Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study

Journal of Industrial Engineering International
Related Papers
Mirko Soković
Dhwani Bhavsar
A quality improvement program whose methodology is to look at processes with a view to analyze their process steps, determine what elements need improvement, develop alternate strategies for improvement and finally select and implement one is called as Six Sigma. The main advantage of selecting Six Sigma project is that it helps to generate potential savings in improving any process which maybe any for example production, administration, services or engineering. This paper exhibits an empirical application of Six Sigma and DMAIC in order to carry out the reduction of product defects within a rubber hose manufacturing organization. It sticks to follow the DMAIC methodology to methodically evaluate the root cause of those defects and hand over a feasible solution to reduce or eliminate them. In particular it was observed that the oven’s temperature as well as the speed of conveyer had a significant impact on the number of defects, so it was necessary to evaluate their optimum values i...
IRJET Journal
The fast changing economic conditions such as global competition, customer demand for high quality product, product variety and reduced lead– time, declining profit margin etc. had a major impact on manufacturing industries. To respond to these needs various industrial engineering and quality management strategies such as ISO 9000, TQM, Kaizen, JIT manufacturing, Enterprise Resource Planning, Business Process Reengineering, Lean management etc. have been developed. A new paradigm in this area of manufacturing strategies is Six sigma. The Six Sigma approach has been increasingly adopted worldwide in the manufacturing sector in order to enhance productivity and quality performance and to make the process robust to quality variations. This project work discusses the quality and productivity improvement in a manufacturing enterprise through Defect Analysis and deals with an application of Six Sigma DMAIC (Define–Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control) methodology in wheel production plant which provides a framework to identify, quantify and eliminate sources of variation in an operational process in question, to optimize the operation variables, improve and sustain performance viz. process yield with well executed control plans to reduce defects happening in Cast wheel production.
IJAERS Journal
— Six sigma is a project-driven management approach that is relevant to all the fields starting from manufacturing to service industries. The main goals of six sigma are improving efficiency, profitability, and process capability. In this paper, six sigma methodology based on DMAIC approach is applied to a foundry industry. The scope of the study is limited to automated high-pressure green sand moulding line. The root causes of different casting defects are identified and various actions are recommended to improve the production process. As a result, the overall sigma level of the industry is improved at an acceptable level.
jiju1968 antony
This article discusses the successful implementation of Six Sigma methodology in a high precision and critical process in the manufacture of automotive products. The Six Sigma define–measure–analyse–improve–control approach resulted in a reduction of tolerance-related problems and improved the first pass yield from 85% to 99.4%. Data were collected on all possible causes and regression analysis, hypothesis testing, Taguchi methods, classification and regression tree, etc. were used to analyse the data and draw conclusions. Implementation of Six Sigma methodology had a significant financial impact on the profitability of the company. An approximate saving of US$70,000 per annum was reported, which is in addition to the customer-facing benefits of improved quality on returns and sales. The project also had the benefit of allowing the company to learn useful messages that will guide future Six Sigma activities.
International Business Management
Rohail Hassan
This is an era of quality management and quality is a parameter for the selection of a product or service because the customer wants a defects free product or service. Six Sigma is a quality improvement approach that aims to reduce the number of defects up to 3.4 parts per million. In the last three decades, it helped several companies to enhance the capability of their processes and to increase the level of quality of their product or service. This case-study based research deals with application of DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control) methodology of Six Sigma to reduce the machine downtime for process improvement. The tools and techniques used during the analysis are Process Mapping (SIPOC Diagram), Process Flow Chart, Process Capability Analysis, Histogram, Pareto Chart, Pie Chart, Cause and Effect Diagram, Brainstorming, Affinity Diagram and ANOVA. The results of this study show that sigma value has improved from 2.79 Sigma to 2.85 Sigma. This study also highlit...
International Journal of Lean Six Sigma
Prof. Vikas Kumar
Islam Sharaf
This is an era of quality management and quality is a parameter for the selection of a product or service because the customer wants a defects free product or service. Six Sigma is a quality improvement approach that aims to reduce the number of defects up to 3.4 parts per million. In the last three decades, it helped several companies to enhance the capability of their processes and to increase the level of quality of their product or service. This case study based research deals with application of DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control) methodology of Six Sigma to reduce the machine downtime for process improvement. The tools and techniques used during the analysis are Process Mapping (SIPOC Diagram), Process Flow Chart, Process Capability Analysis, Histogram, Pareto Chart, Pie Chart, Cause and Effect Diagram, Brainstorming, Affinity Diagram and ANOVA. The results of this study show that sigma value has improved from 2.79 Sigma to 2.85 Sigma. This study also highlighted the five critical problems (reasons) of Downtime, which are i.e. Electricity Problem, Shortage of Material, Quality Issues, Machine Fault and Reactive Maintenance. The valuable principles and practices of Six Sigma will do well by continuously refining the organizational culture. Time and commitment both are required and compulsory to bring change in cultural before they are strongly implanted into the organization. I do assure that this research study will provide opportunities to the organizations for the better implementation of six sigma projects.
Six Sigma is a data-driven leadership approach using specific tools and methodologies that lead to fact-based decision making. This paper deals with the application of the Six Sigma methodology in reducing defects in a fine grinding process of an automotive company in India. The DMAIC (Define–Measure–Analyse–Improve–Control) approach has been followed here to solve the underlying problem of reducing process variation and improving the process yield. This paper explores how a manufacturing process can use a systematic methodology to move towards world-class quality level. The application of the Six Sigma methodology resulted in reduction of defects in the fine grinding process from 16.6 to 1.19%. The DMAIC methodology has had a significant financial impact on the profitability of the company in terms of reduction in scrap cost, man-hour saving on rework and increased output. A saving of approximately US$2.4 million per annum was reported from this project.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Procedia Manufacturing
Maria Teresa Pereira
Proceedings of the 2019 1st International Conference on Engineering and Management in Industrial System (ICOEMIS 2019)
Tania Silvani
sibgat sibzz
Mechanical Engieneering-Scientific Journal
Gligorche Vrtanoski
Sustainability
Jovian Rivaldo
International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management
Darshak Desai
Richard Leramo
IJESRT Journal
Behrooz Noori
International Humanities and Applied Science Journal
Dewi Nusraningrum
Journal of Applied Engineering Science
Umair Sarwar
Mnj Nataraj
Dhiraj Kumar
Annals - Economy Series
Kosta Sotiroski
balasubramaniam manikandan
hairul nurdin
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Romeo Negrea
E3S Web of Conferences
Fatima ACHIBAT
Independent Journal of Management & Production
KAMRUL HASAN
Tushar Shrivastava
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- DOI: 10.1007/S40092-017-0234-6
- Corpus ID: 52263903
Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study
- V. Gupta , Rahul Jain , +1 author G. S. Dangayach
- Published 1 September 2018
- Engineering, Business
- Journal of Industrial Engineering International
63 Citations
Process improvement using six-sigma (dmaic process) in bearing manufacturing industry: a case study, application of six sigma methodology in an automotive manufacturing company: a case study, “a review on implementation of six sigma methodology in transformer manufacturing industry”, applying lean six sigma for waste reduction in a bias tyre manufacturing environment, application of six sigma methodology in an indian chemical company, six sigma implementation in connector and terminals manufacturing company : a case study, the performance improvement analysis using six sigma dmaic methodology: a case study on indian manufacturing company., application of lean six sigma tools for performance improvement in an automobile sector sme, improvement model based on four lean manufacturing techniques to increase productivity in a metalworking company, combined model of lean six sigma and work method for a peruvian ammunition manufacturing, 55 references, process improvement in an indian automotive part manufacturing company: a case study, process improvement: performance analysis of the setup time reduction-smed in the automobile industry, productivity improvement by using six-sigma, implementation of six sigma to reduce cost of quality: a case study of automobile sector, six sigma implementation at an auto component manufacturing plant: a case study, six sigma implementations in supply chain: an application for an automotive subsidiary industry in bursa in turkey., enhancing the performace of an automobile service industry: lean thinking approach, enhancing the performance of an automobile service industry: lean thinking approach, monitoring quality goals through lean six‐sigma insures competitiveness, study and analysis of implementation of six-sigma: a case study of an automobile industry, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. Learn more about DOAJ’s privacy policy.
Hide this message
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.
The Directory of Open Access Journals
Quick search.
Journal of Industrial Engineering International (Sep 2017)
Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study
- Vikash Gupta,
- Rahul Jain,
- M. L. Meena,
- G. S. Dangayach
Affiliations
Read online
Abstract Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define–measure–analyze–improve–control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the potential ways of improvement in the process as well as service industries. In the current research, the DMAIC method was used for decreasing the process variations of bead splice causing wastage of material. This six-sigma DMAIC research was initiated by problem identification through voice of customer in the define step. The subsequent step constitutes of gathering the specification data of existing tire bead. This step was followed by the analysis and improvement steps, where the six-sigma quality tools such as cause–effect diagram, statistical process control, and substantial analysis of existing system were implemented for root cause identification and reduction in process variation. The process control charts were used for systematic observation and control the process. Utilizing DMAIC methodology, the standard deviation was decreased from 2.17 to 1.69. The process capability index (C p) value was enhanced from 1.65 to 2.95 and the process performance capability index (C pk) value was enhanced from 0.94 to 2.66. A DMAIC methodology was established that can play a key role for reducing defects in the tire-manufacturing process in India.
- Developing country
- Process capability
WeChat QR code

Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study
- et al. See more
This article is free to access.
Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define–measure–analyze–improve–control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the potential ways of improvement in the process as well as service industries. In the current research, the DMAIC method was used for decreasing the process variations of bead splice causing wastage of material. This six-sigma DMAIC research was initiated by problem identification through voice of customer in the define step. The subsequent step constitutes of gathering the specification data of existing tire bead. This step was followed by the analysis and improvement steps, where the six-sigma quality tools such as cause–effect diagram, statistical process control, and substantial analysis of existing system were implemented for root cause identification and reduction in process variation. The process control charts were used for systematic observation and control the process. Utilizing DMAIC methodology, the standard deviation was decreased from 2.17 to 1.69. The process capability index (Cp) value was enhanced from 1.65 to 2.95 and the process performance capability index (Cpk) value was enhanced from 0.94 to 2.66. A DMAIC methodology was established that can play a key role for reducing defects in the tire-manufacturing process in India.
Author supplied keywords
- Developing country
- Process capability
Register to see more suggestions
Mendeley helps you to discover research relevant for your work.
CITATION STYLE
Gupta, V., Jain, R., Meena, M. L., & Dangayach, G. S. (2018). Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study. Journal of Industrial Engineering International , 14 (3), 511–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40092-017-0234-6
Readers' Seniority
PhD / Post grad / Masters / Doc 65
Lecturer / Post doc 14
Professor / Associate Prof. 8
Researcher 2
Readers' Discipline
Engineering 110
Business, Management and Accounting 21
Computer Science 4
Chemical Engineering 2
Save time finding and organizing research with Mendeley
Six-Sigma Application in Tire-Manufacturing Company: a Case Study
Total Page: 16
File Type: pdf , Size: 1020Kb
- Abstract and Figures
- Public Full-text
- Implementing SPC for Non-Normal Processes with the I-MR Chart: a Case Study Implementing SPC for non-normal processes with the I-MR chart: A case study Axl Elisson Master of Science Thesis TPRMM 2017 KTH Industrial Engineering and Management Production Engineering and Management SE-100 44 STOCKHOLM Acknowledgements This master thesis was performed at the brake manufacturer Haldex as my master of science degree project in Industrial Engineering and Management at the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) in Stockholm, Sweden. It was conducted during the spring semester of 2017. I would first like to thank my supervisor at Haldex, Roman Berg, and Annika Carlius for their daily support and guidance which made this project possible. I would also like to thank the quality department, production engineers and operators at Haldex for all insight in different subjects. Finally, I would like to thank my supervisor at KTH, Jerzy Mikler, for his support during my thesis. All of your combined expertise have been very valuable. Stockholm, July 2017 Axl Elisson Abstract The application of statistical process control (SPC) requires normal distributed data that is in statistical control in order to determine valid process capability indices and to set control limits that reflects the process’ true variation. This study examines a case of several non-normal processes and evaluates methods to estimate the process capability and set control limits that is in relation to the processes’ distributions. Box-Cox transformation, Johnson transformation, Clements method and process performance indices were compared to estimate the process capability and the Anderson-Darling goodness-of-fit test was used to identify process distribution. Control limits were compared using Clements method, the sample standard deviation and from machine tool variation. [Show full text]
- Process Capability Analysis 6 Process capability analysis In general, process capability indices have been quite controversial. (Ryan, 2000, p. 186) Overview Capability indices are widely used in assessing how well processes perform in relation to customer requirements. The most widely used indices will be defined and links with the concept of sigma quality level established. Minitab facilities for capability analysis of both measurement and attribute data will be introduced. 6.1 Process capability 6.1.1 Process capability analysis with measurement data Imagine that four processes produce bottles of the same type for a customer who specifies that weight should lie between 485 and 495 g, with a target of 490 g. Imagine, too, that all four processes are behaving in a stable and predictable manner as indicated by control charting of data from regular samples of bottles from the processes. Let us suppose that the distribution of weight is normal in all four cases, with the parameters in Table 6.1. The four distributions of weight are displayed in Figure 6.1, together with reference lines showing lower specification limit (LSL), upper specification limit (USL) and Target (T). How well are these processes performing in relation to the customer requirements? In the long term the fall-out, in terms of nonconforming bottles, would be as shown in the penultimate column of Table 6.1. The fall-out is given as number of parts bottles) per million (ppm) that would fail to meet the customer specifications. The table in Appendix 1 indicates that these fall-outs correspond to sigma quality levels of 4.64, 3.50, 2.81 and 3.72 respectively for lines 1–4. [Show full text]
- The Effects of Autocorrelation in the Estimation of Process Capability Indices." (1998) Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1998 The ffecE ts of Autocorrelation in the Estimation of Process Capability Indices. Lawrence Lee Magee Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/gradschool_disstheses Recommended Citation Magee, Lawrence Lee, "The Effects of Autocorrelation in the Estimation of Process Capability Indices." (1998). LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses. 6847. https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/gradschool_disstheses/6847 This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the Graduate School at LSU Digital Commons. It has been accepted for inclusion in LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses by an authorized administrator of LSU Digital Commons. For more information, please contact [email protected] . INFORMATION TO USERS This manuscript has been reproduced from the microfilm master. U M I films the text directly from die original or copy submitted. Thus, some thesis and dissertation copies are in typewriter face, while others may be from any type o f computer printer. The quality o f this reproduction is dependent upon the quality o f the copy submitted. Broken or indistinct print, colored or poor quality illustrations and photographs, print bleedthrough, substandard margins, and improper alignment can adversely affect reproduction. hi the unlikely event that the author did not send UMI a complete manuscript and there are missing pages, these will be noted. Also, if unauthorized copyright material had to be removed, a note w ill indicate the deletion. Oversize materials (e.g., maps, drawings, charts) are reproduced by sectioning the original, beginning at the upper left-hand corner and continuing from left to right in equal sections with small overlaps. [Show full text]
- Improving Process Capability Database Usage for Robust Design Engineering by Generalising Measurement Data Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 25, 2021 Improving process capability database usage for robust design engineering by generalising measurement data Okholm, A.B.; Rask, M.; Ebro, Martin ; Eifler, Tobias; Holmberg, M.; Howard, Thomas J. Published in: 13th International Design Conference - Design 2014 Publication date: 2014 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Okholm, A. B., Rask, M., Ebro, M., Eifler, T., Holmberg, M., & Howard, T. J. (2014). Improving process capability database usage for robust design engineering by generalising measurement data. In 13th International Design Conference - Design 2014 (pp. 1133-1144). Design Society. General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research. You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. INTERNATIONAL DESIGN CONFERENCE - DESIGN 2014 Dubrovnik - Croatia, May 19 - 22, 2014. IMPROVING PROCESS CAPABILITY DATABASE USAGE FOR ROBUST DESIGN ENGINEERING BY GENERALISING MEASUREMENT DATA A. B. Okholm, M. Rask, M. [Show full text]
- Assignment 9 Control Charts, Process Capability and QFD Assignment 9 Control Charts, Process capability and QFD Instructions: 1. Total No. of Questions: 25. Each question carries one point. 2. All questions are objective type. Only one answer is correct per numbered item. 1. How do you find the process capability? a) By Process Capability Ratio = Cp = − b) By USL and LSL only 6 c) By normal distribution curve d) By spread and mean shift of the process 2. In a certain process it is given that USL is 14, LSL is zero. The process has a mean of 10 and standard deviation 2. What will be the Process Capability Ratio? a) 0.83 b) 1.17 c) 1.33 d) 1.5 3. In a process the inverse of process capability ratio is 0.65. Which statement is correct? a) The process is capable. b) The process is incapable. c) The process is capable with tight control. d) None of the above 4. A process having mean 8.80 and process standard deviation 0.12 has spread of specification limit: 9.0±0.4. What will be the process capability index? a) 0.55 b) 1.67 c) 1.33 d) 0.83 5. How is different than ? a) Looks at the centrality of the process. b) Looks at the overall variability of the process. c) Both look at the overall variability of the process. d) Looks at the centrality of the process. 6. A QC scheme is in operation for a process producing ball-bearings. A sample of 6 bearings is taken every hour and diameters is measured. [Show full text]
- Use Process Capability to Ensure Product Quality Use Process Capability to Ensure Product Quality Lawrence X. Yu, Ph.D. Director (acting) Office of Pharmaceutical Science, CDER, FDA FDA/ PQRI Conference on Evolving Product Quality September 16-17, 2104, Bethesda, MD 1 2 Quality by Testing vs. Quality by Design Quality by Testing – Specification acceptance criteria are based on one or more batch data (process capability) – Testing must be made to release batches Quality by Design – Specification acceptance criteria are based on performance – Testing may not be necessary to release batches L. X. Yu. Pharm. Res. 25:781-791 (2008) 3 ICH Q6A: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria… 4 5 Pharmaceutical QbD Objectives Achieve meaningful product quality specifications that are based on assuring clinical performance Increase process capability and reduce product variability and defects by enhancing product and process design, understanding, and control Increase product development and manufacturing efficiencies Enhance root cause analysis and post-approval change management 6 Concept of Process Capability First introduced in Statistical Quality Control Handbook by the Western Electric Company (1956). – “process capability” is defined as “the natural or undisturbed performance after extraneous influences are eliminated. This is determined by plotting data on a control chart.” ISO, AIAG, ASQ, ASTM ….. published their guideline or manual on process capability index calculation 7 Nomenclature Four indices: – Cp: process capability index – Cpk: minimum process capability index – Pp: process [Show full text]
- Mistakeproofing the Design of Construction Processes Using Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) www.cpwr.com • www.elcosh.org Mistakeproofing The Design of Construction Processes Using Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) Iris D. Tommelein Sevilay Demirkesen University of California, Berkeley February 2018 8484 Georgia Avenue Suite 1000 Silver Spring, MD 20910 phone: 301.578.8500 fax: 301.578.8572 ©2018, CPWR-The Center for Construction Research and Training. All rights reserved. CPWR is the research and training arm of NABTU. Production of this document was supported by cooperative agreement OH 009762 from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). The contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NIOSH. MISTAKEPROOFING THE DESIGN OF CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES USING INVENTIVE PROBLEM SOLVING (TRIZ) Iris D. Tommelein and Sevilay Demirkesen University of California, Berkeley February 2018 CPWR Small Study Final Report 8484 Georgia Avenue, Suite 1000 Silver Spring, MD 20910 www. cpwr.com • www.elcosh.org TEL: 301.578.8500 © 2018, CPWR – The Center for Construction Research and Training. CPWR, the research and training arm of the Building and Construction Trades Department, AFL-CIO, is uniquely situated to serve construction workers, contractors, practitioners, and the scientific community. This report was prepared by the authors noted. Funding for this research study was made possible by a cooperative agreement (U60 OH009762, CFDA #93.262) with the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). The contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NIOSH or CPWR. i ABOUT THE PROJECT PRODUCTION SYSTEMS LABORATORY (P2SL) AT UC BERKELEY The Project Production Systems Laboratory (P2SL) at UC Berkeley is a research institute dedicated to developing and deploying knowledge and tools for project management. [Show full text]
- Chapter 6: Process Capability Analysis for Six Sigma Six Sigma Quality: Concepts & Cases‐ Volume I STATISTICAL TOOLS IN SIX SIGMA DMAIC PROCESS WITH MINITAB® APPLICATIONS Chapter 6 PROCESS CAPABILITY ANALYSIS FOR SIX SIGMA © Amar Sahay, Ph.D. Master Black Belt 1 Chapter 6: Process Capability Analysis for Six Sigma CHAPTER HIGHLIGHTS This chapter deals with the concepts and applications of process capability analysis in Six Sigma. Process Capability Analysis is an important part of an overall quality improvement program. Here we discuss the following topics relating to process capability and Six Sigma: 1. Process capability concepts and fundamentals 2. Connection between the process capability and Six Sigma 3. Specification limits and process capability indices 4. Short‐term and long‐term variability in the process and how they relate to process capability 5. Calculating the short‐term or long‐term process capability 6. Using the process capability analysis to: assess the process variability establish specification limits (or, setting up realistic tolerances) determine how well the process will hold the tolerances (the difference between specifications) determine the process variability relative to the specifications reduce or eliminate the variability to a great extent 7. Use the process capability to answer the following questions: Is the process meeting customer specifications? How will the process perform in the future? Are improvements needed in the process? Have we sustained these improvements, or has the process regressed to its previous unimproved state? 8. Calculating process [Show full text]
- Lean Six Sigma Rapid Cycle Improvement Agenda Lean Six Sigma Rapid Cycle Improvement Agenda 1. History of Lean and Six Sigma 2. DMAIC 3. Rapid Continuous Improvement – Quick Wins – PDSA – Kaizen Lean Six Sigma Lean Manufacturing Six Sigma (Toyota Production System) DMAIC • T.I.M.W.O.O.D • PROJECT CHARTER • 5S • FMEA • SMED • PDSA/PDCA • TAKT TIME • SWOT • KAN BAN • ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS • JUST IN TIME • FMEA • ANDON • SIPOC • KAIZEN • PROCESS MAP • VALUE STREAM MAP • STATISTICAL CONTROLS Process Improvement 3 Lean Manufacturing • Lean has been around a long time: – Pioneered by Ford in the early 1900’s (33 hrs from iron ore to finished Model T, almost zero inventory but also zero flexibility!) – Perfected by Toyota post WWII (multiple models/colors/options, rapid setups, Kanban, mistake-proofing, almost zero inventory with maximum flexibility!) • Known by many names: – Toyota Production System – Just-In-Time – Continuous Flow • Outwardly focused on being flexible to meet customer demand, inwardly focused on reducing/eliminating the waste and cost in all processes Six Sigma • Motorola was the first advocate in the 80’s • Six Sigma Black Belt methodology began in late 80’s/early 90’s • Project implementers names includes “Black Belts”, “Top Guns”, “Change Agents”, “Trailblazers”, etc. • Implementers are expected to deliver annual benefits between $500,000 and $1,000,000 through 3-5 projects per year • Outwardly focused on Voice of the Customer, inwardly focused on using statistical tools on projects that yield high return on investment DMAIC Define Measure Analyze Improve Control • Project Charter • Value Stream Mapping • Replenishment Pull/Kanban • Mistake-Proofing/ • Process Constraint ID and • Voice of the Customer • Value of Speed (Process • Stocking Strategy Zero Defects Takt Time Analysis and Kano Analysis Cycle Efficiency / Little’s • Process Flow Improvement • Standard Operating • Cause & Effect Analysis • SIPOC Map Law) • Process Balancing Procedures (SOP’s) • FMEA • Project Valuation / • Operational Definitions • Analytical Batch Sizing • Process Control Plans • Hypothesis Tests/Conf. [Show full text]
- Chapter 15 Statistics for Quality: Control and Capability Aaron_Amat/Deposit Photos Statistics for Quality: 15 Control and Capability Introduction CHAPTER OUTLINE For nearly 100 years, manufacturers have benefited from a variety of statis tical tools for the monitoring and control of their critical processes. But in 15.1 Statistical Process more recent years, companies have learned to integrate these tools into their Control corporate management systems dedicated to continual improvement of their 15.2 Variable Control processes. Charts ● Health care organizations are increasingly using quality improvement methods 15.3 Process Capability to improve operations, outcomes, and patient satisfaction. The Mayo Clinic, Johns Indices Hopkins Hospital, and New York-Presbyterian Hospital employ hundreds of quality professionals trained in Six Sigma techniques. As a result of having these focused 15.4 Attribute Control quality professionals, these hospitals have achieved numerous improvements Charts ranging from reduced blood waste due to better control of temperature variation to reduced waiting time for treatment of potential heart attack victims. ● Acushnet Company is the maker of Titleist golf balls, which is among the most popular brands used by professional and recreational golfers. To maintain consistency of the balls, Acushnet relies on statistical process control methods to control manufacturing processes. ● Cree Incorporated is a market-leading innovator of LED (light-emitting diode) lighting. Cree’s light bulbs were used to glow several venues at the Beijing Olympics and are being used in the first U.S. LED-based highway lighting system in Minneapolis. Cree’s mission is to continually improve upon its manufacturing processes so as to produce energy-efficient, defect-free, and environmentally 15-1 19_psbe5e_10900_ch15_15-1_15-58.indd 1 09/10/19 9:23 AM 15-2 Chapter 15 Statistics for Quality: Control and Capability friendly LEDs. [Show full text]
- Statistical Quality Control and Process Capability Analysis for Variability ering & ine M g a et al., n n E Rábago-Remy Ind Eng Manage 2014, 3:4 a l g a i e r m t s DOI: 10.4172/2169-0316.1000137 e u n d t n I Industrial Engineering & Management ISSN: 2169-0316 Research Article Open Access Statistical Quality Control and Process Capability Analysis for Variability Reduction of the Tomato Paste Filling Process Dulce María Rábago-Remy, Edith Padilla-Gasca and Jesús Gabriel Rangel-Peraza* Departamento de Estudios de Posgrado e Investigación, Instituto Tecnológico de Culiacán, Juan de Dios Batiz 310 Pte. Col. Guadalupe. Culiacán Sinaloa, México Abstract In this research some techniques for process statistical control were applied, such as frequency histograms, Pareto diagrams, process capability analysis and control charts. The purpose of this investigation was to reduce the variability of the canned tomato paste filling process coming from a tomato processing food industry that has problems with the net weight of their processed product. The results of the process capability analysis showed that 35.52% of the observations were out of the specifications during the months in study, which generates a real capability of the process (Cpk) of 0.124, and it indicates that the process does not have enough ability to fulfill the required specifications by the firm. The process potential capability (Cp) is 0.676. Given that Cpk < Cp, then it is concluded that the process is not centered, indicating that the measurement of the filling process is away from the center of the specifications. The process fits 0.371 sigma between the process mean and the nearest specification limit. [Show full text]
- Poka-Yoke and Quality Control on Traub Machine for Kick Starter Driven Shaft Journal of Material Science and Mechanical Engineering (JMSME) Print ISSN: 2393-9095; Online ISSN: 2393-9109; Volume 2, Number 7; April-June, 2015 pp. 10-15 © Krishi Sanskriti Publications http://www.krishisanskriti.org/jmsme.html Poka-Yoke and Quality Control on Traub Machine for Kick Starter Driven Shaft Atif Jamal 1, Ujjwal Kumar 2, Aftab A. Ansari 3, Balwant Singh 4 1,2,3,4 M.Tech Scholar, SET, Sharda University, GN, U.P [email protected] , [email protected] [email protected] , [email protected] Abstract: This study was conducted in manufacturing creation of process stoppages, and provides tools and methods environment and focused at machining operation. Fair Products for designing them. India, which manufactures auto ancillaries, was selected for this research. Fair Products has been facing tremendous pressure of In study Chen et al. (1996) , has also considers that a Poka- quality level and in house rejection due to under sizing of the parts manufactured on Traub Machine. After sometime the yoke is a mechanism for detecting, eliminating, and correcting process begins to fail as number of defects begins to increase as errors at their source, before they reach the customer. such the management has thrown challenge to the manufacturing team to find ways to improve the outgoing quality at machining C M Hinckley (2003) although the occurrence of mistakes is operation. Thus, Error Proofing method was adopted for inevitable, non-conformances and defects is not. To prevent implementation at Traub Machining operation. Experimental defects caused by mistakes, our approach to quality control research was carried out to see the effectiveness of Error must include several new elements. [Show full text]
- Sign into My Research
- Create My Research Account
- Company Website
- Our Products
- About Dissertations
- Español (España)
- Support Center
Select language
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
Welcome to My Research!
You may have access to the free features available through My Research. You can save searches, save documents, create alerts and more. Please log in through your library or institution to check if you have access.

Translate this article into 20 different languages!
If you log in through your library or institution you might have access to this article in multiple languages.

Get access to 20+ different citations styles
Styles include MLA, APA, Chicago and many more. This feature may be available for free if you log in through your library or institution.

Looking for a PDF of this document?
You may have access to it for free by logging in through your library or institution.

Want to save this document?
You may have access to different export options including Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive and citation management tools like RefWorks and EasyBib. Try logging in through your library or institution to get access to these tools.

- Preview Available
- Scholarly Journal
- More like this

Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study
No items selected.
Please select one or more items.
Select results items first to use the cite, email, save, and export options
This is a limited preview of the full PDF
Try and log in through your library or institution to see if they have access.
It appears you don't have support to open PDFs in this web browser. To view this file, Open with your PDF reader
Suggested sources
- About ProQuest
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy

- | Accessibility
- Islamic Azad University (IAU), Tehran
- Journal of Industrial Engineering International, SpringerOpen
Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: A case study

Items in EconStor are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.

Six Sigma Study Guide
Study notes and guides for Six Sigma certification tests

This Tire Manufacturer Sigma Six Case Study
Posted by Ted Hessing
Tires have come a long way since they were used 100 years ago. However, there is still a need for continuous improvement in their design to make them more useful and reliable. To achieve this, tire companies use various tools and methods, including the Six Sigma DMAIC methodology. An Indian tire manufacturer, Apollo Tyres Limited, has studied implementing Six Sigma to improve its process quality. A recent Tire Manufacturer Sigma Six Case Study focuses on reducing the process variations of bead splice, which causes wastage of material. The case study shows how to implement the DMAIC methodology to achieve this goal.
In 2017, Vikash Gupta wrote a study as a requirement for his Master of Technology degree in Industrial Engineering at Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur. The researcher collaborated with Islamic Azad University (IAU), Tehran, to publish the study in the Journal of Industrial Engineering International.
The study aimed to analyze and assess a tire manufacturer’s current processes, determine its capabilities, and improve them using the DMAIC methodology.
This tire manufacturer lean sigma six case study explains how Apollo Tyres Limited implemented the Six Sigma DMAIC methodology.
The Application of Lean Six Sigma Methodology for a Tire Manufacturer
Apollo Tyres Limited researched to improve its process efficiency using Six Sigma.
The team uses “Process Capability” to analyze how well a process works by using statistical tools like the normal curve and control charts . This analysis is done by combining data and engineering judgment. The results help them improve their design, planning, and evaluation techniques. By using process capability, they can also improve the design of machines and reduce defects during production.
Once they decided on what to study and how to do it, they began using the DMAIC cycle. This method helps identify and eliminate unnecessary steps and find ways to improve the process in many industries. Specifically, this research aims to reduce process variations and improve decision-making by creating a system where everyone in the company collects and analyzes data organizationally.
Each step of DMAIC used both qualitative and quantitative techniques. First, they tested the data to ensure it was normal and then calculated the process performance capability index (Cpk) to measure the performance of the process. The information helped the team establish a baseline for the system and identify areas to improve.
DMAIC Phases: Tire Manufacturer Lean Sigma Six Case Study
Here is the six-step approach followed in the research:
Define Phase
The team set goals to improve the bead splice process in the define phase . First, they found a problem by looking at what customers said ( VOC data ). Customers reported excessive material waste due to inconsistent product assembly, costing the company money. They discovered that the way the product was assembled was causing a problem. To solve it, they needed to make adjustments to use more material.
Measure Phase
In the measure phase , the researchers wanted to create a system to measure how well a process works. To do this, the team used the process capability index ( Cp & Cpk ). First, they looked at the variation in the bead splice and used a MINITAB program to analyze it.
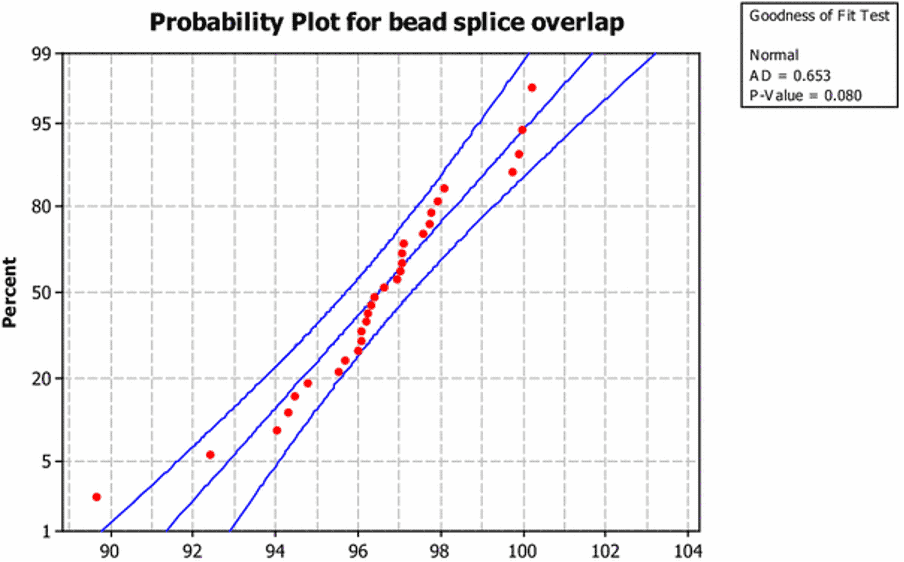
The research found that the Cpk value was 0.94 and the Ppk value was 0.82, less than 1.33. This means the process could be performing better. They also examined the relationship between the sigma level and the process capability indices.
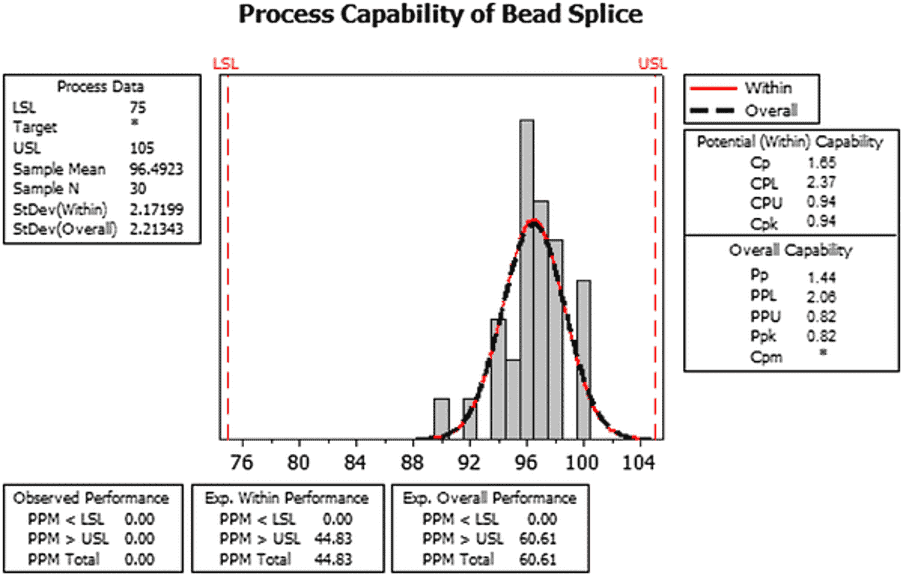
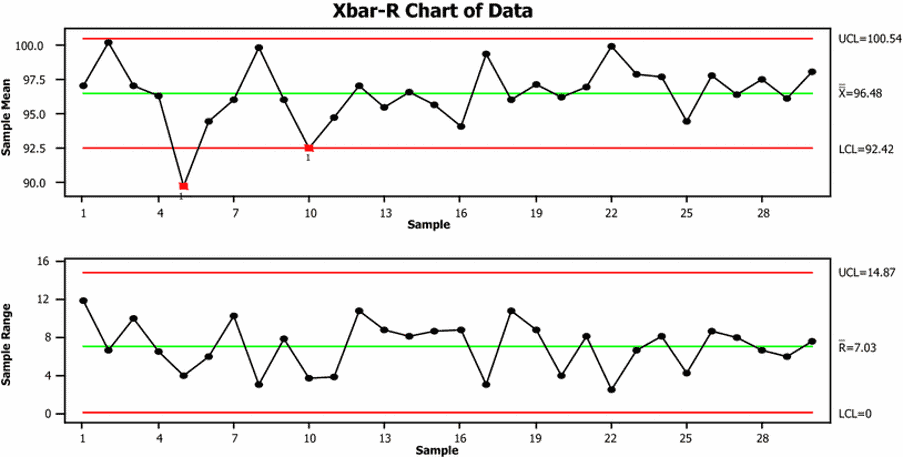
The team used this information to create a system performance evaluation starting point. Again, this was based on the improvement areas they identified in the planning phase.
Analysis Phase
In this step, they looked at the data and made charts to help them understand it better. Then, they used six-sigma quality tools to determine how well things were going. Then, they dug deeper into the data to find out what was causing any problems. To do this, they used the Ishikawa diagram .
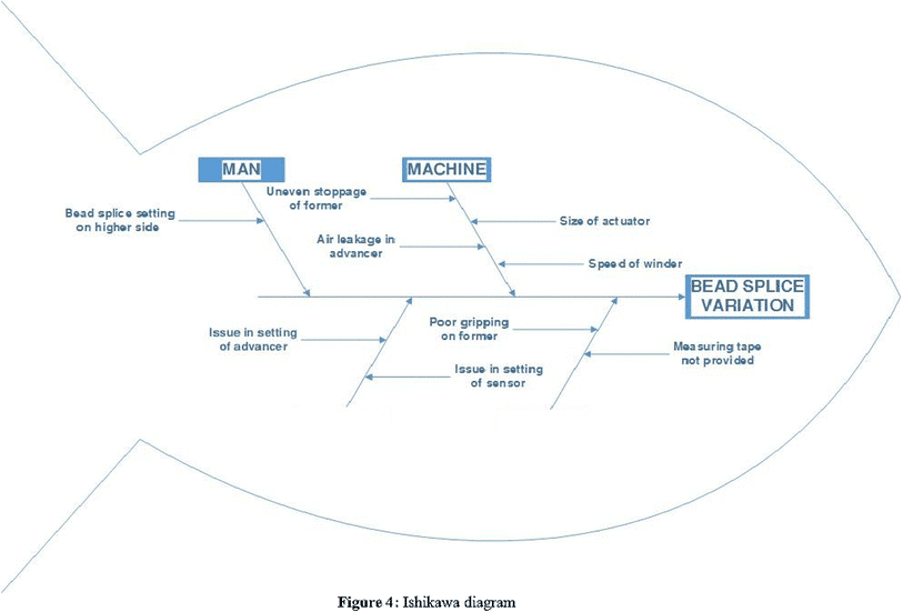
The was discovered that:
- The bead splice setting was too high because the tape slipped from the gripper. This happened because the gripper key was worn out.
- The advancer setting varied because different workers had different skills. There needed to be standard guidelines to follow.
- The sensor setting needed to be adjusted frequently because the diameter of the material changed, but there were no guidelines for how often to do this.
- The last cause was that the workers were not using measuring tape.

Improve Phase
During the improve phase , the team searched for new and creative ways to improve things faster and cheaper. They tried different approaches and suggested statistical methods for continuous improvement.
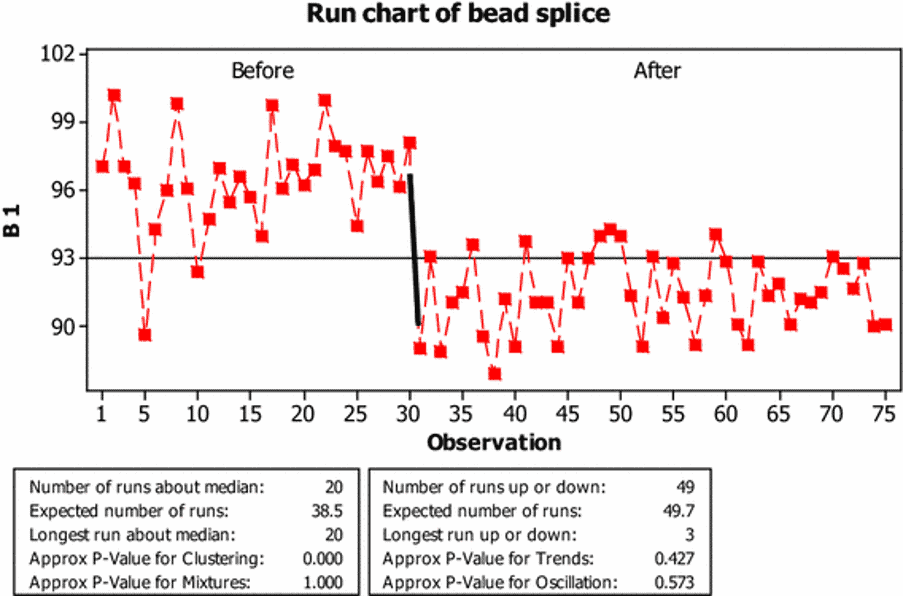
They calculated the process capability index, which measures how well the process can produce good results. After making improvements, the capability index value improved to 2.66, which means the process can now have good results.
Control Phase
To keep the tire manufacturer’s company successful, it’s important to continue the progress made in earlier steps. The control phase helps maintain these improvements in the screening process, ensuring that the organization maintains its high sigma quality level.
After obtaining the result, the first step is to evaluate whether the root cause has been reduced and if there has been any improvement in the sigma level. Additionally, it is important to identify any further actions that may be required to achieve the ultimate goal. It is crucial to take note of the lessons learned during the process and apply them in future endeavors. Finally, it is essential to determine the next steps and plan the remainder of the process accordingly.
Tire Manufacturer Lean Six Sigma Case Study Conclusion
This study uses the six-sigma DMAIC quality method to help decide how to fix a specific problem. It aimed to improve the way the bead splice process works, and this was achieved. The Cp was raised from 1.65 to 2.95, while the Cpk value was increased from 0.94 to 2.66.
This lean sigma six case study found that using the DMAIC methodology can greatly improve a tire manufacturer company’s work. This thesis’s research is not just about tire manufacturer companies but can also apply to other companies.
I originally created SixSigmaStudyGuide.com to help me prepare for my own Black belt exams. Overtime I've grown the site to help tens of thousands of Six Sigma belt candidates prepare for their Green Belt & Black Belt exams. Go here to learn how to pass your Six Sigma exam the 1st time through!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Case Study: Portuguese Tire Manufacturer Saves Thousands Using Six Sigma’s DMAIC Methodology
A tire manufacturing company in Portugal has provided an excellent study in implementing Six Sigma and how it can impact business performance.
Six Sigma already has proven its value in the automobile industry . Companies including Ford and Toyota have made the methodology a key component of their success.
A recent study of implementation of Six Sigma at Continental Mabor, a tire manufacturing company located in Famalicao, Portugal, provides a step-by-step look at putting Six Sigma’s DMAIC methodology into place.
The study, published at the 2017 Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference, was written by F.J.G. Silva, a professor in the school of engineering at Polytechnic of Porto, Portugal. It reported that the use of Six Sigma focused on improving the rubber extrusion process of two tire products: the tread and the sidewall. The primary goal was reduction of wasted material in the process.
Continental Mabor instituted Six Sigma because tire manufacturing is an intensely competitive business around the globe and “continuous flexibility and adaptation” is necessary, Silva wrote, adding that to achieve success, “it is crucial to seek operational excellence.”
Here is an overview of how Continental Mabor approached implementing the Six Sigma methodology of DMAIC , which stands for define, measure, analyze, improve and control.
Doing The Research
Continental Mabor started its Six Sigma journey by researching books and published scientific articles on Six Sigma methodology,
The company focused on improvements in the rubber extrusion process, particularly the mixing, preparation and construction departments. The mixing department receives raw materials that are transformed into compound sheets that are used in the preparation department on seven extrusion lines which focus on tread and sidewall extrusion. The ultimate “customer” for the extrusion process is the construction department.
The amount of material generated in the process – which is later reused for other purposes – is one of the indicators for the company on how efficient the operation is running. The focus is to limit the amount of extra material generated during the tread and sidewall extrusion process, called “work off.”

To accurately define the problem areas in the process, the company drew up a project charter that identifies problems, establishes objectives and defines the scope of the project (including the employee teams involved). A project charter also:
- Establishes the business case for how the project will impact overall organizational strategy
- Clearly measures the impact on the business of the current problem and measures the gap between where things are and the desired state
- Creates a clear scope for the project with identification of the areas where teams will focus to prevent “scope creep” – moving into areas outside the defined perimeter of the project
To create the charter, the company used a Gantt chart, a horizontal chart that maps out a product schedule. They also used a SIPOC diagram to plot the extrusion process in greater detail. SIPOC stands for supplier, inputs, process, outputs and customer. A SIPOC is a way to see an entire process in one graph and see the relationship between inputs and suppliers and the output for customers.
To get a handle on the current state of the extrusion process, Continental Mabor leaders then created a data collection plan . This included measuring the amount of rejected material during the extrusion process. Data was collected for 30 weeks, with 10 three-hour trials conducted each week. After this period of measurement, the company could determine the percentage of unused work off material generated in the tread and sidewall extrusion processes.
With the amount of data collected, the focus then turned to finding the root causes of the defects in the process that caused variation in the amount of materials wasted. The company used a Ishikawa diagram to find the cause and effect relationship between various activities and inputs into the process and the problem of generating unused material. They then used a Pareto chart to prioritize which potential causes seemed to have the most unfavorable impact.
They discovered that one machine in the sidewall extrusion process was not performing as well as others, leading to a significant increase in extra material. In the tread extrusion process, they discovered that the method for feeding the machines was creating problems with machine stoppage and jamming.
In this phase, a list was made of all the problems and root causes, then the subsequent action taken to improve these issues. These include changes to the machinery itself and changes in the methods used by employees to feed material into the machine.
With the improvements in place, data was then collected on the changes in the process. In this case, they were very significant. The company reduced the amount of work off material by five tons per day. After factoring in the cost of improvements to the machinery, the positive impact to the company’s bottom line was $165,000 euros per year, which translates to a little more than $200,000 U.S. dollars.
In his conclusion on the process improvement at Continental Mabor, Silva wrote that “the use of Six Sigma methodology played a decisive role in the achievement of the proposed goal, ensuring that there was a systematic and disciplined approach to the issues at hand through the DMAIC cycle.”
It also provides an excellent step-by-step education in how to implement Six Sigma successfully.

Lean Six Sigma in the Tire Industry
Tires are made through a production process. Lean and Six Sigma have been used in the tire industry to improve manufacturing processes. We’ll look at four case studies of their use: two from India and one each from Portugal and Spain. Then we’ll finish with two videos of how tires are made: one an animation of the process and another of the actual manufacture.
Six Sigma Applied to Variation Reduction in Bead Splice Process: India
In a paper titled “Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study” Authors Vikash Gupta, Rahul Jain, M. L. Meena and G. S. Dangayach discuss the use of Six Sigma to reduce the variation in the bead splice process that was leading to wastage.
Through the use of the DMAIC phases, the process standard deviation was reduced to 1.69 from 2.17 and the process performance capability index was increased to 2.66 from 0-.94.
You can access the case study here .
Using Lean Six Sigma to Reduce the Number of Defective Tires: India
In a case study titled “Monitoring quality goals through Lean Six-Sigma ensures competitiveness” Vipul Gupta, Padmanav Acharya and Manoj Patwardhan describe the use of Lean and Six Sigma tools to reduce the number of defective tires per month.
Included in the case study:
- Flow Diagram for Radial Tire Manufacturer
- Cause and Effect Diagram for Separation, Blisters, Bubbling, and Air Bridging
You can read the case study here .
Six Sigma Used to Reduce Defects in Bead Production: Portugal
In an article titled “Solving quality problems in tyre production preparation process: a practical approach” authors B. Barbosaa, M. T. Pereiraa,b,, F. J. G. Silvaa, and R. D. S. G. Campilhoa discuss the use of the Six Sigma DMAIC phases to achieve improvements in product quality rate and process control and stabilization.
Access the article at this link .
Six Sigma Applied to Improve the Extrusion Process in Tire Manufacture: Spain
Authors T. Costa, F.J.G.SilvaL and Pinto Ferreira cover the use of Six Sigma to improve the extrusion process in tire manufacture in their article titled, “Improve the extrusion process in tire production using Six Sigma methodology.”
Through the use of the DMAIC phases, the project upon completion generated an annual savings of 165 thousand euros.
You can find the article at this link .
[NOTE: Click on View PDF at top of page.]
Two Videos of How Tires are Made
An Animation from the U.S. Tire Manufacturers Association
Share This!
Related posts.

Leave A Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Whether you need a quick refresher on DFSS or want a little history on Motorola’s Six Sigma program, ISSSP has got you covered. ISSSP is excited to announce a series of free webinars for 2021. Register and reserve your seat today!
View Upcoming Webinars
Get exclusive access to our ever-growing list of resources, including presentations, webinars, white papers, and much more.
JOIN ISSSP NOW!
Implementation of lean six sigma (LSS) techniques for tyre manufacturing in small and medium-sized enterprises
- Original Article
- Published: 23 May 2023
- Volume 14 , pages 1208–1217, ( 2023 )
Cite this article

- G. Gokilakrishnan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3876-1759 1 ,
- R. Meenakshi 2 ,
- G. M. Pradeep 3 ,
- R. Kamalakannan 4 &
- V. Manivelmuralidaran 5
530 Accesses
3 Citations
Explore all metrics
National and international markets are seeing the impact of globalization, and all aspects of operations are looking for excellence in the global competitive economy. Six sigma can be an effective solution for achieving good performance in developing small and medium-sized companies, among many high-quality control methods. The DMAIC model has been used in current studies to decrease the process differences of the bead splice triggering material wastage. This six-sigma DMAIC study is being conducted by the customer’s voice in the specified phase by problem identification. The key problem consists of collecting current tire bead specification details. The control charts of the procedure were used for detailed monitoring and process management. The standard deviation was lowered from 2.17 to 1.69, using DMAIC methods. The process capability index (Cp) value was increased from 1.65 to 2.95 and the process capability index (Cpk) value was increased from 0.94 to 2.66, respectively. A DMAIC methodology has been developed that can play a key role in reducing defects in India’s tire fabrication process.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Assessing Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Approach in Manufacturing Industries: An Indian Context

Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma Principles Implementation in the Industry: Case Study
Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study, code availability.
Not applicable.
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Al Ahbabi SA, Singh SK, Balasubramanian S, Gaur SS (2019) Employee perception of impact of knowledge management processes on public sector performance. J Knowl Manag 23(2):351–373. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-08-2017-0348
Article Google Scholar
Alexander P, Antony J, Rodgers B (2019) Lean six sigma for smalland medium-sized manufacturing enterprises: a systematic review. Int J Qual Reliab Manag 36(3):378–397
Alsyouf I, Kumar U, Al-Ashi L, Al-Hammadi M (2018) Improving baggage flow in the baggage handling system at a UAE-based airline using lean six sigma tools. Qual Eng 30(3):432–452
Antony J, Krishan N, Cullen D, Kumar M (2012) Lean six sigma for higher education institutions (HEIs) challenges, barriers, success factors, tools/techniques. Int J Product Perform Manag 61(8):940–948
Arnheiter ED, Maleyeff J (2005) The integration of lean management and six sigma. TQM Mag 17(1):5–18
Basu K (2009) A behavioral model of simultaneous borrowing and saving. MPRA paper 20442. University Library of Munich, Germany, vol 1, no 1, pp 10–17
Bhasin S, Burcher P (2006) Lean viewed as a philosophy. J Manuf Technol Manag 17(1):56–72
Bhuiyan N, Baghel A (2005) An overview of continuous improvement: from the past to the present. Manag Decis 43(5):761–771
Chen M, Lyu J (2009) A lean six-sigma approach to touch panel quality improvement. Prod Plann Control 20(5):445–454
de Mast J, Lokkerbol J (2004) An analysis of the Six Sigma DMAIC method from the perspective of problem solving Author links open overlay panel. Int J Product Econ 139(2):604–614
Duarte BM (2011) An analytical approach to lean six sigma deployment strategies:project identification and prioritization [Doctoral dissertation]. Arizona State University, pp 1–157
Ghaleb AA, El-sharief MA, El-sebaie MG (2014) Study of tools, techniques and factors used in lean six Sigma. Int J Sci Eng Res 5(12):1652–1658
Google Scholar
Gijo EV, Shreeranga B, Jnanesh NA (2014) Application of Six Sigma methodology in a small-scale foundry industry. Int J Lean Six Sigma 5(2):21–29
Gunasekaran A, Forker L, Kobu B (2000) Improving operations performance in a small company: a case study. Int J Oper Prod Manag 20(3):316–336
Harry T, Alexander MT (2010) Six sigma: the breakthrough management strategy revolutionizing the world’s top corporations. Technometrics 43(3):360–368
Hill J, Thomas AJ, Mason-Jones RK, El-Kateb S (2018) The implementation of a lean six Sigma framework to enhance operational performance in an MRO facility. Prod Manuf Res 6(1):26–48
Jha R, Saini AK (2011) Process benchmarking through lean six sigma for ERP sustainability in small & medium enterprises. BIJIT-BVICAM’s. Int J Inform Technol 3(2):382–390
Jie JCR, Kamaruddin S, Azid IA (2014) Implementing the lean six sigma framework in a small medium enterprise (SME)—a case study in a printing company. In: International conference on industrial engineering and operations management, pp 387–396
Kumar M, Antony J, Singh RK, Tiwari MK, Perry D (2006) Implementing the lean sigma framework in an Indian SME: a case study. Prod Plan Control 17(4):407–423
Laureani A, Antony J (2019) Leadership and lean six sigma: a systematic literature review. Total Qual Manag Bus Excell 30(1–2):53–81
Mandahawi N, Fouad RH, Obeidat S (2012) An application of customized lean six sigma to enhance productivity at a paper manufacturing company. Jorden J Mech Ind Eng 6(1):103–109
Mathur A, Mittal ML, Dangayach GC (2012) Improving productivity in indian SMEs. Prod Plann Control Manag Oper 23(10–11):754–768
Mustapha MR, Abu Hasan F, Muda MS (2019) Lean six sigma implementation: multiple case studies in a developing country. Int J Lean Six Sigma 10(1):523–539
Patel R (2011) “Modeling lean six sigma in the small packaging industry in India. Institute of Technology
Pepper MP, Spedding TA (2010) The evolution of lean six sigma. Int J Qual Reliab Manag 27(2):138–155
Protzman C, Mayzell G, Kerpchar J (2018) Leveraging lean in healthcare: transforming your enterprise into a high quality patient care delivery system, p 402
Rockart J (1979) Chief executives define their own data needs. Harv Bus Rev 57(2):238–241
Rose ANM, Deros BM, Rahman MNA (2009) A review of lean manufacturing practices in small and medium enterprises. In: Seminar 3—AMReG 09, 29 Julai 2009, Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia, pp 1–6
Salah S, Rahim A, Carretero JA (2010) The integration of six sigma and lean management. Int J Lean Six Sigma 1(3):249–274
Schroeder RG, Linderman K, Liedtke C, Choo AS (2008) Six Sigma: definition and underlying theory. J Oper Manag 26(4):536–554
Singh M, Rathi R (2018) A structured review of lean six sigma in various industrial sectors. Int J Lean Six Sigma 10:622–664
Sokovic M, Pavletic D (2008) The lean and six sigma synergy. Int J Qual Res 2(4):247–251
Sony M (2019) Lean six sigma in the power sector: frog into prince. Benchmark Int J 26(2):356–370
Sosen AAS, Zohir AH, Saleh SA (2012) Improvement of production quality by using six sigma technique: applied study in the medical syringes factory-Babylon. Tekreet Eng Sci 02:12
Vashishth A, Chakraborty A, Antony J (2019) Lean six sigma in financial services industry: a systematic review and agenda for future research. Total Qual Manag Bus Excell 30(3–4):447–465
Download references
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sri Eshwar College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India
G. Gokilakrishnan
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Karpagam Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India
R. Meenakshi
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Velammal Institute of Technology, Thiruvallur, Tamilnadu, India
G. M. Pradeep
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kongu Engineering College, Erode, Tamilnadu, India
R. Kamalakannan
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kumaraguru College of Technology, Coimbatore, TamilNadu, India
V. Manivelmuralidaran
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GG.: writing—original draft, supervision, writing—review and editing. RM.: writing—original draft, supervision, writing—review and editing. GMP.: writing—original draft, supervision, writing—review and editing. RK.: writing—original draft, supervision, writing—review and editing. VM: writing—original draft, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to G. Gokilakrishnan .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Gokilakrishnan, G., Meenakshi, R., Pradeep, G.M. et al. Implementation of lean six sigma (LSS) techniques for tyre manufacturing in small and medium-sized enterprises. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 14 , 1208–1217 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-01917-0
Download citation
Received : 09 July 2021
Revised : 05 January 2022
Accepted : 06 April 2023
Published : 23 May 2023
Issue Date : August 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-01917-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Lean manufacturing
- Process capability
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

- Six-sigma application in tire-...
- More details
Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: A case study
| Year of publication: | |
|---|---|
| Authors: | ; ; ; |
| Published in: | . - Heidelberg : Springer, ISSN 2251-712X. - Vol. 14.2018, 3, p. 511-520 |
| Publisher: | Heidelberg : Springer |
| Subject: | | | | |
| Type of publication: | Article |
|---|---|
| Type of publication (narrower categories): | Article |
| Language: | English |
| Other identifiers: | |
| Source: |
- EndNote - Citavi, Endnote, RefWorks, ...
- Zotero, Mendeley, RefWorks, ...
Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company : a case study
Gupta, Vikash, (2018)
Enhanced rolled throughput yield : a new six sigma-based performance measure
Saghaei, Abbas, (2012)
An application of quality cost analysis as a tool for quality management
Chansiri Singhtaun, (2017)
Optimisation of labour productivity using work measurement techniques
Jain, Rahul, (2016)
Investigating ergonomic issues among workers in hand block textile printing industries
Meena, M. L., (2014)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the potential ways of improvement in the process as well as service ...
From outcomes of the study, it can be concluded that process performance of a tire-manufacturing plant can be improved significantly by implementing six-sigma DMAIC methodology. Cause and effect diagram was also used in an Indian study by Gupta et al. (2012), although no manufacturing aspects were discussed.
Six sigma aimed to achieve perfection in every single process of a company (Narula and Grover 2015). The term six sigma means having less than 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO) or a success rate of 99.9997%. In six sigma, the term sigma used to represent the variation of the process (Antony and Banuelas 2002).
riers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-. control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This. method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the. potential ways of ...
J Ind Eng Int DOI 10.1007/s40092-017-0234-6 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study Vikash Gupta1 • Rahul Jain1 • M. L. Meena1 • G. S. Dangayach1 Received: 16 February 2017 / Accepted: 13 September 2017 The Author(s) 2017.
The six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) method was used for decreasing the process variations of bead splice causing wastage of material in India. Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve ...
To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the potential ways of improvement in the process as well as service industries. In the current research, the DMAIC method was used for decreasing the process ...
A DMAIC methodology was established that can play a key role for reducing defects in the tire-manufacturing process in India. Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control ...
(2018) Gupta et al. Journal of Industrial Engineering International. Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) ...
ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study. 1 1 1 1 Vikash Gupta • Rahul Jain • M. L. Meena • G. S. Dangayach. Received: 16 February 2017 / Accepted: 13 September 2017 Ó The Author (s) 2017. This article is an open access publication. Abstract Globalization, advancement of technologies, and ...
<p>Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the potential ways of improvement in the process as well as ...
Gale Academic OneFile includes Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a by Vikash Gupta, Rahul Jain, M. L. Meena, . Click to explore.
Explore millions of resources from scholarly journals, books, newspapers, videos and more, on the ProQuest Platform.
Abstract: Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the potential ...
Tire Manufacturer Lean Six Sigma Case Study Conclusion. This study uses the six-sigma DMAIC quality method to help decide how to fix a specific problem. It aimed to improve the way the bead splice process works, and this was achieved. The Cp was raised from 1.65 to 2.95, while the Cpk value was increased from 0.94 to 2.66.
Case Study: Portuguese Tire Manufacturer Saves Thousands Using Six Sigma's DMAIC Methodology. SHARE ON: admin — February 19, 2018. A tire manufacturing company in Portugal has provided an excellent study in implementing Six Sigma and how it can impact business performance. Six Sigma already has proven its value in the automobile industry.
Six Sigma Applied to Variation Reduction in Bead Splice Process: India. In a paper titled "Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study" Authors Vikash Gupta, Rahul Jain, M. L. Meena and G. S. Dangayach discuss the use of Six Sigma to reduce the variation in the bead splice process that was leading to wastage.
Six-sigma application in tire-manufacturing company: a case study ... test was carried out to identify enablers for the effective implementation of lean tools in the Indian radial tire production company. Six sigma is a commodity or service consistency assessment metric and has a caliber for enhancing process reliability and excellence ...
Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wa...
Globalization, advancement of technologies, and increment in the demand of the customer change the way of doing business in the companies. To overcome these barriers, the six-sigma define-measure-analyze-improve-control (DMAIC) method is most popular and useful. This method helps to trim down the wastes and generating the potential ways of improvement in the process as well as service ...