| Registered User | ||
- Home
- About us
- Feedback
- Contact us
- Understanding CCE
- CBSE Question Bank Based on CCE
- Chapterwise Assignments Based on CCE
- Sample Papers Based on CCE
- Model Test Papers Based on CCE
- CBSE Past Year’s Papers Based on CCE
| | | Copyright © 2017 Goyal Brothers Prakashan |

- English USA English UK
- SCAN, WATCH & LEARN

Preview of Goyal's Assignments in English Core for Class 12 (Subject Code 301)

- +91-0120-4655555
- +91-9319391199
- [email protected]

Goyal Brothers Prakashan
- Our Mission
Late Shri Kewal Ram Gupta laid the foundation of the Goyal Brothers Prakashan (GBP) sixty-three years ago when India’s aspirations were taking shape. Education was central to it, and there was a dearth of quality learning resources. Realising this need, our founder established the GBP with a vision to make learning accessible to everyone.
We offer online learning tools and resources, school textbooks (k-12), reading guides, supplementary and competitive exam books, novels, premium notebooks, and more to our learner community. For businesses and corporates, our products include calendars, magazines, posters, notebooks, and custom paper stationery.

To provide learning resources that nurture passion and curiosity and that every parent wants for their children and every teacher recommends to their students.

To make accessible to everyone, anywhere, anytime. We intend to do it by harnessing technology and passion to provide learning experience that is immersive, unique and rooted in our timeless values.

Online Resources
For Teachers & Students
Merit Box Learning App
Merit Box makes learning interactive and engaging. Our online resources include e-books, video lectures, animated lessons, practice exercises, self-assessments, and test paper generators (for teachers). We even meet your stationery requirements.

Bright Tutee Learning App
Bright Tutee has hundreds of hours of high-quality online video lessons / lectures on board, along with MCQs, practice questions, and solutions, which seamlessly offer a 360° learning experience to our students.
Goyal's Target CUET Online Tests
Goyal Brothers Prakashan brings updated online test series for CUET with Unlimited Access on purchase with: ◉ Trend based MCQs ◉ Expert designed questions ◉ Strict adherence to the syllabus.

Safal is Web Based Testing Platform
SAFAL is web-based testing platform that helps students from classes 1 to 9, to do a periodic self-assessment of their academic progress, through our well-designed testing modules in Mathematics and Science. It helps students to identify their strengths and weaknesses much before they face the actual exams in their school curriculum.

Generate Hassel-free Unlimited Number of Quetion Paper For CBSE and ICSE
Create Question Papers Online schools, coaching institutes, teachers and tutors create question papers in minutes.
“Find out what’s latest and exciting. Attend webinars, workshops, book lauch events, exhibitions and more.”
Book Launch
Testimonials.
“Check out what students and teachers say”
I took classes on Merit Box in physics and mathematics. My teachers were good, explained everything well and were keen to know more about me and my interest. I was given regular feedback of learning, and how I could improve it.

Babita Ganguli
I am a prent of a 15 year old. My friend recommended me Merit Box app. I found all the classes were really good. My kid was able to make sense of everything. If he had any doubt, his educators made sure they were resolved. I recommend it.

Sarah Taylor
My son had books recommended for his summer break. When I looked up online to find a suitable book that my child would be able to read with ease and maintain her interese, I found Goyal Prakashan were really good. Easy language and very learner centric.
Meenakshi Rao
I am in 8th grade, and took chemistry and social studies classes. My teachers were really good and helpful. I got supplementary resources to aid my learning and help with difficult homework. I loved all the classes.
I am a state board student. It is difficult to find resources, especially online to state boards. But, on Merit Box I found my state-board syllabus was offered. I am glad that I subscribed, my teacher helped me a lot, and she made sure I understand everything correctly. Thank you Merit Box.
Madhu sen Nanda
I took classes in mathematics for class 11. Teachers was excellent. Every NCERT problem was solved in class and easy explanations were provided.
Sachin Sharma
Our authors.
“Learn about the people helping you learn. Read your favourite author’s bio.”

Prof. J.P. Goel
Prof. J.P. Goel was an eminent and dedicated faculty at Hindu Post Graduate College, Sonipat (Haryana). He retired as Associate Professor & Head of Department of Economics in November, 2009.

S. K. Agarwala
S.K.Aggarwal is an Associate Professor (Retd.), Deshbandhu College, Delhi University.

B K SINGH is an eminent dedicated faculty in teaching of Mathematics. He has been known for his excellent result oriented teaching.

Tinku Bhattacharjee
Tinku Bhattacharjee is qualified and eminent educationist associated with reputed educational coaching institutes.

About the Goyal Group
The Goyal Group as an enterprise has diverse business interests. The group is engaged in educational publishing, digital learning, supply and manufacturing of stationery supplies and school uniforms, exports (books), medical diagnostic services, and fine jewellery. Our 800-plus employees, strong leadership, dedicated in-house experts, and consistent growth driven by excellence and innovation represent our pioneering spirit.


Telegram Channel
DK Goyal Solutions Class 12 Accountancy 2021-22 Edition
- February 19, 2022
- D.K Goyal Solutions (12)
Are you looking for the solutions of DK Goyal book class 12 Accountancy 2021-22 Edition? I have solved all the practical problems of this book and explained them in detail.
DK Goyal offer the 3 volumes of Accountancy Book of Class 12.

Volume – 1 of DK Goyal book class 12 Accountancy consists of two units.
- Not for Profit Organizations.
- Partnership

Partnership Units further divided into following chapters.
- Accounting of Partnership Firms – Fundamentals.
- Admission of Partner
- Retirement/Death of Partner
- Dissolution of Partner
Volume – II of DK Goyal Book Class 12 Accountancy Consists of one unit.
- Accounting for Company
It is further divided into two chapters
- Accounting for Share Capital
- Accounting for Debentures
Volume – III of DK Goyal Book class 12 Accountancy consists of several Chapters.
- Analysis of Financial Statements
- Cash Flow Statement
DK Goyal Book Volume 1 solutions of Class 12 Accountancy 2021 Edition
Following are the links to solutions of All chapter of Volume 1 of DK Goyal Book of Class 12 Accountancy 2021 Edition.
| S.N | Chapters | Link to Solutions |
| 1. | Not For Profit Organisation (NPO) | |
| 2. | Accounting For Partnership Firm – Fundamentals | Solutions |
| 3. | Goodwill- Nature and Valuation | Solutions |
| 4. | Change in Profit – Sharing Ratio | Solutions |
| 5. | Admission of Partner | Solutions |
| 6. | Retirement/Death of a Partner | Solutions |
| 7. | Dissolution of Partnership Firm |
Anurag Pathak
Anurag Pathak is an academic teacher. He has been teaching Accountancy and Economics for CBSE students for the last 18 years. In his guidance, thousands of students have secured good marks in their board exams and legacy is still going on. You can subscribe his Youtube channel for free lectures
Related Posts
Solution of npo chapter dk goyal book 2021-22 edition cbse board.
- January 11, 2022
Class 12 Accountancy free video lectures notes pdf download
- May 19, 2021
Class 12 Commerce free video Lectures, Notes pdf Download
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Trending now

Enter the characters you see below
Sorry, we just need to make sure you're not a robot. For best results, please make sure your browser is accepting cookies.
Type the characters you see in this image:

- DK Goel Solutions
- DK Goel Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy
- Vol 1 Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms - Fundamentals
DK Goel Solutions Vol 1 Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms - Fundamentals
DK Goel Accountancy Class 12 Solutions Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals which is outlined by expert Accountancy teachers from the latest version of DK Goel Accountancy Class 12 textbook solutions. We at BYJU’S provide DK Goel Solutions to assist students to comprehend all the theories in particular. There are numerous concepts in Accountancy, but the concepts of Admission of a partner, Accounting Ratios and Cash Flow Statement (As per AS – 3 Revised) is required.
DK Goel Solutions Class 12 – Chapter 1 – Part A
A and B are partners in a farm. A is entitled to a salary of ₹15,000 p.m and a commission of 10% of net profit before charging any commission. B is entitled to a commission of 10% of net profit after charging his commission. Net profit till 31st March 2018 was ₹4,40,000. Show the distribution of profit.
| Dr. | Profit and Loss of Appropriate Account Till 31st March, 2018 | Cr. | |
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| To A’s Salary | 1,80,000 | By Profit & Loss A/c (Net Profit) | 4,40,000 |
| To A’s Commission (₹4,40,000 x 10/100) | 44,000 | ||
| To B’s Commission (₹4,40,000 x 10/110) | 40,000 | ||
| To Profit transferred to: | |||
| A’s Capital A/c 88,000 B’s Capital A/c 88,000 | 1,76,000 | ||
| 4,40,000 | 4,40,000 | ||
X, Y, and Z are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio 3:2:1. After the final accounts have been prepared, it discovered that interest in drawings@5% p.a had not been taken into consideration. The drawings of the partners were: X ₹1,50,000, Y ₹1,26,000 , Z ₹1,20,000. Prepare a journal entry.
Calculation of Interest on Drawings:
Since the date of the drawing is not given, interest will be charged for 6 months.
X: 5% on ₹1,50,000 for 6 months = ₹ 3,750
Y: 5% on ₹1,26,000 for 6 months = ₹ 3,150
Z: 5% on ₹1,20,000 for 6 months = ₹ 3,700
| Table Showing Adjustments | |||||
| X (₹) | Y (₹) | Z (₹) | Total | ||
| Interest on Drawings Division of ₹5,400 in 3:2:1 | Dr. Dr. | 2,550 2,700 | 1,850 1,850 | 1,000 900 | 5,400 5,400 |
| Difference | Cr.150 | Dr. 50 | DR.100 | ——– | |
Hence, the adjusting entry will be:
| Journal Entry | |||||
| Date | Particulars | L.F | Dr. ₹ | Cr. ₹ | |
| Y’s Capital A/c Z’s Capital A/c | Dr. Dr. | 50 100 | |||
| To X’s Capital A.c (Adjustment in respect of interest on drawing omitted in previous year’s account) | 150 | ||||
Akshara and Samiksha are partners. Business is carried from the property owned by Akshara on a monthly rent of ₹5,000. Akshara is entitled to a salary of ₹40,000 per quarter and Samiksha get a commission of 4% on net sales, which during the year was ₹5,00,000. Net profit till 31st March, 2018 before providing for rent was ₹6,00,000
Prepare a profit and loss appropriate account till 31st March 2018.
| Dr. | Profit and Loss Appropriate Account Till 31st March, 2018 | Cr. | |
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| To Salary to Akshara To commission to Samiksha | 1,60,000 2,00,000 | By Profit & Loss A/c (Net Profit) ( ₹6,00,00 – ₹60,000) | 5,40,000 |
| To Profit transferred to: | |||
| Akshara’s Capital A/c 90,000 Samiksha’s Capital A/c 90,000 | 1,80,000 | ||
| 5,40,000 | 5,40,000 | ||
*Rent paid to a partner is a charge against profits. It will be debited to the Profit & Loss Account.
Ravi and Mohan were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 7:5. Their respective fixed capitals were Ravi ₹10,00,000 and Mohan ₹7,00,000. The partnership deed provided for the following:
- Interest on Capital @ 12% pa.
- Ravi’s salary ₹6,000 per month and Mohan’s salary ₹60,000 per year.
The profit till March 31-3-2019 was ₹5,04,000 which was distributed equally, without providing for the above. Record an adjustment entry.
| Statement of Adjustments | ||||
| Ravi (₹) | Mohan (₹) | Total (₹) | ||
| Interest on Capitals | Cr. | 1,20,000 | 84,000 | 2,04,000 |
| Salary | Cr. | 72,000 | 60,000 | 1,32,000 |
| Profit left* after authorizing interest on capital and salary will be ₹5,04,000 – ₹2,04,000 – ₹1,32,000 = ₹1,68,000. The profit sharing ration will be divided into, i.e, 7:5 | 98,000 | 70,000 | 1,68,000 | |
| Net amount that should have been received | Cr. | 2,90,000 | 2,14,000 | 5,04,000 |
| Less: Profit already distributed equally | Dr. | 2,52,000 | 2,52,000 | 5,04,000 |
| Net Effect | (Cr.) 38,000 | (DR.) 38,000 | ———– | |
*Remaining profit will have to be calculated when profit has already been distributed in wrong profit sharing ratio.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more DK Goel solutions, question papers, sample papers, syllabus and Commerce notifications.
| COMMERCE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

DK Goel Solutions
- DK Goel Solutions Class 12
DK Goel Solutions Chapter 5 Retirement or Death of a Partner
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 12 Chapter 5 Retirement or Death of a Partner . These solutions have been designed based on the latest Class 12 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.
Whenever there is a retirement or death of a partner there can be an accounting impact of this change. students should be able to understand how to account for such kind of events in a partnership form and correctly pass the accounting entries so that the statements reflect the correct position of the partnership firm.
The chapter contains a lot of questions which can be very helpful for Class 12 commerce students of Accountancy and will also help build strong concepts which will be really helpful in your career.
These solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 12 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below
Retirement or Death of a Partner DK Goel Class 12 Accountancy Solutions
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Solution 1 The product of the contributions of all current collaborators in the past is goodwill received by the organization. A percentage of potential gains will accrue regardless of the current goodwill and future earnings will not be shared by the retired or deceased partner. The surviving partners should then reward the retired or deceased partner by entitling him or her to a share of the goodwill of the company.
Question 2.
Solution 2 The handling of a partner’s goodwill at the time of retirement can be achieved in the capital account of the partner. The capital account of the retired or dead partner will be paid with his share of goodwill and the capital account of the continuing partner will be debited into their earnings ratio. Journal Entry Continuing Partner’s Capital A/cs Dr. (Gaining ratio) To Retiring/ Deceased Partner’s Capital A/c (Share of goodwill) (Retirement/deceased partner’s goodwill share In the acquiring percentage, tailored to on going partners)
Question 3.
Solution 3 The following modifications include the retirement of a partner from the company: (i) Calculate the current percentage of gains for all other partners. (ii) The new ratio of the remaining partners is determined. (iii) Measurement of the firm’s goodwill and accounting care. iv) Asset and obligation revaluation. (v) Sharing between all partners of combined gains and losses and reserves. (vi) Shared Life Strategy Treatment. (vii) Settlement of the balance due to the spouse retiring. (iii) Transfer of the remaining partners’ capital accounts to a current profit-sharing ratio.
Question 4.
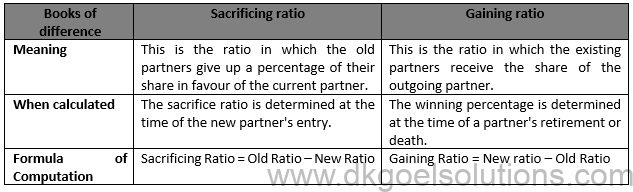
Solution 4 The gaining ratio is the ratio in which the on-going partners receive the share of the withdrawing partner. It is determined by deducting the old proportion from the current proportion. Formula for Calculating Gaining Ratio: Gaining ratio = New ratio – Old ratio.
Question 5.
Question 6.
Solution 6 The deceased partner’s legal executive is entitled to the balance number of the capital account of the deceased partner. The following things are posted in the deceased partner’s capital account on the debit side: (a) Credit balance in a capital account or current account of the deceased spouse. (b) The profit share of the deceased spouse up to the date of his or her death. (c) The share of goodwill of the deceased partner. (d) The share of the deceased spouse in the net reserves and the taxable account. (e) The share of the deceased partner in the gains from the revaluation of assets and liabilities. (f) The share of the deceased partner in the shared life policy. (g) Capital interest and salary or commission, if any, before the date of death.
The following things are posted on the credit side of the deceased partner’s capital account: (a) Debit balance for the capital account and current account of the deceased partner. (b) The sum withheld in the form of drawings before the day of the partner’s death. (c) Curiosity in paintings up to the date of death, if any. (d) The proportion of losses of the deceased partner in the revaluation of assets and liabilities. (e) The share of the loss of the deceased spouse up to the date of death. (f) The dead partner’s share of the company’s cumulative damages.
Question 7.
Solution 7 The executors of the deceased partner shall now be entitled to the share of earnings gained by the company from the beginning of the year until the day of his death if the death of the partner occurred on any day during the year. From any of the following methods, such benefit can be determined: (a) Dependent on Time. (b) On a revenue or turnaround basis.
Question 8.
Solution 8 The products that are attributed to a deceased partner’s account when determining the balance owed to his legal representatives:- 1.) His share of the increase in the appreciation of the company’s goodwill. 2.) The sum that is attributable to his capital account credit. 3.) If given in the partnership deed, interest on money. 4.) His share of gains on asset and obligation revaluation. 5.) His share of the benefit or reserves that are undistributed.
Practical Questions:-
Question 1. (A)
Solution 1 (A) It is given that old Ratio = 6 : 5 : 4. By striking out the share of the withdrawing partner, the current percentage of the remaining partners is determined. The current ratio between B and C will be 5:4 as A retires. The current ratio between A and C will be 6:4 after B retires. The current ratio between A and B will be 6:5 after C retires.
Question 1. (B)
Solution 1 (B) It is given that old Ratio = 5:3:1:2. The new ratio between A and D would be 5:2 if B and C are excluded.
Solution 2 It is given that the old ratio of X, Y and Z is 2/3:1/4:1/12 Take LCM of Denominator 3, 4 and 12 is 12. New ratio is (8 ∶ 3 ∶ 1)/12 New ratio = 8:3:1 The current ratio between Y and Z would be 3:1 after X is removed.
Solution 3 It is given that the old Ratio of L, M and O are 3:2:2. M’s Share will be divided into L and O equally. L’s Gaining and New Ratio:- Gaining Ration of L = 2/7 of 1/2 = 2/14 or 1/7
New Ratio of L = 3/7+1/7=(3+1)/7= 4/7
O’s Gaining and New Ratio:- Gaining Ratio of O = 2/7 of 1/2 = 2/14 or 1/7 New Ratio is O = 2/7+1/7=(2+1)/7= 3/7 Hence, the New Ratio of L and O = 4/7:3/7 or 4 : 3
bIt is given that old Ratio of A, B and C = 4:3:2 We can write it as old Ratio of A, B and C = 4/9:3/9:2/9 The share of B would be split between A and C at a ratio of 3:2.
Gaining Ratio of A = 3/5 of 3/9= 9/45 New Ratio of A = 4/9+9/45=(20+9)/45=29/45
Gaining Ratio of C = 2/5 of 3/9= 6/45 New Ratio of C = 2/9+6/45=(10 + 6)/45=16/45 Hence, the new ratio of A and C = 29/45:16/45 or 29 : 16
Question 5. (A)
Solution 5 (A) It is given that old ratio of A, B and C = 4:3:1 We can write is as old ratio of A, B and C = 4/8:3/8:2/8 A’s share would be split evenly between B and C.
Gaining Ratio of B = 1/2 of 4/8= 1/4 New Ratio B = 3/8+1/4=(3+2)/8=5/8 Gaining Ratio of C = 1/2 of 4/8= 1/4 New Ratio C = 1/8+1/4=(1 + 2)/8=3/8 Hence, the new ratio of B and C = 5/8:3/8 or 5 : 3
Question 5. (B)
Solution 5 (B) It is given that old ratio of A, B and C = 1/2:1/3:1/6 B’s share will be split in a 5:3 ratio between A and C. Gaining Ratio of A = 5/8 of 1/3= 5/24 New Ratio of A = 1/2+5/24=(12+5)/24=17/24 Gaining Ratio of C = 3/8 of 1/3= 3/24 New Ratio of C = 1/6+3/24=(4 + 3)/24=7/24 Hence, the new ratio of A and C = 17/24:7/24 or 17 : 7
Solution 6 It is given that old ratio = 2:2:1 We can write it is as old ratio = 2/5:2/5:1/5 Z has fully taken over Y’s share. New Share of X = 2/5 New Share of Y = 1/5+ 2/5=3/5 Hence, the new ratio of X and Z = 2/5:3/5 or 2:3
Solution 7 It is given that the existing ratio of P and Q = 1/2 and 2/6 P’s acquired from R = 1/6×2/3=2/18 Q’s acquired form R = 1/6×1/3=1/18 New Share of P = 1/2+2/18=11/18 New Share of Q = 2/6+1/18=7/18 Share given by P and S = 1/4×1/3=1/12 Remaining share = 1/4-1/12=(3-1)/12=2/12 = 1/6 S gets it from both P and Q in equal amounts. P and Q each give S 1/2 of 1/6 = 1/12 each.
New Share of P = 11/18-1/12-1/12=(22-3-3)/36=16/36 New Share of Q = 7/18-1/12=(14-3)/36=11/36 P, Q, and S have a new profit-sharing ratio = 16/36:11/36:1/4 P, Q, and S have a new profit-sharing ratio = 16 : 11 : 9.
Question 8. (A)
Solution 8 (A) It is given that old Ratio of A, B and C = 7:5:3 (i) As A retires, B and C have a 5:3 gaining ratio. A retires, resulting in a new 5:3 ratio between B and C. (ii) As B retires, A and C will have a 7:3 benefit ratio. B retires, resulting in a new 7:3 ratio between A and C. (iii) After C retires, A and B will have a 7:5 benefit ratio. C retires, resulting in a new 7:5 ratio between A and B.
Question 8. (B)
Solution 8 (B) It is given that old ratio of X, Y and Z is 1/2:3/10:1/5 We can write it as old ratio of X, Y and Z is 5:3:2 (i) The gaining ratio between Y and Z when X dies is 3:2. When X dies, the new Y:Z ratio is 3:2. (ii) The gaining ratio between X and Z is 5:2 when Y dies. When Y dies, the new X:Z ratio is 5:2. (iii) The gaining ratio between X and Y is 3:2 when Z dies. When Z dies, the new X:Y ratio is 5:3.
Question 8. (C)
Solution 8 (C) It is given that old ratio of P, Q, R and S is 5:4:3:1 P and S retire: Q and R’s Gaining Ratio is 4 : 3 Q and R’s New Ratio is 4 : 3
Question 9. (A)
Solution 9 (A) Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of Ashish = 3/4-2/5=(15 – 8)/20=7/20 Gaining Ratio of Aman = 1/4-1/5=(5 – 4)/20=1/20 Hence, the gaining ratio of Ashish and Aman of 7 : 1
Question 9. (B)
Solution 9 (B) Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of A = 3/5-5/10=(6 – 5)/10=1/10 Gaining Ratio of B = 2/5-2/10=(4 – 2)/10=2/20 Hence, the gaining ratio of A and B of 1 : 2
Question 10. (A)
Solution 10 (A) Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of A = 1/2-1/2=0 Gaining Ratio of B = 1/2-1/3=(3 – 2)/6=1/6 Hence, the gaining ratio B of 1/6
Question 10. (B)
Solution 10 (B) Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of B = 1/3-4/14=(14 – 12)/42=2/42 Gaining Ratio of C = 1/2-3/14=(14 – 9)/42=5/42 Gaining Ratio of D = 1/3-2/14=(14 – 6)/42=8/42 Gaining Ratio of B, C and D = 2/42 ∶ 5/42 ∶8/42 Hence, the gaining ratio of B, C and D = 2 : 5 : 8
Question 11.
Solution 11 Gain from Rekha = 2/5 of 1/3= 2/15
New share Rekha = 1/3+2/15=(5 + 2)/15=7/15
Gain from Suruchi = 3/5 of 1/3= 3/15
New share Suruchi = 1/3+3/15=(5 + 3)/15=8/15 New Ratio of Rekha and Suruchi = 7/15 and 8/15 Hence, the new ratio of Rekha and Suruchi = 7 : 8
Question 12.
Solution 12 Z’s share will be split between X and Y in the following ratio 3/4 ∶ 1/4 Gaining Ratio of X = 3/4 of 5/9= 15/36 New Share of X = 1/9+15/36=(4 + 15)/36=19/36 Gaining Ratio of Y = 1/4 of 5/9= 5/36 New Share of Y = 1/3+5/36=(12 + 5)/36=17/36 New Ratio of X and Y = 19/36 : 17/36 New Ratio of Rekha and Suruchi = 19 : 17 Hence, the gaining ratio of X and Y is 3 : 1
Question 13.
Solution 13 S’s share will be split between Q and R in the following ratio 3 : 2. Gaining Ratio of Q = 3/5 of 2/12= 6/60 New Share of Q = 3/12+6/60=(15 + 6)/60=21/60 Gaining Ratio of R = 2/5 of 2/12= 4/60 New Share of R = 5/12+4/60=(25 + 4)/60=29/60 P’s share will not change 2/12 New Ratio of P, Q and R = 2/12 : 21/60:29/60 New Ratio of P, Q and R = (10 ∶ 21 ∶ 29)/60 Hence, the new ratio of P, Q and R is 10 : 21 : 29 and Gaining Ratio of Q and R = 3 : 2
Question 14.
Solution 14: Computation of Sacrificing Ratio:- Sacrificing Ratio of A = 3/5 of 1/4 = 3/20
Sacrificing Ratio B = 2/5 of 1/4 = 2/20
Computation of New Profit Ratio of A, B and C:- New Profit Sharing Ratio of A = 5/8-3/20=(25-6)/40=19/40 New Profit Sharing Ratio of B = 3/8-2/20=(15-4)/40=11/40 New Profit Sharing Ratio of C = 1/4 New Profit Sharing of A, B and C = 19/40:11/40:1/4 New Profit Sharing A, B and C = (19 ∶ 11 ∶ 10)/40 Hence, The New Profit Sharing of A, B and C = 19 : 11 : 10
(ii) New Profit Sharing Ratio of A, B, C and D:-
New Profit Ratio of A = 19/40-1/10=(19-4)/40=15/40 New Profit Ratio of B = 11/40 New Profit Ratio of C = 10/40-1/15=(30-8)/120=20/120 New Profit Ratio of D = 1/6 New Ratio of A, B, C and D = 15/40:11/40:22/120:1/6 New Ratio of A, B, C and D = (45 ∶ 33 ∶ 22 ∶ 20)/120 Hence, The New Ratio of A, B, C and D = 45 : 33 : 22 : 20
(iii) New Profit Sharing Ratio on A’s death:- Equally share divided in between B, C and D of A’s Share = 45/120×1/3=15/120 New Profit Sharing Ratio B = 33/120+15/120=48/120 New Profit Sharing Ratio C = 22/120+15/120=37/120 New Profit Sharing Ratio D = 20/120+15/120=35/120 New Ratio of B, C and D = 48 : 37 : 35
Question 15.
Solution 15 New Ratio of Y and Z will also be 5 : 4 Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of Y = 5/9-4/12=(20 – 12)/36=8/36 Gaining Ratio of Z = 4/9-3/12=(16 – 9)/36=7/36 Gaining Ratio of Y and Z = 8/36:7/36 Hence, the gaining ratio of Y and Z = 8 : 7
Question 16. (A)
Solution 16 (A)
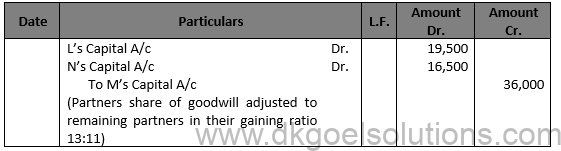
Working Note:- Calculation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of L = 5/8-4/9=(45-32)/72=13/72
Gaining Ratio of N = 3/8-2/9=(27 – 16)/72=11/72
Hence, the gaining ratio = 13 : 11
Point for Students:- It is calculated when a partner retires or dies. When a partner retires or dies, his share of profit is taken over by the remaining partners. The ratio in which the remaining partners share increase is called the gaining ratio. Gaining Ratio is the ratio in which the remaining partners will pay the amount of goodwill to the retiring partner.
Question 16. (B)
Solution 16 (B)
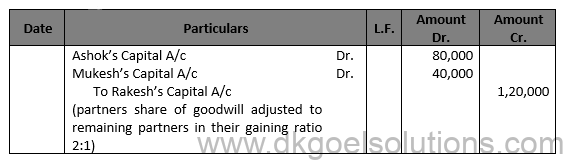
Point for Students:- The retiring or decreased partner is entitled to his share of goodwill at the time of retirement or death because the goodwill earned by the firm is the result of the efforts of all the existing partners in the past. Since a part of the future profits will be accruing because of the present goodwill and the retiring of deceased partner will not be sharing future profits, it will be fair to compensate the retiring or decreased partner for the same.
Question 17.
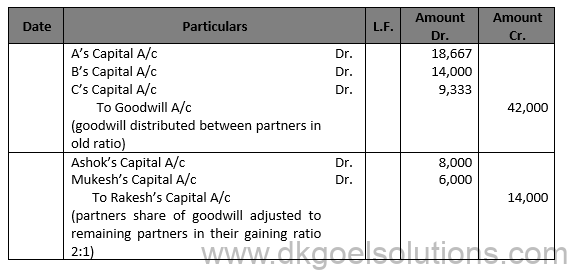
Solution 17
Question 18.(A)
Solution 18

Points for Students:- The following modifications include the retirement of a partner from the company: (i) Calculate the current percentage of gains for all other partners. (ii) The new ratio of the remaining partners is determined. (iii) Measurement of the firm’s goodwill and accounting care. iv) Asset and obligation revaluation. (v) Sharing between all partners of combined gains and losses and reserves. (vi) Shared Life Strategy Treatment. (vii) Settlement of the balance due to the spouse retiring. (iii) Transfer of the remaining partners’ capital accounts to a current profit-sharing ratio.
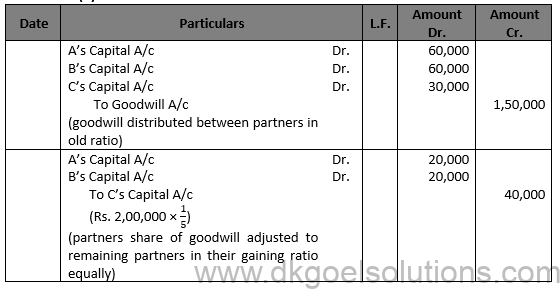
Question 18.(B)
Solution 18 (B)
Question 19.(A)
Solution 19 (A)
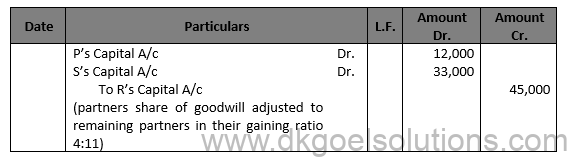
Valuation of Goodwill:- Total Profit for 4 Years = Rs. 1,20,000 + Rs. 60,000 – Rs. 20,000 + Rs. 80,000 = Rs. 2,40,000 Profit to R’s Capital A/c = Rs. 2,40,000 × 3/8 = Rs. 90,000 R’s share of Goodwill = Rs. 90,000 × 1/2 = Rs. 45,000
Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio :- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio
Gaining Ratio of P = 3/5-4/8=(24-20)/40=4/40
Gaining Ratio of S = 2/5-1/8=(16 – 5)/40=11/40
Hence, Gaining ratio = 4 : 11
Question 19.(B)
Solution 19 (B)

Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio
Gaining Ratio of B = 2/6-5/8=(8-15)/24=7/24
Gaining Ratio of D’s gaining = 1/6-3/8=(4 – 9)/24=5/24
Gaining ratio of B and D = 7 : 5
A’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 90,000 × 2/6 = Rs. 30,000
C’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 90,000 × 1/6 = Rs. 15,000
Total Goodwill = Rs. 30,000 + Rs. 15,000 = Rs. 45,000
Point for Students:- The product of the contributions of all current collaborators in the past is goodwill received by the organization. A percentage of potential gains will accrue regardless of the current goodwill and future earnings will not be shared by the retired or deceased partner. The surviving partners should then reward the retired or deceased partner by entitling him or her to a share of the goodwill of the company.
Question 20.
Solution 20

Gaining Ratio of Surender = 1/3-2/6=(2-2)/6=0
Gaining Ratio of Ramesh = 1/3-1/6=(2 – 1)/6=1/6
Gaining Ratio of Mohan = 1/3-1/6=(2 – 1)/6=1/6
Gaining Ratio of Ramesh and Mohan is 1:1.
Question 21.
Solution 21
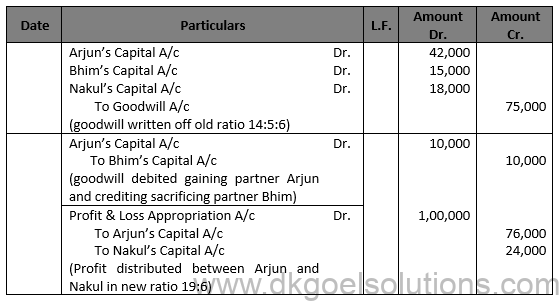
Working Note:- Valuation of Goodwill:- Total Profit for 3 Years = (Rs. 50,000 + Rs. 60,000 + Rs. 55,000)/3 = Rs. 55,000
Super Profit = Average Profit – Normal Profits Super Profit = Rs. 55,000 – Rs. 30,000 Super Profit = Rs. 25,000 Goodwill = Rs. 50,000 × 5/25 = Rs. 10,000
Computation of New Ratio:- A Gaining Ratio of rjun = 14/25+5/25=(14 + 5)/25=19/25 A Gaining Ratio of rjun Nakul = 6/25+0=6/25 Gaining ratio = 19 : 6
Question 22 (A).
Solution 22 (A)

Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio :- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio A’s gaining Ratio = 11/15-6/15=(11 – 6)/15=5/15 (Gain) B’s gaining Ratio = 0-4/15= (-4)/15 (Sacrifice) C’s gaining Ratio = 4/15-5/15=(4 – 5)/15=(-1)/15 (Sacrifice) A’s has gained 5/15 and B and C will sacrificed in the ratio of 4:1.
Question 22. (B)
Solution 22 (B)

Working Note:- 1.) Z’s Share in goodwill = Rs. 30,000 × 1/6 = Rs. 5,000
2.) Computation of Gaining Ratio :- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio
X’s Sacrifice Ratio = 1/3-3/6=(2 – 3)/6=1/6 (Sacrifice) Y’s gaining Ratio = 2/3-2/6= (4 – 2)/6=2/6 (Gain) Y’s will gained 2/6 and X will sacrificed 1/6 in favour of Y.
Question 23.
Solution 23

Working Note:- 1.) C’s Share in goodwill = Rs. 3,60,000 × 3/12 = Rs. 90,000
2.) Computation of Gaining Ratio :- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio A’s Sacrifice Ratio = 9/12-5/12=(9 – 5)/12=4/12 (Gain) B’s gaining Ratio = 2/12-3/12= (2 – 3)/12=(-1)/12 (Sacrifice) C’s Sacrifice Ratio = 0-3/6=(0 – 3)/6=(-3)/6 (Sacrifice) D’s Sacrifice Ratio = 1/12-1/12=(1 – 1)/12=0 A’s will gained 4/12.
Question 24.
Solution 24
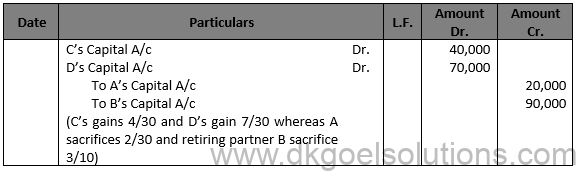
Working Note:- 1.) B’s share of Goodwill = Rs. 3,00,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 90,000
Sacrifice Ratio A = 1/3-4/10=(10 – 12)/30=(-2)/30 (Sacrifice)
Sacrifice Ratio B = 0-3/10= (0 – 3)/10=(-3)/10 (Sacrifice)
Sacrifice Ratio C = 1/3-2/10=(10 – 6)/30=4/30 (Gain)
Sacrifice Ratio D = 1/3-1/10=(10 – 3)/30=7/30 (Gain)
C and D will be debited for their gains, while A and B will be awarded for their sacrifices in the ratio of 2:9.
Point for Students:- The products that are attributed to a deceased partner’s account when determining the balance owed to his legal representatives:- 1.) His share of the increase in the appreciation of the company’s goodwill. 2.) The sum that is attributable to his capital account credit. 3.) If given in the partnership deed, interest on money. 4.) His share of gains on asset and obligation revaluation. 5.) His share of the benefit or reserves that are undistributed.
Question 25.
Solution 25 (i) Record the sale of Y’s share to X and Z:-

(ii) X and Z purchased Y‘s share for Rs. 1,60,000, out of which X pays 1,00,000 and Z pays Rs. 60,000, i.e., X and Z will share Y’s shale of profit in the ratio of 1,00,000 : 60,000 = 5 : 3. New Profit sharing ratios of X and Z will be: X gets 5/8th of Y’s share of 2/6 = 5/8 ×2/6=5/24
X’s old share = 3/6
X’s New share = 3/6+5/24=(12 + 5)/24=17/24
Z gets 3/8th of Y’s share of 2/6 = 3/8 ×2/6=3/24
X’s old share = 1/6
X’s New share = 1/6+3/24=(4 + 3)/24=7/24
New Ratio between X and Z = 17/24:7/24=17:7
(iii) Division of Profit between X and Z: Profit = Rs. 2,40,000 X’s Share = Rs. 2,40,000 × 17/24 = Rs. 1,70,000
Z’s Share = Rs. 2,40,000 × 7/24 = Rs. 70,000
Question 26 (new).
Solution 26 (new).

Question 26.
Solution 26
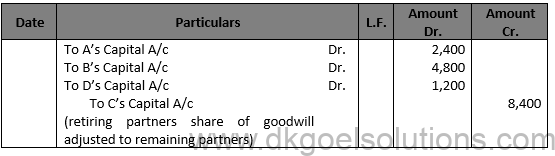
Working Note:- Average Profit :- (Rs.40,000 – Rs.10,000 + Rs.1,00,000 + Rs.1,50,000)/4 = Rs. 70,000
Super Profit = Average Profit – Normal Profits Super Profit = Rs. 70,000 – Rs. 56,000 Super Profit = Rs. 14,000
Goodwill = Rs. Super Profit × Number of year Purchases Goodwill = Rs. 14,000 × 2 Goodwill = Rs. 28,000
C’s Share of goodwill = Rs. 28,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 8,400
Point for Students:- The handling of a partner’s goodwill at the time of retirement can be achieved in the capital account of the partner. The capital account of the retired or dead partner will be paid with his share of goodwill and the capital account of the continuing partner will be debited into their earnings ratio.

Question 27.
Solution 27
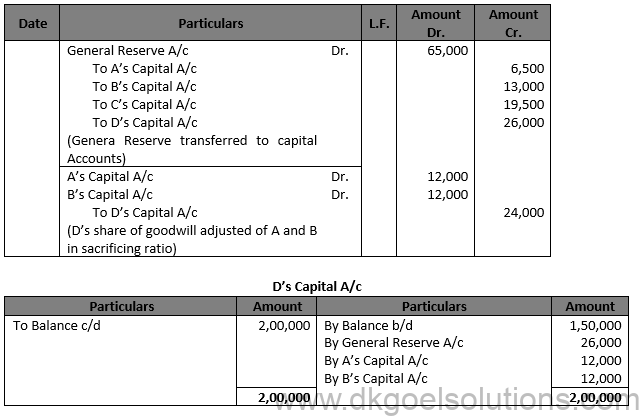
Working Note:- D’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 60,000 × 4/10 = Rs. 24,000
Computation of New Ratio:- D’s share will be split evenly between A and B: A’s Gain = 1/2 of 4/10=2/10
New Share of A = 1/10+2/10=3/10
B’s Gain = 1/2 of 4/10=2/10
New Share of B = 2/10+2/10=4/10
C’s share will remain the same 3/10
New Ratio of A, B and C = 3/10:4/10:3/10
Hence, the new ratio of A, B and C is 3:4:3
Question 28.
Solution 28
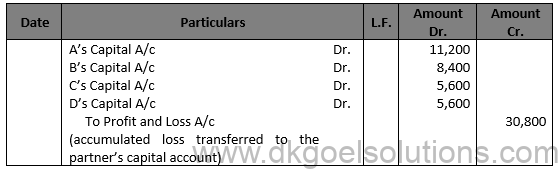
Question 29.
Solution 29
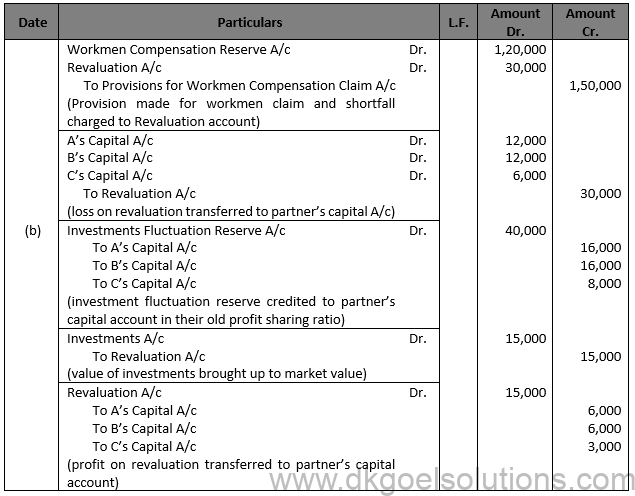
Question 30.
Solution 30
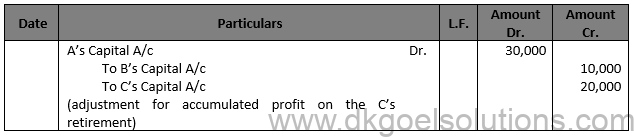
Working Note:- Computation of Net Effect:- Net Effect = General Reserve + Profit & Loss Account – Advertisement Suspense Account Net Effect = Rs. 1,00,000 + Rs. 45,000 – Rs. 25,000 Net Effect = Rs. 1,20,000
Computation of Sacrifice or Gaining Ratio:- A’s Share = 3/6-3/4=(6 – 9)/12=-3/12 (Gain) B’s Share = 2/6-1/4=(4 – 3)/12=1/12 (Sacrifice)
Question 31.
Solution 31
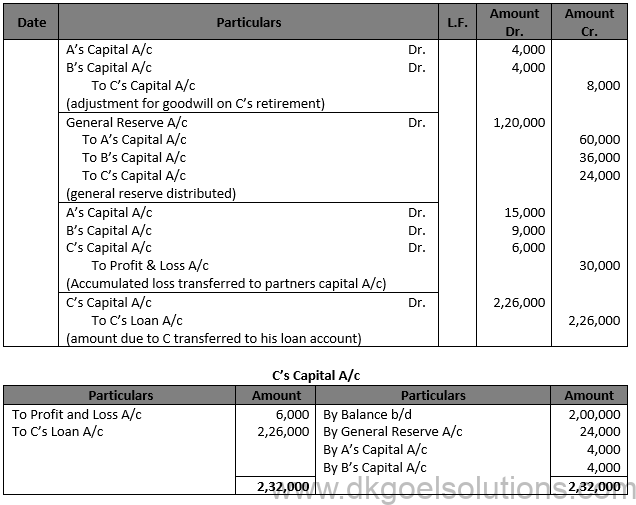
Working Note:- Valuation of Goodwill:- Average Profit = (10,000 + 25,000 – 15,000 + 36,000 + 44,000)/5=Rs.20,000 Goodwill of 2 year Purchases = Rs. 20,000 × 2 = Rs. 40,000 C’s Share = Rs. 40,000 × 2/10 = Rs. 8,000
Computation of Gaining and Sacrificing Ratio:- A’s Share = 6/10-5/10=1/10 B’s Share = 4/10-3/10=1/10 Gaining Ratio = 1 : 1
Question 32. (A)
Solution 32 (A)

Working Note:- Goodwill = (Rs. 1,20,000+Rs. 1,00,000+Rs.95,000)/3 = Rs. 1,05,000 Z’s Share of goodwill = Rs. 1,05,000 × 1/3 = Rs. 35,000
Question 32. (B)
Solution 32 (B)
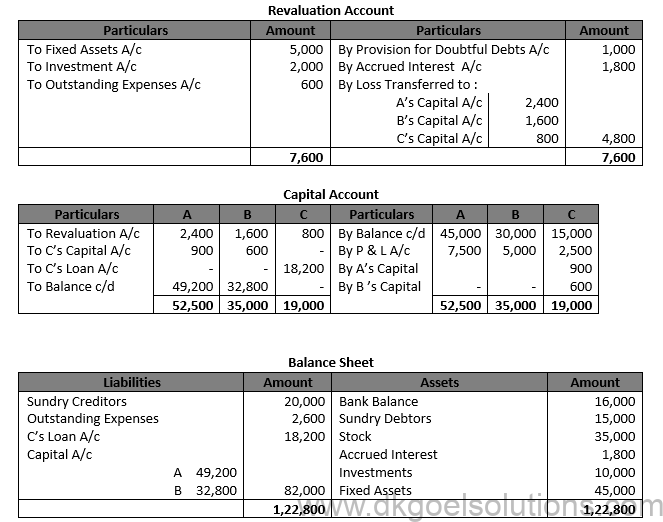
Working Note: C’s share of Goodwill = 9,000 x 1/6 = Rs. 1,500. It will be credited to C’s Capital A/c and debited to A and B’s Capital A/cs in their gaining ratio of 3 : 2.
Point for Students:- The goodwill is not shown in the books of a firm. However, if at the time of retirement of death of a partner, it appears in the balance sheet of a firm, it will be written off by debiting all the partner’s capital accounts in their old profit sharing ratio and crediting the goodwill account.
Question 33.
Solution 33
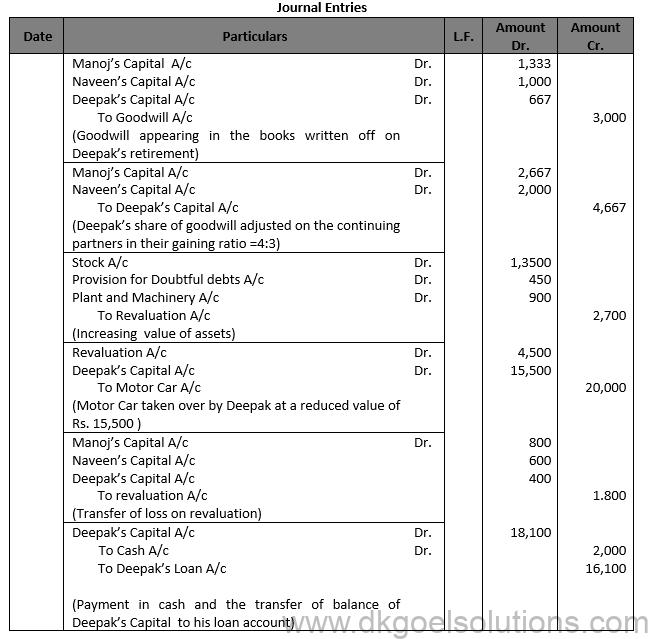
Question 34.
Solution 34

Question 35 (new).
Solution 35 (new).
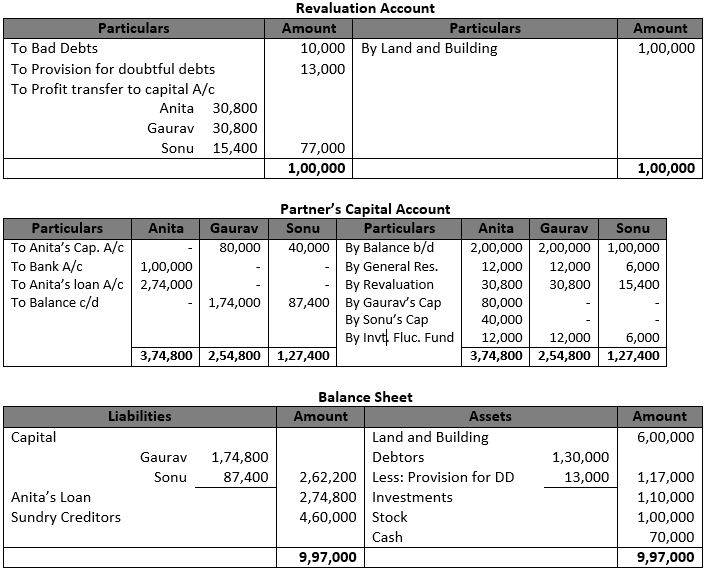
Question 35. .
Solution 35.

Working Note:- 1.) Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Yasmin’s Gaining Ratio = 3/5-3/10=(6 – 3)/10=3/10 Saloni’s Gaining Ratio = 2/5-3/10=(4-3)/10=1/10 Gaining Ratio = 3 : 1
2.) Net Debtors = Rs. 90,000 – Rs. 4,000 = Rs. 86,000
| Provision @ 5% on Rs. 86,000 | Rs. 4,300 |
| Less: Current Provision Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 4,000 | Rs. 6,000 |
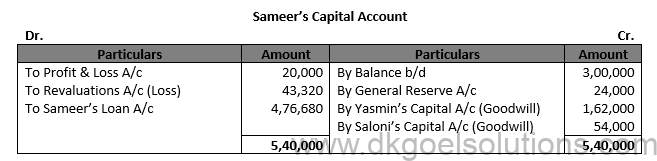
Question 36.
Solution 36.
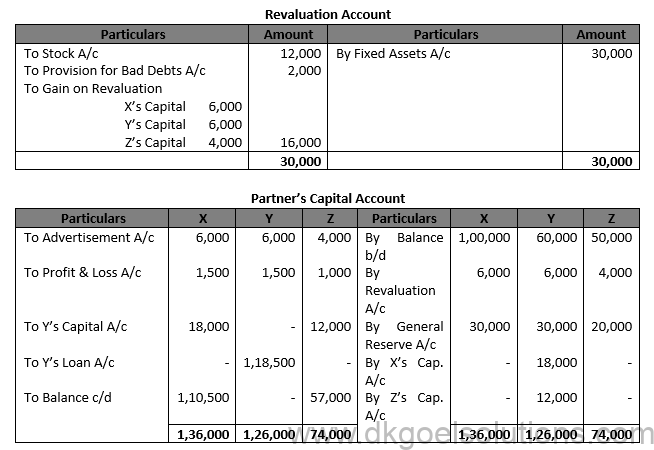
Working Note:- 1.) Y’s Share of goodwill = Rs. 80,000 × 3/8 = Rs. 30,000 X and Z in their Gaining Ratio of 3:2 X’s Gain = Rs. 80,000 × 3/5 = Rs. 18,000 Z’s Gain = Rs. 30,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 12,000
Question 37. (A)
Solution 37. (A)
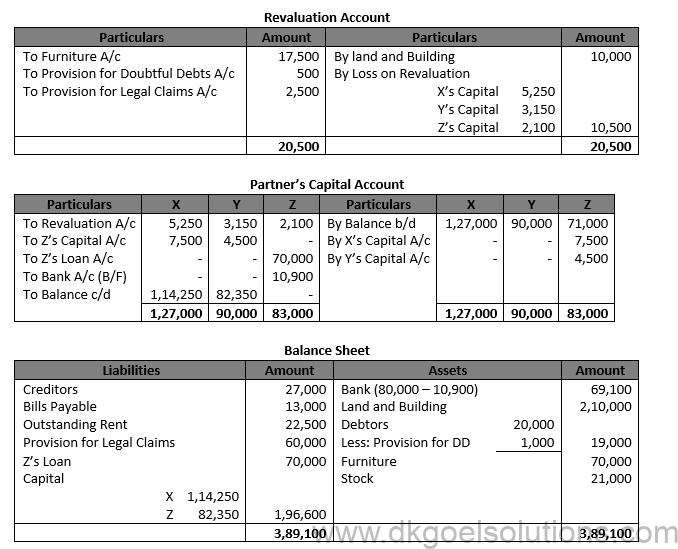
Working Note:- 1.) Z’s Share of goodwill = Rs. 60,000 × 2/10 = Rs. 12,000 X and Z in their Gaining Ratio of 5:3 X’s Gain = Rs. 12,000 × 5/8 = Rs. 7,500 Z’s Gain = Rs. 12,000 × 3/8 = Rs. 4,500
Question 37. (B)
Solution 37. (B)

Working Note:- 1.) Computation of Gaining Ratio: B’s Share = 5/8-2/5=(25- 16)/40=9/40 C’s Share = 3/8-1/5=(15- 8)/40=7/40 Gaining Ratio = 9 : 7
2.) A’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 60,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 24,000 B will be debited by Rs. 24,000 × 9/16 = Rs. 13,500 C will be debited by Rs. 24,000 × 7/16 = Rs. 10,500
3.) Computation of Bank Overdraft: Bank Overdraft = Bank Balance as per Balance Sheet – Amount required to pay off Bank Overdraft = Rs. 44,800 – Rs. 1,24,800 Bank Overdraft = Rs. 80,000
Question 38.
Solution 38.
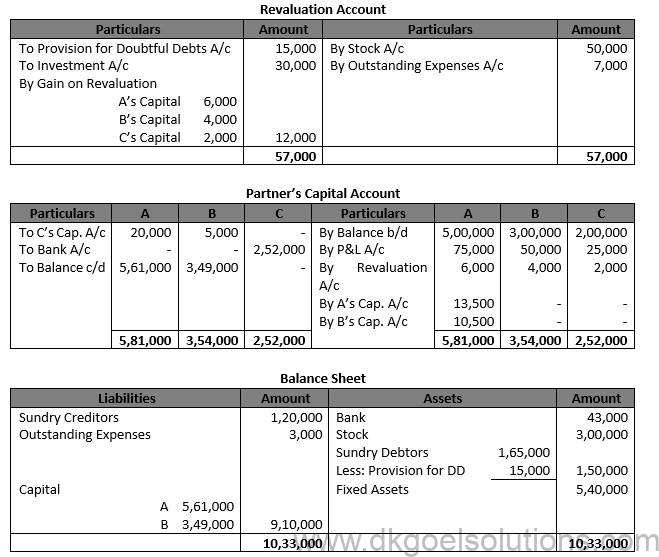
Question 39.
Solution 39.
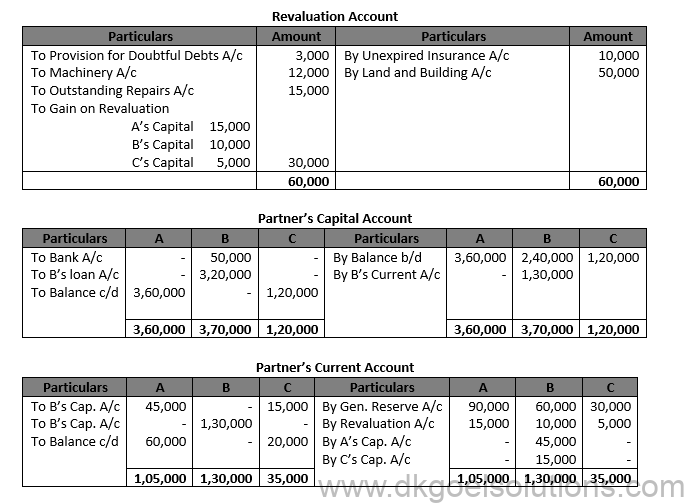
Question 40.
Solution 40.
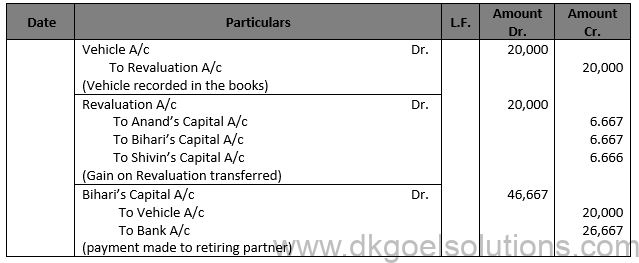
Question 41.
Solution 41.
Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio:- X’s Gain = 1/2-5/12=(6-5)/12=1/12 Z’s Gain = 1/2-3/12=(6-3)/12=3/12 Y’s Share of goodwill = Rs. 16,200 × 4/12 = Rs. 5,400
Question 42.
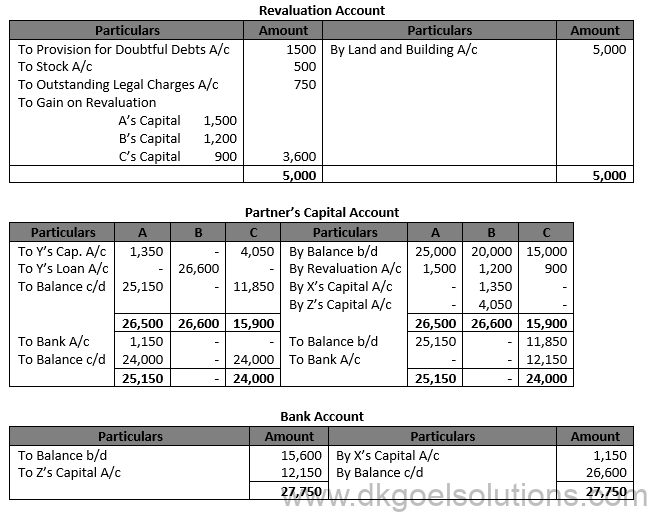
Solution 42.
Working Note:- 1.) Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Saman’s Gain = 3/5-2/7=(21-10)/35=11/35 Meeta’s Gain = 2/5-2/7=(14-10)/35=4/35 Gaining Ratio = 11:4
2.) Harish’s Share of goodwill = Rs. 5,60,200 × 3/7 = Rs. 2,40,000 Saman’s Share = Rs. 2,40,000 × 11/15 = Rs. 1,76,000 Meeta’s Share = Rs. 2,40,000 × 4/15 = Rs. 64,000
3.) Total Capital new firm = Rs. 35,00,000 Saman’s Capital = Rs. 35,00,000 × 3/5 = Rs. 21,00,000 Meeta’s Capital = Rs. 35,00,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 14,00,000
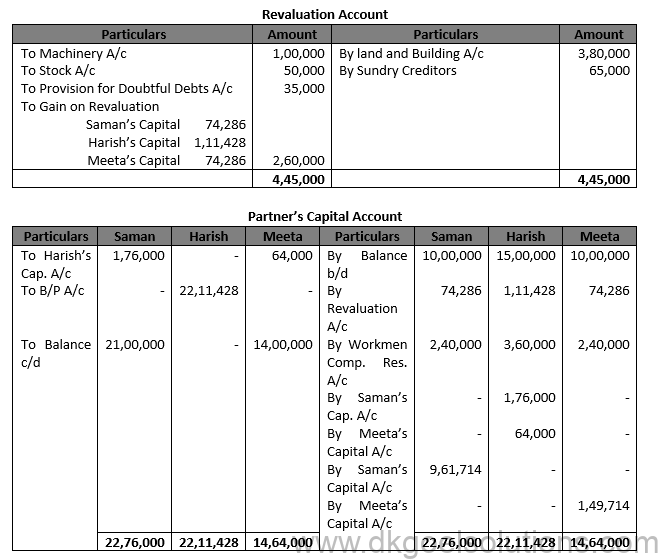
Question 43 (new).
Solution 43 (new).
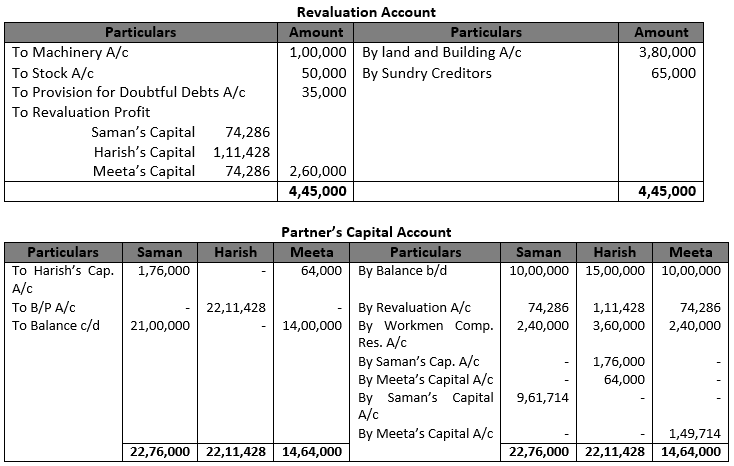
Working Note:- 1.) Calculation of Gaining Ratio:- Saman’s Gain = 3/5-2/7=(21-10)/35=11/35 Meeta’s Gain = 2/5-2/7=(14-10)/35=4/35 Gaining Ratio = 11:4
Question 43.
Solution 43.

Total Capital of Ajay and Sanjay = Rs. 2,00,000 + Rs. 1,00,000 = Rs. 3,00,000 Profit Sharing Ratio = 5:3 Ajay’s Capital = Rs. 3,00,000 × 5/8 = Rs. 1,87,500 Cash withdrawn by Ajay = Rs. 2,00,000 – Rs. 1,87,500 = Rs. 12,500 Sanjay’s Capital = Rs. 3,00,000 × 3/8 = Rs. 1,12,500 Cash bought by Sanjay = Rs. 1,12,500 – Rs. 1,00,000 = Rs. 12,500
Question 44.
Solution 44. After X’s retirement, the new ratio of Y and Z is 2:1. Y’s Capital in the new firm should be = Rs. 2,10,000 × 2/3= Rs. 1,40,000 Cash withdrawn by Y = Y’s New Capital – Y’s existing Capital Cash withdrawn by Y = Rs. 1,40,000 – Rs. 1,45,000 Cash withdrawn by Y = Rs. 5,000
Z’s Capital in the new firm should be = Rs. 2,10,000 × 1/3 = Rs. 70,000 Cash withdrawn by Y = Y’s New Capital – Y’s existing Capital Cash withdrawn by Y = Rs. 70,000 – Rs. 63,000 Cash withdrawn by Y = Rs. 7,000
Question 45.
Solution 45.
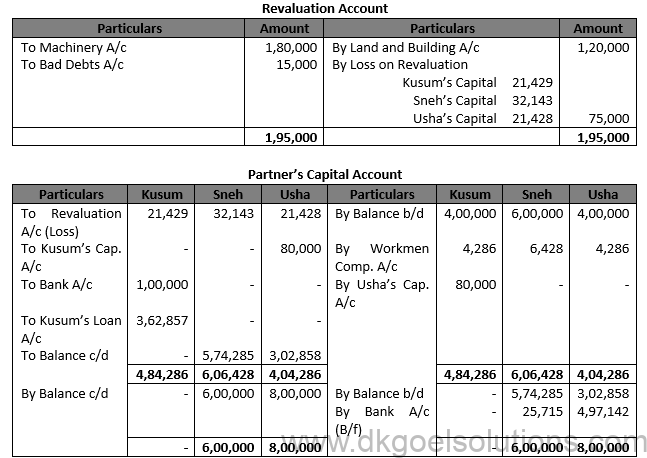
Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Sneh’s Gain = 3/7-3/7=0 Usha’s Gain = 4/7-2/7=(4-2)/17=2/7
Total Capital of Ajay and Sanjay = Rs. 2,00,000 + Rs. 6,00,000 + Rs. 3,00,000 = Rs. 14,00,000 Profit Sharing Ratio = 5:4 Sneh’s Capital = Rs. 14,00,000 × 3/7 = Rs. 6,00,000 Ush’s Capital = Rs. 144,00,000 × 4/7 = Rs. 8,00,000
Question 46.
Solution 46.

Working Note:- C’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 80,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 24,000 Old Ratio A, B and C = 4:3:3 New Ratio of A and B = 6:4
Computation of Gaining ratio:- A’s Gain = 6/10-4/10=2/10 B’s Gain = 4/10-3/10=1/10 Gaining Ratio = 2:1
Question 47.
Solution 47.
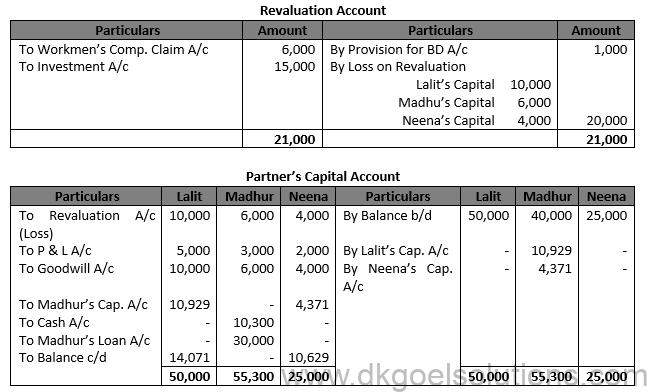
Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Madhur’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 51,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 15,300
Question 48.
Solution 48

Question 49.
Solution 49.

Question 50 A (new) .
Solution 50 A (new) .

Working Note:- G’s share in Goodwill = Rs. 15,000 × 3/6 = Rs. 7,500
Question 50. (A)
Solution 50 (A)

Question 50. (B)
Solution 50 (B)
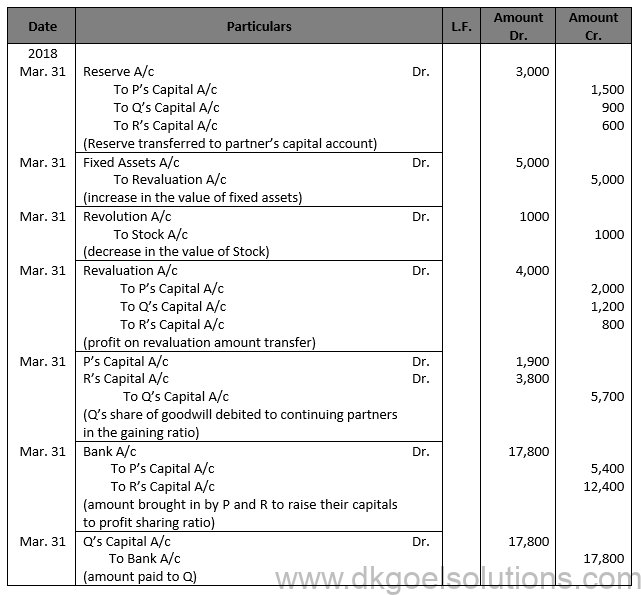
Working Note:- 1.) Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio P’s Gaining Ratio = 3/5-5/10=(6 – 5)/10=1/10 R’s Gaining Ratio = 2/5-2/10=(4-2)/10=2/10 Gaining Ratio = 1 : 2
2.) Total Capital of the New Firm = Rs. 21,600 + Rs. 17,800 + Rs. 5,600 = Rs. 45,000
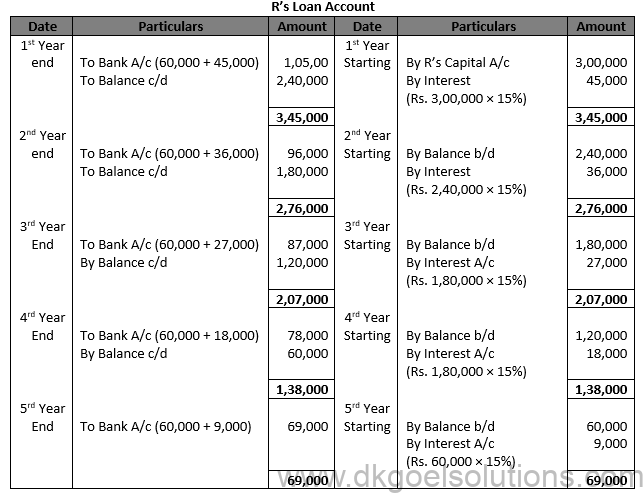
Question 51.
Solution 51. (i)
Question 52.
Solution 52.

Working Note:-

Question 53.
Solution 53.
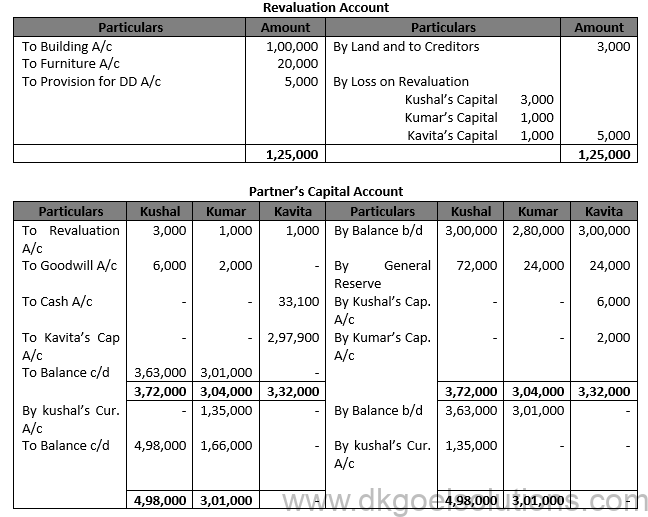
Point for Students:- The products that are attributed to a deceased partner’s account when determining the balance owed to his legal representatives:- 1.) His share of the increase in the appreciation of the company’s goodwill. 2.) The sum that is attributable to his capital account credit. 3.) If given in the partnership deed, interest on money. 4.) His share of gains on asset and obligation revaluation.
Question 54.
Solution 54.

Working Note:- Computation of New Capital: New Profit = A’s Capital Account + C’s Capital Account – Amount payable to B Total Capital = Rs. 1,90,000 + Rs. 80,000 – 1,50,000 Total Capital = Rs. 4,20,000 A’s New Ratio = Rs. 4,20,000 × 5/7 = Rs. 3,00,000 C’s New Ratio = Rs. 4,20,000 × 2/7 = Rs. 12,00,000
| A (Rs.) | B (Rs.) | |
| Capital required | 3,00,000 | 1,20,000 |
| Less: – Existing Capital | 1,90,000 | 80,000 |
| Rs. 110,000 | Rs. 40,000 |
Question 55.
Solution 55.
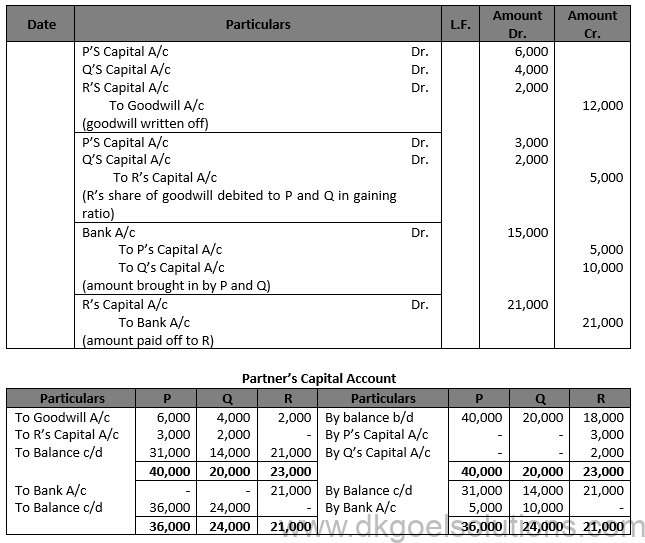
P’s New Capital = Rs. 6,00,000 × 3/5 = Rs. 36,000 Q’s New Capital = Rs. 6,00,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 24,000 Amount to be brought in P and Q:

Question 56.
Solution 56.
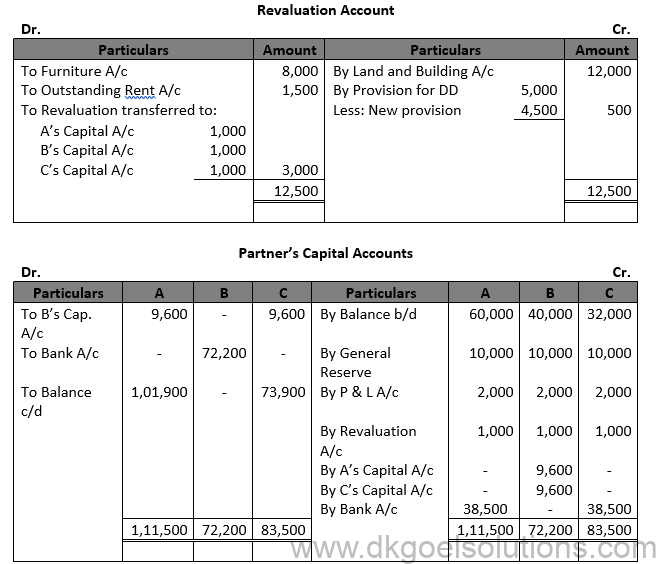
Working Note:- Gaining Ratio =New Ratio – Old Ratio A’s Gain = 1/2-1/3=(3-2)/6=1/2 B’s Gain = 1/2-1/3=(3-2)/6=1/6 B’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 57,600 × 1/3 = Rs. 19,200
Question 57.
Solution 57.

Question 58.
Solution 58. Average Profit = (Rs.40,000 + 50,000 +72,000 )/3 = Rs. 54,000 Five month’s profit, i.e, from 1st April, 2018 to 31st August, 2018= Rs. 54,000 X 5/12 = Rs. 22,500 Share of B till his death = Rs. 22,500 X 1/3 = Rs. 7,500. (i) when there is no change in the profit sharing ratio of A and C;

(ii) When there is change in the profit sharing ratio of A and C and the new ratio is 7 : 5. A Gains: 7/12- 1/3 = (7-4)/12 =3/12 C Gains: 5/12 – 1/3 = (5-4 )/12 = 1/12 Hence, Gaining Ratio of A and C = 3:1

Question 59.
Solution 59.
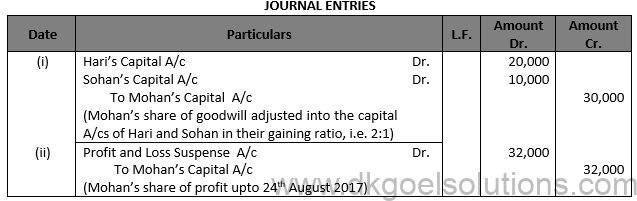
Working Notes: (i) Mohan’s share of goodwill = Rs. 75,000 X2/5 = Rs. 30,000. It will be debited to the Capital Accounts of hari and Sohan in their gaining ratio, i.e., 2:1. (ii) Number of days from March 31 to August 24 = 146 Mohan’s share of profit = 2,00,000 X 146/(365 ) X 2/5 = Rs. 32,000.
Question 60.
Solution 60. Profit from 1st April 2019 to 31st December, 2019 on the basis of sales If sales are Rs. 4,00,000, profit is Rs. 60,000 If sales are Rs. 3,30,000 profit will be 60,000/(4,00,000 ) × 3,30,000= Rs. 49,500 A’s share will be = Rs. 49,500 × 4/(9 ) = Rs. 22,000
Question 61.
Solution 61.

Question 62 (new).
Solution 62 (new).
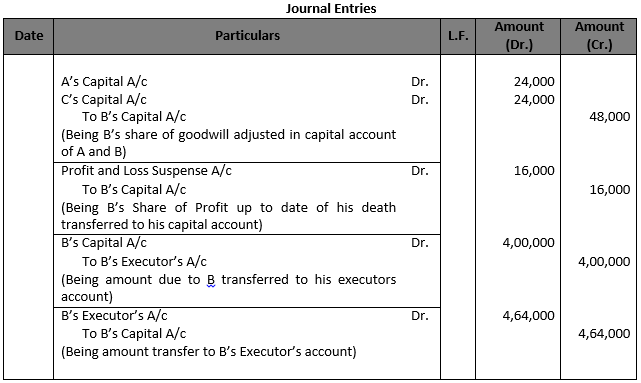
Working Note:- Calculation of Goodwill:- Total goodwill of firm = Rs. 80,000 × 1.5 year Total goodwill of firm = Rs. 1,20,000 B’s share in goodwill = Rs. 1,20,000 × 2/5 = 48,000
Calculation of Profit:- Profit of the firm = Rs. 80,000 B’s Profit = Rs. 80,000 × 2/5 × 6/12 = Rs. 16,000
Question 62.
Solution 62.

Working Note: 1.Computation of Goodwill: Goodwill = 2 year’s purchase of average profit of the last three years Goodwill = 2 X Rs. 80,000 Goodwill = Rs. 1,60,000 Sindhu’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 1,60,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 48,000 Gaining ratio = 3 : 4
Rahul’s Contribution = Rs. 48,000 × 3/7 = Rs. 20,571 Kamlesh’s Contribution = Rs. 48,000 × 4/7 = Rs. 27,429
Question 63 (new).
Solution 63 (new).

Working Note: 1.Calculation of Goodwill: Goodwill = 2 year’s purchase of average profit of the last three years Goodwill = 2 × Rs. 80,000 Goodwill = Rs. 1,60,000 Sindhu’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 1,60,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 48,000 Gaining ratio = 3 : 4
Rahul’s Contribution = Rs. 48,000 × 3/7 = Rs. 20,571 Kamlesh’s Contribution = Rs. 48,000 × 4/7 = Rs. 27,429
Question 63.
Solution 63.
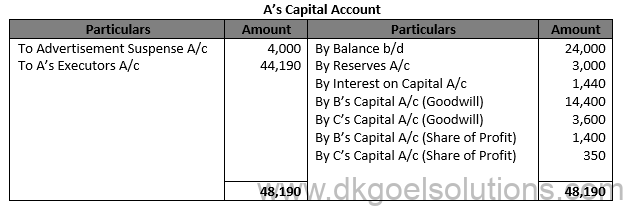
Working Note:- (i) Computation of Gaining Ratio:- B’s Share = 7/10-3/10=4/10
C’s Share = 3/10-2/10=1/10 Gaining Ratio = 4:1
(ii) Valuation of Goodwill:- Total Profit = Rs. 8,000 + Rs. 12,000 + Rs. 7,000 Total Profit = Rs. 27,000
Average Profit = (Total Profit )/(Number of years)
Average Profit = (Rs. 27,000 )/3 Average Profit = Rs. 9,000
Goodwill at 4 year purchases = Rs. 9,000 × 4 = Rs. 36,000 A’s Goodwill = Rs. 36,000 × 5/10 = Rs. 18,000
(iii) Share of profit payable to A = Rs. 7,000 × 6/12 × 5/10 = Rs. 1,750
Question 64.
Solution 64.
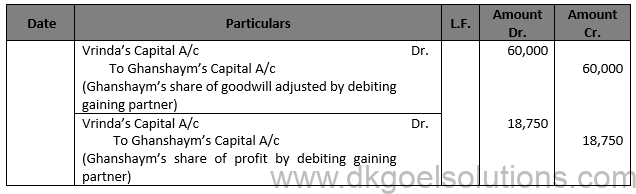
Working Note:- (i) Computation of gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Share – Old Share Ram’s Share = 1/2-4/8=Nil
Vrinda’s Share = 1/2-1/8=(4-1)/8=3/8 Vrinda is the only gaining partner.
(2) Computation of Gaining ratio:- Total Profit of last 4 year = Rs. 1,20,000 + Rs. 80,000 + Rs. 40,000 + Rs. 80,000 = Rs. 3,20,000 Firms Goodwill = Rs. 3,20,000 × 3/8 = Rs. 1,20,000
Ghanshaym’s Goodwill = Rs. 1,20,000 × 1/2 = Rs. 60,000
(3) Ghanshaym’s share of profit:- Average profit of past two years = (Rs.40,000+Rs.80,000)/2 = Rs. 60,000
Profit for 10 months (from 1st April, 2014 to 1st February 2015) = Rs. 60,000 × 10/12 = Rs. 50,000 Ghnashaym’s Profit = Rs. 50,000 × 3/8 = Rs. 18,750
Question 65.
Solution 65.
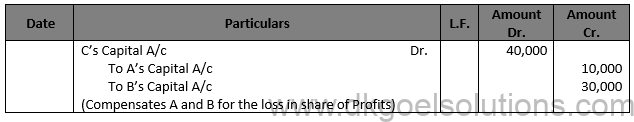
Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio A’s Share = 1/3-4/9=(3-4)/9=1/9 (Sacrifice)
B’s Share = 2/3-2/9=(6-2)/9 = 4/9 (Gain)
Total Goodwill of the Firm = Rs. 30,000 × 3/1 = Rs. 90,000
A’s share = Rs. 90,000 × 1/9 = Rs. 10,000
C’s share = Rs. 90,000 × 4/9 = Rs. 40,000
Question 66 (new).
Solution 66 (new).
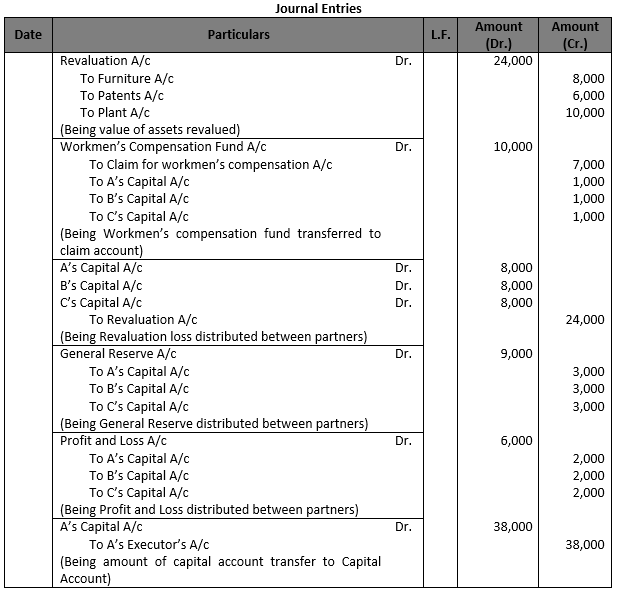
Question 66.
Solution 66.

Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio A’s Share = 1/3-5/12=(4-3)/12=1/12(Sacrifice) B’s Share = 0-3/12=3/12 (Sacrifice) C’s Share = 1/3-2/12=(4-2)/12=2/12 (Gain) D’s Share = 1/3-2/12=(4-2)/12=2/12 (Gain)
Question 67 A (new).
Solution 67 A (new).
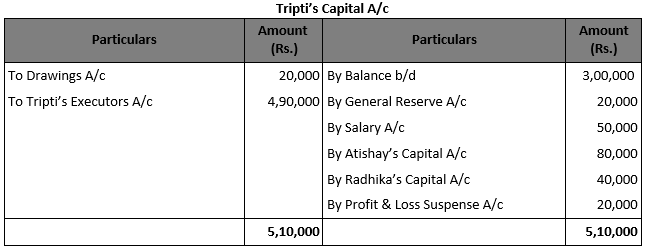
Working Notes:- (1) Calculation of Goodwill:- Average Profit = (1,00,000 + 1,50,000 + 2,00,000)/3 Average Profit = Rs. 1,50,000
Goodwill of the firm = Average Profits of the last three years × Number of Years’ Purchase Goodwill of the firm = Rs. 1,50,000 × 2 Goodwill of the firm = Rs. 3,00,000
Tripti’s share of goodwill = Rs. 3,00,000 × 2/5 Tripti’s share of goodwill = Rs. 1,20,000
(2) Calculation of Tripti’s Share of Profit Last Year’s profit = Rs. 2,00,000
Profit till the date of death = Rs. 2,00,000 × 3/12 = Rs. 50,000 Tripti’s Share of Profits = Rs. 50,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 20,000
Question 67(A).
Solution 67 (A).
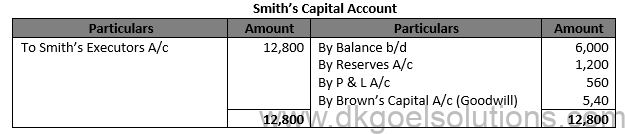
Working Note:- Profit Sharing Ratio of Brown and Smith = 1/2:1/3 Profit Sharing Ratio of Brown and Smith =3 : 2
(ii) Share in Profit:- Average Profit = (Total Profit )/(Number of years)
Average Profit = (Rs. 4,200 +Rs. 3,900 + Rs. 4,500 )/3 Average Profit = Rs. 4,200
Share in Profit = Rs. 4,200 × 4/12 × 2/5 = Rs. 560
(iii) Share in Goodwill:- Goodwill = Rs. 4,200 + Rs. 3,900 + Rs. 4,500 = Rs. 12,600 Share in goodwill = Rs. 12,600 × 2/5 = Rs. 5,040
Question 67. (B)
Solution 67. (B)
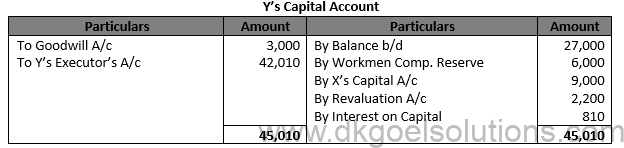
Working Note:- Share in Goodwill:- Average Profit = (Total Profit )/(Number of years)
Average Profit = (Rs. 9,000 +Rs. 20,000 + Rs. 16,000 )/3 Average Profit = Rs. 15,000 Total Goodwill of the firm = Rs. 15,000 × 90/1000×2 = Rs. 27,000
Y’s Share = Rs. 27,000 ×1/3 = Rs. 9000
Question 68.
Solution 68
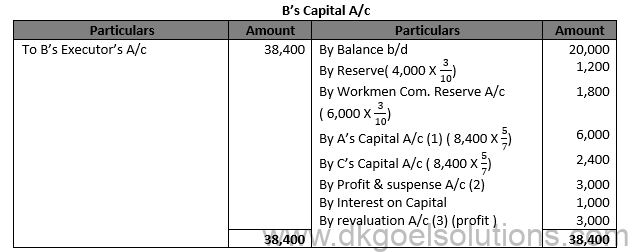
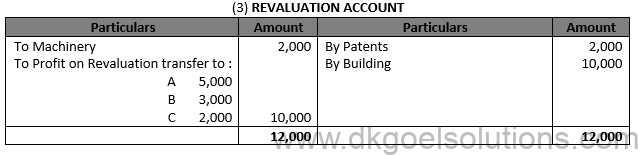
Working Note: (1) Firm’s Goodwill = (10,0000 + 13,000 + 12,000 +15,000+20,000)/5 X 2 = 14,000 X 2 = Rs. 28,000 B’s share of Goodwill = Rs. 28,000 X 3/10 = Rs. 8,400 which is contributed by A and C in their gaining ratio i.e. 5:2. (2) B’s Share of profit till the date of death = 20,000 X 6/12 X 3/10 = Rs. 3,000
Question 69.
Solution 69 (i) Computation of Goodwill:- Goodwill = (33,500 + 41,000 + 40,500 )/3 X 2 = Rs. 77,000
A’s share of Goodwill = Rs. 77,000 X 2/3 = Rs. 51,333 It will be credited to A and will be debited to B and C in their gaining ratio i.e., 1/6:1/6 or equally.
(ii) Share of profit:- A ‘s share = 40,500 × 3/12 × 2/3 = Rs. 6,750.

Question 70.
Solution 70.
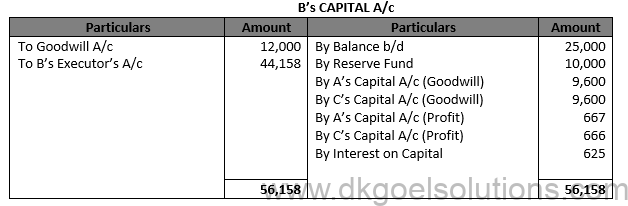
Working Note:- 1.) Valuation of Goodwill Total Profit = Rs. 15,000 + Rs. 17,000 + Rs. 19,000 + Rs. 13,000 = Rs. 64,000 Average Profit = 64,000/4 Average Profit = Rs. 16,000
Goodwill of Firm = 3 × Average Profit Goodwill of Firm = 3 × Rs. 16,000 Goodwill of Firm = Rs. 48,000
B’s Share = Rs. 48,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 19,200
Profit and Loss = (Rs. 64,000)/4×2/5×2.5/12 = Rs. 1,333
Interest on Capital = Rs. 25,000 × 12/100×2.5/12 = Rs. 625
Question 71.
Solution 71.
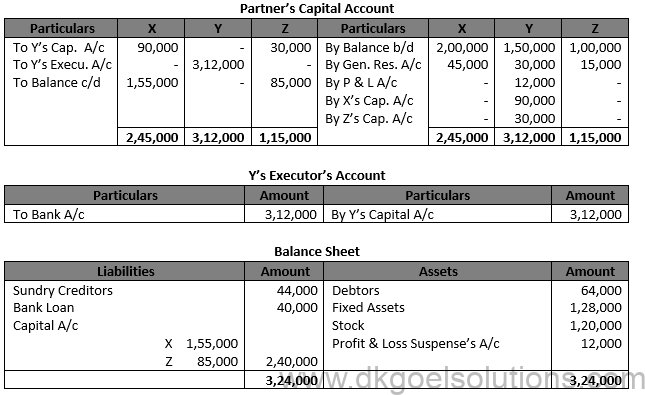
Working Note:- 1.) Total Profit for last three Years = Rs. 80,000 + Rs. 1,30,000 + Rs. 1,50,000 = Rs. 3,60,000 Average Profit = (Rs. 3,60,000)/3 Average Profit = Rs. 1,20,000
Profit from 1st April to 31st July, 2018 = Rs. 1,20,000 × 4/12 = Rs. 40,000
Y’s Share of Profit = Rs. 40,000 × 2/6 = Rs. 13,333 Less = 10% of Rs. 13,333 = 1,333 Y’s Share of Profit = 13,333 – Rs. 1,333 Y’s Share of Profit = Rs. 12,000
(2) Y’s Share of Goodwill:- Total Profits of last three year = Rs. 3,60,000 Y’s Share in Profit = Rs. 3,60,000 × 2/6 Y’s Share in Profit = Rs. 1,20,000

Question 72.
Solution 72.
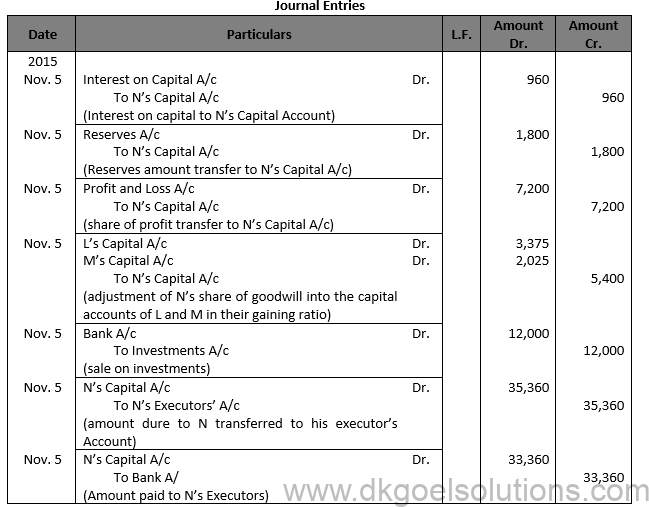
Working Note: (1) Computation of Interest on Capital : Number of days from April 1,2025 to November 5,2015 = 2019 Interest on Capital = 20,000 X 219/365 X 8/100 = Rs. 960
(2) Computation of Goodwill:
Average Profit = (10,500 + 12,000 + 12,500 +13,000)/4 = 12,000 Less: 25% of 12,000 = 3,000 Goodwill = 9,000 X 3 = Rs. 27,000
N’s share of Goodwill = 27,000 X 2/(10 ) =Rs. 5,400 It will be credited to the Capital Account of N and will be debited to the Capital Account of L and M in their gaining ratio i.e., 5:3.
Question 73 (new).
Solution 73 (new).

Working Notes: (1) Valuation of Firm’s Goodwill: Average Profit = (Rs. 2,20,000 + Rs. 1,10,000 + Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 1,60,000 )/5 = Rs. 66,000
Values of Firm’s Goodwill = Average Profit X Number Of Years’ Purchase Firm’s Goodwill = Rs. 66,000 × 3 = Rs. 1,98,000 R’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 1,98,000 × 9/(20 ) = Rs. 89,100
(2) R’s Share of Profit/ Loss till the date of his death: R’s Share of Profit /Loss will be Calculated on the basis of the profit or loss for the year ending 31-3-2016. In this year firm incurred a loss of Rs. 1,60,000
Hence, R’s Share of Loss = Rs. 1,60,000 × 1/12 × 9/(20 ) = Rs. 6,000
Question 73.
Solution 73.

Values of Firm’s Goodwill = Average Profit X Number Of Years’ Purchase Firm’s Goodwill = Rs. 66,000 × 3 = Rs. 1,98,000
R’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 1,98,000 × 9/(20 ) = Rs. 89,100
(2) R’s Share of Profit/ Loss till the date of his death: R’s share of benefit / loss will be determined for the year ending 31-3-2016 on the basis of profit or loss. A loss of Rs. 1,60,000 was suffered by the company this year.
Question 74.
Solution 74
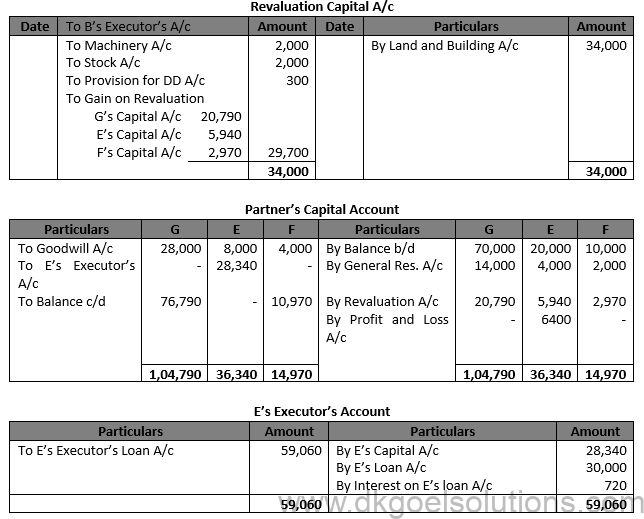
Working Note:- 1.) Computation of E’s Share in profit for 146 days:- = Rs. 80,000 × 2/10×146/365 = Rs. 6,400
2.) Interest o E’s Loan = Rs. 30,000 × 6/10×146/365 = Rs. 720
3.) Computation of adjusted Capitals of G and F: G’s Capital + F’s Capital = Rs. 76,790 + Rs. 10,970 = Rs. 87,760
New Profit sharing ratio of G and F = 7:1
G’s Capital = Rs. 87,760 × 7/8 = Rs. 76,790
F’s Capital = Rs. 87,760 × 1/8 = Rs. 10,970
Question 75.
Solution 75.

Question 76.
Solution 76. Old Ratio of A, B, C and D = 4 :3 :2 : 1. When A and C retire, the new ratio between B and D 3 : 1.
Question 77.
Solution 77. Old Ratio of A, B and C = 1/2:3/8:1/8 It can be written as = (4∶ 3 ∶ 1)/8 So, when C retires, the new ratio between A and B will be 4 : 3.
Question 78.
Solution 78. B’s share will be divided between A and C in the ratio of 1 : 1 A’s Gain 1/2 of 4/15 = 2/15
A’s New Share = 8/15+2/15=(8+2)/15=10/15
C’s Gain 1/2 of 4/15 = 2/15
C’s New Share = 3/15+2/15=(3+2)/15=5/15
New Ratio of A and C = 10/15 ∶ 5/15 New Ratio of A and C = 2 : 1.
Question 79.
Solution 79. Old Ratio of Shiv, Mohan and Hari = 5 : 5 : 4 Mohan’s share will be divided between Shiv and Hari in the ratio of 1 : 1 Shiv’s Gain 1/2 of 5/14 = 28/28
Shiv’s New Share = 5/14+5/28=(10+5)/28=15/28
Hari’s Gain 1/2 of 5/14 = 5/28
Hari’s New Share = 4/14+5/28=(8+5)/28=13/28
New Ratio of A and C = 15/28 ∶ 13/28 New Ratio of A and C = 15 : 13.
Question 80.
Solution 80. Old Ratio of A, B and C = 1/5 : 1/3 7/15 Mohan’s share will be divided between A and B in the ratio of 3 : 2 A’s Gain 3/5 of 7/15 = 21/75
A’s New Share = 1/5+21/75=(15+21)/75=36/75
B’s Gain 2/5 of 7/15 = 14/75
B’s New Share = 1/3+14/75=(25+14)/75=39/75
New Ratio of A and B = 36/75 ∶ 39/75 New Ratio of A and B = 36 : 39 = 12 : 13
Question 81.
Solution 81. Old Ratio of X, Y and Z = 4/9 ∶3/9 ∶2/9 X’s share will be divided between Y and Z in the ratio 2:1 Y will gain 2/3 of 4/9 = 8/27
Y’s New Share = 3/9+8/27=(9 + 8)/27=17/27
Z will gain 1/3 of 4/9 = 4/27
Z’s New Share = 2/9+4/27=(6 + 4)/27=10/27
New ratio between Y and Z = 17/27:10/27 New ratio between Y and Z = 17 : 10.
Question 82.
Solution 82. Old Ratio of A, B and C = 4 : 3 : 2 = 4/9 ∶3/9 ∶2/9
(i) When B’s share is taken up by A and C in the ratio of 2:1 A will gain 2/3 of 3/9 = 2/27
A’s New Share = 4/9+2/9=(4 + 2)/9=6/9
C will gain 1/3 of 3/9 = 1/9
C’s New Share = 2/9+1/9=(2 + 1)/9=3/9
New ratio between Y and Z = 6/9:3/9 New ratio between Y and Z = 2 : 1.
(ii) When B’s share is taken up by A and C equally. A will gain 1/2 of 3/9 = 1/6
New Share of A = 4/9+1/6=(8 + 3)/18=11/18
C will gain 1/2 of 3/9 = 1/6
New Share of C = 2/9+1/6=(4 + 3)/18=7/18
New ratio between A and C = 11/18:7/18 New ratio between Y and Z = 11 : 7.
(iii) When B’s share is taken up by A alone:- New Share of A = 4/9+3/6=(4 + 3)/9=7/9
New Share of C = 2/9
New ratio between A and C = 7/9:2/9 Hence, the new ratio between Y and Z = 7 : 2.
Question 83.
Solution 83. Ratio of H, P and S is 4 : 3 : 3. H’s Gain = 3/10×20/100=3/50 H’s new share = 4/10+3/50= (20 + 3)/50=23/50 S’s Gain = 3/10×80/100=12/50 S’s new share = 3/10+12/50= (15 + 12)/50=27/50 New Profit sharing Ratio of H and S is 23:27
Question 84.
Solution 84. Calculation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio — Old Ratio
Gaining Ratio of Mangli = 3/8-3/9=(45 – 24)/72=21/72
Gaining Ratio of Sanvali = 3/8-2/9=(27 – 16)/72=11/72
Hence, the gaining ratio between of Mangli and Sanvali 21 : 11.
Question 85.
Solution 85. Calculation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio — Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of A = 7/12-1/3 Gaining Ratio of A =(7 – 4)/12 Gaining Ratio of A =3/12
Gaining Ratio of C = 5/12-1/3 Gaining Ratio of C =(5 – 4)/12 Gaining Ratio of C =1/12 Gaining Ratio between A and C is 3 : 1.
Question 86.
Solution 86 Old Ratio of A, B and C is 1,00,000 : 75,000 : 50,000 or 4 : 3 : 2 or 4/9:3/9:2/9 C’s share will be split in a 2:1 ratio between A and B. A will gain 2/3 of 2/9 = 4/27
New Share of A = 4/9+4/27=(12 + 4)/27=16/27
B will gain 1/3 of 2/9 = 2/27
New Share of B = 3/9+2/27=(9 + 2)/27=11/27
New ratio between A and B = 16/27:11/27
New ratio between A and B = 16 : 11 Hence, the gaining ratio = 2:1
Question 87.
Solution 87. Old Ratio of A, B and C = 1/3:1/3:1/3 C’s share will be split in a 2:1 ratio between A and B. Gaining ratio of A 3/5 of 1/3 = 3/15
New Share of A = 1/3+3/15=(5 + 3)/15=8/15
Gaining ratio of B 2/5 of 1/3 = 2/15
New Share of B = 1/3+2/15=(5 + 2)/15=7/15
New ratio between A and B = 8/15:7/15
New ratio between A and B = 8 : 7 Gaining Ratio = 3:2
Question 88.
Solution 88.
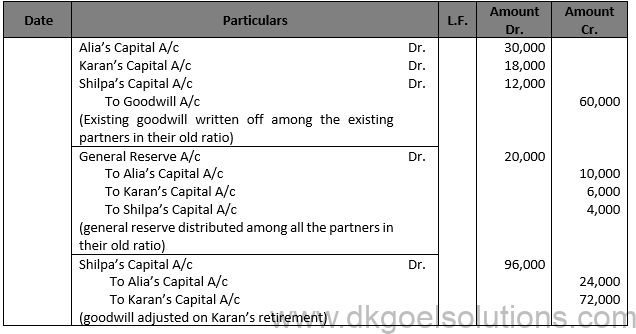
Working Note:- Calculation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio — Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of Alia’s = 2/5-5/10=(4 – 5)/10=-1/10 (sacrifice) Gaining Ratio of Shilpa’s = 3/5-2/10=(6 – 2)/10=4/10 (Gain)
Question 89.
Solution 89.

Working Note:- Computation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio — Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of M = 1/2-3/6=(3 – 3)/6=0 Gaining Ratio of O = 1/2-1/6=(3 – 1)/6=2/6 (Gain)
Points for Students:- If the death of a partner occurs on any day during the year, the executors of the deceased partner will also be entitled to the share of profits earned by the firm from the beginning of the year till the date of his death. Such profit may be ascertained from any of the following methods: (A) On time Basis (B) On Turnover or Sales Basis.
Question 90.
Solution 90.
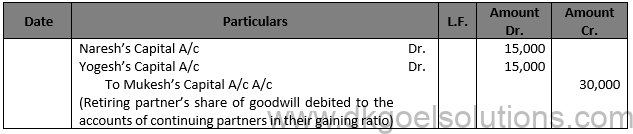
Working Note:- Calculation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio — Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of Ravi = 1/3-2/6=(2 – 2)/6=0 Gaining Ratio of Naresh = 1/3-1/6=(2 – 1)/6=1/6 (Gain) Gaining Ratio Yogesh = 1/3-1/6=(2 – 1)/6=1/6 (Gain)
Question 91.
Solution 91.

Working Note:- Calculation of Gaining Ratio:- Gaining Ratio = New Ratio — Old Ratio
Gaining Ratio of L = 2/6-1/2=(2 – 3)/6=1/6 (Gain)
Gaining Ratio of N = 1/6-1/2=(1 – 3)/6=2/6 (Gain)
M’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 3,60,000 × 2/6 = 1,20,000
O’s Share of Goodwill = Rs. 3,60,000 × 1/6 = 60,000
Question 92.
Solution 92. (a) A’s Share is taken up by B and C equally. B’s Gain = 1/2×5/10=5/20
B’s new share = 3/10+5/20= (6 + 5)/20=11/20
C’s Gain = 1/2×5/10=5/20
C’s new share = 2/10+5/20= (4 + 5)/20=9/20
New Profit sharing Ratio of B and C is 11/20:9/20 or 11 : 9 Gaining ratio = 1:1.
(b) A’s share of Goodwill = Rs. 2,00,000 × 5/10= Rs. 1,00,000

Question 93.
Solution 93.

Working Note:- Gaining Ratio of O = 2/3-2/6=2/6
Sacrifices Ratio of M = 1/3-3/6=1/6
O gains 2/6, including 1/6 that M sacrificed in favour of O. As a result, O must reimburse M for such a sacrifice.
Question 94.
Solution 94.

Working Note:- X will get only 1/2 of his previous share.
X’s New share = 1/2 of 3/6=1/4
Remaining 1/4 will be divided between Y and Z equally.
Gaining Ratio of Y = 1/2 of 1/4=1/8
New share of Y = 2/6+1/8= (8 + 3)/24=11/24
Gaining Ratio of Z = 1/2 of 1/4=1/8
New share of Z = 1/6+1/8= (4 + 3)/24=7/24
New Share of X, Y and Z = 1/4:11/24:7/24
New Share of X, Y and Z = (6 ∶ 11 ∶ 7)/24 Hence, The New Share of X, Y and Z = 6 : 11 : 7.
Question 95.
Solution 95.
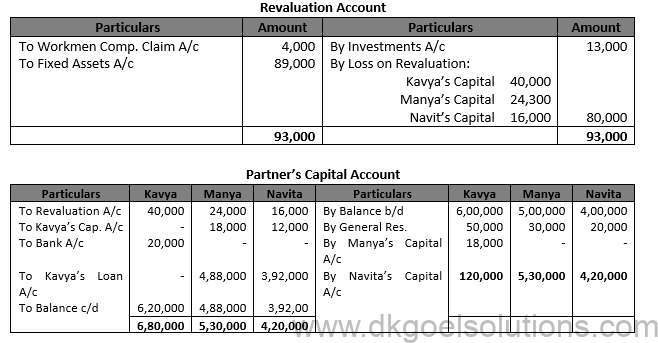
Question 96.
Solution 96.
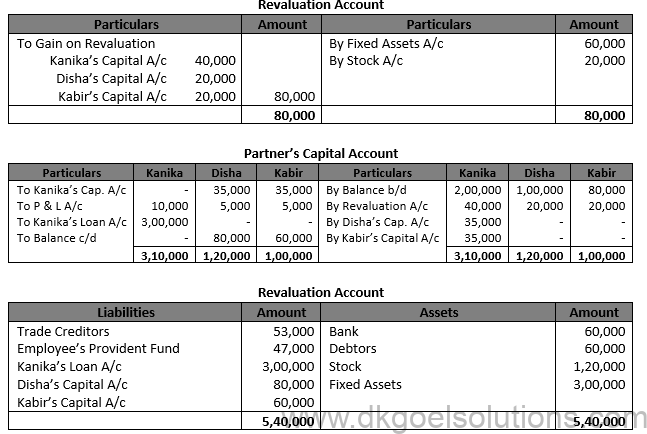
Working Note:- Calculation of Valuation of Goodwill: Valuation of Goodwill = Profit for 2013-14 + Profit for 2014-15 – Loss for 2015-16 Valuation of Goodwill = Rs. 1,00,000 + Rs. 1,30,000 – Rs. 20,000 Valuation of Goodwill = Rs. 2,10,000
Calculation of Average Profit:- Average Profit = 2,10,000/3 Average Profit =Rs.70,000
2 year’s Purchase of goodwill = Rs. 70,000 × 2 = Rs. 1,40,000 Kanika’s share of goodwill = Rs. 1,40,000 × 2/4 = Rs. 70,000
Question 97 (new).
Solution 97 (new) .
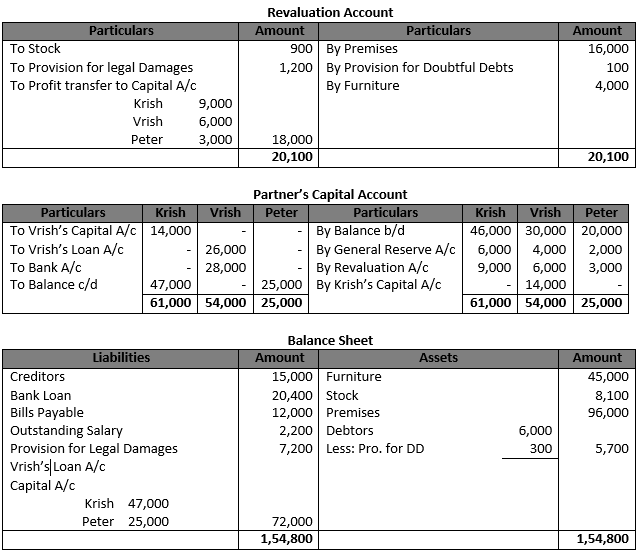
Question 97.
Solution 97.
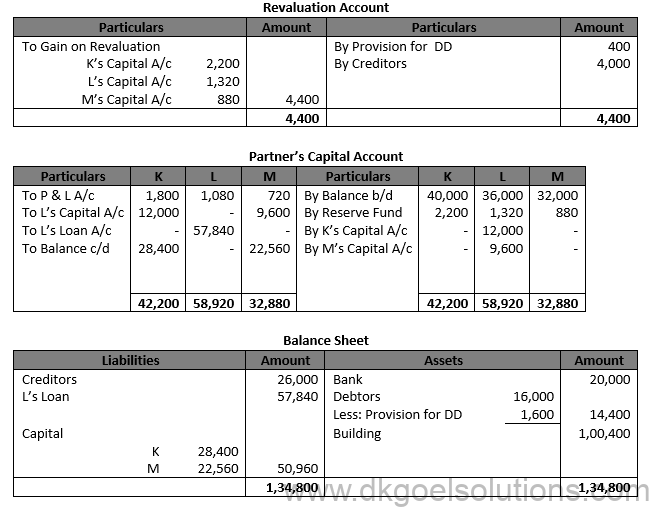
Working Note:- 1.) Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of K = 2/3-5/10=(20 – 15)/30=5/30 Gaining Ratio of M = 1/3-2/10=(10 – 6)/30=4/30 Gaining Ratio = 5 : 4
2.) L’s Goodwill Contribution = Rs. 72,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 21,600
Question 98.
Solution 98.
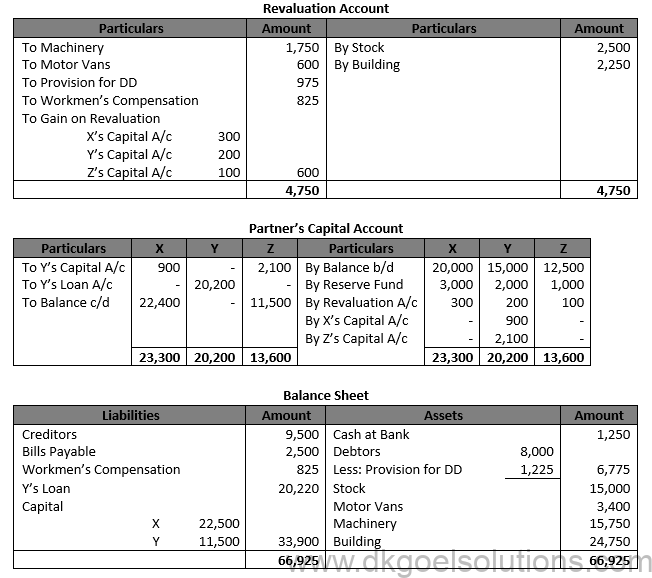
Working Note:- 1.) Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of X = 3/5-1/2=(6 – 5)/10=1/10 Gaining Ratio of Z = 2/5-1/6=(12 – 5)/30=7/30 Gaining Ratio = 1/10:7/30 Gaining Ratio = 3 : 7
2.) Y’s portion of goodwill = Rs. 90,000 × 1/3 = Rs. 3,000 X’s sacrifice for Y = Rs. 3,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 900 Z’s sacrifice for Y = Rs. 3,000 × 7/10 = Rs. 2,100
Question 99 (new).
Solution 99 (new).
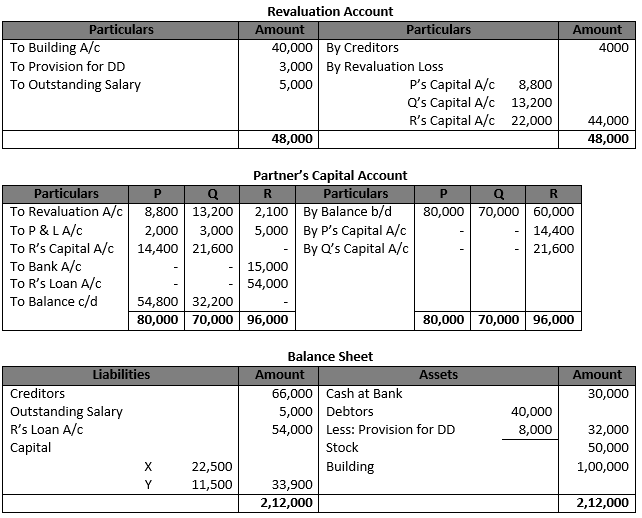
Working Note:- 1.) R’s Share of goodwill = Rs. 72,000 × 5/10 = Rs. 36,000 P = Rs. 36,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 14,400 Q = Rs. 36,000 × 3/5 = Rs. 21,600
Question 99.
Solution 99.
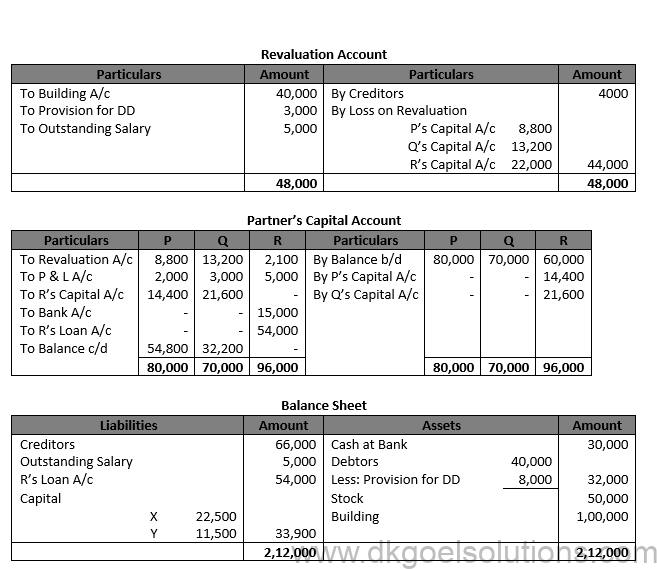
Working Note:- Share of Goodwill of R = Rs. 72,000 × 5/10 = Rs. 36,000 Share of P in Goodwill = Rs. 36,000 × 2/5 = Rs. 14,400 Share of Q in Goodwill = Rs. 36,000 × 3/5 = Rs. 21,600
Question 100.
Solution 100
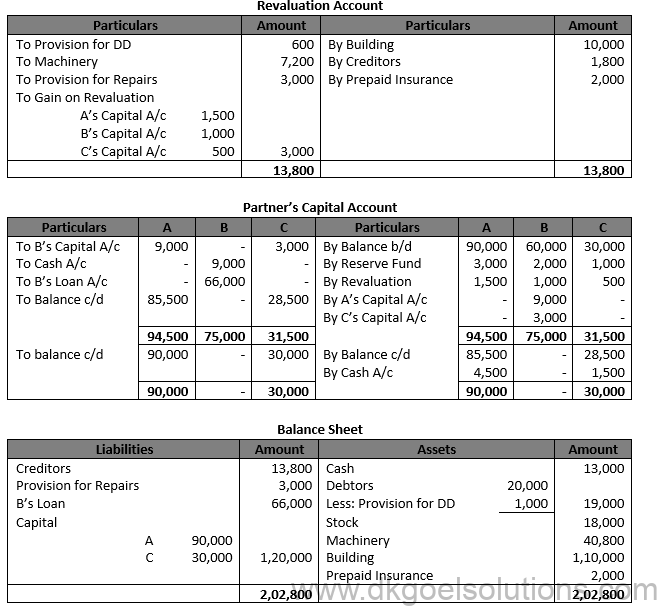
Working Note:- 1.) Calculation of Cash Balance:- Cash Balance = Opening Balance + Cash Brought in by partners – Cash paid to B Cash Balance = Rs. 16,000 + Rs. 4,500 + Rs. 1,500 + Rs. 9,000 Cash Balance = Rs. 13,000
2.) Adjustment of Capital of A:- Adjusted Capital of A = Capital in new firm – Existing Capital Adjusted Capital of A = 90,000 – 85,500 Adjusted Capital of A = 4,500
Adjustment of Capital of C:- Adjusted Capital of C = Capital in new firm – Existing Capital Adjusted Capital of C = 30,000 – 28,500 Adjusted Capital of C = 1,500
Question 101.
Solution 101.
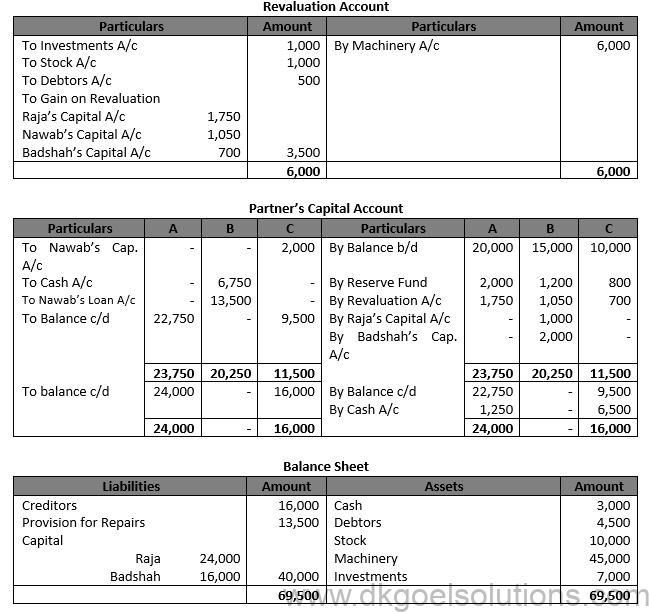
Working Note:- 1.) Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio Gaining Ratio of Raja = 3/5-5/10=(6 – 5)/10=1/10
Gaining Ratio of Badshah = 2/5-2/10=(4 – 2)/10=2/10
Gaining Ratio = 1/10:2/10 = 1 : 2
Share of Goodwill of Nawab = Rs. 10,000 × 3/10 = Rs. 3,000
Question 102.
Solution 102
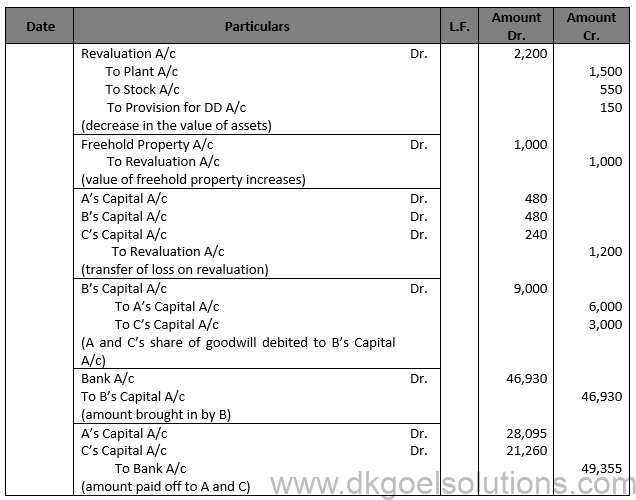
Question 103.
Solution 103.

Question 104 (new).
Solution 103 (new).
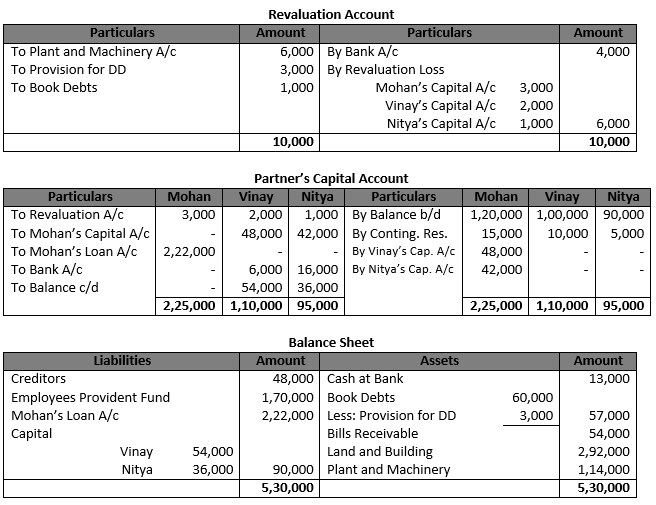
The gaining ratio plays an important role in case a member is eliminated from a firm either due to Retirement or death. Here the gaining ratio must be calculated to formulate the amount of goodwill payable by the existing members to the retired or deceased member.
In case a profit holder of the firm gets retired or deceased, the profit gets distributed among the existing members of the firm as per the old profit-sharing ratio.
In case a partner of a firm decreases, the partnership immediately comes to an end. Although the firm may run with the remaining partners, the partnership of the deceased member is excluded. However, the deceased member’s family is offered a share of the firm as per the guidelines of the partnership agreement.
Here are the two significant deductions that may be made from the funds to be paid to the deceased partner are as follows – ● Drawings made by the deceased member before his/her death. ● Deceased member’s share of loss on the revaluation of liabilities and assets of the firm.
If a firm’s partner dies on any date after the framing of the firm’s balance sheet, then his/her share of profit is formulated from the beginning of the financial year to his/her date of death on the grounds of time or sales.
In case of admission, Retirement, or the death of a partner, the existing members of a firm may decide to change their existing profit-sharing ratio. This may output in gain for few partners and a loss for a few. However, the partners who make a profit in this change must mandatorily compensate the sacrificing members of the firm.
Also refer to TS Grewal Solutions for Class 12

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Explore Goyal's Assignments in English Core for Class 12 (Subject Code 301) authored by Dr. Mandabi Bhaduri. This guide offers a comprehensive approach to reading comprehension, note-making, summarizing, writing skills, and literature analysis. Perfect for CBSE students. Order now! Enhance your English skills with Goyal's Assignments in English Core (Subject Code 301) for CBSE Class 12 by Dr ...
Goyal's Assignments in English (Core) Course for Class XII (With Online Support) : Editorials: Amazon.in: Books
Goyal's Assignments in English Core Class 12, a comprehensive practice book, is strictly designed according to the latest syllabus prescribed by the CBSE, New Delhi. This book is divided into the following sections.
GoyalAssignments.com provides Free Downloads of Study materials (Assignments, Model Test Paper, Sample Paper, Previous Paper) of all subjects for CBSE Class 9 & 10 students.
Preview of Goyal's Assignments in English Core for Class 12 (Subject Code 301) About. Goyal Brothers Prakashan is a leading publishing house in India. We publish school textbooks, novels, reading guides, and premium notebooks for schools, corporates and other requirements.
Here are the conditions when the shares can be issued at a discount -. If a company desires to issue the share at a price lower than the face value, it must mandatorily get approval from the relevant authority. The discount on share comes with a limitation, i.e., the discount rate cannot exceed 10%.
Read below DK Goel Solutions Class 12 Chapter 3 Changing in Profit-Sharing Ratio among the Existing Partners.These solutions have been designed based on the latest Class 12 DK Goel Accountancy book used by commerce stream students issued for the current year and the questions given in each chapter.. When a partnership firm is formed there can be a requirement to change the profit-sharing ratio ...
Goyal Brothers Prakashan - Goyal's Assignments English Language & Literature (Subject Code 184) for Class X. Buy Notebooks. 0120-4655555; 9319391199; My Account. Register; Login; Wish List (0) Shopping Cart; ... Project work & Laboratory Manual for Class XII; NOVEL; DIGI SMART BOOKS - UNDERSTANDING NCERT;
DK Goyal offer the 3 volumes of Accountancy Book of Class 12. Volume - 1 of DK Goyal book class 12 Accountancy consists of two units. Not for Profit Organizations. Partnership. Partnership Units further divided into following chapters. Accounting of Partnership Firms - Fundamentals. Goodwill.
Solution 1. Here are the problems that need be changed at the time of a partner's admission: (i) Net Gains, Reserves and Losses Adjustment. (ii) Goodwill Change. Question 2. Solution 2. (i) New partner brings his share of goodwill in cash: Bank A/c Dr.
Goyals Assignments in English (Core) Course for Class XI (With Online Support) : Editorials: ... ₹435.00 with 12 percent savings -12% ... Goyal Brothers Prakashan (1 January 2015) Language ...
DK Goel Solutions Class 12 - Chapter 1 - Part A. Question 1. A and B are partners in a farm. A is entitled to a salary of ₹15,000 p.m and a commission of 10% of net profit before charging any commission. B is entitled to a commission of 10% of net profit after charging his commission. Net profit till 31st March 2018 was ₹4,40,000.
These solutions are free and will help you to prepare for Class 12 Accountancy. Just scroll down and read through the answers provided below. Cash Flow Statements DK Goel Class 12 Accountancy Solutions. Short Answer Questions. Q1. Solution 1 (a) Increase in Trade Receivable:- Less (b) Decrease in Inventory:- Add (c) Decrease in Bills Payable:- Less
Solution 6. The deceased partner's legal executive is entitled to the balance number of the capital account of the deceased partner. The following things are posted in the deceased partner's capital account on the debit side: (a) Credit balance in a capital account or current account of the deceased spouse.