectly clear to them what you are requesting.
3) End a Speech With a Summary
There is a simple formula for any talk:
- Tell them what you are going to tell them.
- Then, tell them what you told them.
As you approach the end of your talk, say something like,
“Let me briefly restate these main points…”
You then list your key points, one by one, and repeat them to the audience, showing how each of them links to the other points.
Audiences appreciate a linear repetition of what they have just heard. This repetition helps make your message memorable and ensures that your key points leave a lasting impression.
This makes it clear that you are coming to the end of your talk.
4) Close with a Story
As you reach the end of your talk, you can say,
“Let me tell you a story that illustrates what I have been talking about…”
You then tell a brief story with a moral and then tell the audience what the moral is. Using effective body language, such as maintaining eye contact, smiling, and using open gestures, can make your story more impactful and leave a lasting impression.
Don’t leave it to them to figure out for themselves.
Often you can close with a story that illustrates your key points and then clearly links to the key message that you are making with your speech.
To learn more about storytelling in speaking, you can read my previous blog post “8 Public Speaking Tips to Wow Your Audience.”
5) Make Them Laugh
You can close with humor.
You can tell a joke that loops back into your subject and repeats the lesson or main point you are making with a story that makes everyone laugh.
During my talks on planning and persistence, I discuss the biggest enemy that we have, which is the tendency to follow the path of least resistance. I then tell this story.
Ole and Sven are out hunting in Minnesota and they shoot a deer. They begin dragging the deer back to the truck by the tail, but they keep slipping and losing both their grip and their balance.
A farmer comes along and asks them, “What are you boys doing?”
They reply, “We’re dragging the deer back to the truck.”
The farmer tells them, “You are not supposed to drag a deer by the tail. You’re supposed to drag the deer by the handles. They’re called antlers. You’re supposed to drag a deer by the antlers.”
Ole and Sven say, “Thank you very much for the idea.”
They begin pulling the deer by the antlers. After about five minutes, they are making rapid progress. Ole says to Sven, “Sven, the farmer was right. It goes a lot easier by the antlers.”
Sven replies, “Yeah, but we’re getting farther and farther from the truck.”
After the laughter dies down, I say…
“The majority of people in life are pulling the easy way, but they are getting further and further from the ‘truck’ or their real goals and objectives.”
A memorable statement like this can make the humor more effective by condensing the core message into a crisp and authentic sound bite.
That’s just one example of closing using humor.
6) Make It Rhyme
You can close with a poem.
There are many fine poems that contain messages that summarize the key points you want to make. Here are some practical tips for selecting and delivering a poem: choose a poem that resonates with your message, practice your delivery to ensure it flows naturally, and use appropriate pauses to emphasize key lines.
You can select a poem that is moving, dramatic, or emotional.
For years I ended seminars with the poem, “Don’t Quit,” or “Carry On!” by Robert W. Service. It was always well received by the audience.
7) Close With Inspiration for A Lasting Impression
You can end a speech with something inspirational as well.
If you have given an uplifting talk, remember that hope is, and has always been, the main religion of mankind.
People love to be motivated and inspired to be or do something different and better in the future.
Here are a few of my favorite inspirational quotes that can be tied into most speeches. You can also read this collection of leadership quotes for further inspiration.
Remember, everyone in your audience is dealing with problems, difficulties, challenges, disappointments, setbacks, and temporary failures.
For this reason, everyone appreciates a poem, quote, or story of encouragement that gives them strength and courage.
Here are 7 Tips to Tell an Inspiring Poem or Story to End Your Speech
- You have to slow down and add emotion and drama to your words.
- Raise your voice on a key line of the poem, and then drop it when you’re saying something that is intimate and emotional.
- Pick up the tempo occasionally as you go through the story or poem, but then slow down on the most memorable parts.
- Especially, double the number of pauses you normally use in a conversation.
- Use dramatic pauses at the end of a line to allow the audience to digest the words and catch up with you.
- Smile if the line is funny, and be serious if the line is more thought-provoking or emotional.
- When you come to the end of your talk, be sure to bring your voice up on the last line, rather than letting it drop. Remember the “exclamation point” at the end to reinforce your main message and leave a lasting impression.
Try practicing on this poem that I referenced above…
Read through “Carry On!” by Robert Service
Identify the key lines, intimate parts, and memorable parts, and recite it.
8) Make it Clear That You’re Done
When you say your final words, it should be clear to everyone that you have ended. A strong closing statement is crucial in signaling the end of your speech, leaving a lasting impression, and ensuring that the audience remembers the key points. There should be no ambiguity or confusion in the mind of your audience. The audience members should know that this is the end.
Many speakers just allow their talks to wind down.
They say something with filler words like, “Well, that just about covers it. Thank you.”
This isn’t a good idea…
It’s not powerful…
It’s not an authoritative ending and thus detracts from your credibility and influence.
When you have concluded, discipline yourself to stand perfectly still. Select a friendly face in the audience and look straight at that person.
If it is appropriate, smile warmly at that person to signal that your speech has come to an end.
Resist the temptation to:
- Shuffle papers.
- Fidget with your clothes or microphone.
- Move forward, backward, or sideways.
- Do anything else except stand solidly, like a tree.
9) Let Them Applaud
When you have finished your talk, the audience members will want to applaud. Using effective body language, such as maintaining eye contact, smiling, and using open gestures, can signal to the audience that it is time to begin clapping.
What they need from you is a clear signal that now is the time to begin clapping.
How do you signal this?
Some people will recognize sooner than others that you have concluded your remarks.
In many cases, when you make your concluding comments and stop talking, the audience members will be completely silent.
They may be unsure whether you are finished.
They may be processing your final remarks and thinking them over. They may not know what to do until someone else does something.
In a few seconds, which will often feel like several minutes, people will applaud.
Then another…
Then the entire audience will begin clapping.
When someone begins to applaud, look directly at that person, smile, and mouth the words thank you.
As more and more people applaud, sweep slowly from person to person, nodding, smiling and saying, “Thank You.”
Eventually, the whole room will be clapping.
There’s no better reward for overcoming your fear of public speaking than enjoying a round of applause.
BONUS TIP: How to Handle a Standing Ovation
If you’ve given a moving talk and really connected with your audience, someone will stand up and applaud. To encourage a standing ovation, make your message memorable by using repetition of your keyword or phrase and incorporating relevant visuals or metaphors to leave a lasting impression on the audience. When this happens, encourage others by looking directly at the clapper and saying, “Thank you.”
This will often prompt other members of the audience to stand.
As people see others standing, they will stand as well, applauding the whole time.
It is not uncommon for a speaker to conclude his or her remarks, stand silently, and have the entire audience sit silently in response.
Stand Comfortably And Shake Hands
But as the speaker stands there comfortably, waiting for the audience to realize the talk is over, one by one people will begin to applaud and often stand up one by one. Using positive body language, such as maintaining eye contact, smiling, and using open gestures, can leave a lasting impression on the audience.
If the first row of audience members is close in front of you, step or lean forward and shake that person’s hand when one of them stands up to applaud.
When you shake hands with one person in the audience, many other people in the audience feel that you are shaking their hands and congratulating them as well.
They will then stand up and applaud.
Soon the whole room will be standing and applauding.
Whether you receive a standing ovation or not, if your introducer comes back on to thank you on behalf of the audience, smile and shake their hand warmly.
If it’s appropriate, give the introducer a hug of thanks, wave in a friendly way to the audience, and then move aside and give the introducer the stage.
Follow these tips to get that standing ovation every time.
« Previous Post Goal Setting for Success & Developing SMART Habits Next Post » 7 Tips for Writing Motivation: Stay Motivated When Writing a Book
About Brian Tracy — Brian is recognized as the top sales training and personal success authority in the world today. He has authored more than 60 books and has produced more than 500 audio and video learning programs on sales, management, business success and personal development, including worldwide bestseller The Psychology of Achievement. Brian's goal is to help you achieve your personal and business goals faster and easier than you ever imagined. You can follow him on Twitter , Facebook , Pinterest , Linkedin and Youtube .
- Most Recent
- Top 10 Leadership Qualities of Great Leaders
- How to Write a Book: Proven Start-to-Finish Steps
- 117 Leadership Quotes for Inspiration
- 7 Tips for Writing Motivation: Stay Motivated When Writing a Book
- Free Webinar: How To Write a Book and Become a Published Author
- Free Video Series: 3-Part Sales Mastery Training Series
- Free Assessment: The Confidence Factor
- Free Assessment: Discovering Your Talents
Browse Categories
- Financial Success
Follow Brian & Join the Discussion
- Free Resources
- Best Sellers
- Knowledge Base
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Policy
- About Brian
- Brian Recommends
Your Privacy is Guaranteed. We will never give, lease or sell your personal information. Period!
© Copyright 2001-2024 Brian Tracy International. All Rights Reserved.
How to End a Speech: The Best Tips and Examples
I like building and growing simple yet powerful products for the world and the worldwide web.
Published Date : February 16, 2024
Reading Time :
As the introduction sets the stage, your conclusion seals the deal. The question, “How do you end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ?” is an essential query that each presenter or speaker must ask, given the final words’ impact and weight on your audience.
Since your final words eventually have a lasting effect, you must make a striking thought to the people. Your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s ending is your last opportunity to reiterate the fundamental idea, inspire the listeners , motivate a group to take action, change an individual’s perspective, or make a final impression on them.
If you are still wondering how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that can appease your audience, then be worry-free because this guide can help you. Read this article to learn how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , a graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , and more because it contains the best tips and examples.
Why is a Conclusion Important?
The audience is more likely not to forget the latest thing a speaker said due to the “Recency Effect” in learning. Hence, the conclusion of a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech serves as a signal to the audience that it is nearing the end, helping them recall the entire topic’s essential points.
You can’t just suddenly stop speaking in front of your listeners because that will disappoint and confuse them. It is best to ensure they are left satisfied and knowledgeable about your speeches by closing them smoothly.
Additionally, it is vital always to link your conclusion back to your introduction. The most effective way to do this method is through going back to your attention grabber or “hook.”
At the end of your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , it is where most of your audience’s lasting impression of everything you have said will form. Thus, if you ask how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , use its conclusion to secure the necessary components in your listeners’ minds.
You might confuse, disappoint, or even leave the audience unconvinced without a satisfactory conclusion. With these thoughts, we can tell that it has a two-fold purpose: to signal the Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s end and reinforce the speaker’s message to the people.
The Key Elements of a Good Conclusion
When contemplating how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , remember that your introduction is the appetizer, while your conclusion is its dessert. Conclusions must round off the topic and make a strong impression on people’s minds.
To create a conclusion that will satisfy and sum up all the vital information from your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , consider these three key elements:
1. Reiterate the main idea
What is the central idea of your message? That is a secure place to start your conclusion.
Above all, you have directed each part of your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech to support your topic, subject, or information. To start your conclusion, by all means, reiterate your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s main idea.
Of course, making it different and fresh to the listeners would be best. You do not want to repeat it verbatim, making the audience feel like you are just redoing things.
Somewhat loosen it up as you prepare to remind your audience why they would be well-provided to adopt your viewpoint or follow your suggestion.
2. Summarize three primary points
Another vital element to answer your question on how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is summarizing. For your overall summary, getting three main points is a good benchmark.
You do not have to restate each argument or claim because you can eventually pick three that you think are the most remarkable. In regards to your main idea, do not be dry and monotonous.
Avoid merely repeating three points; show your audience how those points strengthened your claim or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Draw them together into a single special force, supplementing weight to your primary idea.
3. Close on a high note
Leave your audience pleased and satisfied but also wanting more. When you are closing your conclusion, consider ending it with a capturing, thought-provoking concept.
You may want to raise a rhetorical question or state a notable quote from your research. From time to time, good quotations serve as illustrations, stating what we want to mention with a bit of Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence and style.
Another method to add some “food for thought” to your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s conclusion is to connect your primary idea to a more in-depth scenario. Also, note that your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s closing line needs extra effort .
The portion acts as your last opportunity to make it stick, so never introduce new information in your ending. Additional information can confuse your listeners and take them away from the essential features of a conclusion, which are:
- Restatement of your primary idea
- Summary of three main points
- Remarkable closing line
What are the Considerations on How to End a Speech?
When you imagine how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation, there are several things to consider when it comes to their close, which include:
- Is your ending engaging?
- Does your conclusion restate your message?
- Have you identified the next step you want your listeners to take clearly?
Too often, speakers or presenters believe that people will infer what they should act next. The reality or truth is that even the most talented speaker can benefit from setting off a clear call to action to their audience.
When it is particular, uncomplicated to perform, and aligns with the audience’s concerns, needs, and wants, they are more likely to take upon your persuasion , especially if you are making a persuasive speech.
Always consider that an impactful ending encourages, empowers, and motivates people. See the best tips in the next part to learn how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
What are some Good Ways to End a Speech?
A study shows that when they need to recall information, they best remember the beginning and the end. Therefore, impacting your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s closing is essential because people will mostly think of that part.
Here are seven different ways to choose and make an unforgettable ending for your audience if you still doubt how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech most appealingly.
1. The Summary Close
This method on how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is about the most direct, specific, and straightforward one on the list. The history of how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation also refers to this as a “recap” close.
If you end your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a summary, clarify your most significant idea and convey to the listeners that it is what you want them to take. However, that does not imply that your summary close is not engaging.
2. The Surprise Close
Several of the best movie endings of all time were surprising conclusions, outright shockers, and wicked twists. Why do you think they are so memorable?
It is because the viewers or the audience did not expect that ending. When we experience something we did not anticipate, it turns out that our brains are more active.
In other cases, we might have also expected a different or another scenario for the conclusion. Hence, we become notably accustomed to what occurs when a pattern breaks.
Closing a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a hint of surprise at its ending is like signaling your audience to listen to you.
3. The Illustrative Close
Another method to close your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is to do it in this way. The artistry in an illustrative close comes from your skill to correct the following:
- first or third-person anecdote
It can also refer to another storytelling device representing your illustration of the primary points you created during your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Many speakers use this manner at the start and end of their talks.
4. The Forward-looking Close
This method of closing a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is a better option if you discuss suggestions for future trends that could bear your topic. To help your audience visualize what you desire to accomplish, make a vibrant and vivid picture of it because it is essential.
For example, you are a financial consultant talking to a crowd 15 years away from retirement. During your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , share your company’s approach to investment or a portfolio of your products.
5. The Backward-looking Close
Besides the forward-looking close, there is also a backward-looking close. This way, you move away from the future and go into the past instead.
Let’s say you are wondering how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech as the bride’s sister and has spent so many years and memories with her. During your message, you can recall those moments. Then, from those past happenings, close your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech by wishing her a happy future with her husband.
6. The Metaphor Close
You might feel like you are drowning in options regarding how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . However, if you carefully look at your topic or subject and what you must convey, you will eventually find it easy as pie.
Welcome to the metaphor close. Yes, I just used some metaphors in the earlier part. Perhaps you had noticed them already before I pointed it out.
Metaphors are figures of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that indirectly compare two figuratively similar things but are distinct. You do not take it in a literal sense that you are drowning in options, but you can feel that way.
If you still don’t know how to end a graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , this method may be one of your best options.
7. The Provocative Close
Provocative refers to the tendency to provoke, stimulate, or excite. Of course, as the speaker or presenter, you hope to encourage your audience, but using a provocative close snaps them to attention.
Check the table for some examples of how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech provocatively.
| You close your " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0">speech by admitting that you disagree with the listeners in some areas but agree earnestly about the one you discussed in your message. | |
| You may also conclude with a forceful persuasion. This method can be remarkably convincing when you have power over the individuals you present. | |
| Another way is by mentioning the consequences if they choose not to act regarding your topic. You may want to picture an “if we fail to act” perspective, but it is also necessary to take it easy. |
How to End a PowerPoint Presentation?
When you provide cluttered visual presentations , instead of an illustration that draws the people in, you can use PowerPoint to make a memorable close.
You can encourage and bring out their curiosity through powerful visualization. To help you with this matter, we have provided options for ending a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a PowerPoint slide.
Here are a couple of samples of what you can project:
- A humorous image but has a profound significance.
- A photo that is supposedly unrelated to your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech subject or topic needs your explanation.
- A line graph shows two possible outcomes in which the audience may get involved.
How Should You End a Presentation Slideshow?
Since you have learned what you can project in your PowerPoint presentation and how useful it is to end your talk, let us get into several essential tips on finishing a formal presentation slideshow.
Here are ways you can do to make it memorable and impactful to your audience:
- Have a clear and concise message
To close your formal presentation slideshow, bring your fundamental message to the forefront and align it with your objectives. You must give your final message down to a notable point so that your audience can walk away remembering what you have said.
- Utilize the best final PowerPoint slide.
Your final slide will differ according to the type of presentation you are delivering.
For example, if you are still having second thoughts regarding how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech uniquely, maybe you can opt to make a slideshow presentation for your sister’s wedding. There are creative ways to give your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , especially when you are too nervous about Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking .
You only have to ensure that you are using a powerful final PowerPoint graphic slide to showcase your concluding information. Of course, you should fit its theme at the event.
- Use animation to highlight something.
Adding a hint of animation in your presentation or slideshow is one of the best ways to bring the significant element onto your slide at the perfect period. A program like PowerPoint has features, such as built-in animations, that you can efficiently utilize.
How to End a Speech Dos and Don’ts
After discussing the key elements of ending a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and ways to close your presentation, we should tackle how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s dos and don’ts.
We have compiled a few things that you must consider. See them in this table:
| Do give a signal. | Do not introduce extra or new material at the end of your " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0">speech. |
| Your conclusion should echo your " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0">speech. | Your conclusion must not be improvised or ad-libbed. |
| All your primary points must have already been well-explained in the body of your " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0">speech. | Avoid including unnecessary hand . |
| Summarize the primary points of your " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0">speech. | Do not move backward. |
| Emphasize in one line the essence of your " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0">speech to the listeners. | Do not lose focus. |
| Do not rush to gather your materials or other stuff. | |
| Do not be inconsistent with your message to the audience. |
How to End Your Speech Examples (video examples)
We have made your work easier if you seek the best examples of closing a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Be worry-free about how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , graduation address, and other presentations.
How to End a Graduation Speech
Here are four tips on how to end a graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that would give you big applause from the crowd:
- Plan every word of your closing remarks.
- Close it with a story.
- Insert a little humor and make the audience laugh.
- Close your graduation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with inspiration.
How to End a Maid of Honor Speech
Are you worried about how to end a maid of honor Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ? The following are the typical phrases used for the maid of honor speech ending:
- Let us all toast for the happiness of the newly married couple!
- Best wishes to the happy and lovely couple!
- Please raise your glasses in honor of the bride and groom.
- Cheers to the newlyweds!
- Wishing years of bliss to the bride and groom!
- What a beautiful wedding day, so let us toast wherever their lives may lead.
How to Close a Sales Presentation
Another example of how to end a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech we have is closing a Sales Pitch <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:394">A <strong>sales pitch</strong> is a persuasive presentation, often concise and direct, to convince a potential customer to purchase a product, service, or idea. While <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> can present a hurdle, effective communication remains critical. Consider exploring resources like <strong>speaking coaches</strong> to overcome anxiety and deliver pitches that resonate with confidence.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:134"><strong>Compelling value proposition:</strong> Communicate the unique benefits of your offering and how it solves the customer's problem.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:94"><strong>Targeted message:</strong> Tailor your pitch to the specific needs and interests of the customer.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:85"><strong>Strong opening:</strong> Grab attention with a catchy introduction or relevant question.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:102"><strong>Social proof:</strong> Leverage testimonials, statistics, or case studies to build trust and credibility.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Call to action:</strong> Clearly state your desired outcome, whether a purchase, investment or further discussion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:39"><strong>Benefits of a Powerful Sales Pitch:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:88"><strong>Increases sales and conversions:</strong> Converts interest into action and drives revenue.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:107"><strong>Builds rapport and trust:</strong> Connects with the customer personally and establishes credibility.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:104"><strong>Differentiates from competitors:</strong> Highlights the unique value proposition compared to alternatives.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:94"><strong>Educates and informs:</strong> Explain how your offering solves the customer's problem.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Generates leads and interest:</strong> Captures attention and encourages further conversation or consideration.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:35"><strong>Crafting a Winning Sales Pitch:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:92"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Research the customer's needs, challenges, and buying preferences.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:95"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Hone your delivery, timing, and responses to potential objections.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:106"><strong>Focus on benefits, not features:</strong> Explain how your offering improves the customer's life or business.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:95"><strong>Use storytelling:</strong> Weave a narrative that showcases the impact of your product or service.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Be enthusiastic and passionate:</strong> Convey your belief in the value you offer.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:56"><strong>Overcoming Fear of Public Speaking in Sales Pitches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:113"><strong>Focus on the customer's needs:</strong> Shift your focus away from your anxieties and onto helping the customer.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:102"><strong>Deep breathing exercises:</strong> Calm your nerves and improve oxygen flow before and during your pitch.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:98"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Replace negative thoughts with affirmations and focus on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:91"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practice and gain feedback in a supportive environment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Consider a speaking coach:</strong> They can provide personalized techniques to manage anxiety and improve delivery.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:464"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:464">A <strong>sales pitch</strong> is a conversation, not a monologue. By understanding the key elements, tailoring your message to the customer, and overcoming any <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>, you can deliver pitches that resonate, connect, and drive successful sales conversions. Consider exploring resources like <strong>speaking coaches</strong> for further support refining your communication skills and building the confidence to deliver winning sales pitches.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/sales-pitch/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">sales pitch . An outstanding presentation turns off if you do not try to create a great closing. To make your customers eager to purchase, try the tips we recommend.
- Go back to your opening idea.
- Close it with a challenge to your audience.
- Indulge your listeners into a metaphorical mission.
- Share a story.
- End your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with a quote.
How can you effectively call your audience to action?
To ignite action, be crystal clear with your desired action, use persuasive language to spark urgency, and highlight the benefits they’ll reap. Back it up with evidence, repeat it for impact, and remove any hurdles that stand in their way. Finally, it tugs at their heartstrings to connect and motivate them to follow through. This winning formula fuels effective calls to action!
What are some creative ways to end a presentation?
Spice up your presentation ending! Ditch the boring summary and opt for storytelling, metaphors, inspiring quotes, actionable steps, thought-provoking questions, surprising elements, laughter, or genuine gratitude. Choose what fits your style and leave your audience with a bang, not a whimper!
What should you not do when ending a presentation?
When concluding a presentation, it is important to avoid certain practices. One thing you should not do is end your presentation with a slide that simply asks “Questions?” This approach is commonplace and lacks originality, making it forgettable for your audience. Instead, it is crucial to consider alternative techniques for concluding your presentation on a strong and memorable note.
How can something from the opening be repeated to close a presentation?
Start strong, end strong! Bookend your presentation by repeating a thought-provoking question, concluding a captivating story, or tying back to your title. This creates a unified message, satisfying closure, and a lasting impression on your audience. They’ll leave remembering “the answer,” “the ending,” or “the meaning,” solidifying your impact.
What can be used instead of a “thank you” slide?
Ditch the “thank you” slide! Show gratitude verbally and utilize a summary slide with key points, a call to action, and your contact details. More text is okay here; use bullet points for Clarity <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:269">In <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>clarity</strong> refers to the quality of your message being readily understood and interpreted by your audience. It encompasses both the content and delivery of your speech, ensuring your message resonates and leaves a lasting impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:133"><strong>Conciseness:</strong> Avoid unnecessary details, digressions, or excessive complexity. Focus on delivering the core message efficiently.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Simple language:</strong> Choose words and phrases your audience understands readily, avoiding jargon or technical terms unless you define them clearly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:145"><strong>Logical structure:</strong> Organize your thoughts and ideas logically, using transitions and signposts to guide your audience through your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:136"><strong>Effective visuals:</strong> If using visuals, ensure they are clear, contribute to your message, and don't distract from your spoken words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:144"><strong>Confident delivery:</strong> Speak clearly and articulately, avoiding mumbling or rushing your words. Maintain good eye contact with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Active voice:</strong> Emphasize active voice for better flow and avoid passive constructions that can be less engaging.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:24"><strong>Benefits of Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:123"><strong>Enhanced audience engagement:</strong> A clear message keeps your audience interested and helps them grasp your points easily.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:123"><strong>Increased credibility:</strong> Clear communication projects professionalism and expertise, building trust with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:111"><strong>Improved persuasiveness:</strong> A well-understood message is more likely to resonate and win over your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Reduced confusion:</strong> Eliminating ambiguity minimizes misinterpretations and ensures your message arrives as intended.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-27:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:129"><strong>Condensing complex information:</strong> Simplifying complex topics without sacrificing crucial details requires skill and practice.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:128"><strong>Understanding your audience:</strong> Tailoring your language and structure to resonate with a diverse audience can be challenging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:85"><strong>Managing nerves:</strong> Nerves can impact your delivery, making it unclear or rushed.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-27:0"><strong>Avoiding jargon:</strong> Breaking technical habits and simplifying language requires constant awareness.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="28:1-28:22"><strong>Improving Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="30:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:117"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> The more you rehearse your speech, the more natural and clear your delivery will become.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:107"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech with others and ask for feedback on clarity and comprehension.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:161"><strong>Consider a public speaking coach:</strong> A coach can provide personalized guidance on structuring your message, simplifying language, and improving your delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:128"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practicing in a supportive environment can help you gain confidence and refine your clarity.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Listen to effective speakers:</strong> Analyze how clear and impactful others achieve communication.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Clarity</strong> is a cornerstone of impactful <strong>public speaking</strong>. By honing your message, focusing on delivery, and actively seeking feedback, you can ensure your audience receives your message clearly and leaves a lasting impression.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/clarity/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">clarity . It helps during Q&A; attendees might even snap a picture for a handy takeaway.
How can a running clock be used to emphasize the urgency of a message?
Tick-tock! Adding a running clock to your time-sensitive message visually screams urgency. It shows limited time, fuels action, grabs attention, and boosts your message’s credibility. Don’t let your audience miss out – let the clock do the talking!
How can a surprising fact re-engage the audience’s attention?
Attention fading? Drop a surprising fact with stats! It jolts your audience awake, adds credibility, and keeps them hooked. Find it online, but cite your source to be extra legitimate. Facts rock; use them to rule your presentation!
How can the rule of three be used in communication?
Group in threes! This communication rule makes your message stick. Break down ideas, stories, or anything you say into triplets. It’s easy to remember, catchy and keeps your audience engaged with your message long after you’re done. So go forth and conquer with the power of three!
How can the main points be linked to the key message in the conclusion?
Ditch the swim, find the gem! Your conclusion reflects your whole Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Summarize key points, deliver a lasting impact, and tie it all together. Don’t leave it as an afterthought – make it resonate, leaving your audience nodding, satisfied, and remembering your message long after you’re done.
How can a visual image be used to end a presentation?
Don’t bore your audience with text! Ditch the cluttered slides and use a powerful image to end your presentation. Funny, thought-provoking, or a line graph with a choice – pick one to intrigue and make them think. Leave it on the screen for impact, let them ponder; your message will stick long after you’re done. Just remember, image and message go hand in hand!
How can a compelling story be used to conclude a presentation?
Forget jokes and platitudes. Close with a powerful story! Not just any story, one that makes them laugh, feel your message and remember it all. Your article mentions this, but their article goes deeper. They say to make it personal, relatable, and tied to your key points. This creates empathy, connection, and an unforgettable ending that leaves your audience wanting more. Go beyond the basics and tell a story they’ll remember long after the presentation.
What are the different ways to end a presentation or speech?
Ditch the panic. Pick your closing! Consider metaphors to leave a deep impression, challenge your audience with a “what if” scenario, or use visuals to stimulate their minds. Summarize key points, deliver a powerful message, and practice your ending for polish. Do avoid rambling, awkward gestures, or rushing out. Remember, a strong closing leaves a lasting mark. Now go captivate them!
In making your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s ending, do not make your conclusion only an afterthought. It should support everything you have said in your talk and remind the audience why your topic matters.
Leave the people nodding in agreement or satisfied by ending your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech remarkably. Yes, you can’t win everybody over your talk, but you can significantly make them pause and think.
We hope this article has imparted enough knowledge and answered your question about ending a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Download the Orai Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech app for an AI-powered Speech Coach <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:411">A <strong>speech coach</strong> is a trained professional who provides personalized guidance and support to individuals seeking to improve their <strong>public speaking</strong> skills. Whether you aim to <strong>master public speaking</strong> for professional presentations, overcome stage fright, or simply hone your everyday communication, a <strong>speech coach</strong> can tailor their expertise to meet your needs and goals.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:32"><strong>What Does a Speech Coach Do?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:124"><strong>Conduct assessments:</strong> Analyze your strengths, weaknesses, and communication style through evaluations and observations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Develop personalized plans:</strong> Create a customized roadmap with exercises, techniques, and feedback to address your specific areas of improvement.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:167"><strong>Offer expert instruction:</strong> We will guide you through various aspects of public speaking, including vocal control, body language, content delivery, and overcoming anxiety.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:168"><strong>Provide practice opportunities:</strong> Facilitate mock presentations, simulations, and role-playing scenarios to refine your skills in a safe and supportive environment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:114"><strong>Offer constructive feedback:</strong> Identify areas for improvement and suggest strategies for achieving your goals.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Boost confidence and motivation:</strong> Encourage and support you throughout your journey, empowering you to become a confident and impactful communicator.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:40"><strong>Who Can Benefit from a Speech Coach?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:174"><strong>Professionals:</strong> Refining public speaking skills can benefit executives, entrepreneurs, salespeople, leaders, and anyone who presents in professional settings.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:160"><strong>Students:</strong> Teachers, public speakers, debaters, and students wanting to excel in presentations or classroom settings can gain valuable skills with a coach.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:176"><strong>Individuals who fear public speaking:</strong> Coaching can help those who experience anxiety or nervousness when speaking in public develop strategies and gain confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Anyone seeking to improve communication:</strong> A coach can provide guidance to individuals seeking to enhance their communication skills for personal or professional development.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:28"><strong>Types of Speech Coaches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:110"><strong>Private coaches:</strong> Work one-on-one with individuals to provide highly personalized attention and feedback.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:130"><strong>Group coaches:</strong> Offer workshops or classes in group settings, often at a lower cost but with less individualized attention.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Specialization coaches:</strong> Some coaches specialize in executive communication, storytelling, or presentation design.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:35"><strong>Finding the Right Speech Coach:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-33:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:91"><strong>Identify your goals:</strong> What areas do you want to improve? What are your specific needs?</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:109"><strong>Research credentials and experience:</strong> Look for qualified coaches with relevant experience and expertise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:122"><strong>Consider availability and budget:</strong> Set a budget and explore options that fit your schedule and financial constraints.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-33:0"><strong>Schedule consultations:</strong> Talk to potential coaches to assess their personality, approach, and compatibility with your needs.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418">Investing in a <strong>speech coach</strong> can be a transformative experience, enhancing your communication skills, boosting your confidence, and empowering you to achieve your communication goals. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, consider exploring the potential of working with a <strong>speech coach</strong> to unlock your full potential as a communicator and <strong>master public speaking</strong>.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech-coach/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech coach for interactive and fun lessons!
Good luck with your presentation!
You might also like
How many words is a 5-minute speech, good attention getters for speeches with 10+ examples, quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

11 Best Closing Remarks To Use In A Speech
Quoting Yehuda Berg, “Words are singularly the most powerful force available to humanity .”
Your closing remarks in a speech help the audience remember the main points of your address and the reason you gave it. It’s a summary of your most essential points. As a result, more people will remember what you say at the beginning and end of your speech than anything said in between.
If you don’t end your speech with a power statement or call-to-action, it loses its appeal and the power you’ve built up. Closing remarks keep you from leaving your audience feeling confused and let down.
This guide can assist you if you want to design a Ted-style talk that can land you future speaking opportunities. Here are 11 of the finest closing remarks examples for speeches.
1. Using the Circle Concept to End Your Speech
The circle concept involves taking listeners on an adventure and bringing them back to where they began. In other words, you refer to the material you started your speech with by restating it at the end of your talk. Most speakers use quotes from movies, in-demand books, or popular phrases.
Our client, Christine Ramsay, often uses the circle concept in her speeches. One particular example is in a speech she gave on ‘ The Extraordinary Power of Neurodiversity ’ where she starts her address by quoting the famous movie, Toy Story: “To infinity and beyond.”

She concludes her speech with the exact same statement. This ending encourages her audience to release the inner brilliance and extraordinary powers of neurodivergent individuals for the benefit of all!
2. Using Humor In Speeches
Humor is an effective instrument in any speaker’s repertoire when used correctly, and it can have enormous benefits:
- It establishes a connection with the audience
- It energizes and keeps people interested
- It has the potential to provide emotional relief to the audience
- It aids the audience in remembering your points
- It gives the audience a favorable opinion of the speaker
So, whatever statement your speaker is attempting to convey, adding humor to the mix will make it a more prosperous and unforgettable speech. It will also give the audience the opportunity for better takeaways from speeches.
This is especially true if they choose to inject some humor into the speech’s closing remarks.
3. The Rule of Three Closing Remarks in a Speech
The Rule of Three is a useful method that helps you say what you want to say more clearly by highlighting your points and making your message easier to remember.
People are usually good at recognizing patterns; three is the lowest number to make a pattern. It can also have the most impact if you say it in the right tone of voice at the close of a speech. When information is given in groups of three, we remember it better than when in groups of, say, four or five.
Two very famous examples of using the rule of three in a speech are:
“Friends, Romans, Countrymen. Lend me your ears.” – Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar
“Government of the people, by the people, for the people.” – Abraham Lincoln’s famous Gettysburg speech
This example from Lincoln is also a great example of parallelism in a speech .
4. Tell a Story
Storytelling is a great way to make your speech stand out. Because stories connect with us as people, a short story can be an effective way to end an address. But it has to be pertinent to your speech and not go on for too long.
Using this method, you could end your speech with the same story you began in the introduction. This approach is mainly better for strong emotional appeal speech.

For example, Michelle Obama’s DNC speech was praised for its emotional appeal by discussing her life story of growing up on Chicago’s South Side and leaving an extensive law career for public service.
5. Finish Your Speech Using a Poem
Poetry effectively conveys your message as it helps you leave a mark on your audience’s minds. You can conclude your talk using a poem that sums up everything you’ve said. You can either create your own or choose one that works best with your speech. Keep in mind that if you choose one, quote the source.
While reciting a poem, use inflections of emotion and drama by raising your voice on a key phrase and pausing when necessary for emphasis.
6. Closing Off With a Quote to Remember
Another way to end is using quotes in speeches related to the topic of the address. Consider whether your goal was to finish on a compelling or enlightening note when you use a quote.
Some quotations call for action, whereas others will summarize or provoke thought.
Quoting strengthens your ideas. A quote adds a second voice to your claims, making them more powerful.
Maya Angelou best describes the impact emotions can have on a speech when she says,
“I’ve learned that people will forget what you said, people will forget what you did, but people will never forget how you made them feel.” Maya Angelou
7. Using Questions as Closing Remarks
Questions can become overwhelming for an audience if used too much throughout a speech. However, asking one at the end of the address is effective because your question will linger in the minds of your audience.

One example of a compelling closing remark question is what President Jimmy Carter asked during his campaign debate in 1980. Reagan asked the audience , “Are you better off than you were four years ago?”
Since then, this message has become a frequent question during every campaign season.
8. Throw Your Audience a Challenge
In addition to questions, challenges are exemplary alternative closing remarks. A challenge is an invitation to participate in an activity that requires extra effort.
What do you want your audience to do? Would you like them to take action? Such as voting, donating, signing up, or hiring you for their following speech?
By answering these questions, you can distinguish between a good speech and one that gets people to act.
For example, a presenter could conclude a speech on the importance of fund-raising by giving the audience a challenge to raise 15% more than their initial forecasts.
Make a challenge that is both ambitious and reasonable at the same time. The challenge should be seen as something to work towards but not impossible.
9. Use Inspiration With Your Closing Statement
Inspire means to move or excite. An inspirational concluding remark aims to stir someone’s emotions in a specific way that appeals to the audience’s values and emotions.
What’s the number one thing someone wants to hear about? Themselves, of course. So, if you want to inspire your audience, your content should be about them and how they can blossom.
When drafting your speech, create an image of your audience’s viewpoint and how your talk can help them reach that vision. Then, you can use stories or personal past experiences to relate to your audience and bring your message to life.
“I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed — we hold these truths to be self-evident: that all men are created equal.” Martin Luther King Jr.
One example of using inspiration in a closing statement is Martin Luther King Jr.’s “ I Have A Dream Speech .” He paints the picture of what life could be like if black and white people worked together. In doing so, he inspires thousands of individuals to make a difference in their communities.
10. Use Factual Evidence to End Your Speech
Your audience may yawn if you only use facts in a speech; however, they can empower a speech if you use them at the right time.
Using facts as a speech closing remark can help you re-engage your audience and keep them captivated. Only include facts pertinent to your topic. For example, Barack Obama used facts and logic to convince the audience of his views.
This is particularly apparent when he spoke in honor of the late Nelson Mandela during a speech in South Africa. In that speech, he mentions:
“You have to believe in facts. Without facts, there’s no basis for cooperation.” Barack Obama
Throughout the many speeches, he gives facts and issues to rally the American public to action.
11. Using an Appeal to Conclude Your Speech
The best approach to composing an impactful emotional appeal is understanding who you’re attempting to persuade. Use these questions if you’re having difficulty understanding your audience :
- What is their current state of mind?
- What is the focus of their emotions?
- Why are their feelings being guided in this manner?
Finally, remember that persuasion depends on you, the speaker, and your audience. If you can plug into an audience’s emotions during your speech, you’ll be more effective at touching their hearts and convincing them of your points.
Give Your Speech That Final Punch!
Your closing remarks can empower an audience, depending on your speech. That can include asking them to do something, changing their attitude toward a specific individual or topic, or simply making them understand what you’re trying to say.
Nonetheless, your closing remarks aim to leave the audience optimistic about you and the topic of the speech. According to poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, “Great is the art of beginning, but greater is the art of ending.”
Do you need help with your closing remarks in a speech? Then, book a session with us today! We provide premium public speaking training!

Check out more great articles from the Thought-Leader Blog covering TEDx Talks, success mindsets, and everything else in between
How to Get a TED Talk
How to prepare a ted talk, how to market yourself effectively, how to become a keynote speaker, how to speak professionally.

How to END a speech with power and impact
The universe has no end.
Doesn’t that blow your mind a little? When you look up in the sky, it doesn’t end.
Han Solo and Chewbacca could travel at light speed in the Millennium Falcon forever, and they’d never get to the ‘far reaches of the galaxy’, because it just keeps going on and on. (Which is what some presentations feel like.)
This is difficult for humans to fathom. Our brain can’t process things that don’t end. It causes overwhelm, which shuts down our processing and recall faculties.
This, however, creates a unique opportunity. The human mind yearns for structure and defined limits – a clearly defined start and end. When we provide this to our listeners, they process what you say with less effort and find it easier to remember .
You know how to start a speech , here’s how to end a speech or presentation.
Last words linger. Don’t waste them
The end of your talk is automatically a focal point for your audience. Your last words to end a speech give you a singular opportunity to embed a message into the mind of your listeners.
How often have you sat through a presentation that trails off and ends a speech with no real point? It’s amazing how many presenters seem surprised by the ending of their own talk! The final slide comes up and the speaker says, “Oh um, I guess that’s it. So…um, any questions?”
And yet, the end of your presentation is your golden moment to leverage all the words you’ve said until then.
End a speech with more credibility
Worse still, a weak ending diminishes your credibility. Why? When the audience doesn’t get the structure they crave, your ideas seem weaker, less important, less memorable, less complete .
And because you’re the speaker who delivered this unsatisfying combination, you don’t appear to have as much authority.
People expect completion . That’s what an end of a speech is. Completion, ahhh.
Conversely, having a strong, relevant ending boosts your credibility, satisfies your audience and increases their trust in you.
Your last words can crystallize your message and activate your audience.
Just end it!
Learn to observe what an ending feels like. Good comedians often end on a strong joke and good audience reaction – rather than the ending they planned. They are attuned to the opportunity of closing on a high note.
They become experts at endings. You can too.
I watched a much-loved sports legend capture an audience for 30 minutes at a conference. Great stories with a lesson or two from an icon. At one point it felt like the talk was coming to an end and I remember thinking ‘Good work. Tidy speech’.
But he was enjoying himself so much he kept talking . More stories and more wisdom. Unfortunately it ruined his talk. There was no structure to his stories now and we didn’t know how to process his random points of wisdom.
Do you see what can happen? Even when you engage your audience, not having a clear ending can effect their perception of the WHOLE presentation.
“How was the speech?”
“Confusing.”
Options to end a speech and engage them:
1.plan the final message first ..
Plan to end a speech by establishing your take-home message at the very start of your planning. Think of it as the first thing you plan and last thing you say.
Write it down, but in the words you would say when talking . So many people write in ‘corporate speak’ which doesn’t flow comfortably when it comes out of your mouth. Picture your audience and craft a 1 or 2 sentence message you want them to take away.
Example: “This product will save you money by…” or “We are where we need to be with this month’s sales targets because…” or “There are 2 reasons why this project is needed. Firstly X, secondly Y.”
2. End a speech with a statement, not a question.
Upward inflection is a question. Downward inflection is a statement. A question and/or upward inflection imply there is more coming. So it doesn’t work well to end.
And when you know you have a strong ending, you automatically speak with certainty – which makes it easier to add impact with your voice and emphasise your message.
3. Give them a sign
Give your audience a signal that the end is coming to prime them for your memorable end.
For example: Face the audience. Take a big breath or long pause before your final statement. Say something like; ‘To wrap up,’ ‘In conclusion’ or ‘Here’s what to do next’.
This sets their mind up for your memorable statement to end a speech.
4. End a speech by telling them what to DO
Many speakers are hoping their audience will take action, but they fail to ask for it. If you want your audience to do something you better say it, end a speech with a call-to-action or show them how-to steps. For example: “Allocate a budget to fund stage 2 of the project so we can ensure benefits X, Y, Z” or “We need you to give us feedback within 24 hours…”
5. Refer back to an earlier point in your presentation
A Top-and-Tail is a term we used in radio for placing an ad or promo at the start and end of a break. The top-and-tail leverages the mind’s response to structure in your presentation as well. At the start you provide a quote, example, story, a shocking fact or figure that emphasises the need for change etc. Then you repeat this at the end and it comes to life because the content of your talk has given it greater meaning.
A Title Close is where you give your speech a provocative title that encapsulates your message. Your presentation fleshes out your argument. Then, use the title of your speech as your closing words to stir your audience and embed your message.
6. Blank the screen
If you’re using slides, consider blanking the screen (using the B key) which changes the mood of the room and refocuses the audience on you as you deliver your vivid message.
The holy grail of communication is a transferable message 🔴⇨⇨🔴.
It can create word of mouth momentum that can make or break the success of a project.
The ultimate test of your message: would the key members of your audience repeat it to their friends or colleagues?
Test your message out loud and see if you can ‘hear’ them repeating it. Does it flow from their lips? If it does, you know you’ve got a powerful end to your presentation. Could they recall your message a day later? A week later? Could they repeat it to their colleagues in the big meeting next month when they actually make the decision??
This is what you’re speaking for; message recall.
You are there to get a message across that can be recalled later, and if don’t end a speech well, you jeopardize the recall. —– If you’d like to develop your presentation skills, consider:
- Presentation Skills Training
- Presentation Skills public course
- Personal Coaching
- Message Development Sessions
Want to be a great speaker? Get the kindle ebook from amazon.com: What’s Your Message? Public Speaking with Twice the Impact, Using Half the Effort
- Delivery Techniques →
Speech Conclusion: 12 Ways to End a Presentation the Best Way

If you’ve learned anything about speech writing, you’ll know that there’s a recommended formula to use in designing the best presentation.
Essentially, your talk should have a short opening where you engage your audience , a middle part where you coherently cover the details of your speech topic and an ending that neatly sums everything up .
Remember, people have come to hear you talk when there are definitely other ways that they could be spending their time.
They’re looking to be entertained, or moved in some way. They want to leave the room better informed, educated and possibly curious to study more about your subject.
Therefore, you owe it to your listeners to put together the best presentation that you can – that includes a dynamite finish that they’ll reflect on afterwards.
Let’s take a closer look at how to approach the task. We’ll begin by discussing what not to do .
How NOT to End Your Speech: What Not to Do
Sure, when your talk is coming to an end you might be feeling relieved to have gotten through what you have to say without any obvious missteps.
It’s understandable if you’re ready to quickly exit stage left, and take your seat again with the audience members. After all, you’ve earned that privilege – right?
This is a natural temptation and another good reason why you really must take the time to write a proper wrap up.
Having said that, when it comes to crafting an effective ending, it’s not quite as simple as it sounds. Here’s what not to do.

Regurgitating remarks
We’ve already mentioned that the ending is the place where you sum up the main message of your speech in some fashion.
However, you don’t want to repeat so much of your talk that your audience’s eyes start to glaze over.
Going on too long about what you’ve already said is a definite no-no. People may just think that you’re doubting their intelligence!
Taking a tangent
As well, you mustn’t go off on a tangent and introduce some new thoughts that are unrelated to what you’ve just spent some time telling listeners.
This will only confuse people.
Furthermore, the participants may second guess what your topic really was all about, and whether they’ve heard you properly.
Stopping abruptly
Take care not to finish abruptly. People need to know by what you say that you’re getting ready to wind things up.
It should not come as a shock that it’s already time for them to applaud.
Trailing off
You also shouldn’t stop with a whimper, so to speak.
You voice has to remain clear and strong right up until you’ve delivered your last statement. Keep the volume up and don’t mumble!
Offer an apology
Seriously! Don’t do this!
It could be that you believe your speech wasn’t up to your own standards. Maybe you got off track a little, or missed making a minor point that you’d intended.
Whatever it is, your listeners in all likelihood didn’t notice. Even if they did, they’ve already moved on and forgiven you.
Therefore, you certainly don’t want to draw their attention to anything that you felt wasn’t up to par.

12 Best Ways to End a Speech to be Remembered
Be mindful that your final comments are probably going to be the most memorable part of your talk.
As people file out of the auditorium or meeting room, what you said last will be ringing in their ears. In addition, they may be sharing their reaction to your words with others in attendance.
Therefore, you want to leave them with a good impression.
Now that you can appreciate the importance of finishing off your presentation well − and some of the pitfalls to avoid – you’re ready to learn about a number of great ideas for speech endings.
Following are the different ways you can go.
1. Paraphrase the main points
Take a minute to recap the main points of your presentation.
Tell people again what you just told them, but be sure to do it in a very succinct way.
While you shouldn’t just say verbatim what you’ve relayed already, it’s quite acceptable to repeat a phrase or sentence from your opening as a way to reinforce your main point. Whatever you choose, keep it short.
One approach to paraphrasing is to package the information in three points.
It has been shown that patterns of three can have some staying power in the minds of listeners. Here are a few examples that illustrate this:
“...government of the people, by the people, for the people.” – Abraham Lincoln
“I came. I saw. I conquered.” – Julius Caesar
Basically, paraphrasing reinforces the main message of your talk so that those participating are much more likely to bring it to mind later on.
2. Give them a take-away
This approach is somewhat similar to the above idea. It involves giving people the single most important message that you want them to leave with.
Since you’re asking them to focus on only one thought, they’re more apt to commit it to memory.
Plus, boiling the information you’ve just delivered down to a central idea can be very impactful.

Listeners will take to heart that there’s one single take-away they should really pay attention to. They’re more likely to recall the main point you made, and even relay it in conversation with colleagues, friends and family.
One very effective method of doing this is to tell your audience upfront that you want them to recall something. For instance, you could preface your point with one of these phrases:
“When you leave here today, I want you to remember . . .”
“If you take anything away from my presentation today, it should be that . . .”
And say your point.
3. Call them to action
This is a very popular way to end a speech and, no wonder, when you think of how it can affect those listening.
Essentially, you’re going to ask people to do something as a result of absorbing your talk.
Maybe they’ve been swept away by the inspiration you’ve demonstrated in telling them a moving story of overcoming adversity. Perhaps they’re intrigued by the new ideas you’ve presented to manage personal stress.
At the end of your speech, the time is ripe to call them to an action of some sort. Here are some examples, using slightly different approaches:

“The next time you look at the stars in the night sky, I urge you to think about how incredibly vast is our universe.”
“When you see another television commercial about hunger, are you going to change the channel, or are you going to call the number on the screen and make a donation?”
Demanding something of your audience will cause them to reflect on your presentation and especially so when they next find themselves in the situation you’ve described.
Regardless of whether or not they decide to follow through on what you’ve asked, they’ll be thinking of what you said.
4. Repeat the title
Here’s a simple idea that you might have seen used.
Granted, we’ve already explained why you shouldn’t regurgitate your speech in your closing remarks.
However, just repeating the title of your speech can be a great way to sum up and refocus the audience on what your presentation was about.
Of course, this calls for creating an excellent title that will stand on its own as a representation of your talk.
Moreover, your title could be in the form of a provocative question, or employ an alliteration to make it really interesting and memorable.
5. Position with power
End your speech with a powerful bang by making a bold statement that links back to your talk.
Employ strong words or unique turns of phrase. This can be accomplished by writing out your closing statement and searching for synonyms for certain words that will convey more emotion, or spark increased interest.
Emphasize what you have to say with a confident posture that matches.

Another approach to show your power is to make a grand physical gesture. If, for example, your closing statement is “What I want the whole world to know is . . .” you could spread your arms wide in a circle to suggest that you’re reaching out across the globe.
Listeners will remember your words for the strength and enthusiasm behind them.
6. Use your body language
If you’ve done any public speaking, you’ll already appreciate the importance of experimenting with body language . The right posture and gestures can convey so much!
It’s just as critical to display impactful body language at the end of your speech since this is the last thing people will see.
What you do physically on stage should help your audience recall you for the right reasons.
Certainly, you can take a little bow and then walk confidently away from the podium. However, wouldn’t it make people recall you and what you told them better if you did something different?
Maybe you want to shimmy off stage with a dance move, skip or give a few low sweeping bows while blowing kisses to the audience? Use your imagination and find something that fits with your speech topic .
In the following video, Vikram did a somersault to conclude his speech and the audience went wild! (starts at 6:42)
7. Use a prop or visual
If you’ve brought a prop on stage and referred to it earlier in your speech, bring the attention of your participants back to it as you make your closing remarks.
Perhaps you’ve rolled a little suitcase behind you when you first walked to the podium as a visual about the personal baggage that we all carry. Well, grab the handle and give the case a little twirl to bring the audience’s eyes back to it.
Have you arrived on stage wearing a funny wig? You’ve probably set it aside so as not to distract from your words, but pop it back on your head at the end of your speech to help people make a connection to your entire message.
At the start of the following speech recording, the 2014 World Champion of Public Speaking Dananjaya Hettiarachchi pulled out the petals of a flower and threw them into a trash can. At the end of his speech, he pulled out a whole flower from the trash can to make a point.
It was a 'wow' moment.
There are other options for leaving people with a visual that they’ll remember. Here are a few:
- Display a photograph – Try an eye-catching picture on a screen behind you that represents your talk. It could be an image of an endangered species or a clean shoreline if your topic was about the environment, for example.
- Unveil a hidden prop – Removing a cover from a prop that participants haven’t seen can indelibly lodge it in their mind’s eye (i.e., a scale model of building you’ve spoken about).
- Project a cartoon – Finish your speech with a funny cartoon or short video. This is entertainment that people really enjoy.
- Throw something – You could toss out a few small gifts into the audience, shower the first few rows of people with confetti or do something else entirely.
Don’t forget, your prop or visual aid should relate back to your topic. If you’re talking about a wedding , then a confetti shower could be an unforgettable finish!
8. Surprise them
There are so many amazing ways to do this. The sky might just be the limit!
Your listeners will perk up at the mention of something unexpected and take the time to reflect on how it connects to your topic.
A club member once gave a speech about online Zoom meetings, and I suggested to her to wear a formal attire for her top, and home clothes for her bottom, so that at the end of her speech, she could stand up to reveal that juxtaposition and walk away.
That would be a surprise humorous ending.
Here are a couple of other methods to consider:
- Reveal an identity – If your speech relates somehow to your own experience, keeping this information until the end can have people tuning in. On the other hand, there could be someone in the room that you want to introduce as having had a role in your story.
- State a fact – End your talk with a startling piece of data that’s unfamiliar to your listeners.
- Give a timeline − A variation on offering a fact that can have added oomph is to tell people something that has happened in the world during the time they’ve been listening to you – such as the number of births.
As always, have your surprise flow from the subject of your presentation.
9. Envision the future
Give your audience your take on the future. This will ignite a sense of curiosity, especially if they start to contemplate what it might mean for them personally.
Envisioning the future could be as simple as explaining what, in your mind, comes next or what you suggest needs to happen. Prepare a few words about what action needs to be taken to make a positive change, for instance.
Alternatively, you could forecast a future time when everyone will, or won’t, be doing something. Imagining the end of all wars around the world is one example.
Make your future image compelling with lots of detail. Draw on as many senses as you can to help participants to see, smell and hear your dream for the near or longer term.
You’ll have people quickly trying to connect the dots and the meaning of your speech.
10. Share a story
Polishing off your presentation with a short anecdote is another impactful method.

It should be a brief story that relates back to your speech. Tell people a tale that illustrates the point of your talk, and ensure that it’s both captivating and relatable.
You might want to give the ending to an anecdote that you spoke about earlier in your presentation, or a piece that just wraps everything up nicely.
When you think about, people will often quickly become engrossed in a story . It makes what you have to say more digestible, and more readily recalled.
11. Show your scholarly side
Construct a noteworthy closing by harnessing the strength of a few novel ideas. The following tips can, for sure, increase the memorability of your speech:
- Connect a quote − Ending with an inspirational quote, especially if it’s one the audience is familiar with, is a solid option. You can have a bit of fun with it, but be sure that it’s something that those listening can relate to, and not miss any cultural relevance.
- Rhyme your word s – You could try your hand at writing a few lines of original poetry, or find something else that fits the bill.
- Try a metaphor – A metaphor can breathe more life into your final message. Albert Einstein used a metaphor when he said “All religions, arts and sciences are branches of the same tree.”
Any of these ideas will leave your listeners with something catchy, or special, to remember your presentation.
12. Thank them
Here’s another suggestion for a speech ending.
Say a few words of thanks.
You might express your appreciation directly to those in attendance that have been, hopefully, hanging on your every word. Thank them for showing up and giving you their time.
Additionally, you can talk briefly about your appreciation for others who may have invited you to speak or supported your presentation in some way.
This shows people very clearly that you’ve finished speaking.
However, if you had a strong conclusion, I wouldn't suggest this as it would weaken the impact of your conclusion and Call to Action.
How to Choose the Best Ending
Some of the ideas offered might lend themselves more to particular speech purposes. For instance, if your talk is intended to inspire it’s quite appropriate to finish off with a call to action.
And, you might feel more comfortable with certain options and gravitate towards them more readily.
Maybe you’ve already tired one or two of these methods?
Whatever the case, consider how your listeners are likely to respond to these examples, and decide on the ones that will work well with your speech.
Final Thoughts on Concluding a Speech
Once you’ve selected how you’re going to end your talk, prepare your lines .
There’s actually one school of thought that it makes sense to write your ending first and then build your speech from there. So, that’s something you might want to give a shot to.
Ideally, you’ll become practiced enough at public speaking , over time, that you’ll be able to memorize what you have to say. While it doesn’t have to be exactly what you wrote when you drafted your talk , it should be close enough.
In the meantime, your closing remarks are one of the two sections in your speech (the other is your opening) where you absolutely should memorize your lines .
This will help you ace your delivery, especially if you’re trying out a new way to end a speech that’s a little outside your comfort zone.
Happy experimenting!

How to End a Speech: The 15 Best Tips and Examples To Elevate Your Speech Closing
When it comes to giving a speech, the conclusion is just as important as the introduction and body. It’s the final impression you leave on your audience, and it can make or break your entire presentation. A powerful and memorable conclusion can leave your audience inspired, informed, and engaged.
Crafting a Memorable Conclusion

1. Summarize Your Key Points
One of the best ways to conclude a speech is to focus on the key points you’ve made throughout your presentation. This helps highlight your message and ensures that your audience remembers the most important takeaways.
For example, if you were giving a speech on the importance of environmental conservation, you could conclude by summarizing the key actions individuals can take, such as reducing waste and conserving energy.
Before that, it is crucial to memorize the speech , and each detail of it in the right order. That will help you to act like a pro in your presentation.
2. End with a Powerful Quote
Quotes can be a powerful tool to end a speech, as they can encapsulate your message and leave a lasting impression. Choose a quote that relates to your topic and resonates with your audience.
For instance, if you were giving a motivational speech, you could end with a quote like, “Success is not final, failure is not fatal: It is the courage to continue that counts,” by Winston Churchill.
Engaging Your Audience

3. Ask a Thought-Provoking Question
Engage your audience by asking a thought-provoking question in your conclusion. This can encourage them to reflect on the topic and even initiate discussions after your speech.
If you were delivering a speech on the future of technology, you could ask, “What do you envision for the future of human-technology interaction?” This prompts your audience to consider the possibilities.
4. Tell a Personal Anecdote
Sharing a personal anecdote related to your speech topic can humanize you as a speaker and make a deep connection with your audience . This can be particularly effective when giving a persuasive or motivational speech.
In case you were speaking about overcoming adversity, you could share a personal story of a challenging experience you faced and how you persevered. This personal touch can leave a lasting impact on your audience.
Creating a Memorable Conclusion

5. End with a Call to Action
If your speech is meant to inspire action, a strong call to action in your conclusion is essential. Clearly state what you want your audience to do or how you want them to apply the information you’ve provided.
If your speech is about volunteer opportunities in your community, conclude by encouraging your audience to sign up for a specific event or join a local organization.
6. Use Visual Aids
Visual aids can be a compelling way to conclude your speech, especially if you’ve used them throughout your presentation . You can end with a powerful image, graph, or chart that reinforces your message.
For example, if you were giving a speech on the effects of deforestation, you could conclude by displaying a before-and-after image of a deforested area that has been restored.
Captivating Your Audience

7. Employ Humor
Ending your speech with a touch of humor can be a great way to leave your audience with a smile. A well-timed joke or witty remark related to your topic can help lighten the mood and make your conclusion more memorable.
However, be cautious with humor , as it should be appropriate and inoffensive to your audience.
8. Use a Visual Metaphor
Visual metaphors are a creative way to conclude your speech. They involve using a physical object or action that symbolizes your message. For instance, if your speech is about the power of unity, you could conclude by bringing two puzzle pieces together to illustrate how unity can solve complex problems.
Demonstrating Confidence and Gratitude

9. Express Gratitude
Showing appreciation to your audience is a gracious way to conclude your speech. Thank your listeners for their time, attention, and engagement. Expressing gratitude not only leaves a positive impression but also reinforces the connection you’ve established with your audience.
You can say, “I want to express my sincere gratitude to each of you for being here today and for your dedication to our cause.”
10. Maintain Eye Contact
Maintaining eye contact with your audience during the conclusion is crucial. It conveys confidence and sincerity, making your message more impactful. Avoid looking down at your notes or staring at a distant point. Instead, connect with individual members of your audience as you wrap up your speech.
Inspiring and Motivating

11. End with a Vision
Paint a vivid picture of the future in your conclusion. Share a vision that inspires and motivates your audience. This approach works well in speeches related to goals, aspirations, or change.
When you are speaking about the future of renewable energy, describe a world where clean energy sources power our cities and protect our environment.
12. Leave a Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question in your conclusion can leave your audience pondering your message long after your speech has ended. It encourages reflection and engages your listeners on a deeper level.
Moreover, if you’re delivering a speech on the importance of education, you could conclude with a rhetorical question like, “Can we afford to neglect the potential of the next generation?”
Achieving Impactful Closure

13. Connect to Your Opening
A powerful technique for closing a speech is to circle back to your opening statement or anecdote. This creates a sense of closure and reinforces the theme or message you introduced at the beginning.
If you began your speech with a personal story, bringing that story full circle in your conclusion can be particularly impactful.
14. Use a Poignant Quote or Poem
Consider ending your speech with a meaningful quote or a short poem that encapsulates your message. Poetry, in particular, can evoke strong emotions and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Choose a quote or poem that resonates with your speech’s theme and delivers a profound message.
Practice and Feedback
15. rehearse and seek feedback.
Lastly, practice and feedback are essential for a successful conclusion . Rehearse your ending multiple times to ensure that your delivery is confident and polished. Seek feedback from trusted individuals who can provide constructive suggestions to help you refine your conclusion further.
Should I memorize my conclusion word-for-word, or is it okay to improvise?
Memorizing your conclusion word-for-word is generally not recommended. While it’s crucial to know the key points and structure of your conclusion, sounding too rehearsed can come across as insincere. Instead, aim to understand the main ideas and transitions in your conclusion, allowing for some flexibility in your delivery. This approach can make your conclusion feel more authentic and engaging.
Can I use multiple techniques in a single conclusion?
The key is to maintain coherence and relevance. For instance, you can end with a powerful quote followed by a call to action or a thought-provoking question, as long as they flow naturally and support your speech’s objectives.
Is it acceptable to use humor in the conclusion of a serious or formal speech?
It can be acceptable to use humor in the conclusion of a serious or formal speech, but it should be used judiciously and in a way that is contextually appropriate. Humor can help break the tension or lighten the mood, but it should not detract from the overall message or tone of your speech. Ensure that your humor is respectful and relevant to your audience and topic.
The Bottom Line
Ending a speech effectively is a skill that can be honed with practice and attention to detail. Remember that the conclusion is your final opportunity to connect with your audience, so make it count by crafting a memorable and impactful ending.
Related Posts:
- 7 Must-Watch TED Talks for Students in 2023 - #4…
- 5 Inspiring TED Talks That'll Boost Your Self-Confidence
- How to Write a Demonstrative Speech? - Guide for…
- 8 Steps To Memorize a Speech: Present Like a Pro
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
How to End a Speech with Impact
Last Updated: February 13, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Lynn Kirkham . Lynn Kirkham is a Professional Public Speaker and Founder of Yes You Can Speak, a San Francisco Bay Area-based public speaking educational business empowering thousands of professionals to take command of whatever stage they've been given - from job interviews, boardroom talks to TEDx and large conference platforms. Lynn was chosen as the official TEDx Berkeley speaker coach for the last four years and has worked with executives at Google, Facebook, Intuit, Genentech, Intel, VMware, and others. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 41,362 times.
If you're hoping to wow your audience as you end your speech, there are lots of ways you can capture their attention and leave a lasting impression. Repeating the main points in your speech is a great way to make sure your listeners remember your message. You can also do things like tell a personal story, refer to a famous quote , or add humor to the end of your speech to make it really stand out.

Choosing an Impactful Strategy

- If you had three main points in your speech, try to summarize your topics by having one sentence for each point.
- You might even summarize your points in one sentence by saying, “Remember, tell your family you love them, spend time outdoors, and make time for your hobbies.”

- You might challenge the audience to spend more time with their loved ones, volunteer in the community, or smile at five people each day.
- For example, if your speech was about the importance of taking a break from technology, you might challenge the audience to spend a couple hours a day technology-free.
- Ending your speech by encouraging people to take action will leave them feeling motivated, and they'll be more likely to remember your main talking points.

- For example, if you're speaking about volunteering, you might tell a story about a family's reaction to the house they were given after you spent time building it.
- While your story shouldn't be too long, give enough details for it to make sense and create a full picture for the audience.

- Your line might be, “Take time to listen,” or “Make positive change.”
- If you've repeated it several times throughout the speech, the audience might even say it back with you at the end.

- You might quote Martin Luther King, Jr. by saying, “Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that.”
- Search for the perfect quote by pulling up your online search engine and typing in “quotes about” and then a general theme that you'd like to convey, such as “hard work” or “hope.”

- If you're giving a speech at a school, you might finish it by asking, “What are you going to do to make time for reading?” or “How are you going to use your knowledge to impact the future?”

- For example, you might say, "I hope my speech kept you on the edge of your seats—hopefully because you were interested and not thinking about getting up to leave."
Perfecting Your Tone

- If you find yourself speaking quickly, take a breath in between each sentence to help slow you down.

- Practice mastering your voice inflection in front of a mirror before your speech, paying attention to how your voice sounds as you're speaking.
- For example, you might raise your voice when saying super important points in your speech, or end a question in a higher voice to get your point across.

- Stand up tall and look at the crowd as you're finishing your speech.
- If you notice yourself getting a little louder as you're ending your speech, this means the passion is coming through in your voice.
Expert Q&A

- Your conclusion should be about 10-15% of your speech. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 3
- Avoid ending your speech abruptly without signaling that it's coming to an end. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 3

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://uark.pressbooks.pub/speaking/chapter/closing-a-speech/
- ↑ https://westsidetoastmasters.com/article_reference/12_ways_to_end_your_speech.html
- ↑ Lynn Kirkham. Public Speaking Coach. Expert Interview. 20 November 2019.
- ↑ http://canuwrite.com/speech_one_liners.php
- ↑ https://courses.lumenlearning.com/publicspeakingprinciples/chapter/chapter-12-vocal-aspects-of-delivery/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Priya Wrollet
Sep 30, 2022
Did this article help you?

Sep 14, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Methodology
- Specialized
- Train-the-Trainer
- Build Your Own Program
How To End A Speech

Putting together and delivering an effective speech takes time and the right strategy. One of the most challenging aspects is figuring out how to end a speech effectively. You might have prepared a fantastic opening and delivered a compelling message, but if you fail to wrap up your speech in a powerful and memorable way, your audience may leave feeling unsatisfied or even forget what you said altogether.
Many speakers struggle with their closing words, whether it’s because they run out of time, they lose their train of thought, or they simply don’t know how to bring everything together in a cohesive and impactful way. This can lead to a lack of confidence, anxiety, and even embarrassment, all of which can significantly hinder your ability to communicate your message effectively.
In this article we’ll explore some proven tips and strategies, show you three simple techniques that summarize your message and key ideas, and explain how to get your audience members to take action. You’ll start delivering the final words of your speeches with confidence and know you’re leaving a lasting impression on your audience. Whether you’re a seasoned speaker looking to polish your skills or a newcomer to public speaking , this article will help you overcome the hurdles of ending a great speech so you can deliver a powerful and memorable message every time. Your last words will be your most impactful words.
Why is a Conclusion Important?

“Great is the art of beginning, but greater is the art of the ending.” Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
The conclusion of your speech is arguably the most critical part. It’s the pinnacle of your persuasion, the culmination of everything you’ve talked about so far, and it’s the moment when you state your final call to action. This is why it’s crucial to devote sufficient time and attention to crafting your last inspiring words and final point.
Your conclusion is where you’ll leave your audience with the most significant take away from your speech. These closing words are the last impression they’ll have of you and your key message, and it’s where you can reinforce the key message points you’ve made throughout your presentation. By reiterating your main message and summarizing your key arguments, you can ensure that your audience remembers your message long after your speech is over in such a way that inspires them to take action.
The conclusion is also where you summarize your entire speech and make your final call to action. Whether it’s encouraging your audience to remember and take specific actions, supporting a particular cause, or adopting a new way of thinking, your conclusion is the time to motivate your audience to act. This is where you can challenge them to make a difference, do something, or think differently about a particular issue.
Most importantly, your conclusion can make or break your speech. A weak or ineffective ending can leave your audience feeling unimpressed or even confused, undermining the impact of your entire presentation up to that point. Conversely, a strong and impactful conclusion can leave a lasting impression on your audience, motivating them to take action and inspiring them to share your message with others. It even has the potential to turn an average persuasive speech into an unforgettable speech.
Because the conclusion of your speech is so important, it’s worth taking the time to ensure that your final words are as effective as possible. By crafting a strong and impactful conclusion, you can leave your audience with a lasting impression, and ensure that your message is remembered long after your closing statement.
BE AN EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATOR Suasive Presentation Coaching
What is a good closing message?

A good closing is a bookend to your opening, but is much more concise. It should resolve the entire presentation. In the beginning you grab your audience’s attention. Next you navigate them through all the parts. Finally you introduce your call to action so the audience knows what to expect. Your speech’s closing message should fulfill the classical requirements of any story: a strong beginning, a solid middle, and a decisive end.
To fully understand how your closing message connects with your opening you’ll need to first understand the three parts of your opening and how to think about them: Opening Gambit, USP, and Point B.
Opening Gambit
The Opening Gambit is a series of short sentences to get the audience engaged and establish a need for your idea, concept, or solution. Suasive recommends the following seven Opening Gambits .
- Rhetorical question Get your audience thinking about your message by posing a meaningful question that is relevant to them. Scott Cook, the founding CEO of Intuit, used a rhetorical phrase when making a presentation at the Robertson, Stephens, and Company Technology Investment Conference in San Francisco. He began with: “Let me begin today’s presentation with a question. How many of you balance your checkbooks? May I see a show of hands?” Almost everyone’s hand went up. “Okay. Now how many of you like doing it?” Everyone’s hand went down. He had their focus because he got them moving their body and used an easy question that would resonate with everyone. If he had launched into his presentation with a detailed description of Quicken accounting software, he likely would have lost them. Instead, he engaged the audience with a personal question and got them focused on thinking about their checkbooks.
- Factoid You can convert any question to a simple, striking statistic or factual statement to capture your audience’s attention. For instance, instead of asking, “How many iPhones are sold each year?” (which cedes control of the floor), turn it into a Factoid: “185 million iPhones are sold every year.” The Factoid you choose should be related to the main theme of your presentation and not just dropped in for shock value. We’ve all heard off-the-wall statements that only serve to throw the audience off track all the while never coming back to the main point thread or thesis.
- Retrospective/Prospective A Retrospective (backward) or Prospective (forward) look allows you to grab your audience’s attention by moving them in one direction or another, away from their present, immediate concerns. Consider this technique as a flashback or flashforward, or “That was then, this is now.” For instance, you could refer to the way things used to be done, the way they are done now, and the way you project them being done in the future. Technology companies often choose to start their presentations with a look back to earlier functions to contrast how their new technology disrupts the same functionality: library search before the internet, cassette tapes before digital music, brick and mortar shopping before e-commerce, a rat’s nest of tangled wiring before Bluetooth, and keypad entry before facial recognition.
- Anecdote An anecdote is a brief human interest story. “Personal stories” have recently become the holy grail of storytelling . A tsunami of consultants, courseware, workshops , seminars, blogs, and publications are now advising individuals and businesses to develop their great speeches and presentations by reaching deep inside themselves for a heartwarming opening anecdote. People naturally identify with other people, and a personal story can create empathy.
- Quotation You can also use a relevant quotation from a well-known, reliable source such as William Shakespeare, Winston Churchill , John F. Kennedy, Tom Peters or, as many businesspeople do, Sun Tzu’s The Art of War . Yet the best famous quotation is something from a third party that credentializes you, your idea, or your company. Whichever you use, be sure to tie the quotation closely to your content.
- Aphorism An aphorism is a well-known saying, maxim, or idiom. Because of its familiarity, as soon as you state an Aphorism, it rings a bell in your audience’s minds. They may not even recognize the source, but it brings them to attention.
- Analogy Analogies help explain complex subjects. If your business involves highly technical or specialized products, services, or systems, a simple analogous comparison can help clarify. During the early days of the internet, companies developing networking products analogized the web to highways: with main roads to represent carriers, interchanges to represent routing and switching equipment, on-ramps and off-ramps to represent local carriers, and tolls to represent revenues.
COMMUNICATION WITH PURPOSE
Unique Selling Proposition
Once you’ve stated your Opening Gambit, it’s time for your Unique Selling Proposition (USP). The USP is a succinct summary of your business, describing the basic premise that describes what your company, product, or service does. One of the most common complaints about presentations is “I listened to them for 30 minutes, and I still don’t know what they do!” The USP is what they do.
The Opening Gambit grabbed your viewer’s attention and established need, and your USP demonstrates your solution to that need with maximum clarity. It summarizes the body or middle part of your speech. The best USPs are short and are communicated in one sentence.
Which company’s USP is “Melt in your mouth, not in your hand?”
Did you guess it? M&Ms of course.
Point B is your call to action. It’s how you end your speech with a bang and plan to bring your audience to action. The Opening Gambit, USP, and Point B are all connected in a sequence that feeds into one another.
Here’s an example of a full sequence from Opening Gambit to Point B.
- Opening Gambit (Anecdote): Last year, one of Acme’s customers had a flood in their home. The sprinkler system broke and damaged all the furniture, carpets, and other possessions. Not only did they lose their home, they took a big financial hit.
- Link: This customer is like many customers who purchase a basic policy not customized to their individual needs. That means being just one step away from disaster.
- USP: Acme Insurance has a solution. We can provide you with a customized, value-added package of insurance that provides for your Individual needs to protect you against serious financial loss.
- Proof of Concept (POC)–evidence that your USP is worthy: That’s why Acme is one of the fastest-growing insurance brokers in the state.
- Link: I know that you’ll want to take advantage of this opportunity…
- Point B: …and sign up for this important coverage today.
You can see how all three elements feed into each other. One can’t effectively exist without the other. What’s great about the three steps is they compromise your entire speech outline on a macro level, and you can also use them again on a micro level within the closing section of your presentation.
Three Ways to Close a Speech Effectively

“Tell ’em what you’ve told ’em” is a classic closing technique that involves summarizing your main points and reiterating your message in a clear and concise way. This technique helps to reinforce your key ideas and ensure that your audience remembers them long after your speech is over. By summarizing your main points and restating your message, you can drive home the key takeaways and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
“Tell ‘em what you’ve told ‘em” is your closing, a bookend to your opening, and includes three key elements: a Bookend Gambit (like the Opening Gambit but more concise), Recap (of the agenda and your main points), and Point B (call to action).
The Bookend Gambit is a powerful technique that involves referencing your Opening Gambit in your closing remarks. This technique creates a sense of closure and brings your presentation full circle, leaving your audience feeling satisfied and fulfilled.
A brief Recap of your agenda is the second element of the closing technique. By summarizing what you’ve covered you can reinforce the key points you’ve made and drive home your message in a powerful and impactful way.
Point B is the third element and involves making a clear and compelling call to action in your closing remarks. This technique encourages your audience to take specific actions based on the message you’ve delivered, whether it’s signing a petition, making a donation, or simply changing their behavior. By providing a clear and actionable next step, you can motivate your audience to take action and make a difference.
What is a Strong Concluding Statement?
A strong concluding statement is critical for leaving a long-term impression on your audience and motivating them to take action. You want to end your speech with your audience thinking about your objective, willing to do what you want them to do. It’s the last thing they hear you say at the end of your speech, and for many leading speakers it holds the most weight.
One of the most effective ways to close your speech with a bang is with a clear and concise call to action, also known as Point B as discussed above. This final remark should be a short and powerful statement that encapsulates the central message of your presentation and inspires your audience to act.
For example, let’s suppose that in your opening statement you said, “So that we can control our own destiny, I’m seeking your approval and a budget to start this unit.” In your closing statement, you might shorten this message to “All we need is your approval.” This statement is short, clear, and to the point, emphasizing the importance of your request.
Need Help Closing Your Speech?
Putting all the pieces of your speech or presentation together takes know how. The good news is because it’s more science than art, anyone can learn how to do it with the right training. A good presentation has all the parts of a good compelling story – a beginning, middle, and end. The only difference is the pacing and delivery techniques, but story is still at the heart. With practice and preparation, you can improve your speech writing and delivering skills, and make sure your ideas are heard and considered.
So whether you are preparing for a job interview, a presentation at work, or an entire speech in front of a large audience, remember to believe in yourself, focus on your key points, and prepare to the best of your ability. When it’s time to deliver your closing remarks, be sure to incorporate the three techniques you learned in this article and we’re confident you’ll make an impact.
How to tell your story so the audience feels it’s their story.
Suasive, Inc. is a Silicon Valley-based communication consulting company that offers public speaking classes for organizations and individuals. To date, we’ve coached over 600 CEOs and helped individuals in some of the world’s largest companies including Netflix , eBay , Sonos , Lyft , and Freshworks .
Start Your public speaking Training
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
The Throughline Blog
Practical Media Training and Public Speaking Tips
How to Close a Speech – 15 Unique Ways

The question of how to close a speech is an important one that every presenter must ask, given the weight those final words have on your audience.
As the open of your speech sets the stage, your close seals the deal. It is your last chance to restate a key idea, make a final impression, inspire the audience, move a group to action, or change a person’s perspective. A tall order, yes, but it’s far from impossible.
When speakers think about how to close a presentation, there are several key elements to consider when it comes to their close:
- Is it engaging?
- Does it reiterate your message?
- Have you clearly identified the next step you want your audience to take?
Too often, speakers mistakenly believe that the audience will be able to infer what they should do next. The truth of the matter is even the most talented presenter can benefit from sending the audience off with a clear call to action . When it is specific, easy to execute, and aligns with their needs, wants, and concerns, they are more likely to take you up on your request.
Since these final words are so important, you’ll want to make a singular impression.
Here, we offer 15 unique ways to close a speech.
15 Unique Ways to End a Speech
These presentation closes highlight many different approaches in how to end a speech that work for our clients in our public speaking classes . What they are not are recipes for quick escapes. Save the “thank you for your time,” “feel free to email or call me with questions,” and “that’s all I have for today” for another day. Your close is what you want them to remember, so make sure it’s something they can’t forget.
1. The Summary Close – Let’s talk turkey. This close is about the most straightforward, direct, and unequivocal one in the list. In the annals of how to close a presentation speech, it also could be called the “recap” close. If you opt to close a speech with a summary, you want to be clear with your biggest idea and convey to the audience that it is what you want them to remember. That doesn’t mean, however, the summary close is never engaging.
For example, you’re a doctor who is encouraging an audience to adopt lifestyle changes that can lead to longevity. You could end your talk by saying:
“In conclusion, while genetics plays an important role in our lifespans, there are decisions you can make that can improve your chances for a longer and more productive life. There are three letters I want you to remember, “i”, “a,” and “n.” Why? They come at the end of three important words: octogenarian, nonagenarian, and centenarian. If you plan to be active in your 80s, 90s, and 100s, you better start eating better, getting more exercise, eliminating unnecessary stress, and scheduling those routine screenings. A thriving future is in your hands.”

2. The Illustrative Close – The artistry in this close comes from your ability to appropriate a first- or third-person anecdote, case study, or fable; an apocryphal (fictional but plausible) tale; or another storytelling device to serve as an illustration of the main points you made during your talk. Quick tip: Many talks begin and end in this manner.
Example No. 1: You are a senior vice president of a nonprofit that provides health and humanitarian care to locations around the world. You are talking to a group of would-be donors about the significance of their contributions. You decide to end your speech with a personal experience.
“I’ve spent the past 20 minutes encouraging you to dig into those pockets to help make the world a better place for others. I want to tell you one more story. It’s about a personal decision I made some 10 years ago after visiting a coffee shop. I plunked down my two dollars, grabbed my coffee, and headed out the door. During my five-minute walk back to my office, my one-minute walk up the stairs, and the four minutes I spent catching up on email, I had finished it. In 10 minutes, I had managed to spend and consume the amount of money that the world’s poorest people live on in a day. Could I give up that coffee to help others? You bet I could, and I did. Since then, no matter what else I donate each year, it always contains $520, what I call my “coffee fund.” Simple measures not only add up but have the power to change lives.”
Example No. 2:
You are a guidance counselor who is speaking to a group of students who are applying to college. Throughout your talk, you impress upon them the importance of planning and setting deadlines. You could end your speech by referencing Aesop’s fable The Ants and the Grasshopper .
“I want to tell you all a story, and perhaps it is one you remember. Long ago, a grasshopper decided to spend his summer making music and otherwise lazing about. In contrast, a group of ants busily set aside food for the winter. The grasshopper thought he would be fine if he waited to the last minute. He wasn’t, nor will you be if you put off the tasks that need to be done today. Applying for college is an intense and important process that can’t be rushed at the end.”
3. The Surprise Close – Some of the best movie endings of all time were wicked twists, surprising conclusions, and outright shockers. Why are they so memorable? First, they are unexpected. It turns out our brains are more active when we experience something we didn’t anticipate. Second, we expected a different conclusion. When a pattern is broken, we become particularly attuned to what comes next . When you close a speech with a surprise ending , you are signaling to your audience to listen up. Here are some ways to do that:
- Your talk is about how positive thinking gives you the power to overcome overwhelming obstacles. Your talk has been about a woman who “beat the odds.” At the end, you reveal that person is you.
- You lead a school building committee, and you are giving a presentation about the renovation plans for an 80-year-old school. You want to persuade the community to back the plan. As you end your speech, you concede that speaking about the design is a lot less effective than seeing it. You could close with this:
“We all know seeing is believing. So, while I do not have an actual building to show you, I want to take you on a virtual tour of our new middle school. You are the first to see this. (You reveal a screen and project a short video.) This plan provides for the students’ futures and doesn’t keep them stuck in the past.”
4. The Metaphor Close – When it comes to how to close a speech, you may feel that you are drowning in options, but if you take a careful look at your topic and what you want to convey, you will find it’s as easy as pie. We bet that’s music to your ears. Welcome to the metaphor close. We just gave you three. Metaphors are figures of speech that make an indirect comparison between two things that are symbolically similar but literally different. You are not literally drowning in options, but it sure can feel that way.
Here’s a way to employ this close: You are a spokesperson for a technology company that is releasing a new residential surveillance product. You outlined its merits throughout your talk and have arrived at the end. Here, we show you two closes, one without and one with a metaphor.
Example No. 1 (Without)
“Our proprietary technology makes our product stand out. By installing our surveillance system, you have – at your fingertips – one of the industry’s strongest lines of defense against would-be thieves, intruders, and other unwanted visitors.”
Example No. 2 (With)
“When you install our surveillance system, it is as if you have dozens of lookouts guarding your home.”
5. The Forward-Looking Close – Calling all dreamers and visionaries: Paint a picture of what the world might look like in the future. This speech close is a good option if you are talking about recommendations to adopt or future trends that could have a bearing on your topic. It’s important to create a vivid and vibrant picture to help the audience better visualize what it is you hope to accomplish. Say you are a financial advisor talking to a group 15 years away from retirement. During your talk, you have shared a portfolio of products and your firm’s approach to investment. Your close could be this:
“I have shared with you some tips and techniques that will help you to grow your money, so you have it when you need it most. We have talked about your bottom line, market variability, and the strategies that go into investing. But, I want to leave you with a different picture. When you pay attention to your investments today, your tomorrows will be spent poolside, hiking mountains, traveling the globe, learning a new skill, or finally attaining what you have always dreamed of doing. You will no longer be working for your money. Your money will be working for you.”

6. The Backward-Looking Close – We move away from the future and reach into the past. Some audiences, including those who are discouraged or complacent, may need to be reminded of how far they have come. Say you are the manager of a sales team that has spent the past two years working full tilt to hit revenue goals. During your speech, you outlined an ambitious approach to the coming year that some audience members believe is unattainable. Your close, then, encourages them to move forward with confidence, given their past successes. You could offer this:
“I know how hard you all worked these past two years to increase revenue and create a more thriving and vibrant environment. You may not think it, but I can hear your silent groans of frustration. Yes, we do have an ambitious path before us. However, I have no doubts that you are all up to the task. In the past two years, you have taken a company with $500,000 a year in sales to one that clears $1 million. The expressions of doubt and concern that face me now were the same I saw two years ago. But guess what? During these past two years, whatever challenges we faced were met and managed quickly – and that is entirely due to your work ethic. I know we can do this. I know we will do this.”
7. The Next Steps Close – You probably have several to-do lists in your life. There are those that cover daily needs; others focus on short-term goals. There’s likely one lurking out there for long-term dreams, too. Although the timeframe may be different, each list has its own set of tasks that must be met to ensure that things get done. You can close a speech with a similar list. In this case, you want to lay out the sequence and timeline of steps needed to make a decision or achieve a goal.
8. The Rhetorical Question Close – You don’t have to wait until the end, as rhetorical questions are effective throughout a talk. However, asking one at the conclusion of your presentation is powerful since the audience leaves with your question rattling around their minds. One of the most famous rhetorical questions came during a 1980 presidential debate between President Jimmy Carter and his challenger, Governor Ronald Reagan. In the ensuing years, Reagan’s message has become an oft-asked question during every presidential election cycle: “Are you better off than you were four years ago?” Here’s what he said to end that 1980 debate:
“Next Tuesday is Election Day. Next Tuesday all of you will go to the polls, will stand there in the polling place, and make a decision. I think when you make that decision, it might be well if you would ask yourself, are you better off than you were four years ago? Is it easier for you to go and buy things in the stores than it was four years ago? Is there more or less unemployment in the country than there was four years ago? Is America as respected throughout the world as it was? Do you feel that our security is as safe, that we’re as strong as we were four years ago?” And if you answer all of those questions yes, why then, I think your choice is very obvious as to whom you will vote for. If you don’t agree, if you don’t think that this course that we’ve been on for the last four years is what you would like to see us follow for the next four, then I could suggest another choice that you have.”
9. The Provocative Close – Merriam-Webster defines provocative as “serving or tending to provoke, excite, or stimulate.” Of course, every presenter hopes to stimulate the minds of their audiences, but a provocative close snaps people to attention. Here’s how to end a presentation speech provocatively. For instance, you are:

- Delivering a wake-up call – You conclude with a forceful call to action. This is particularly effective if you have power or hold sway over the group to whom you are presenting. For example, you have just delivered a talk to employees about a new technology they are going to have to learn – no ifs, ands, or buts.
- Talking to a group that resists change – You could end with the consequences if no action is taken regarding your topic. You want to paint an “if we fail to act” vision, but it’s also important to take it easy. Too much negativity could lead to a sense of hopelessness, and hopelessness is not the greatest of motivators.
10. The PowerPoint Close – When you dispense with cluttered visual presentations and instead offer an image that draws your audience in, PowerPoint can create a memorable close. Powerful visuals encourage curiosity. Here are a few options to close a speech with a PowerPoint slide. You might project:
- A photo that is seemingly unrelated to your speech topic and requires your explanation.
- An image that is humorous but makes a profound point.
- A line graph showing two potential outcomes – one if the audience gets involved and another if they don’t.
11. The Recommendation Close – In the long-running game show “Let’s Make a Deal,” contestants, who are dressed in outlandish costumes, are urged to, yes, make a deal for cash and prizes. They must choose a prize or gamble for another, which is often behind a curtain or some other wall or obstruction. “Let’s Make a Deal” contestants don’t know what’s behind the curtain, but your audience will. With the recommendation close, you provide your audience with the plusses and minuses of several different options – no curtains or costumes needed.
To be viewed as credible, however, you should offer honest pros and cons for each recommendation. It should not appear to the audience as if you are stacking the odds in favor of one column over the other. Just be mindful not to tip your hat, and the audience will get an unvarnished look at the options before them.
12. The Activity Close – As you can see, how to conclude a presentation speech is as unique to the presenter as it is to the message. In this close, you engage in an activity that drives your main message home. For instance, you could employ a group “pop quiz” to see how many of your key points landed. ( Added bonus: The feedback affords one more opportunity to clarify and reiterate what you want the audience to remember.) You could also end with some of the following activities:
You are a representative for a cosmetics company and are unveiling a new foundation. For your close, you break the audience into groups, provide samples, and ask the groups how it delivered. You run a government agency that is implementing a new program for requests for proposal. You are running some information sessions for contractors, consultants, and other businesses. For your close, you could lead participants through one test round of the system.
13. The Takeaway Close – Parents of young toddlers and teenagers do this every day, to mixed results, but when used to close a speech it can be entirely effective. You ask the audience to reflect on two or three things they heard you say that resonated with them the most. You might even ask them to write them down. The exercise has a twofold benefit – you get to see whether your messages stuck, and the audience is forced to recall what you said, but on their terms.
14. The “Since I Started Speaking” Close – This close works well when talking about a health issue, a societal phenomenon, or anything that can be explained through statistics and further broken down into concrete examples. Say, for instance, you are a spokesperson for a smoking cessation program, and you are talking to a group of employees about the dangers of smoking. After you have outlined how smoking leads to disease and is the leading cause of preventable death in the United States, you could end with this:
“In the 60 seconds it will take me to finish my presentation, someone in the United States will have died from cigarette smoking. That happens every minute, making smoking the leading cause of preventable death in the United States. The dangers are real, and the dire consequences of smoking are relentless, yet it remains an unhealthy habit that too many are unable to quit. What will it take to make that change? After you leave here today, why don’t you take a minute and think of how much it costs you to smoke. Then think of what you could be doing with the money instead. Vacations? Home renovations? New bikes? A new wardrobe? Philanthropic pursuits? Find the incentive that finally gets you to stop lighting up. Quitting is difficult, but it isn’t impossible. And we’ll be here to help you, even if you fall down a few times along the way.”

15. The Relevance Close – In today’s fast-paced society, yesterday’s news ain’t what it used to be. A fresh tidbit during the morning news cycle is stale by lunchtime. Such an environment can make it hard for a presenter whose talk is historical or retrospective in nature. How to close a speech in this scenario? Connect old ways or thoughts to contemporary norms or thinking. Perhaps, you find that your topic reflects an adage that stands the test of time. Say you are a museum curator whose latest exhibition delves into the history of work and the machines that revolutionized different industries. You have just wrapped up a presentation about the show to a group of donors. You have laid out the main points and are heading for the close. Here are some closing techniques:
You might remind the audience how the machines of yesterday were once the state-of-art technology of their day. Then, encourage them to think about what will replace current technology and how that will affect the nature of work. Map out the historical line between an object of today with its predecessors to show how the technology of work is ever evolving. Find an adage or quote that covers the overall theme of how technology and human industry have been and will be linked into the future.
One caveat: For most talks, speakers would want to establish such a relevance early on (i.e., what now seems old was once state of the art). However, for some talks, such as the one referenced above, the moment might have more impact and resonance if it is saved until the end.
Need Help Closing Your Speech?
While every presenter needs to think about how to close a speech, the answer is not always going to be the same. It’s a personal decision that should reflect your personality, your goals, and the content of your presentation. You might choose one that is straightforward, traditional, creative, or innovative.
Whichever you choose, aim to end on a high note. This is not the time for quick goodbyes, mumbled thank-yous, or body language that suggests all you really want to do is flee. There are many public speaking tips we share with our clients, and a key one is to remember that a presentation’s close is one of its most important parts.
It’s your last chance to make an impression on your audience – which in turn will help you to inspire them to think big, persuade them to change their perspective, or move them to action. Make it count!
Most speakers benefit from teaming any of these unique endings with a second close, which can make for a more powerful and memorable ending. Want to learn more? In this post , we delve into the art of wrapping up your talk with two closes, rather than just one.
- close a speech
- presentation closes
- presentation skills
- presentation training
- public speaking skills
- speech closes
Share this article
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Email
STAY UP TO DATE WITH THE THROUGHLINE NEWSLETTER
Join the thousands of professionals who receive our email newsletter. Improve your public speaking and media interviewing skills—and enhance your career— by signing up.
Public Speaking Skills Training
Since 2004, we have helped speakers prepare for the world’s biggest stages, including TED, the World Economic Forum, and a presidential announcement speech. We’re committed to your long-term growth, and we’ll be with you every step of the way.
More from the throughline blog

In Presentation Training How to Hide a Lavalier Mic Wire

In Presentation Training Are Your Stories Making You Appear Inauthentic?

In Presentation Training Why You Should Have Three Speech Opens
This website or its third party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the privacy policy . If you want to know more or withdraw your consent to all or some of the cookies, please refer to the privacy policy. By closing this banner or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
NEW!!! Free Training Starts in

- Communication , Public Speaking
The 7 Most Powerful Ways To End A Speech
By: solomon asine.
- December 26, 2019
Table of Contents
The ending of your speech. It contains the last words your audience will hear you say. They might also be the words that change everything. And so, knowing how to end a speech is very important. In my article on how to start a speech , I mentioned that the two most important parts of a speech are the introduction and the conclusion.
One reason why the introduction and conclusion are very important is the Primacy and Recency effect, also called the Serial-position effect . It is a cognitive bias of how humans remember series of events. We tend to remember the beginning and ending more than the middle. And so, when you treat the conclusion of your speech with levity, it not only makes you look unprofessional, it also depletes the overall strength and impact of your speech.
Unfortunately, some too many speakers do not take the conclusion of their speech seriously. I have seen cases where a speaker comes to the end of a slide and says, “oops! I guess this is the end,” or any other statement that reflects a thoughtless ending. You don’t want to be that person.
The conclusion of your speech is your last impression you have on your audience; it lingers. It is just like a good movie with a terrible ending. No matter how good the beginning and middle of the movie is, you leave the theater disappointed. And you most likely wouldn’t recommend it to a friend.
There are two things that you should do in the conclusion of a speech, no matter the approach you decide to adopt in your closing. Let’s look at these two things before we discuss the seven strategies to end a speech.
When you get to the conclusion of your speech, you have to slow down. Make each word count with the use of more pauses. Be intentional and emphatic. You want your audience to know that you are wrapping up. Doing this will enhance the impact of your closing message.
Give a call to action
I think every speech, particularly persuasive speeches, should have a call to action. What do you want your audience to do based on what you just told them? Don’t ever assume they would use their initiative and take action. If you need them to do something, tell them at the end of your speech.
Now let’s look at some of the most effective ways to end a speech.

Mindset Makeover
1. end with a summary.
You’ve spent some time talking to your audience about a subject. One of the most important things that you can do is to recap all that you’ve said. You want them to remember and take to heart all you just told them. Example:
“ I will end by reminding us of these very important points… ”
Some speeches might not require you to list every point. But what is the one thing that you talked about that you want them to remember? Example;
“ If you forget every other thing that I have said today, I want you to remember this one thing… ”
2. End with a story
Just as opening with a story if effective, closing with a story is very powerful. Not just any story, but a story that relates to your subject matter and one that has a call to action. Because stories are easy to remember, your conclusion, and ultimately the message of your speech, stays with your audience for a very long time. For example, I still remember some of the speeches that I heard as a child. Such is possible because they contained stories.
3. End with a quote
Saying a relevant and preferably memorable quote can make your ending impactful. There are many quote out there. Quotes from famous figures (preferable). Those that you can tie to your speech. Find a quote that leaves a strong impression on your audience. For example, in a speech on climate change, you could end like this:
I will end with the words of Barack Obama, “Climate change is no longer some far-off problem; it is happening here; it is happening now.”
4. End with the introduction
Going back to your introduction is also a great way to end your speech. It is an indication that your speech has gone through a full circle. If you started with a story, you could end be revisiting the moral of the story as your call to action.
Take this example. I started a speech telling the story of an eagle hatched with chickens. I ended the speech along the lines of:
“Are you like the eagle hatched with chickens? Do you feel like you are living a life that is beneath you? Just as that eagle came to itself…”
5. End with a question
Sometimes you want your audience to keep thinking about what you just told them. Nothing could be more effective than asking a question or series of questions. Remember, questions make us think. For example. Let’s say your speech is on physical fitness. You could end your speech like this:
“What are you going to do about your physical health when you walk out of these doors? Are you going to sit and complain about how bad things are? Or are you going to take control of your life and make transformational changes? I urge you to make the right choice.”
6. End with a stylistic device
Stylistic devices or rhetorical devices are key elements in persuasive speeches. Some examples of rhetorical devices are anadiplosis, anaphora, asyndeton, polysyndeton, synecdoche, and a host of others. Ending with a rhetorical device leaves the audience motivated, energized, and excited. Here is how Winston Churchill ended his “We Shall Fight on the Beaches” speech with anaphora:
“We shall go on to the end. We shall fight in France; we shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be. We shall fight on the beaches; we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender…”
7. End on a high note
No matter how dreary your speech is, you want to leave your audience cheerful, motivated, aware, having an assurance that things could be better, that there is a solution, and so forth. So, make sure to end your speech on a positive note.
You just read through the most effective ways to end a speech. I encourage you to practice and use these strategies to end your speeches. When you do, you will notice a phenomenal difference in your speeches.
July 31, 2024 2:00 PM | Online
Developing unshakeable self-esteem in a challenging world.
To empower you to cultivate a strong self-esteem that transforms your relationships and equips you to overcome life’s obstacles with resilience
New!!! Free Training Replay in...
Recent Articles
Check out our latest articles. Boost your social intelligence

Leaving a Toxic Job: 10 Steps to Get Out
Have you ever found yourself stuck in a job that drains the life out of you? A challenging 9 to 5 job can be difficult

11 Tips on How to Exude Confidence as an Introvert
You can express yourself confidently without feeling shy or experiencing burnout. Here is how to exude confidence as an introvert. As an introvert, maintaining your

How to Be Interesting as an Introvert
Anyone, including introverts, can live an interesting and fun-filled life. Here is how to be interesting as an introvert. Generally, many people believe that introverts

Can Two Introverts Be In a Relationship?
We sometimes wonder if going into a relationship with a fellow introvert is a good idea. I mean, won’t the relationship be as boring as hell? Maybe not really!

How to Be an Entrepreneur as an Introvert and Become Successful
Are you ready to get out of your shell to start your dream business? Here is how to be an entrepreneur as an introvert and become successful!

Can Introverts Be Successful in Business?
As an introvert, you might be wondering if you really can become successful as a business owner. Read on to know how business success works for introverts.

Think Fast Speak Smart
Sign up for our mailing list and you will receive the first chapter free!
By signing up, you agree to our terms and privacy policy .
Privacy Overview
How to build a deep connection with anyone during a conversation.
Warning: Apply The Methods in This Training Responsibly

MINDSET MAKEOVER
Building unbreakable self-esteem in a difficult world.

Sign up for our mailing list and get the first chapter for free!
By signing up, you agree to our terms and privacy policy

Closing Remarks for Speech
Ai generator.

Closing remarks are the concluding part of a Speech where the speaker wraps up their presentation. This section typically summarizes the key points discussed, reinforces the main message, and leaves the audience with a final thought or call to action. Closing remarks are important as they provide a sense of closure and can have a lasting impact on the audience.
What is Closing Remarks for Speech?
Closing remarks are the final statements in a speech, where the speaker brings everything to a conclusion. This part of the speech is designed to recap the main points, emphasize the central message, and offer a final takeaway for the audience. It ensures that the speech ends on a strong note, leaving a lasting impression on the listeners.

Closing Remarks for Speech Bundle Download
Closing Remarks for Speech Format
1. summarize key points.
Briefly recap the main ideas or arguments presented in your speech. Example : “Today, we discussed the importance of time management, practical strategies to implement it, and the benefits it brings.”
2. Reinforce the Main Message
Emphasize the core message or takeaway you want the audience to remember. Example: “Remember, effective time management is crucial for reducing stress, increasing productivity, and achieving your goals.”
3. Call to Action
Encourage the audience to take specific actions or steps based on your speech. Example: “I encourage each of you to start using a planner, set specific goals, and tackle your most important tasks first.”
4. Thank the Audience
Express gratitude for their time and attention. Example: “Thank you all for your attention and engagement today.”
5. End with a Memorable Closing
Finish with a powerful quote, a thought-provoking statement, or an inspiring note. Example: “As the saying goes, ‘The bad news is time flies. The good news is you’re the pilot.’ Make the most of your time and steer your life towards success.”
Closing Remarks for Speech Example
Today, we’ve explored the importance of effective time management, discussed practical strategies to implement it, and highlighted the numerous benefits it brings. Remember, managing your time well is crucial for reducing stress, increasing productivity, and achieving your goals. I encourage each of you to start using a planner, set specific goals, and tackle your most important tasks first. By doing so, you will take control of your time and pave the way for a more balanced and successful life. Thank you all for your attention and engagement today. As the saying goes, “The bad news is time flies. The good news is you’re the pilot.” Make the most of your time and steer your life towards success. Thank you!
Short Closing Remarks for Speech Example
Today, we explored the importance of effective time management and practical strategies to achieve it. Remember, managing your time well reduces stress, increases productivity, and helps you reach your goals. I encourage you to start using a planner, set specific goals, and tackle your most important tasks first. Thank you for your attention. As the saying goes, “The bad news is time flies. The good news is you’re the pilot.” Make the most of your time and steer your life towards success. Thank you!
Closing Remarks for Speech for Graduation
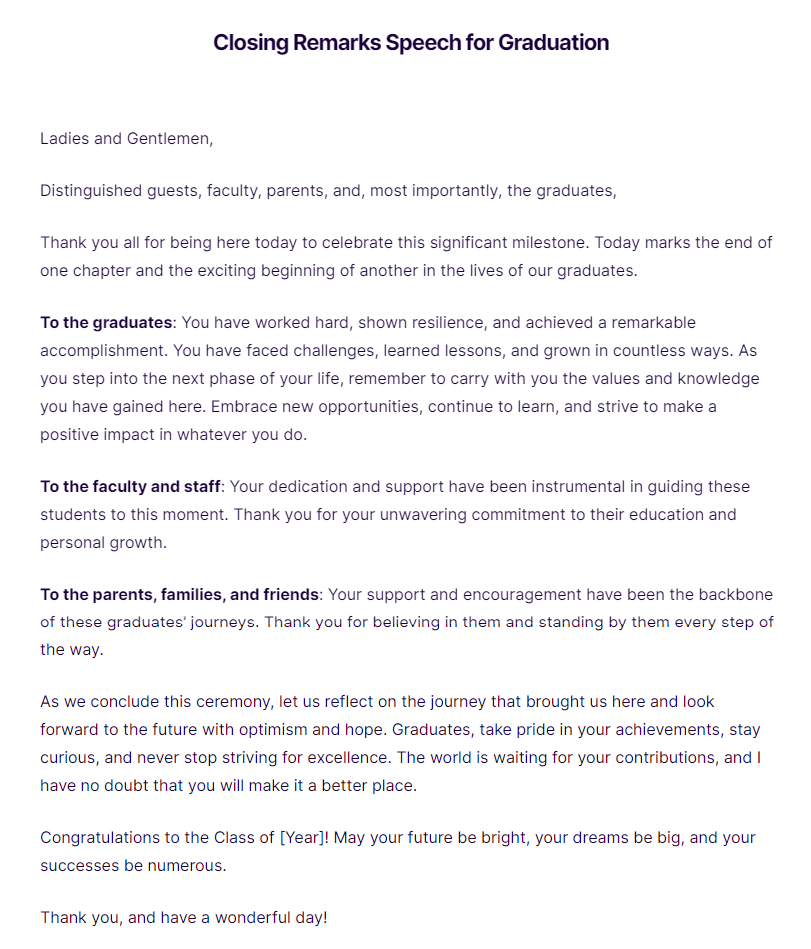
Closing Remarks for Speech for School Program

Closing Remarks for Speech for Recognition Day
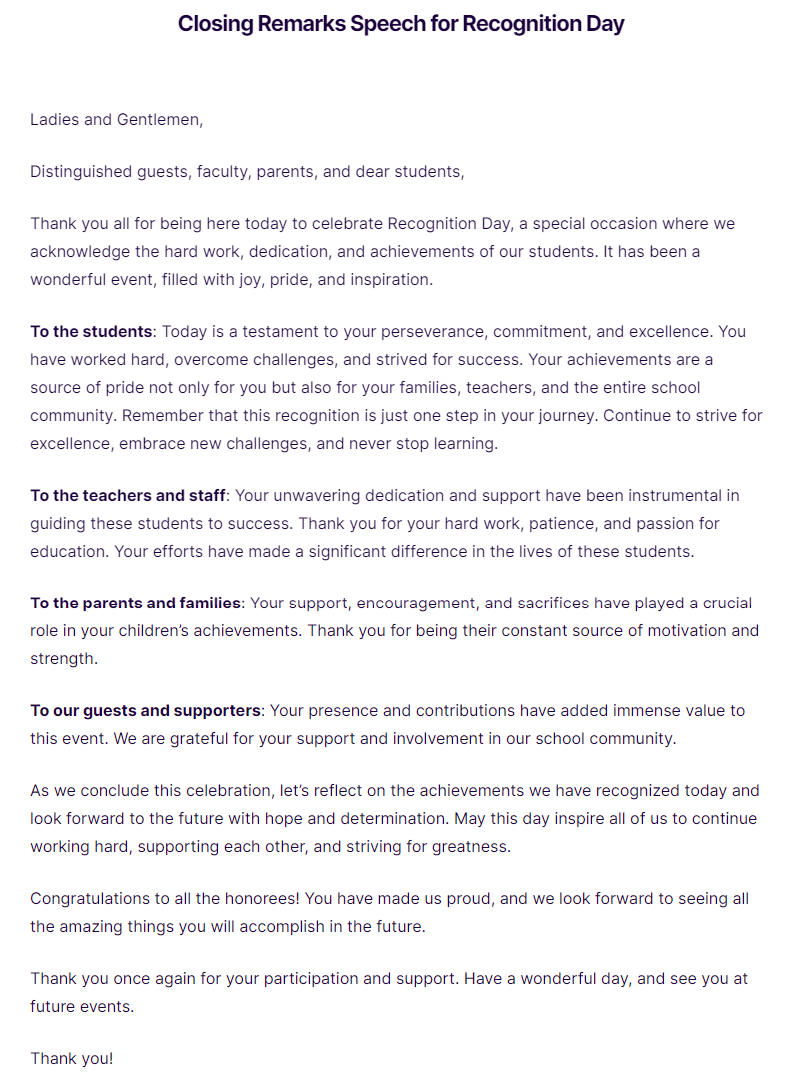
More Closing Remarks for Speech Topics
- Closing Remarks Speech for an Event
- Closing Remarks Speech for Seminar
- Closing Remarks Speech for Teachers Day
- Closing Remarks Speech for Christmas Party
- Closing Remarks Speech for Valedictorian
- Closing Remarks for Speech Contest
- Closing Remarks Speech for Wedding
- Closing Remarks Speech for Conference
- Closing Remarks Speech for Award Ceremony
- Closing Remarks Speech for Farewell
- Closing Remarks Speech for Workshop
- Closing Remarks Speech for Business Meeting
- Closing Remarks Speech for Retirement
- Closing Remarks Speech for Fundraiser
- Closing Remarks Speech for Community Event
- Closing Remarks Speech for Gala
- Closing Remarks Speech for Annual General Meeting
- Closing Remarks Speech for Orientation
- Closing Remarks Speech for Leadership Summit
- Closing Remarks Speech for Charity Event
- Closing Remarks Speech for Memorial Service
- Closing Remarks Speech for Family Reunion
- Closing Remarks Speech for Corporate Event
- Closing Remarks Speech for Product Launch
- Closing Remarks Speech for Training Session
- Closing Remarks Speech for Cultural Festival
- Closing Remarks Speech for Political Rally
How to Write Closing Remarks for Speech
Briefly recap the main ideas or arguments presented.
Example: “Today, we discussed the importance of time management, practical strategies to implement it, and the benefits it brings.”
Emphasize the core message or takeaway you want the audience to remember.
Example: “Remember, effective time management is crucial for reducing stress and achieving your goals.”
Encourage the audience to take specific actions based on your speech.
Example: “I encourage you to start using a planner and prioritize your tasks.”
Express gratitude for their time and attention.
Example: “Thank you all for your attention.”
Finish with a powerful quote, a thought-provoking statement, or an inspiring note.
Example: “As the saying goes, ‘The bad news is time flies. The good news is you’re the pilot.’ Make the most of your time.”
Tips to Deliver Closing Remarks for Speech
1. Summarize Key Points : Briefly recap the main ideas discussed in your speech.
2. Reinforce the Main Message : Emphasize the core message you want the audience to remember.
3. Call to Action : Encourage the audience to take specific steps or actions based on your speech.
4. Express Gratitude : Thank the audience for their time and attention.
5. End with a Memorable Closing : Finish with a powerful quote, thought-provoking statement, or inspiring note.
Why are closing remarks important?
They reinforce the message, ensure audience retention, and provide a clear, memorable conclusion.
How should I structure closing remarks?
Summarize key points, thank the audience, and end with a powerful, memorable statement or call to action.
Can I include a quote in my closing remarks?
Yes, a relevant and impactful quote can effectively reinforce your message and leave a lasting impression.
What should I avoid in closing remarks?
Avoid introducing new information, being too lengthy, or ending abruptly without a clear conclusion.
How do I make my closing remarks engaging?
Use a strong, positive tone, include a personal touch or story, and connect emotionally with the audience.
Can humor be part of closing remarks?
Yes, appropriate humor can leave a positive impression and end your speech on a high note.
How long should closing remarks be?
Closing remarks should be concise, typically lasting no more than a few minutes.
What is a call to action in closing remarks?
A call to action urges the audience to take specific steps or actions related to your speech’s message.
Should I thank the audience in my closing remarks?
Yes, thanking the audience shows appreciation and fosters a positive connection.
Can I use a rhetorical question in my closing remarks?
Yes, a rhetorical question can provoke thought and leave the audience reflecting on your message.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

- Theater-Based Techniques
- Dr. Gary Genard
- What Our Clients Say
- Client List
- Dr. Genard in the Media
- Leadership Communication
- Fearless Speaking
- Voice and Speech Improvement
- Presentation Coaching
- Speaking Virtually
- Presentation Skills
- Executive Speech Coaching
- The Benefits of Deep Breathing
- How to Calm Your Nerves Before Speaking
- Leadership Skills: The 5 Essential Speaking Techniques
- 5 Ways to Captivate an Audience
- The Body Language Rules: 12 Ways to be a More Powerful Speaker
- 4 Characteristics of an Influential Speaker
- 6 Skills Building Exercises for Effective Body Language
- 7 Tips for Overcoming Audience Resistance
- 5 Rules for Succeeding with PowerPoint
- Great Speaking? – It's About Performance Over Content!
- 5 Key Tools of Vocal Dynamics
- 5 Secrets of Powerful Body Language
- 10 Ways to Stay Fully Focused when Speaking
- 25 Words or Phrases to Avoid in Speeches and Presentations
- 6 Rules of Effective Public Speaking
- 7 Key Components of Successful Presentations
- 12 Easy Ways to Achieve Presence and Charisma
- 6 Skills Building Exercises Video
Gary Genard's
Speak for success.
"Be a voice not an echo." - Albert Einstein
Bravo! — How to End a Speech Vividly and Memorably

Do you know how to hook an audience, then conclude powerfully every time you speak? Here's how to end a speech vividly and memorably.
Great public speakers know they have to begin and end their speeches strongly. That's because of two concepts concerned with an audience's engagement and attentiveness.
Primacy states that audiences will remember most vividly what they experience at the start of a talk. And recency says that they'll also remember what's said at the end. In terms of public speaking, that means your introduction and conclusion.
Want to command attention as a speaker? Learn how to stay in "The Zone" for maximum presence. Get my free cheat sheet , " 10 Ways to Stay Fully Focused when Speaking ."
Engaging Listeners in Your Opening and Closing
Speakers throughout history have understood the importance of a strong beginning and ending. Even today, the smart presenter spends the time and attention necessary to craft a "hook" or "grabber" that immediately and powerfully gets an audience onboard.
Some types of openings are guaranteed to get an audience on your wavelength right away. I call them "grabbers." They are actually rhetorical devices designed for speeches, presentations, pitches , lectures, and all examples of public speaking. Here are a dozen of these effective opening gambits:
- Startling statement
- Personal anecdote or experience
- Expert opinion
- Sound effect
- Model or demonstration
- Testimony or success story

How to Create a Strong Conclusion to Your Speech
Let's say you've taken that advice in the paragraphs above, and you've launched your speech powerfully using one of these approaches. You've also managed to keep everyone's attention as you developed your message. Now you're ready for the other critically important segment of your presentation: your conclusion.
Remember, recency states that listeners will likely retain the last thing you say. So you don't want to end weakly, with a presentation that falls to earth like a leaking balloon. "Quit while you're ahead," and "Always leave 'em laughing," are two well-known sayings that embody the principle that a speech should end as strongly as it begins.
Now, think about the conclusions to all the speeches and presentations you've listened to over the past year. How many of them were memorable? How many of them even had a conclusion?
One of the most common public speaking shortcomings, in fact, is the lack of a memorable closing that drives home your message. For audience members, this can feel like being on the receiving end of a shaggy dog story. Or to put it another way: a speech without a conclusion leaves listeners hungry for a last satisfying mouthful.
Why would you want to leave your audience without dessert?
Just as you grabbed listeners' attention at the start of your speech, you must ensure that your conclusion is memorable. It should also vividly re-focus listeners on your core message.
Want to raise the bar on your next talk? Get the 2nd expanded edition of the PUBLIC SPEAKING HANDBOOK, How to Give a Speech . Discover 101 tips to speak with charisma!
As with your introduction, a solid conclusion takes thought, and sometimes a dash of creativity. But here's some good news: The same list of a dozen springboard devices I mentioned above as openers, can be used to conclude your speech. After all, the goal is the same: to be dramatic, provocative, or engaging enough so your message is "sticky."
And along with those devices, here is a "Triple-T" of powerful clinchers that can help seal the deal with audiences:
- Thesis-Antithesis
- Triad (any list of three)

Use Expert Opinion as a Public Speaking Tool
A witticism from Oscar Wilde or Mark Twain , or a quotation from Mother Teresa or Mahatma Gandhi, can do wonders to conclude your talk. I also suggest looking outside your narrow field of expertise to find a connection that's unexpected and therefore invigorating.
As Yogi Berra said: 'It ain't over till it's over, " so why not use your last opportunity to bring your message home?
Here are examples of outstanding conclusions that use my "Triple-T" of powerful clinchers :
- John F. Kennedy, Inaugural Address: "And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man ." (Thesis-Antithesis)
- Abraham Lincoln , Gettysburg Address: "It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us: that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion — that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain--that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom — and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth . (Triad)
- Ladybird Johnson's 1964 speech on Eleanor Roosevelt: "Let us today earnestly resolve to build the true foundation for Eleanor Roosevelt 's memory — to pluck out prejudice from our lives, to remove fear and hate where it exists, and to create a world unafraid to work out its destiny in peace. Eleanor Roosevelt has already made her own splendid and incomparable contribution to that foundation. Let us go and do likewise, within the measure of our faith and the limits of our ability. Let Eleanor Roosevelt teach us all how to turn the arts of compassion into the victories of democracy. (Tribute)
And you noticed as well the triad in that last example, didn't you?
Some more of my blogs on this topic:
- Grab Your Audience! -- 12 Foolproof Ways to Open a Speech
- Start Strong! -- Give Your Audience a Greeting They'll Remember
- Curtain Up! -- Adding Drama to Your Speeches and Presentations
This blog was originally published in 2015. It is updated here.
You should follow me on Twitter here .

Tags: public speaking training , public speaking , Mark Twain quotes , Mark Twain humor , speech Conclusion , how to end a speech , rhetoric , John F. Kennedy inaugural , ending a speech , conclusion , how to start a speech , speech introduction , Abraham Lincoln , TEDx , TED , speech hooks , speech grabbers
Subscribe to Email Updates
Subscribe to the blog, follow gary genard.

- Training Techniques
Main Office - Boston
[email protected] 617-993-3410
- Executive Presentation Skills
- Rehearsal & Preparation
- Group Presentation Skills

- Speech Writing
- Delivery Techniques
- PowerPoint & Visuals
- Speaker Habits
- Speaker Resources
Speech Critiques
- Book Reviews
- Browse Articles
- ALL Articles
- Learn About Us
- About Six Minutes
- Meet Our Authors
- Write for Us
- Advertise With Us
5 Keys to End Your Speech with a Great Call-to-Action
Yet many speakers miss a fantastic opportunity with a call-to-action that is wishy-washy, hypothetical, or ill-constructed. Even worse, some speakers omit the call-to-action entirely.
A poor call-to-action undermines the effectiveness of your speech; a great call-to-action stirs your audience to act enthusiastically.
In this article, we reveal the qualities of a strong speech call-to-action which will lead your audience to act.
What is a Speech Call-To-Action?
A speech call-to-action is an explicit appeal to your audience to take a specific action following your speech. A call-to-action is most often made at the conclusion of a persuasive speech.
“ If you have been persuasive and your audience is emotionally invested, the best time for action is now. ”
For example, you might call on your audience to…
- … adopt a new business process
- … sponsor an event
- … attend an event
- … fund a research initiative
- … register to vote
- … join a club
- … train for a marathon
- … read out loud to their children
- … donate money to a charity
- … travel to Saskatchewan
- … buy a fire extinguisher
- … eat more vegetables
- … use public transit
Guidelines for a Strong Speech Call-to-Action
Your call-to-action and your approach to delivering it may vary according to your audience and your speaking style. While there is no rigid formula, there are a number of guidelines which will improve the effectiveness of your call-to-action.
- Make your call-to-action clear and direct.
- Have your audience act quickly.
- Lower barriers to action.
- Focus on benefits for your audience.
- Customize your call-to-action for each person.
1. Make your call-to-action clear and direct.
Don’t hint. Don’t imply. Don’t suggest.
It’s not a whisper-to-think-about- action; it’s a call-to -action.
Use direct language, and eliminate wishy-washy phrases.
- Instead of “Maybe you could think about joining…”, say “Join…”
- Instead of “It would be good to train for…”, say “Train for… “
Don’t assume that your audience will “figure out” what needs to be done. (I have made this mistake in the past and regretted it.) If members of your audience walk out of the room thinking “Wow, this sounds great, but I’m just not sure what to do…”, your call-to-action was not clear enough.
2. Have your audience act quickly.
If you have been persuasive and your audience is emotionally invested, the best time for action is now. The longer it takes to initiate the action, the more likely that your audience will lose motivation.
So, an ideal call-to-action is one which your audience can act on immediately, perhaps even before they leave the room. If this isn’t feasible, then aim for actions which can reasonably be completed (or at least started) within hours or a day or two.
3. Lower barriers to action.
To help your audience act quickly, eliminate as many (trivial or non-trivial) barriers as you can.
For example, ask the following questions about your audience.
- Do they need to sign up? Bring forms and pens and pass them out.
- Do they need to read additional information? Bring handouts, or copies of books, or website references.
- Do they need approval before they can act? Make the first call-to-action to organize the meeting with stakeholders.
- Do they need to pay? Accept as many forms of payment as possible.
A common psychological barrier is the perception that the suggested action is too big or too risky. This is a legitimate concern, and is often best handled by dividing the call-to-action into several small (less risky) actions.
For example, “train for a marathon” may be too large of a call-to-action for a non-runner. A better call-to-action would be to join a running club or train for a shorter race.
4. Focus on benefits for your audience.
“ A poor call-to-action undermines the effectiveness of your speech; a great call-to-action stirs your audience to act enthusiastically. ”
Always frame your call-to-action in the audience’s best interest.
For example, don’t say this:
- What I’d really like you to do is…
- It would make me so happy if you…
- My foundation has set a target of X that we can reach with your help…
Making you (the speaker) happy is (probably) not highly motivating for your audience.
Instead, say this:
- Build your financial wealth by…
- Make your community a safer place to live for yourself and your children by…
- When you volunteer, you build your skills and gain valuable experience…
Surround the call-to-action with a description of how their lives will be improved when they act. Paint a prosperous vision.
5. Customize your call-to-action for each person.
Audiences don’t act; individuals act. Rather than addressing the group as a whole, focus your call-to-action on each individual in your audience.
Suppose your goal is to have a new business process adopted. Each individual in the room may play a different role in accomplishing this.
- For the person who controls the budget, the call-to-action is to allocate the necessary funds.
- For the personnel manager, the call-to-action is to delegate staff to work on the initiative.
- For others, the call-to-action may be to attend in-depth training about the new process.
Audience analysis is critical . If you know who is in your audience, and understand their motivations and capabilities, you will be able to personalize the call-to-action for them.
Put it into Practice
By working on the planning and execution of the call-to-action in your speeches, you’ll become a more persuasive and effective speaker.
Look back to your last persuasive speech.
- Did you make a clear and direct call-to-action?
- Was your audience able to act quickly on it?
- Did you make an extra effort to lower barriers to action?
- Did you highlight the benefits for your audience?
- Did you address individuals rather than the group with a personal call-to-action?
If the answer to any of the above questions was “no”, then how could your call-to-action have been improved?
Please share this...
This is one of many public speaking articles featured on Six Minutes . Subscribe to Six Minutes for free to receive future articles.
Image credit: Megaphone man at the Metro 4 by Hazzat ( CC BY 2.0 )
Add a Comment Cancel reply
E-Mail (hidden)
Subscribe - It's Free!
| Follow Us |
Similar Articles You May Like...
- 10 Ways to End Your Speech with a Bang
- The Ladder of Abstraction and the Public Speaker
- Speech Critique: Dan Pink (TED 2009)
- Bookending Your Speech: A Master Technique
- Speech Analysis: Gettysburg Address – Abraham Lincoln
- Presentation Power: Four Ways to Persuade
Find More Articles Tagged:
11 comments.
This is a great article. I found in it very useful tactics. thanks a lot.
Brilliant!… can’t wait to put into action. thank you
I really like your tips #3 & 4 about focusing on audience benefits and lowering barriers to action.
Not sure how the tip about personalising the call-to-action should work though. Might you have (say) 3 calls to action if there are 3 decision-makers in the audience?
Very useful to my line of work. Thanks. Keep it up
What would be a good call to action for drug abuse?
Thank you, I found this very helpful in some situations. I definitely recommend this.
My teacher sent me here It really helped. Thank you for taking your precious time to make something to help others even though you didn’t have to. It is very much appreciated
Thank you soooo much it really helped me on my essay for school thank you so much .😊😊😊
I am working on reframing a call to action for a speech THANK YOU for the help ahead of time
How do you write a call-to-action about global warming?
I appreciate your six minute articles Thank you
Recent Tweets
5 Keys to End Your Speech with a Great Call-to-Action https://t.co/a8rputDpUk by @6minutes — @red_suraj Nov 6th, 2017
“A poor call-to-action undermines the effectiveness of your speech; a great call-to-action stirs your audience to a… https://t.co/VbYz3VcxvH — @ToppComm Jul 3rd, 2018
Ending a speech in a meaningful, impactful way is CHALLENGING! Luckily, we have helpful guidelines from @6minutes o… https://t.co/3z46iJn6Os — @speakupcamb Aug 7th, 2018
5 Keys to End Your Speech with a Great Call-to-Action https://t.co/8E7KimKeRE by @6minutes — Mel Sherwood – Pitch & Presentation Specialist (@MelSherwood_) Sep 7th, 2018
5 Keys to End Your Speech with a Great Call-to-Action https://t.co/vkMpPLLHwK by @6minutes — Marcie Hill (@Marcie_Hill) Sep 17th, 2018
5 Keys to End Your Speech with a Great Call-to-Action https://t.co/W8ctelzMPc — @surajd_ Oct 25th, 2018
As a #publicspeaker, you want to see your listeners taking action because of you. To help your audience take action… https://t.co/d4Vf5nSgtS — @GregoryCNSmith Nov 14th, 2018
What is a Speech Call-To-Action? In this article, we reveal the qualities of a strong speech call-to-action which w… https://t.co/nrUtrhIzPS — Free You Up VA (@freeyouupva) Dec 29th, 2018
As Toastmasters, or public speakers, we are usually trying to persuade our audience to take action. Check out his… https://t.co/Tf9LF5ocKj — IS Toastmasters 1424 (@istm1424) Mar 4th, 2019
“Surround the call-to-action with a description of how their lives will be improved when they act. Paint a prospero… https://t.co/ZPGExX28nM — Oke’ Toastmasters (@oketoast) Mar 4th, 2019
Featured Articles
- Majora Carter (TED, 2006) Energy, Passion, Speaking Rate
- Hans Rosling (TED, 2006) 6 Techniques to Present Data
- J.A. Gamache (Toastmasters, 2007) Gestures, Prop, Writing
- Steve Jobs (Stanford, 2005) Figures of speech, rule of three
- Al Gore (TED, 2006) Humor, audience interaction
- Dick Hardt (OSCON, 2005) Lessig Method of Presentation
Books We Recommend
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| Follow Six Minutes |
Six Minutes Copyright © 2007-2022 All Rights Reserved.
Read our permissions policy , privacy policy , or disclosure policy .
Comments? Questions? Contact us .

30 Examples: How to Conclude a Presentation (Effective Closing Techniques)
By Status.net Editorial Team on March 4, 2024 — 9 minutes to read
Ending a presentation on a high note is a skill that can set you apart from the rest. It’s the final chance to leave an impact on your audience, ensuring they walk away with the key messages embedded in their minds. This moment is about driving your points home and making sure they resonate. Crafting a memorable closing isn’t just about summarizing key points, though that’s part of it, but also about providing value that sticks with your listeners long after they’ve left the room.
Crafting Your Core Message
To leave a lasting impression, your presentation’s conclusion should clearly reflect your core message. This is your chance to reinforce the takeaways and leave the audience thinking about your presentation long after it ends.
Identifying Key Points
Start by recognizing what you want your audience to remember. Think about the main ideas that shaped your talk. Make a list like this:
- The problem your presentation addresses.
- The evidence that supports your argument.
- The solution you propose or the action you want the audience to take.
These key points become the pillars of your core message.
Contextualizing the Presentation
Provide context by briefly relating back to the content of the whole presentation. For example:
- Reference a statistic you shared in the opening, and how it ties into the conclusion.
- Mention a case study that underlines the importance of your message.
Connecting these elements gives your message cohesion and makes your conclusion resonate with the framework of your presentation.
30 Example Phrases: How to Conclude a Presentation
- 1. “In summary, let’s revisit the key takeaways from today’s presentation.”
- 2. “Thank you for your attention. Let’s move forward together.”
- 3. “That brings us to the end. I’m open to any questions you may have.”
- 4. “I’ll leave you with this final thought to ponder as we conclude.”
- 5. “Let’s recap the main points before we wrap up.”
- 6. “I appreciate your engagement. Now, let’s turn these ideas into action.”
- 7. “We’ve covered a lot today. To conclude, remember these crucial points.”
- 8. “As we reach the end, I’d like to emphasize our call to action.”
- 9. “Before we close, let’s quickly review what we’ve learned.”
- 10. “Thank you for joining me on this journey. I look forward to our next steps.”
- 11. “In closing, I’d like to thank everyone for their participation.”
- 12. “Let’s conclude with a reminder of the impact we can make together.”
- 13. “To wrap up our session, here’s a brief summary of our discussion.”
- 14. “I’m grateful for the opportunity to present to you. Any final thoughts?”
- 15. “And that’s a wrap. I welcome any final questions or comments.”
- 16. “As we conclude, let’s remember the objectives we’ve set today.”
- 17. “Thank you for your time. Let’s apply these insights to achieve success.”
- 18. “In conclusion, your feedback is valuable, and I’m here to listen.”
- 19. “Before we part, let’s take a moment to reflect on our key messages.”
- 20. “I’ll end with an invitation for all of us to take the next step.”
- 21. “As we close, let’s commit to the goals we’ve outlined today.”
- 22. “Thank you for your attention. Let’s keep the conversation going.”
- 23. “In conclusion, let’s make a difference, starting now.”
- 24. “I’ll leave you with these final words to consider as we end our time together.”
- 25. “Before we conclude, remember that change starts with our actions today.”
- 26. “Thank you for the lively discussion. Let’s continue to build on these ideas.”
- 27. “As we wrap up, I encourage you to reach out with any further questions.”
- 28. “In closing, I’d like to express my gratitude for your valuable input.”
- 29. “Let’s conclude on a high note and take these learnings forward.”
- 30. “Thank you for your time today. Let’s end with a commitment to progress.”
Summarizing the Main Points
When you reach the end of your presentation, summarizing the main points helps your audience retain the important information you’ve shared. Crafting a memorable summary enables your listeners to walk away with a clear understanding of your message.
Effective Methods of Summarization
To effectively summarize your presentation, you need to distill complex information into concise, digestible pieces. Start by revisiting the overarching theme of your talk and then narrow down to the core messages. Use plain language and imagery to make the enduring ideas stick. Here are some examples of how to do this:
- Use analogies that relate to common experiences to recap complex concepts.
- Incorporate visuals or gestures that reinforce your main arguments.
The Rule of Three
The Rule of Three is a classic writing and communication principle. It means presenting ideas in a trio, which is a pattern that’s easy for people to understand and remember. For instance, you might say, “Our plan will save time, cut costs, and improve quality.” This structure has a pleasing rhythm and makes the content more memorable. Some examples include:
- “This software is fast, user-friendly, and secure.”
- Pointing out a product’s “durability, affordability, and eco-friendliness.”
Reiterating the Main Points
Finally, you want to circle back to the key takeaways of your presentation. Rephrase your main points without introducing new information. This reinforcement supports your audience’s memory and understanding of the material. You might summarize key takeaways like this:
- Mention the problem you addressed, the solution you propose, and the benefits of this solution.
- Highlighting the outcomes of adopting your strategy: higher efficiency, greater satisfaction, and increased revenue.
Creating a Strong Conclusion
The final moments of your presentation are your chance to leave your audience with a powerful lasting impression. A strong conclusion is more than just summarizing—it’s your opportunity to invoke thought, inspire action, and make your message memorable.
Incorporating a Call to Action
A call to action is your parting request to your audience. You want to inspire them to take a specific action or think differently as a result of what they’ve heard. To do this effectively:
- Be clear about what you’re asking.
- Explain why their action is needed.
- Make it as simple as possible for them to take the next steps.
Example Phrases:
- “Start making a difference today by…”
- “Join us in this effort by…”
- “Take the leap and commit to…”
Leaving a Lasting Impression
End your presentation with something memorable. This can be a powerful quote, an inspirational statement, or a compelling story that underscores your main points. The goal here is to resonate with your audience on an emotional level so that your message sticks with them long after they leave.
- “In the words of [Influential Person], ‘…'”
- “Imagine a world where…”
- “This is more than just [Topic]; it’s about…”
Enhancing Audience Engagement
To hold your audience’s attention and ensure they leave with a lasting impression of your presentation, fostering interaction is key.
Q&A Sessions
It’s important to integrate a Q&A session because it allows for direct communication between you and your audience. This interactive segment helps clarify any uncertainties and encourages active participation. Plan for this by designating a time slot towards the end of your presentation and invite questions that promote discussion.
- “I’d love to hear your thoughts; what questions do you have?”
- “Let’s dive into any questions you might have. Who would like to start?”
- “Feel free to ask any questions, whether they’re clarifications or deeper inquiries about the topic.”
Encouraging Audience Participation
Getting your audience involved can transform a good presentation into a great one. Use open-ended questions that provoke thought and allow audience members to reflect on how your content relates to them. Additionally, inviting volunteers to participate in a demonstration or share their experiences keeps everyone engaged and adds a personal touch to your talk.
- “Could someone give me an example of how you’ve encountered this in your work?”
- “I’d appreciate a volunteer to help demonstrate this concept. Who’s interested?”
- “How do you see this information impacting your daily tasks? Let’s discuss!”
Delivering a Persuasive Ending
At the end of your presentation, you have the power to leave a lasting impact on your audience. A persuasive ending can drive home your key message and encourage action.
Sales and Persuasion Tactics
When you’re concluding a presentation with the goal of selling a product or idea, employ carefully chosen sales and persuasion tactics. One method is to summarize the key benefits of your offering, reminding your audience why it’s important to act. For example, if you’ve just presented a new software tool, recap how it will save time and increase productivity. Another tactic is the ‘call to action’, which should be clear and direct, such as “Start your free trial today to experience the benefits first-hand!” Furthermore, using a touch of urgency, like “Offer expires soon!”, can nudge your audience to act promptly.
Final Impressions and Professionalism
Your closing statement is a chance to solidify your professional image and leave a positive impression. It’s important to display confidence and poise. Consider thanking your audience for their time and offering to answer any questions. Make sure to end on a high note by summarizing your message in a concise and memorable way. If your topic was on renewable energy, you might conclude by saying, “Let’s take a leap towards a greener future by adopting these solutions today.” This reinforces your main points and encourages your listeners to think or act differently when they leave.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some creative strategies for ending a presentation memorably.
To end your presentation in a memorable way, consider incorporating a call to action that engages your audience to take the next step. Another strategy is to finish with a thought-provoking question or a surprising fact that resonates with your listeners.
Can you suggest some powerful quotes suitable for concluding a presentation?
Yes, using a quote can be very effective. For example, Maya Angelou’s “People will forget what you said, people will forget what you did, but people will never forget how you made them feel,” can reinforce the emotional impact of your presentation.
What is an effective way to write a conclusion that summarizes a presentation?
An effective conclusion should recap the main points succinctly, highlighting what you want your audience to remember. A good way to conclude is by restating your thesis and then briefly summarizing the supporting points you made.
As a student, how can I leave a strong impression with my presentation’s closing remarks?
To leave a strong impression, consider sharing a personal anecdote related to your topic that demonstrates passion and conviction. This helps humanize your content and makes the message more relatable to your audience.
How can I appropriately thank my audience at the close of my presentation?
A simple and sincere expression of gratitude is always appropriate. You might say, “Thank you for your attention and engagement today,” to convey appreciation while also acknowledging their participation.
What are some examples of a compelling closing sentence in a presentation?
A compelling closing sentence could be something like, “Together, let’s take the leap towards a greener future,” if you’re presenting on sustainability. This sentence is impactful, calls for united action, and leaves your audience with a clear message.
- How to Build Rapport: Effective Techniques
- Active Listening (Techniques, Examples, Tips)
- Effective Nonverbal Communication in the Workplace (Examples)
- What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
- 2 Examples of an Effective and Warm Letter of Welcome
- 8 Examples of Effective Interview Confirmation Emails
- Closing your Speech with Impact (4 Keys)
- Uncategorized >>

Craig Valentine at MIP Conference
Closing your speech with impact can open up the doors of opportunities because what you say last determines how your audience members feel once they walk out of the doors and go back to their lives. You can give a wonderful speech but if the ending is weak, your audience will walk away feeling like the speech wasn’t very strong. So here are 4 tools you can use to strengthen your closing and henceforth your speech.
Before you close your speech, you should signal that you are closing. Tell the audience that the end is near. Be more creative than saying, “In conclusion” or “In summary” or something to that effect.
I like to use picture words such as “Let’s wrap this message up” or “As we come to the end” or “I’ll leave you with this…” Whatever you do, let them know you are closing because here’s what will happen:
They’ll listen again!
That’s right. People have been trained to know that your closing means you are most likely going to reiterate your message and so their antennas go up and they often begin to take notes.
As you move into your closing, make sure you call back to each of the major points you made. For example, listen to this quick wrap-up of one of my new keynotes. Listen for the 3 Ls (my main points) as well as how I let them know the speech is coming to a close.
Important Point: You can either call back first or signal first depending on what makes better sense for the flow of your speech. In this case, you heard me call back first and then signal that I’m closing.
You just heard me call back to my main points. However, there is also another very important way to review your message. Have them say it! I blogged about this before, so click this link for details on how to get your audience to say your message.
Questions and Answers (Q & A)
You have probably heard me say, “Never end with the Q & A.” Why? It’s because people remember best what they hear first and what they hear last. Your message needs to be the absolute last thing in their ears. Therefore, it’s okay to have a Q & A, but just don’t end with it. Have it about 90% of the way through your speech. Listen to this quick audio of what happened to me when I didn’t heed this advice and I closed with the Q & A.
[audio:https://craigvalentine.com/wp-content/uploads/Questions1.mp3|titles=Questions]
Lasting Anchor
Finally, once you’ve signaled that you’re closing, called back to your major points, and held a Q & A if appropriate, it’s time to move into your lasting anchor, which will most likely be a story. However, just like you should have be doing throughout your entire speech as you transition from one point to the next, it’s extremely important to tease them before you tell them .
They’re probably wondering, “I already have got the message so why should I listen to this last piece?”
Your answer is the tease. Tease them to let them know what’s in it for them to stick around mentally for this last piece. Listen to how I tease and then go into my final story. This is for my 4 Rs to Remarkable Results In Leadership message.
[audio:https://craigvalentine.com/wp-content/uploads/Tease.mp3|titles=Tease]
Once you tease them before you tell them, go ahead and give them a powerful closing story that provides them with hope and proof that your message will work for them. In doing so, you will close your speech in a way that opens doors for more engagements.
- Recent Posts
- 2 Ways to Get Your Audience to Buy-Into You and Your Message - July 17, 2024
- How to Get Your Audience to Trust You as You Keep them Engaged, Excited, and Entertained - July 10, 2024
- How to Find Humor In Your Serious Speech - May 31, 2024
Leave a Reply 7 comments
Leave a reply:.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Trump’s plans if he returns to the White House include deportation raids, tariffs and mass firings
President Joe Biden has a lot of unfinished business from his first term that he intends to continue if reelected. It’s a far different vision for the country than Donald Trump has outlined during his own campaign. (Nov. 12)
FILE - Former President Donald Trump speaks at the Republican Party of Florida Freedom Summit, Nov. 4, 2023, in Kissimmee, Fla.Trump is already laying a sweeping set of policy goals should he win a second term as president. Priorities on the Republican’s agenda include a mass deportation operation, a new Muslim ban and tariffs on all imported goods. (AP Photo/Phelan M. Ebenhack, File)
- Copy Link copied
FILE - President Donald Trump pumps his fist after speaking in the East Room of the White House, early Wednesday, Nov. 4, 2020, in Washington. Trump is already laying a sweeping set of policy goals should he win a second term as president. Priorities on the Republican’s agenda include a mass deportation operation, a new Muslim ban and tariffs on all imported goods. (AP Photo/Evan Vucci, File)
FILE - Republican presidential candidate, former President Donald Trump speaks during a campaign rally, July 29, 2023, in Erie, Pa. Trump is already laying a sweeping set of policy goals should he win a second term as president. Priorities on the Republican’s agenda include a mass deportation operation, a new Muslim ban and tariffs on all imported goods.. (AP Photo/Sue Ogrocki, File)
FILE - Former President Donald Trump speaks at the New Hampshire Federation of Republican Women Lilac Luncheon, June 27, 2023, in Concord, N.H. Trump is already laying a sweeping set of policy goals should he win a second term as president. Priorities on the Republican’s agenda include a mass deportation operation, a new Muslim ban and tariffs on all imported goods.. (AP Photo/Steven Senne, File)
FILE - Republican presidential candidate former President Donald Trump gestures after speaking Oct. 11, 2023, at Palm Beach County Convention Center in West Palm Beach, Fla. (AP Photo/Rebecca Blackwell, File)
Former President Donald Trump speaks at a campaign rally in Hialeah, Fla., Wednesday, Nov. 8, 2023. (AP Photo/Lynne Sladky)
NEW YORK (AP) — A mass deportation operation. A new Muslim ban. Tariffs on all imported goods and “freedom cities” built on federal land.
Much of the 2024 presidential campaign has been dominated by the myriad investigations into former President Donald Trump and the subsequent charges against him. But with less than a year until Election Day, Trump is dominating the race for the Republican nomination and has already laid out a sweeping set of policy goals should he win a second term.
His ideas, and even the issues he focuses on most, are wildly different from President Joe Biden’s proposals . If implemented, Trump’s plans would represent a dramatic government overhaul arguably more consequential than that of his first term. His presidency, especially the early days, was marked by chaos, infighting and a wave of hastily written executive orders that were quickly overturned by the courts.
What to know today about Super Tuesday elections
- Nikki Haley, Trump’s major GOP challenger, suspends her campaign after being soundly defeated across the country.
- Not-so-Super Tuesday? What the primary elections can tell us about November.
- The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information for elections. See the results for elections across the U.S. here.
Some of his current ideas would probably end up in court or impeded by Congress. But Trump’s campaign and allied groups are assembling policy books with detailed plans.
A look at his agenda:
DISMANTLING THE ‘DEEP STATE’
Trump would try to strip tens of thousands of career employees of their civil service protections. That way, they could be fired as he seeks to “totally obliterate the deep state.”
He would try to accomplish that by reissuing a 2020 executive order known as “Schedule F.” That would allow him to reclassify masses of employees, with a particular focus, he has said, on “corrupt bureaucrats who have weaponized our justice system” and “corrupt actors in our national security and intelligence apparatus.” Given his anger at the FBI and federal prosecutors pursuing criminal cases against him, Trump probably would target people linked to those prosecutions for retribution.
Beyond the firings, he wants to crack down on government officials who leak to reporters. He also wants to require that federal employees pass a new civil service test.
THE U.S.-MEXICO BORDER
Trump has pledged to “immediately stop the invasion of our southern border” and end illegal immigration.
As part of that plan, he says he would immediately direct U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement to undertake the largest domestic deportation operation in American history. He would target people who are legally living in the United States but harbor “jihadist sympathies” and revoke the student visas of those who espouse anti-American and antisemitic views.
In a bid to secure the U.S.-Mexico border, Trump says he will move thousands of troops currently stationed overseas and shift federal agents, including those at the Drug Enforcement Administration and FBI, to immigration enforcement. He also wants to build more of the border wall.
Trump wants to reimpose his travel ban that originally targeted seven Muslim-majority countries and expand it to “keep radical Islamic terrorists out of the country.” In the wake of the Hamas attack on Israel, he has pledged to put in place “ideological screening” for immigrants. His aim: bar “dangerous lunatics, haters, bigots, and maniacs,” as well as those who “empathize with radical Islamic terrorists and extremists.”
To deter migrants, he has said he would end birthright citizenship, using an an executive order that would introduce a legally untested interpretation of the 14th Amendment. The order would prevent federal agencies from granting automatic citizenship to the children of people who are in the U.S. illegally. It would require that at least one parent be a U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident for their children to be eligible for passports, Social Security numbers and other benefits.
What to know about the 2024 Election
- Today’s news: Follow live updates from the campaign trail from the AP.
- Ground Game: Sign up for AP’s weekly politics newsletter to get it in your inbox every Monday.
- AP’s Role: The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information on election night, with a history of accuracy dating to 1848. Learn more.
Trump says he will institute a system of tariffs of perhaps 10% on most foreign goods. Penalties would increase if trade partners manipulate their currencies or engage in other unfair trading practices.
He will urge that Congress pass a “Trump Reciprocal Trade Act,” giving the president authority to impose a reciprocal tariff on any country that imposes one on the U.S.
Much of the agenda focuses on China. Trump has proposed a four-year plan to phase out Chinese imports of essential goods, including electronics, steel and pharmaceuticals. He wants to ban Chinese companies from owning vital U.S. infrastructure in sectors such as energy, technology and agriculture, and says he will force Chinese owners to sell any holdings “that jeopardize America’s national security.”
FOREIGN POLICY
Trump claims that even before he is inaugurated, he will have settled the war between Russia and Ukraine. That includes, he says, ending the “endless flow of American treasure to Ukraine” and asking European allies to reimburse the U.S. for the cost of rebuilding stockpiles.
It is unclear whether he would insist that Russia withdraw from territory in Ukraine it seized in the war that it launched in February 2022.
Trump has said he will stand with Israel in its war with Hamas and support Israel’s efforts to “destroy” the militant group. He says he will continue to “fundamentally reevaluate” NATO’s purpose and mission.
TRANSGENDER RIGHTS
Trump says he will ask Congress to pass a bill establishing that “only two genders,” as determined at birth, are recognized by the United States.
As part of his crackdown on gender-affirming care, he will declare that hospitals and health care providers that offer transitional hormones or surgery no longer meet federal health and safety standards and will be blocked from receiving federal funds, including Medicaid and Medicare dollars.
He would push Congress to prohibit hormonal or surgical intervention for transgender minors in all 50 states.
Doctors typically guide kids toward therapy before medical intervention. At that point, hormone treatments such as puberty blockers are far more common than surgery. They have been available in the U.S. for more than a decade and are standard treatments backed by major doctors’ organizations, including the American Medical Association.
Trump’s goal, he says, is for the U.S. to have the lowest-cost energy and electricity of any nation in the world, including China.
Under the mantra “DRILL, BABY, DRILL,” he says he would ramp up oil drilling on public lands and offer tax breaks to oil, gas, and coal producers. He would roll back Biden administration efforts to encourage the adoption of electric cars and reverse proposed new pollution limits that would require at least 54% of new vehicles sold in the U.S. to be electric by 2030.
And again, he says, he will exit the Paris Climate Accords, end wind subsidies and eliminate regulations imposed and proposed by the Biden admiration targeting incandescent lightbulbs, gas stoves, dishwashers and shower heads.
Trump has pledged to terminate the Department of Education, but he also wants to exert enormous influence over local school districts and colleges.
He would push the federal government to give funding preference to states and school districts that abolish teacher tenure, adopt merit pay to reward good teachers and allow the direct election of school principals by parents.
He has said he would cut funding for any school that has a vaccine or mask mandate and will promote prayer in public schools.
Trump also wants a say in school curricula, vowing to fight for “patriotic education.” He says that under his administration, schools will “teach students to love their country, not to hate their country like they’re taught right now” and will promote “the nuclear family” including “the roles of mothers and fathers” and the “things that make men and women different and unique.”
To protect students, he says he will support school districts that allow trained teachers to carry concealed weapons. He would provide federal funding so schools can hire veterans, retired police officers, and other trained gun owners as armed school guards.
HOMELESSNESS
Trump wants to force the homeless off city streets by building tent cities on large open parcels of inexpensive land. At the same time, he says he will work with states to ban urban camping, giving violators the choice between being arrested or receiving treatment.
He also wants to bring back large mental institutions to reinstitutionalize those who are “severely mentally ill” or “dangerously deranged.”
PUBLIC SAFETY
Trump would again push to send the National Guard to cities such as Chicago that are struggling with violence. He would use the federal government’s funding and prosecution authorities to strong-arm local governments.
He says he will require local law enforcement agencies that receive Justice Department grants to use controversial policing measures such as stop-and-frisk. As a deterrent, he says local police should be empowered to shoot suspected shoplifters in the act. “Very simply, if you rob a store, you can fully expect to be shot as you are leaving that store,” he said in one recent speech.
Trump has called for the death penalty for drug smugglers and those who traffic women and children. He has also pledged a federal takeover of the nation’s capital, calling Washington a “dirty, crime-ridden death trap” unbefitting of the country.
15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines (And How to Create Your Own)
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

Powerful speech opening lines set the tone and mood of your speech. It’s what grips the audience to want to know more about the rest of your talk.
The first few seconds are critical. It’s when you have maximum attention of the audience. And you must capitalize on that!
Instead of starting off with something plain and obvious such as a ‘Thank you’ or ‘Good Morning’, there’s so much more you can do for a powerful speech opening (here’s a great article we wrote a while ago on how you should NOT start your speech ).
To help you with this, I’ve compiled some of my favourite openings from various speakers. These speakers have gone on to deliver TED talks , win international Toastmaster competitions or are just noteworthy people who have mastered the art of communication.
After each speaker’s opening line, I have added how you can include their style of opening into your own speech. Understanding how these great speakers do it will certainly give you an idea to create your own speech opening line which will grip the audience from the outset!
Alright! Let’s dive into the 15 powerful speech openings…
Note: Want to take your communications skills to the next level? Book a complimentary consultation with one of our expert communication coaches. We’ll look under the hood of your hurdles and pick two to three growth opportunities so you can speak with impact!
1. Ric Elias
Opening: “Imagine a big explosion as you climb through 3,000 ft. Imagine a plane full of smoke. Imagine an engine going clack, clack, clack. It sounds scary. Well I had a unique seat that day. I was sitting in 1D.”
How to use the power of imagination to open your speech?
Putting your audience in a state of imagination can work extremely well to captivate them for the remainder of your talk.
It really helps to bring your audience in a certain mood that preps them for what’s about to come next. Speakers have used this with high effectiveness by transporting their audience into an imaginary land to help prove their point.
When Ric Elias opened his speech, the detail he used (3000 ft, sound of the engine going clack-clack-clack) made me feel that I too was in the plane. He was trying to make the audience experience what he was feeling – and, at least in my opinion, he did.
When using the imagination opening for speeches, the key is – detail. While we want the audience to wander into imagination, we want them to wander off to the image that we want to create for them. So, detail out your scenario if you’re going to use this technique.
Make your audience feel like they too are in the same circumstance as you were when you were in that particular situation.
2. Barack Obama
Opening: “You can’t say it, but you know it’s true.”
3. Seth MacFarlane
Opening: “There’s nowhere I would rather be on a day like this than around all this electoral equipment.” (It was raining)
How to use humour to open your speech?
When you use humour in a manner that suits your personality, it can set you up for a great speech. Why? Because getting a laugh in the first 30 seconds or so is a great way to quickly get the audience to like you.
And when they like you, they are much more likely to listen to and believe in your ideas.
Obama effortlessly uses his opening line to entice laughter among the audience. He brilliantly used the setting (the context of Trump becoming President) and said a line that completely matched his style of speaking.
Saying a joke without really saying a joke and getting people to laugh requires you to be completely comfortable in your own skin. And that’s not easy for many people (me being one of them).
If the joke doesn’t land as expected, it could lead to a rocky start.
Keep in mind the following when attempting to deliver a funny introduction:
- Know your audience: Make sure your audience gets the context of the joke (if it’s an inside joke among the members you’re speaking to, that’s even better!). You can read this article we wrote where we give you tips on how you can actually get to know your audience better to ensure maximum impact with your speech openings
- The joke should suit your natural personality. Don’t make it look forced or it won’t elicit the desired response
- Test the opening out on a few people who match your real audience. Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary
- Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you
4. Mohammed Qahtani
Opening: Puts a cigarette on his lips, lights a lighter, stops just before lighting the cigarette. Looks at audience, “What?”
5. Darren Tay
Opening: Puts a white pair of briefs over his pants.
How to use props to begin your speech?
The reason props work so well in a talk is because in most cases the audience is not expecting anything more than just talking. So when a speaker pulls out an object that is unusual, everyone’s attention goes right to it.
It makes you wonder why that prop is being used in this particular speech.
The key word here is unusual . To grip the audience’s attention at the beginning of the speech, the prop being used should be something that the audience would never expect. Otherwise, it just becomes something that is common. And common = boring!
What Mohammed Qahtani and Darren Tay did superbly well in their talks was that they used props that nobody expected them to.
By pulling out a cigarette and lighter or a white pair of underwear, the audience can’t help but be gripped by what the speaker is about to do next. And that makes for a powerful speech opening.
6. Simon Sinek
Opening: “How do you explain when things don’t go as we assume? Or better, how do you explain when others are able to achieve things that seem to defy all of the assumptions?”
7. Julian Treasure
Opening: “The human voice. It’s the instrument we all play. It’s the most powerful sound in the world. Probably the only one that can start a war or say “I love you.” And yet many people have the experience that when they speak people don’t listen to them. Why is that? How can we speak powerfully to make change in the world?”
How to use questions to open a speech?
I use this method often. Starting off with a question is the simplest way to start your speech in a manner that immediately engages the audience.
But we should keep our questions compelling as opposed to something that is fairly obvious.
I’ve heard many speakers start their speeches with questions like “How many of us want to be successful?”
No one is going to say ‘no’ to that and frankly, I just feel silly raising my hand at such questions.
Simon Sinek and Jullian Treasure used questions in a manner that really made the audience think and make them curious to find out what the answer to that question is.
What Jullian Treasure did even better was the use of a few statements which built up to his question. This made the question even more compelling and set the theme for what the rest of his talk would be about.
So think of what question you can ask in your speech that will:
- Set the theme for the remainder of your speech
- Not be something that is fairly obvious
- Be compelling enough so that the audience will actually want to know what the answer to that question will be
8. Aaron Beverley
Opening: Long pause (after an absurdly long introduction of a 57-word speech title). “Be honest. You enjoyed that, didn’t you?”
How to use silence for speech openings?
The reason this speech opening stands out is because of the fact that the title itself is 57 words long. The audience was already hilariously intrigued by what was going to come next.
But what’s so gripping here is the way Aaron holds the crowd’s suspense by…doing nothing. For about 10 to 12 seconds he did nothing but stand and look at the audience. Everyone quietened down. He then broke this silence by a humorous remark that brought the audience laughing down again.
When going on to open your speech, besides focusing on building a killer opening sentence, how about just being silent?
It’s important to keep in mind that the point of having a strong opening is so that the audience’s attention is all on you and are intrigued enough to want to listen to the rest of your speech.
Silence is a great way to do that. When you get on the stage, just pause for a few seconds (about 3 to 5 seconds) and just look at the crowd. Let the audience and yourself settle in to the fact that the spotlight is now on you.
I can’t put my finger on it, but there is something about starting the speech off with a pure pause that just makes the beginning so much more powerful. It adds credibility to you as a speaker as well, making you look more comfortable and confident on stage.
If you want to know more about the power of pausing in public speaking , check out this post we wrote. It will give you a deeper insight into the importance of pausing and how you can harness it for your own speeches. You can also check out this video to know more about Pausing for Public Speaking:
9. Dan Pink
Opening: “I need to make a confession at the outset here. Little over 20 years ago, I did something that I regret. Something that I’m not particularly proud of. Something that in many ways I wish no one would ever know but that here I feel kind of obliged to reveal.”
10. Kelly McGonigal
Opening: “I have a confession to make. But first I want you to make a little confession to me.”
How to use a build-up to open your speech?
When there are so many amazing ways to start a speech and grip an audience from the outset, why would you ever choose to begin your speech with a ‘Good morning?’.
That’s what I love about build-ups. They set the mood for something awesome that’s about to come in that the audience will feel like they just have to know about.
Instead of starting a speech as it is, see if you can add some build-up to your beginning itself. For instance, in Kelly McGonigal’s speech, she could have started off with the question of stress itself (which she eventually moves on to in her speech). It’s not a bad way to start the speech.
But by adding the statement of “I have a confession to make” and then not revealing the confession for a little bit, the audience is gripped to know what she’s about to do next and find out what indeed is her confession.
11. Tim Urban
Opening: “So in college, I was a government major. Which means that I had to write a lot of papers. Now when a normal student writes a paper, they might spread the work out a little like this.”
12. Scott Dinsmore
Opening: “8 years ago, I got the worst career advice of my life.”
How to use storytelling as a speech opening?
“The most powerful person in the world is the storyteller.” Steve Jobs
Storytelling is the foundation of good speeches. Starting your speech with a story is a great way to grip the audience’s attention. It makes them yearn to want to know how the rest of the story is going to pan out.
Tim Urban starts off his speech with a story dating back to his college days. His use of slides is masterful and something we all can learn from. But while his story sounds simple, it does the job of intriguing the audience to want to know more.
As soon as I heard the opening lines, I thought to myself “If normal students write their paper in a certain manner, how does Tim write his papers?”
Combine such a simple yet intriguing opening with comedic slides, and you’ve got yourself a pretty gripping speech.
Scott Dismore’s statement has a similar impact. However, just a side note, Scott Dismore actually started his speech with “Wow, what an honour.”
I would advise to not start your talk with something such as that. It’s way too common and does not do the job an opening must, which is to grip your audience and set the tone for what’s coming.
13. Larry Smith
Opening: “I want to discuss with you this afternoon why you’re going to fail to have a great career.”
14. Jane McGonigal
Opening: “You will live 7.5 minutes longer than you would have otherwise, just because you watched this talk.”
How to use provocative statements to start your speech?
Making a provocative statement creates a keen desire among the audience to want to know more about what you have to say. It immediately brings everyone into attention.
Larry Smith did just that by making his opening statement surprising, lightly humorous, and above all – fearful. These elements lead to an opening statement which creates so much curiosity among the audience that they need to know how your speech pans out.
This one time, I remember seeing a speaker start a speech with, “Last week, my best friend committed suicide.” The entire crowd was gripped. Everyone could feel the tension in the room.
They were just waiting for the speaker to continue to know where this speech will go.
That’s what a hard-hitting statement does, it intrigues your audience so much that they can’t wait to hear more! Just a tip, if you do start off with a provocative, hard-hitting statement, make sure you pause for a moment after saying it.
Silence after an impactful statement will allow your message to really sink in with the audience.
Related article: 5 Ways to Grab Your Audience’s Attention When You’re Losing it!
15. Ramona J Smith
Opening: In a boxing stance, “Life would sometimes feel like a fight. The punches, jabs and hooks will come in the form of challenges, obstacles and failures. Yet if you stay in the ring and learn from those past fights, at the end of each round, you’ll be still standing.”
How to use your full body to grip the audience at the beginning of your speech?
In a talk, the audience is expecting you to do just that – talk. But when you enter the stage and start putting your full body into use in a way that the audience does not expect, it grabs their attention.
Body language is critical when it comes to public speaking. Hand gestures, stage movement, facial expressions are all things that need to be paid attention to while you’re speaking on stage. But that’s not I’m talking about here.
Here, I’m referring to a unique use of the body that grips the audience, like how Ramona did. By using her body to get into a boxing stance, imitating punches, jabs and hooks with her arms while talking – that’s what got the audience’s attention.
The reason I say this is so powerful is because if you take Ramona’s speech and remove the body usage from her opening, the entire magic of the opening falls flat.
While the content is definitely strong, without those movements, she would not have captured the audience’s attention as beautifully as she did with the use of her body.
So if you have a speech opening that seems slightly dull, see if you can add some body movement to it.
If your speech starts with a story of someone running, actually act out the running. If your speech starts with a story of someone reading, actually act out the reading.
It will make your speech opening that much more impactful.
Related article: 5 Body Language Tips to Command the Stage
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Final Words
So there it is! 15 speech openings from some of my favourite speeches. Hopefully, these will act as a guide for you to create your own opening which is super impactful and sets you off on the path to becoming a powerful public speaker!
But remember, while a speech opening is super important, it’s just part of an overall structure.
If you’re serious about not just creating a great speech opening but to improve your public speaking at an overall level, I would highly recommend you to check out this course: Acumen Presents: Chris Anderson on Public Speaking on Udemy. Not only does it have specific lectures on starting and ending a speech, but it also offers an in-depth guide into all the nuances of public speaking.
Being the founder of TED Talks, Chris Anderson provides numerous examples of the best TED speakers to give us a very practical way of overcoming stage fear and delivering a speech that people will remember. His course has helped me personally and I would definitely recommend it to anyone looking to learn public speaking.
No one is ever “done” learning public speaking. It’s a continuous process and you can always get better. Keep learning, keep conquering and keep being awesome!
Lastly, if you want to know how you should NOT open your speech, we’ve got a video for you:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Brag Like a Pro as a Speaker

Less is More! Tips to Avoid Overwhelming Your Audience

What does it mean to Resonate with the Audience- Agreement, Acceptance, Approval

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
'America, I gave my best to you': watch as President Joe Biden speaks at DNC convention
President Joe Biden spoke Monday at the first night of the Democratic National Convention , saying he loved his country after the crowd finally quieted down from prolonged "WE LOVE JOE" cheers.
Before Biden even started speaking, tears appeared in the eyes of some audience members and Biden wiped away his own after an emotional introduction from his daughter Ashley Biden .
Biden's speech is likely much different than what he would have been planning less than two months ago, before the debate that would begin the end of his candidacy . Still, he recounted his tenure from candidacy until this convention as a fight for democracy , and linked some of his administration's achievements to Vice President Kamala Harris .
"I love the job, but I love my country more," Biden said toward the end of his remarks, as the crowd broke into another round of cheers.
Biden capped his speech quoting from "American Anthem": "America, I gave my best to you."
Watch President Joe Biden's full speech at the DNC convention here
Democratic convention live updates: What time does Joe Biden speak tonight? How can I watch?
President Joe Biden at DNC convention
- Who is he: Joe Biden is the current and 46th president of the U.S.
- What role does he play: Biden was the presumed Democratic nominee, until a disastrous June debate led to mounting calls for him to step aside. He bowed out of the race on July 21, and quickly endorsed Vice President Kamala Harris to replace him on the ticket.
- In his words: "You cannot say you love your country only when you win," he said. "On the step of the Capitol on a cold January day, I raised my right hand, I swore an oath to you and to God to preserve, protect and defend the Constitution...I believe then and I believe now, that progress was and is possible...our best days are not behind us, they're before us."
How to watch and stream the 2024 DNC
The convention is taking place Monday through Thursday this week at the United Center, home of the Chicago Bulls and Blackhawks, will be the main venue for the DNC. Chicago has hosted the Democratic Convention 11 times, most recently in 1996 when the United Center saw President Bill Clinton was nominated for a second time.
The convention will air live on its website , from the United Center in Chicago between 6:15 p.m. and 11 p.m. Eastern (5:15 p.m. to 10 p.m Central) on Monday, and 7 p.m to 11 p.m. Eastern (6 p.m. to 10 p.m. Central) the other days.
USA TODAY will provide livestream coverage on YouTube each night of the DNC, Monday through Thursday.
What are the themes for each night of the DNC?
The DNC announced nightly themes for the convention. The title of the convention is "For the People, For Our Future."
Here are the themes for each night:
- Monday: "For the People"
- Tuesday: "A Bold Vision for America's Future"
- Wednesday: "A Fight for our Freedoms"
- Thursday: "For our Future"
Trump says he may end EV tax credit; is open to naming Elon Musk as an adviser
- Medium Text
- Trump considers ending $7,500 EV tax credit, citing inefficiency
- Trump open to naming Elon Musk as adviser, praises his intelligence
- Trump plans new tariffs on Mexican-made cars, open to Chinese automakers building in U.S

Sign up here.
Reporting by David Shepardson in York, Pennsylvania Editing by Matthew Lewis
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Obama night at the DNC: Barack, Michelle rouse crowd for Harris
Former U.S. President Barack Obama and his wife Michelle Obama delivered a one-two punch at the Democratic National Convention on Tuesday night, urging Americans to back Kamala Harris in her 11th-hour presidential bid against Republican Donald Trump.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
5. Melissa Butler. Speech Ending: When you go home today, see yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all your greatness that you embody, accept it, love it and finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn't look like you. 6.
A speech closing is not just about the words you say, but it is also the way you say it. Change the pace near the end of your speech. Let your tone alone should signal the end is near. It is about deliberate voice control, don't let your voice weakly away. In the next section, I will cover these ways to end your speech:
2) Simon Sinek. Speech ending line: "Listen to politicians now, with their comprehensive 12-point plans. They're not inspiring anybody. Because there are leaders and there are those who lead. Leaders hold a position of power or authority, but those who lead inspire us.
For example: 'Sorry for going on so long. I know it can be a bit boring listening to someone like me.'. adding new material just as you finish which confuses your audience. The introduction of information belongs in the body of your speech. making the ending too long in comparison to the rest of your speech.
Here's a Speech Call To Action Example "We have great challenges and great opportunities, and with your help, we will meet them and make this next year the best year in our history!" Consider ending with a thought-provoking question to challenge the audience to think differently and inspire them to take action.
Ditch the panic. Pick your closing! Consider metaphors to leave a deep impression, challenge your audience with a "what if" scenario, or use visuals to stimulate their minds. Summarize key points, deliver a powerful message, and practice your ending for polish. Do avoid rambling, awkward gestures, or rushing out.
Lend me your ears.". - Shakespeare's Julius Caesar. "Government of the people, by the people, for the people.". - Abraham Lincoln's famous Gettysburg speech. This example from Lincoln is also a great example of parallelism in a speech. 4. Tell a Story. Storytelling is a great way to make your speech stand out.
For example: Face the audience. Take a big breath or long pause before your final statement. Say something like; 'To wrap up,' 'In conclusion' or 'Here's what to do next'. This sets their mind up for your memorable statement to end a speech. 4. End a speech by telling them what to DO.
Moreover, your title could be in the form of a provocative question, or employ an alliteration to make it really interesting and memorable. 5. Position with power. End your speech with a powerful bang by making a bold statement that links back to your talk. Employ strong words or unique turns of phrase.
For example, if you were giving a speech on the effects of deforestation, you could conclude by displaying a before-and-after image of a deforested area that has been restored. Captivating Your Audience. 7. Employ Humor. Ending your speech with a touch of humor can be a great way to leave your audience with a smile.
Tell a story to make the ending personal. A personal anecdote is a great way to make your speech memorable and relatable. Tell the audience a compelling story that shows an example of what you talked about in your speech, tugging at people's emotions and allowing them to visualize your message. For example, if you're speaking about volunteering, you might tell a story about a family's reaction ...
Let say your phrase is: "Together, we can win.". You repeat that phrase over and over again. Then just before your close, you say: "I know that all of you are talented, all of you are driven. I know that none of us can do this alone, but (pause) Together (pause) we can (pause until the audience responds.)
Putting together and delivering an effective speech takes time and the right strategy. One of the most challenging aspects is figuring out how to end a speech effectively. You might have prepared a fantastic opening and delivered a compelling message, but if you fail to wrap up your speech in a powerful and memorable way, your audience may leave feeling unsatisfied or even forget what you said ...
Quick tip: Many talks begin and end in this manner. Example No. 1: You are a senior vice president of a nonprofit that provides health and humanitarian care to locations around the world. You are talking to a group of would-be donors about the significance of their contributions. You decide to end your speech with a personal experience.
Indicate that the speech is close to the end. An experienced speaker will always signal that the speech is about to end so that the audience is mentally ready for a conclusion. For example- In a novel, the author uses Epilogue as a tool to let the readers know that the story is going to get over soon.
6. End with a stylistic device. Stylistic devices or rhetorical devices are key elements in persuasive speeches. Some examples of rhetorical devices are anadiplosis, anaphora, asyndeton, polysyndeton, synecdoche, and a host of others. Ending with a rhetorical device leaves the audience motivated, energized, and excited.
Example: "Thank you all for your attention." 5. End with a Memorable Closing. Finish with a powerful quote, a thought-provoking statement, or an inspiring note. Example: "As the saying goes, 'The bad news is time flies. The good news is you're the pilot.' Make the most of your time." Tips to Deliver Closing Remarks for Speech. 1.
Great public speakers know they have to begin and end their speeches strongly. That's because of two concepts concerned with an audience's engagement and attentiveness. Primacy states that audiences will remember most vividly what they experience at the start of a talk. And recency says that they'll also remember what's said at the end.
Customize your call-to-action for each person. 1. Make your call-to-action clear and direct. Don't hint. Don't imply. Don't suggest. It's not a whisper-to-think-about- action; it's a call-to -action. Use direct language, and eliminate wishy-washy phrases. Instead of "Maybe you could think about joining…", say "Join…".
30 Example Phrases: How to Conclude a Presentation. 1. "In summary, let's revisit the key takeaways from today's presentation.". 2. "Thank you for your attention. Let's move forward together.". 3. "That brings us to the end. I'm open to any questions you may have.".
You can give a wonderful speech but if the ending is weak, your audience will walk away feeling like the speech wasn't very strong. So here are 4 tools you can use to strengthen your closing and henceforth your speech. Signal. Before you close your speech, you should signal that you are closing. Tell the audience that the end is near.
CNN's Daniel Dale fact-checks President Joe Biden's speech at the Democratic National Convention in Chicago.
Jo Hayes, a CEO, etiquette expert of 13 years and speech-language pathologist who completed her master's thesis on manners and modern etiquette, says her #1 go-to for politely ending small talk ...
In her speech at the Democratic National Convention in Chicago, former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton received a standing ovation, praised Vice President Kamala Harris and slammed former ...
But by leaving now, and ending a contest between an 81-year-old and a 78-year-old, Biden has allowed his vice president and the new Democratic nominee to run with the aura of the change candidate ...
Last night President Biden delivered an energetic, 52-minute speech very late on the first night of the Democratic National Convention in Chicago. It was a perfectly fine speech that served as a ...
To deter migrants, he has said he would end birthright citizenship, using an an executive order that would introduce a legally untested interpretation of the 14th Amendment. ... you can fully expect to be shot as you are leaving that store," he said in one recent speech. Trump has called for the death penalty for drug smugglers and those who ...
Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary. Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you. 4. Mohammed Qahtani.
"I love the job, but I love my country more," Biden said toward the end of his remarks, as the crowd broke into another round of cheers. Biden capped his speech quoting from "American Anthem ...
Trump considers ending $7,500 EV tax credit, citing inefficiency; Trump open to naming Elon Musk as adviser, praises his intelligence; Trump plans new tariffs on Mexican-made cars, open to Chinese ...