- Home |
- About |
- Contact Us |
- Privacy |
- Newsletter |
- Shop |
- 🔍 Search Site
- Easter Color By Number Sheets
- Printable Easter Dot to Dot
- Easter Worksheets for kids
- Kindergarten
- All Generated Sheets
- Place Value Generated Sheets
- Addition Generated Sheets
- Subtraction Generated Sheets
- Multiplication Generated Sheets
- Division Generated Sheets
- Money Generated Sheets
- Negative Numbers Generated Sheets
- Fraction Generated Sheets
- Place Value Zones
- Number Bonds
- Addition & Subtraction
- Times Tables
- Fraction & Percent Zones
- All Calculators
- Fraction Calculators
- Percent calculators
- Area & Volume Calculators
- Age Calculator
- Height Calculator
- Roman Numeral Calculator
- Coloring Pages
- Fun Math Sheets
- Math Puzzles
- Mental Math Sheets
- Online Times Tables
- Online Addition & Subtraction
- Math Grab Packs
- All Math Quizzes
- 1st Grade Quizzes
- 2nd Grade Quizzes
- 3rd Grade Quizzes
- 4th Grade Quizzes
- 5th Grade Quizzes
- 6th Grade Math Quizzes
- Place Value
- Rounding Numbers
- Comparing Numbers
- Number Lines
- Prime Numbers
- Negative Numbers
- Roman Numerals
- Subtraction
- Add & Subtract
- Multiplication
- Fraction Worksheets
- Learning Fractions
- Fraction Printables
- Percent Worksheets & Help
- All Geometry
- 2d Shapes Worksheets
- 3d Shapes Worksheets
- Shape Properties
- Geometry Cheat Sheets
- Printable Shapes
- Coordinates
- Measurement
- Math Conversion
- Statistics Worksheets
- Bar Graph Worksheets
- Venn Diagrams
- All Word Problems
- Finding all possibilities
- Logic Problems
- Ratio Word Problems
- All UK Maths Sheets
- Year 1 Maths Worksheets
- Year 2 Maths Worksheets
- Year 3 Maths Worksheets
- Year 4 Maths Worksheets
- Year 5 Maths Worksheets
- Year 6 Maths Worksheets
- All AU Maths Sheets
- Kindergarten Maths Australia
- Year 1 Maths Australia
- Year 2 Maths Australia
- Year 3 Maths Australia
- Year 4 Maths Australia
- Year 5 Maths Australia
- Meet the Sallies
- Certificates

Mean Median Mode Range Worksheets and Help
Welcome to the Math Salamanders Mean Median Mode Range Worksheets. Here you will find a wide range of free printable Worksheets, which will help your child learn how to find the mean, median, mode and range of a set of data points.
These worksheets are aimed at students in 5th and 6th grade.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
Here are the instructions how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
Mean Median Mode Range Quicklinks
Quicklinks to ...
- Median Help
Mean Median Mode Range Worksheets
- Mean Median Mode Range Online Quiz
- More related Math resources
What is the Mean?
The mean is the average of a set of numbers.
It is found by adding up the set of numbers and then dividing the total by the number of data points in the set.
How to find the mean
Step 1) Add up all the numbers in the set.
Step 2) Divide the total by the total number of data points in the set.
Example 1) Find the mean of 5, 7, 8 and 4
Step 1) Add up the numbers to give a total of 5+7+8+4=24
Step 2) Divide the total by the number of data points. 24 ÷ 4 = 6
Answer: the mean is 6.
Example 2) Find the mean of 8, 2, 5, 7 and 13
Step 1) Add up the numbers to give a total of 8+2+5+7+13=35
Step 2) Divide by the number of data points. 35 ÷ 5 = 7
Answer: the mean is 7.
What is the Median?
The median is the midpoint (or middle value) of a set of numbers.
It is found by ordering the set of numbers and then finding the middle value in the set.
How to find the median
Step 1) Order the numbers in the set from smallest to largest.
Step 2) Find the middle number.
- If there is an odd number of values in the set, then the median is the middle value.
- If there is an even number of values in the set, then the median is the average of the two middle values.
Example 1) Find the median of 5, 7, 8, 2 and 4
Step 1) Put the numbers in order: 2, 4, 5, 7, 8
Step 2) There is an odd number of values in the set so the median is the middle value which is 5.
Answer: the median is 5.
Example 2) Find the median of 23, 27, 16, 31
Step 1) Put the numbers in order: 16, 23, 27, 31
Step 2) There is an even number of values in the set, so the median is the average of the middle two values.
(23+27) ÷ 2 = 25
Answer: the mean is 25
Example 3) Find the median of 7, -4, 9, -7, -2, 5
Step 1) Order the numbers: -7, -4, -2, 5, 7, 9
To get the average, simply add the two values together and divide by 2:
(-2 + 5) ÷ 2 = 1.5
Answer: the mean is 1.5
What is the Mode?
The mode is the most common (or the data point that appears most often) in a set of data.
It can be found by putting the data into an ordered list and seeing which data point occurs most often.
How to find the mode
Step 1) Put the data into an ordered list.
Step 2) Check that you have got the same number of data points.
Step 3) The mode is the data point which is the most common.
Finding the Mode Examples
Example 1) Find the mode of 3, 6, 4, 3, 2, 4, 7, 8, 6, 3, 9
This gives us: 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9
Step 2) Check the number of data points in both lists is the same.
Both lists have 11 data points.
Step 3) The mode is the number which occurs most often.
Answer: the mode is 3.
Example 2) Find the mode of 0.6, 0.3, 0.4, 0.2, 0.4, 0.7, 0.6, 0.1, 0.4, 0.9
This gives us: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 0.6, 0.6, 0.7, 0.9
Both lists have 10 data points.
Answer: the mode is 0.4.
Back to Top
What is the Range?
The range is the gap between the smallest and largest data point.
It is found by putting the data into an ordered list and find the difference between the largest and smallest amount.
How to find the range
Step 3) The range is the difference between the largest and smallest data point.
To find the range simply subtract the smallest number from the largest number.
Finding the Range Examples
Example 1) Find the range of 14, 21, 9, 32, 27, 15, 12, 30
This gives us: 9, 12, 14, 15, 21, 27, 30, 32
Both lists have 8 data points.
Step 3) The range is the difference or gap between the largest and smallest numbers.
Answer: the range is 32-9=23.
Example 2) Find the range of 6, 2, -7, 2, -5, 11, 3, -4, 0, 9
This gives us: -7, -5, -4, 0, 2, 2, 3, 6, 9, 11
Answer: the range is 11-(-7)=18.
These printable mean median mode range worksheets have been carefully graded to ensure a progression in the level of difficulty.
Sheets 1, 2 and 3 are designed for 5th graders involve ordering and calculating using positive integers and decimals.
Sheets 4, 5 and 6 are designed for 6th graders and involve ordering and calculating with positive and negative numbers and decimals.
The first sheet involve finding the mean, median, mode and range of some positive whole numbers.
The 2nd sheet involves the use of decimals to 1dp.
The 3rd sheet is similar to the 2nd sheet but has many more data points.
The 4th sheet involves decimals and negative numbers.
The 5th and 6th sheets are similar to the 4th sheets but with increased number of data points.
- Mean Median Mode and Range Sheet 1
- PDF version
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 2
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 3
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 4
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 5
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 6
Mean Median Mode Range Problems
These printable mean median mode range problem sheets will help your child to use and apply their skills to solve problems.
The first problem sheet is more suitable for 5th grade and the second sheet is aimed at 6th graders.
- Median Mean Mode and Range Problems 1
- Median Mean Mode and Range Problems 2
Mean Median Mode Range Walkthrough Video
This short video walkthrough shows the problems from our Median Mean Mode and Range Problems Sheet 2 being solved and has been produced by the West Explains Best math channel.
If you would like some support in solving the problems on these sheets, check out the video!
More Recommended Math Worksheets
Take a look at some more of our worksheets similar to these.
- Mean Worksheets
The sheets in this section will help you to find the mean of a range of numbers, including negative numbers and decimals.
There are a range of sheets involving finding the mean, and also finding a missing data point when the mean is given.
- Median Worksheets
The sheets in this section will help you to find the median of a range of numbers, including negative numbers and decimals.
On some of the easier sheets, only odd numbers of data points have been used.
On the harder sheets, both odd and even numbers of data points have been included.
- Mode and Range Worksheets
The sheets in this section will help you to find the mode and range of a set of numbers, including negative numbers and decimals.
There are easier sheets involving fewer data points, and harder ones with more data points.
The sheets in this section will help you to solve problems involving bar graphs and picture graphs.
There are a range of sheet involving reading and interpreting graphs as well as drawing your own graphs.
- Box Plot Worksheets
Here are our selection of box plot worksheets to help you practice creating and interpreting box plots.
Mean, Median, Mode and Range Online Quiz
Our quizzes have been created using Google Forms.
At the end of the quiz, you will get the chance to see your results by clicking 'See Score'.
This will take you to a new webpage where your results will be shown. You can print a copy of your results from this page, either as a pdf or as a paper copy.
For incorrect responses, we have added some helpful learning points to explain which answer was correct and why.
We do not collect any personal data from our quizzes, except in the 'First Name' and 'Group/Class' fields which are both optional and only used for teachers to identify students within their educational setting.
We also collect the results from the quizzes which we use to help us to develop our resources and give us insight into future resources to create.
For more information on the information we collect, please take a look at our Privacy Policy
We would be grateful for any feedback on our quizzes, please let us know using our Contact Us link, or use the Facebook Comments form at the bottom of the page.
This quick quiz tests your knowledge and skill at finding and using the mean, median, mode and range of a set of data.
How to Print or Save these sheets 🖶
Need help with printing or saving? Follow these 3 steps to get your worksheets printed perfectly!
- How to Print support
Subscribe to Math Salamanders News
Sign up for our newsletter to get free math support delivered to your inbox each month. Plus, get a seasonal math grab pack included for free!

- Newsletter Signup
Return to 6th Grade Math Worksheets
Return to Statistics Hub page
Return from Mean Median Mode Range to Math Salamanders Homepage
Math-Salamanders.com
The Math Salamanders hope you enjoy using these free printable Math worksheets and all our other Math games and resources.
We welcome any comments about our site or worksheets on the Facebook comments box at the bottom of every page.
New! Comments
TOP OF PAGE
© 2010-2024 Math Salamanders Limited. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy

Child Login
- Kindergarten
- Number charts
- Skip Counting
- Place Value
- Number Lines
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Word Problems
- Comparing Numbers
- Ordering Numbers
- Odd and Even
- Prime and Composite
- Roman Numerals
- Ordinal Numbers
- In and Out Boxes
- Number System Conversions
- More Number Sense Worksheets
- Size Comparison
- Measuring Length
- Metric Unit Conversion
- Customary Unit Conversion
- Temperature
- More Measurement Worksheets
- Writing Checks
- Profit and Loss
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Tally Marks
- Mean, Median, Mode, Range
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Stem-and-leaf Plot
- Box-and-whisker Plot
- Permutation and Combination
- Probability
- Venn Diagram
- More Statistics Worksheets
- Shapes - 2D
- Shapes - 3D
- Lines, Rays and Line Segments
- Points, Lines and Planes
- Transformation
- Quadrilateral
- Ordered Pairs
- Midpoint Formula
- Distance Formula
- Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines
- Scale Factor
- Surface Area
- Pythagorean Theorem
- More Geometry Worksheets
- Converting between Fractions and Decimals
- Significant Figures
- Convert between Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
- Proportions
- Direct and Inverse Variation
- Order of Operations
- Squaring Numbers
- Square Roots
- Scientific Notations
- Speed, Distance, and Time
- Absolute Value
- More Pre-Algebra Worksheets
- Translating Algebraic Phrases
- Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Polynomials
- Inequalities
- Sequence and Series
- Complex Numbers
- More Algebra Worksheets
- Trigonometry
- Math Workbooks
- English Language Arts
- Summer Review Packets
- Social Studies
- Holidays and Events
- Worksheets >
- Statistics >
- Mean, Median, Mode and Range
Central Tendency Worksheets: Mean, Median, Mode and Range
Mean, median, mode and range worksheets contain printable practice pages to determine the mean, median, mode, range, lower quartile and upper quartile for the given set of data. The pdf exercises are curated for students of grade 3 through grade 8. Interesting word problems are included in each section. Sample some of these worksheets for free!
Finding Average
Average or mean worksheets have plentiful exercises to find the average of numbers, numbers with practical units and decimals.
(49 Worksheets)

Finding Range
Identify the maximum and minimum values to find the range of the given data. Word problems are included for practice.
- Download the set

Finding Median
In these worksheets, 3rd grade and 4th grade children identify the median (middle value) of the represented data. Two word problems included.

Finding Quartiles
Determine the first (lower) quartile, second (median) quartile and the third (upper) quartile of the given data. One word problem included in each pdf worksheet for 5th grade and 6th grade students.

Mean, Median, Mode and Range: Level 1
These printable central tendency worksheets contain a mixed review of mean, median, mode and range concepts. Around 8 data are used in level 1.

Mean, Median, Mode and Range: Level 2
Find the mean, median, mode and range of each set of data. Each sheet has six problems with around 15 data.

Word Problems: Level 1
This exclusive section has five word problems to find the mean, median, mode and range of the given data.

Word Problems: Level 2
A variety of informative data are included as word problems in these central tendency worksheet pdfs requires 7th grade and 8th grade students to determine the values of mean, median, mode and range.
Related Worksheets
» Line Plot
» Mean Absolute Deviation
» Stem and Leaf Plot
» Box and Whisker Plot
Become a Member
Membership Information
Printing Help
How to Use Online Worksheets
How to Use Printable Worksheets
Privacy Policy
Terms of Use
Copyright © 2024 - Math Worksheets 4 Kids
This is a members-only feature!

Mean, Median, Mode and Range
Finding the mean, median, mode and range.
The three distinct calculations associated with the Measure of Central Tendency are the Mean , Median , and Mode . Each measurement is an attempt to capture the essence of how a typical entry or number in the data set may look like. The idea is to compute a single value that can represent the entire elements of the set.
In this lesson, I have prepared eight (8) worked examples to illustrate how to perform the required computations.
Measures of Central Tendency
Let’s first go over the main ideas of each measure of the central tendency.
Description:
“Average” value of the set of numbers
How to find…
Add all numbers to get a total, then divide by the number of entries (number count of values you added).
Advantages:
- Takes into account every number in the data set. That means all numbers are included in calculating the mean.
- Easy and quick way to represent the entire data values by a single or unique number due to its straightforward method of calculation.
- Each set has a unique mean value.
Disadvantages:
Its value is easily affected by extreme values known as the outliers.
Description:
Middle value of the set of numbers
- Organize the numbers in increasing order, the median is the middle or centermost number.
- If there are two middle numbers, add them and divide by 2 to get the median.
- Not affected by the outliers in the data set. An outlier is a data point that is radically “distant” or “away” from common trends of values in a given set. It does not represent a typical number in the set.
- The concept of the median is intuitive and thus can easily be explained as the center value.
- Each set has a unique median value.
Its value is perceived as it is. It cannot be utilized for further algebraic treatment.
Most common or frequent value or item of the set
Tally or count how many times a number appears in the list of data. The mode is the one that shows the most.
- Just like the median, the mode is not affected by outliers.
- Useful to find the most “popular” or common item. This includes data sets that do not involve numbers.
If the set contains no repeating values, the mode is irrelevant. In contrast, if there are many values that have the same count, then mode can be meaningless. I did not include the range in the tabs above because it is not really a measure of central tendency. However, the concept of range is usually discussed alongside Mean, Median, and Mode. So, what is it then?
Range (in statistics) is the difference between the maximum and minimum values of the set. What the range provides is a quick and rough estimate of the spread of data values within a set.
Consider the two scenarios below. Here we have two classes taking Algebra 1 and the ages of the students in each class.
- Algebra Class A
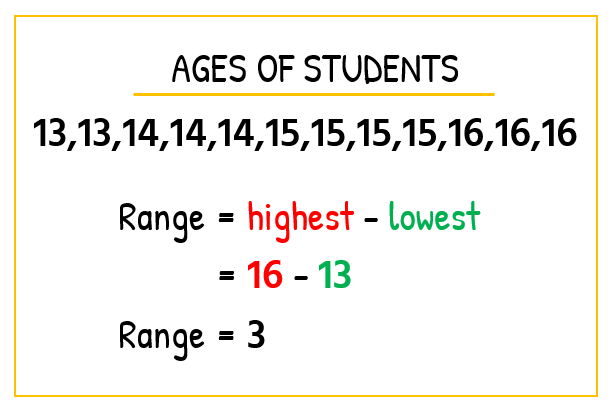
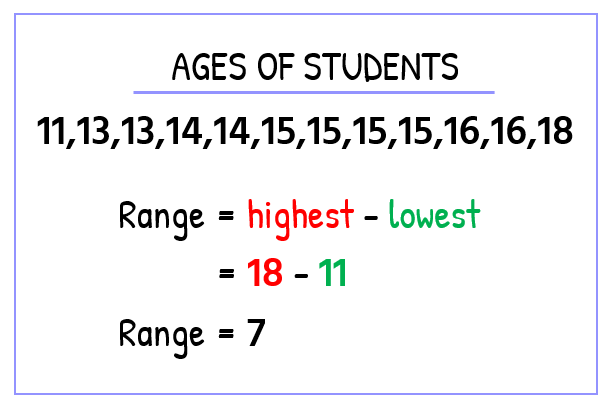
- Algebra Class B
Observations :
- Since the range of Class A is smaller than in Class B, can we claim that the age distribution in Class A is more clustered (closely related) than in Class B? In other words, are the ages listed in Class A more uniform than in Class B?
Not so fast! This is, in fact, the biggest limitation of using the range to describe the spread of data within a set. The reason is that it can drastically be affected by outliers (values that are not typical as compared to the rest of the elements in the set).
- Notice that when we disregard the outliers in Class B (ages 11 and 18), the “new” range becomes…
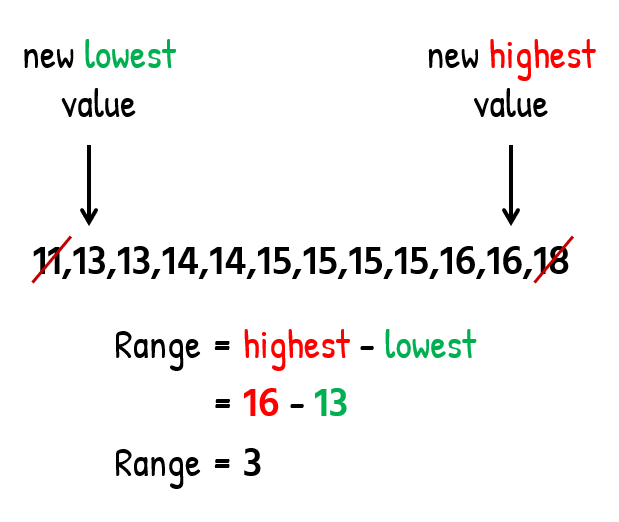
…which is now equal to the range of Class A. So the “big take” from this example is to be very careful when interpreting the values of the range, especially when comparing two sets.
Examples of How to Find the Mean, Median, Mode, and Range
Example 1: Find the mean, median, mode, and range for the following list of values
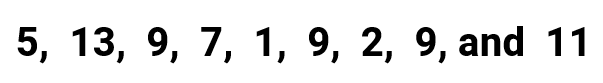
The mean is commonly known as the “average” which is calculated by getting the sum of all values in the list and then divided by the number of entries. The symbol used to represent the mean is [latex]\bar X[/latex], often read as “x-bar”.
- To find the mean:

I rounded off the final answer to the nearest whole number because all the numbers in the set are also whole numbers. To be more specific, I rounded off the mean to the nearest “ones” place or digit.
Rounding off is an approximation so I use the wavy equal symbol [latex]\left( \approx \right)[/latex] to suggest that it is an estimate and not an exact answer. However, be proactive by asking your teacher how many decimal places to round off your final answer.
- To find the median:
I must organize the numbers from lowest to highest, and identify the “middle” value.
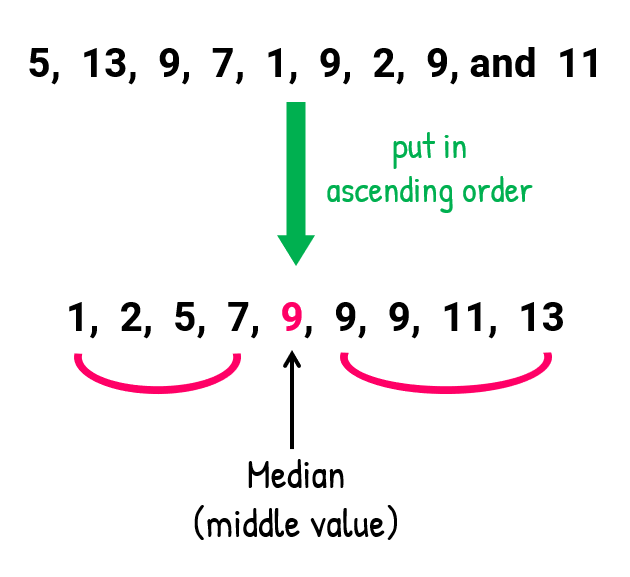
In addition, since the number count of entries is odd , it is guaranteed to have a middle value. A quick shortcut to determine which entry is the median is to add the number of entries (call it [latex]x[/latex]) by 1 then divide by 2. Use the output value here to count from either the left or right of the ordered list to pinpoint the exact location of the median.
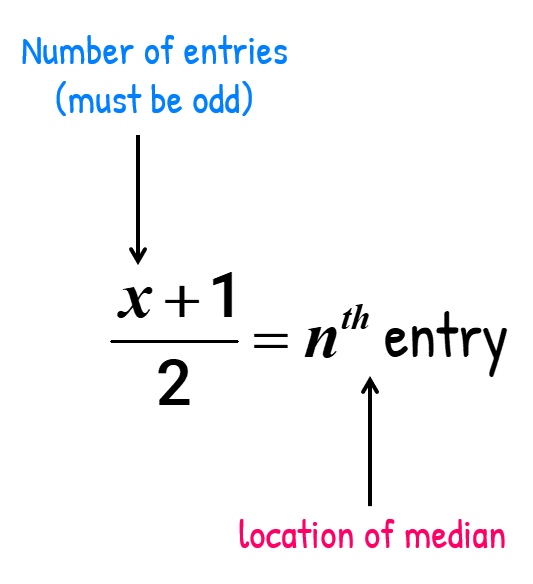
From our previous problem, the number of count of elements in the set is [latex]x = 9[/latex] so we have
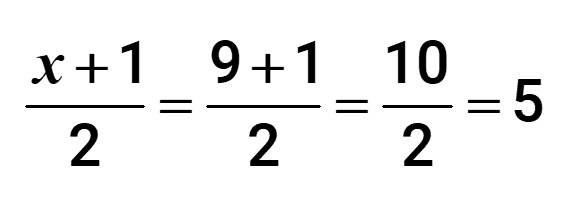
Therefore, the median is located by finding the 5 th entry when counted from either the left or right of the ordered list.
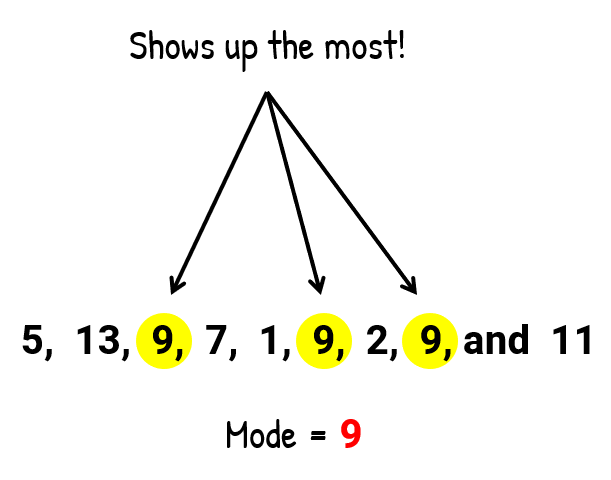
- To find the mode:
The mode is the number in the list that appears the most, which in this case, the number 9. This number is repeated three times.
- To find the range:
We don’t need to organize the list into numerical order to find the lowest and highest values. You should be able to pick those required two values by quick inspection.
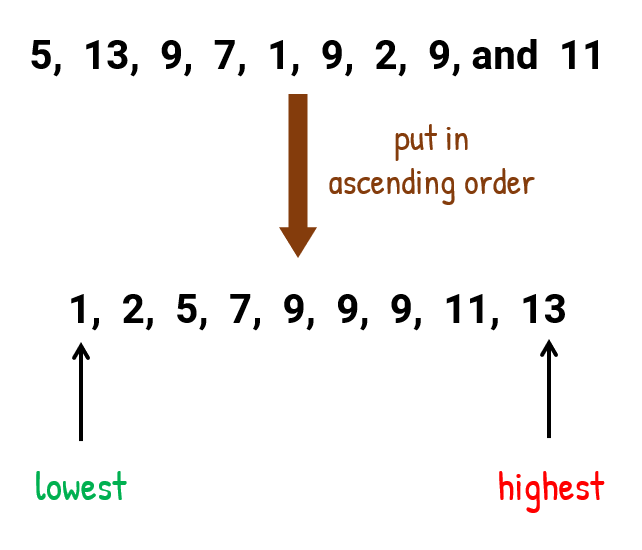
Since the range is the difference between the highest and lowest value, thus, range = highest − lowest = 13 − 1 = 12.
Example 2: Find the mean, median, mode, and range for the following list of values
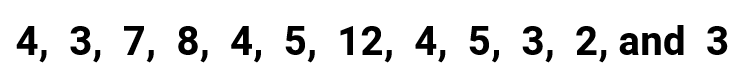
Another way to solve for the mean is to use the formula
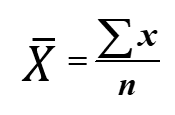
where the numerator is read as “the summation of all [latex]x[/latex] values”, and the denominator [latex]n[/latex] is just the number count of values in a set.
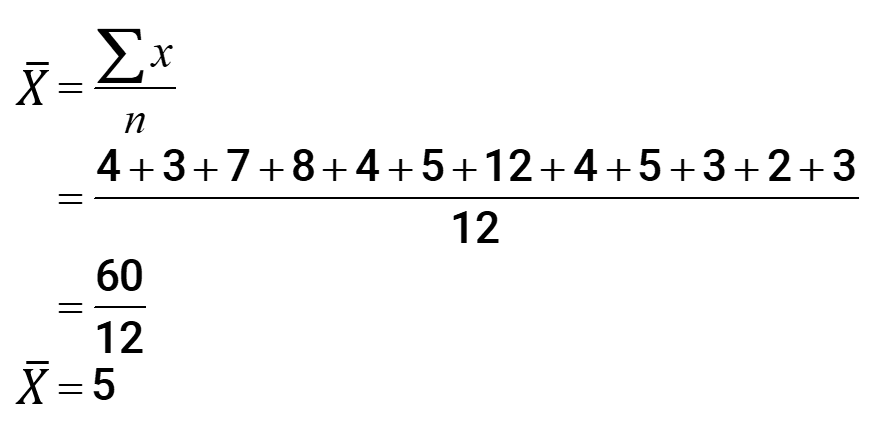
If we list the values in numerical order, the median is found at the “centermost” location. But here we have no single value at the center of the list. To address this issue, we are going to solve for the median by finding the average or mean of the two middle values .
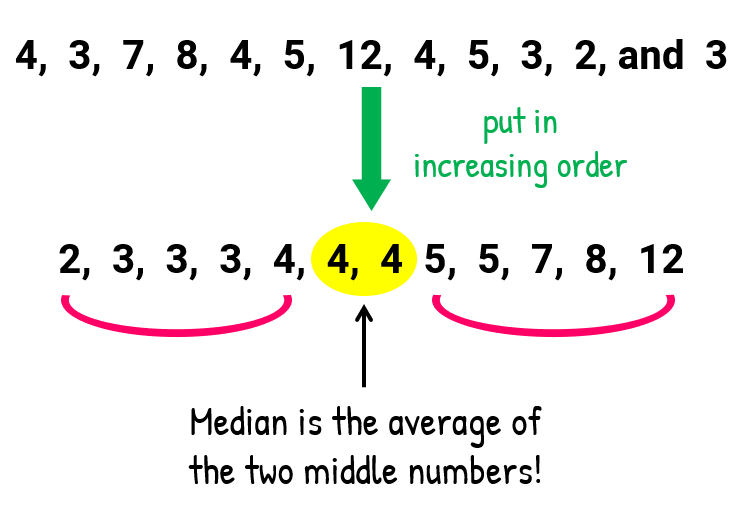
It just happens that the two center values are the same, therefore the average of two equal numbers will equal the same number.
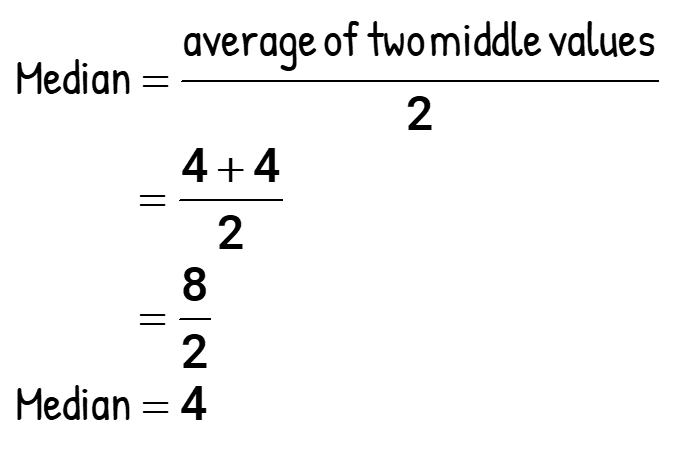
By quick inspection, we should observe that two numbers (3 and 4) appear most frequently on the list. Can we say that we have a tie because they both repeat three times on the list? That precisely is the case. We have a situation here where two modes exist! Some textbooks would call this set bimodal, which means having two modes.
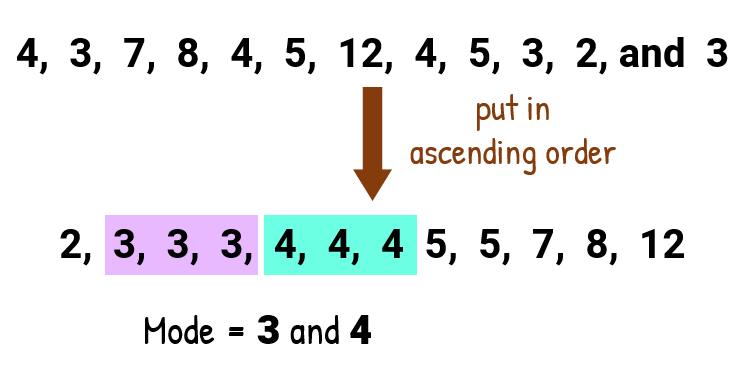
Range is equal to maximum value minus minimum value which gives us: 12 − 2 = 10 .
Example 3: Find the mean, median, mode and range for the following list of values
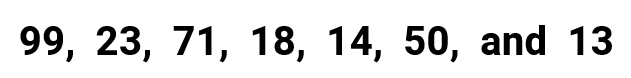
To determine the value of the mean, obtain the total of all the numbers and then divide by the number of numbers in the list. Since all given values are whole numbers, then it makes sense to have the final answer also expressed as a whole. Therefore, I will round it off to the nearest ones’ place.
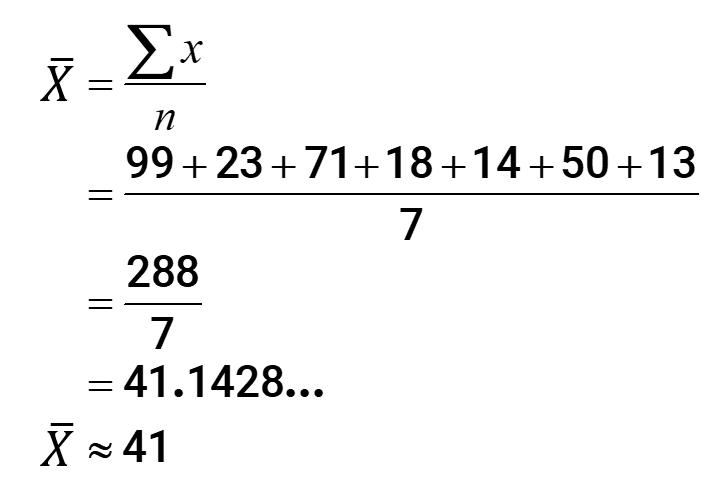
To solve for the median, let’s arrange the list in increasing order and then pick the center value. Obviously, the median here equals 23.
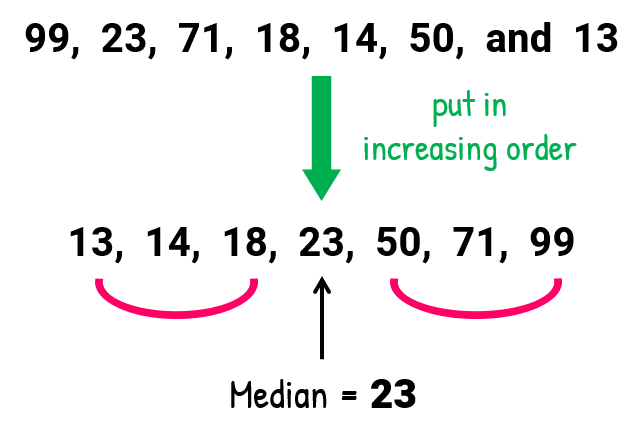
To solve for the mode, identify the most “popular” value or entry in the list. Is there an element that appears more often in the list?
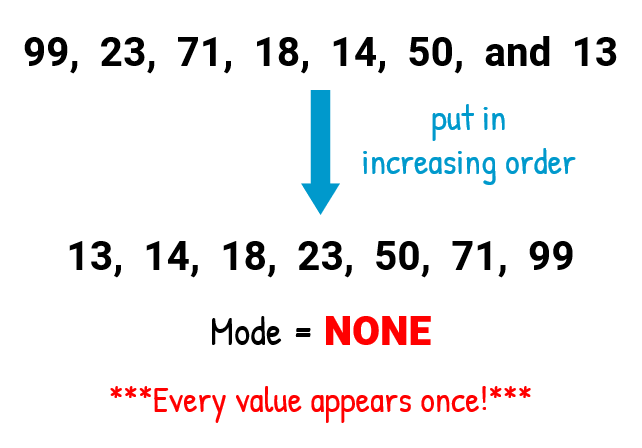
It is apparent that no value is repeated more often than the other. In fact, each unique number only shows up one time. So, this set has no mode .
The range is the easiest to find, Range = highest value minus lowest value. This gives us RANGE = 99 − 13 = 86 .
Example 4: Find the mean, median, mode, and range for the following list of values
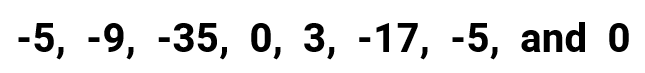
This is an interesting example because the elements in the set now contain zeroes, a positive, and negative numbers. However, the methods that are used to solve for the mean, median, mode, and range do not change.
- So for the mean , I will solve it as usual by finding its “average”. Since we are dealing with negative numbers, it is a good practice to place them inside the parenthesis to caution us to be careful in combining them. Round off your answer to the nearest ones’ place.
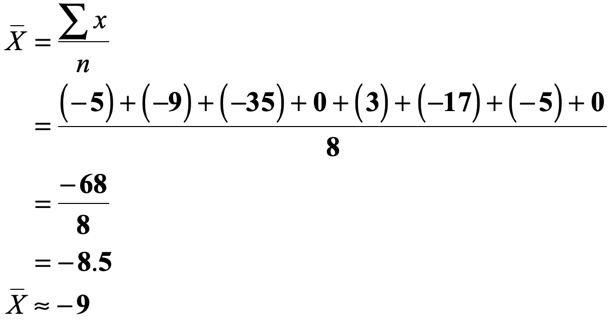
- For the median , we need to be careful in rearranging the numbers in increasing order because of the negative numbers. Remember that zero is always greater than any negative numbers. More so, to compare which of the two negative numbers is greater than the other, we need to compare both using their absolute values. The negative number with the smaller absolute value is the larger number!
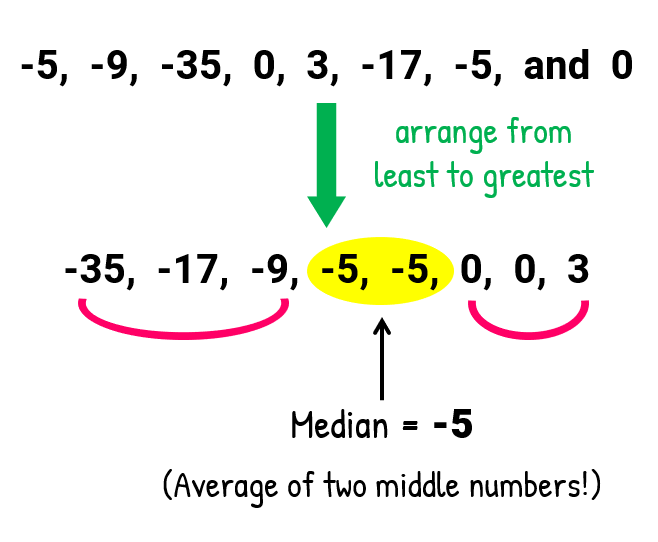
It just happens that the two middle numbers are equal. Thus, their average will simply be the number itself.
- For the mode , find the elements of the set that appears more often. It looks like we also have a tie! Both − 5 and 0 repeat themselves twice. The modes then are − 5 and 0 .
- The range is computed as follows:
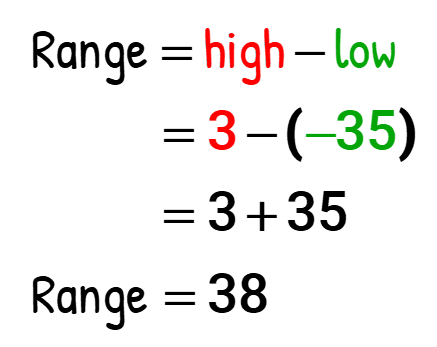
Remember that two negative signs turn out to be positive . Make sure that you always remember this simple rule to prevent any unnecessary algebraic mistakes.
Example 5: Find the mean, median, mode, and range for the following list of values
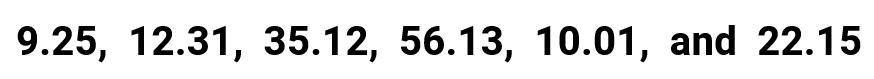
This example contains a set wherein all numbers have two decimal places. The rule of thumb is to ensure that any results of our computations must also be rounded off to the same decimal places. Again, it wouldn’t hurt if you ask advice from your teacher on how many decimals to round off as this part of the solution may be open to different interpretations.
- Finding the mean:
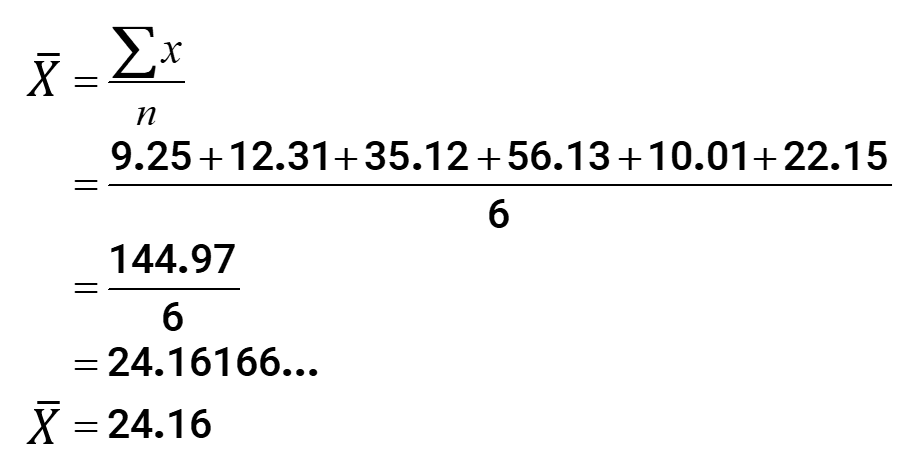
As you can see, I rounded off the final value of the mean to two decimal places.
- Finding the median:
Arrange the numbers in increasing order – that is, from least to greatest. By having an even number of entries in the set suggests that we will have two middle numbers. This is always the case! You should anticipate getting the average of the two middle values to obtain the answer for the median.
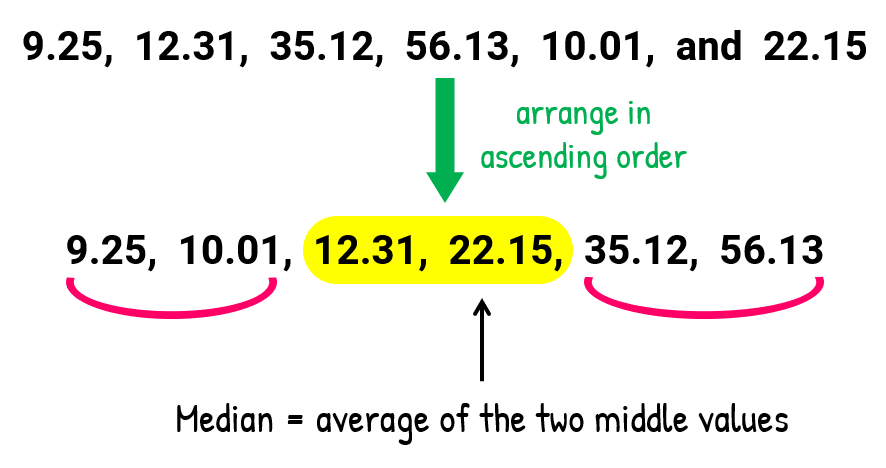
Here is the computation of the median…
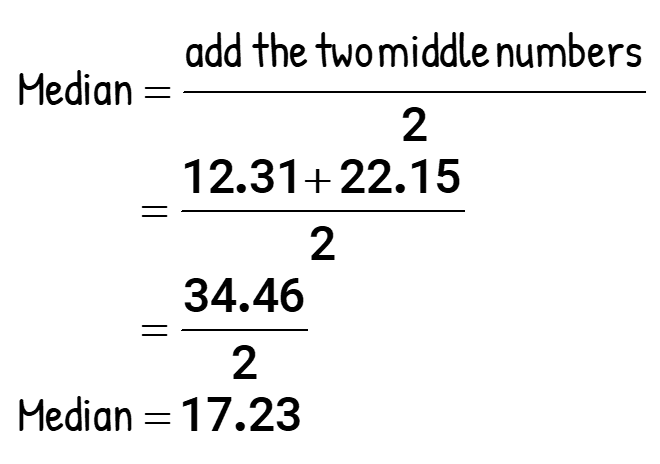
After dividing the sum of two middle numbers by 2 yields an answer with two decimal places. This is perfect! No need to do some rounding off.
- Finding the mode:
Since each element in the set appears just once (no repeating values), we say that this set has no mode .
- Finding the range:
The highest value is 56.13, while the lowest value is 9.25. The range is just the difference between them.
Range = 56.13 − 9.25 = 46.88
Example 6: Find the mean, median, mode, and range for the following list of values
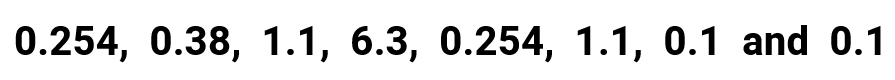
By quick inspection, the values in this set contain numbers that have different decimal places. Hopefully, you start by wondering how many decimal places should we round off the final answer. Again, this is open to interpretations. Therefore, I suggest that you ask your teacher for further clarification.
NOTE: For this problem though, I decided to round it off based on the number with the largest decimal places. I see that entry 0.254 contains three digits after the decimal point which is the biggest among others. So accordingly, I will keep in mind to round off the final answer for the mean with three digits after the decimal point.
- Determining the mean:
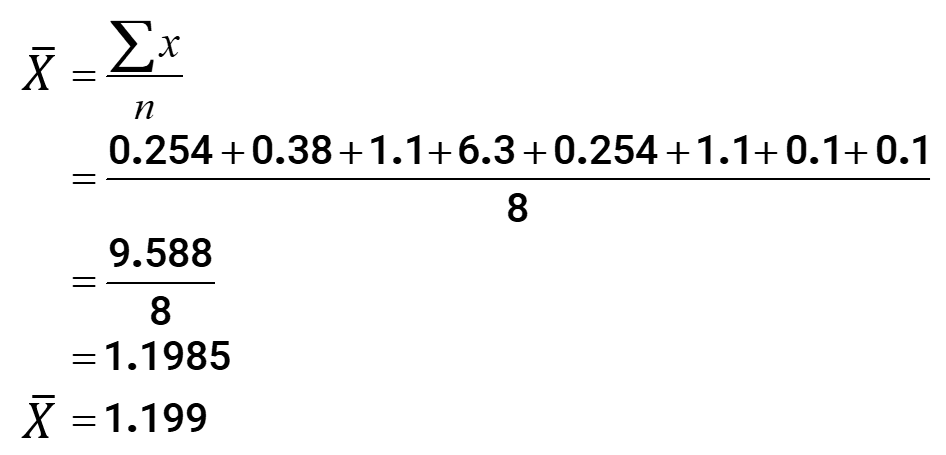
- Determining the median :
Similar to example 5, this set has an even count of entries. Expect to average the middle two values to solve for the median. Remember to round off your answer to the nearest three decimal places just like when we solved for the mean.
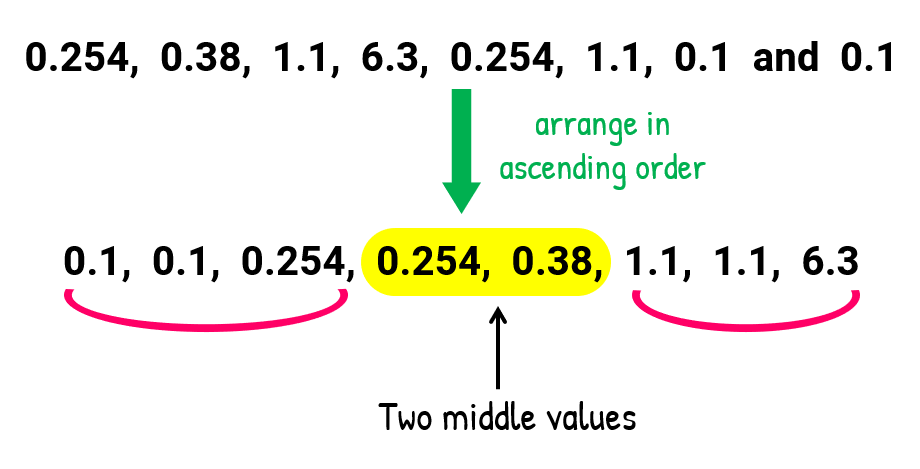
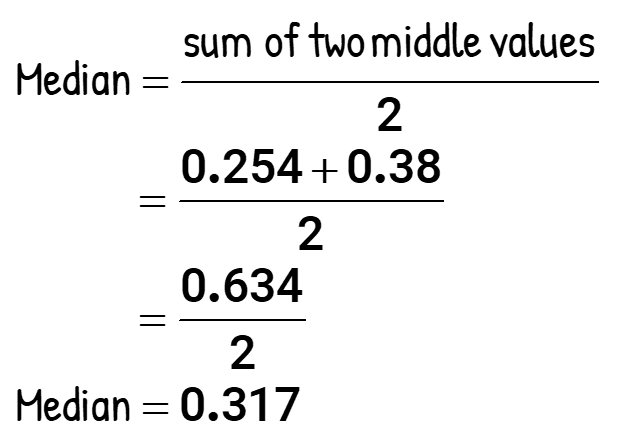
Here is the calculation for the median…
- Determining the mode:
We have three modes (trimodal) in this set which are 0.1, 0.254, and 1.1. They all repeat twice on the list!
- Determining the range:
The maximum value in the list is 6.3, while the minimum value is 0.1. Therefore the range is computed as follows…
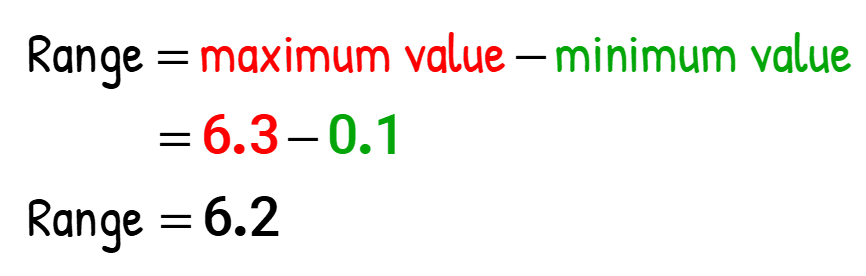
Example 7: Leroy wants to achieve an overall grade of B on his quizzes. Currently, he has the following scores from his previous eleven quizzes: 75, 83, 96, 86, 69, 74, 83, 86, 90, 60, and 80 . What should be his next score in order to get a quiz average of 80?
Let “[latex]x[/latex]” be the unknown test score that Leroy needs to get. In order to set up the correct average, we need to make an adjustment on the number of entries being added: that is, from 11 to 12.
The working equation that can solve for the missing value of “[latex]x[/latex]” is the following…
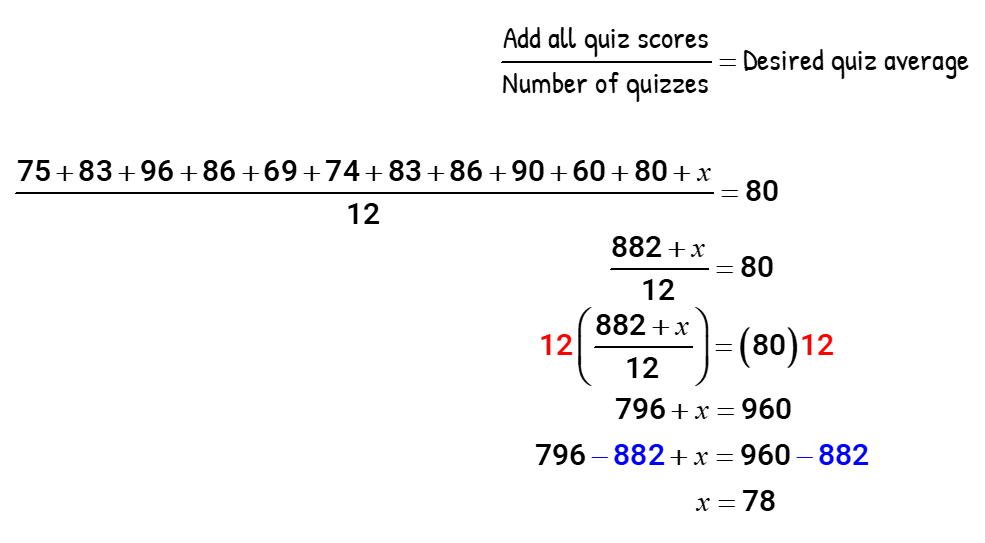
Leroy needs to score 78% on his next quiz in order to get a quiz average of 80%.
Example 8: Lisa is aware that she needs to take five major exams in the semester. Unfortunately, due to medical reasons, she is only able to take two exams with scores of 85 and 89 . To accommodate her, the professor gives her a make-up exam that would count as three test grades. What score does she need to get on this make-up exam to garner a 90% average in all exams?
Assign a variable to the unknown score. Let’s call it “[latex]y[/latex]”. The total number of exams is 5 because of her existing two exam scores which is added to the make-up exam that is counted as three. The desired equation to solve for the required score is…
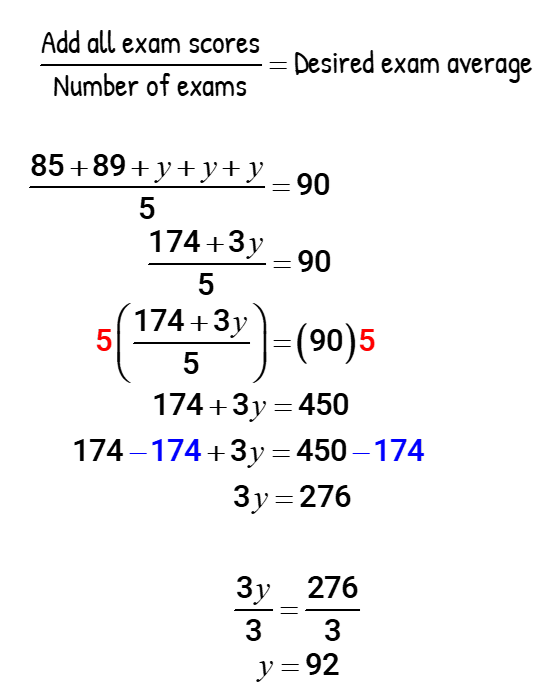
Lisa needs to score 92% on this single exam that’s counted as three test grades to achieve an overall exam of 90%.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS ON MEAN MEDIAN AND MODE
Problem 1 :
Find the (i) mean (ii) median (iii) mode for each of the following data sets :
a) 12, 17, 20, 24, 25, 30, 40
b) 8, 8, 8, 10, 11, 11, 12, 12, 16, 20, 20, 24
c) 7.9, 8.5, 9.1, 9.2, 9.9, 10.0, 11.1, 11.2, 11.2, 12.6, 12.9
d) 427, 423, 415, 405, 445, 433, 442, 415, 435, 448, 429, 427, 403, 430, 446, 440, 425, 424, 419, 428, 441
Problem 2 :
Consider the following two data sets :
Data set A : 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 10, 12
Data set B : 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 10, 20
a) Find the mean for both Data set A and Data set B.
b) Find the median of both Data set A and Data set B.
c) Explain why the mean of Data set A is less than the mean of Data set B.
d) Explain why the median of Data set A is the same as the median of Data set B
Problem 3 :
The table given shows the result when 3 coins were tossed simultaneously 40 times. The number of heads appearing was recorded.
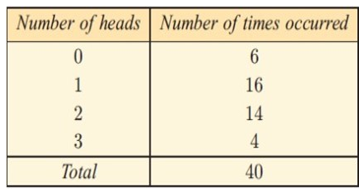
Calculate the : a) mean b) median c) mode
Problem 4 :
The following frequency table records the number of text messages sent in a day by 50 fifteen-years-olds
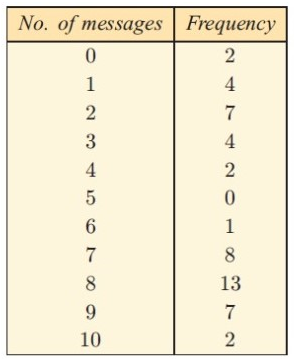
a) For this data, find the : (i) mean (ii) median (iii) mode
b) construct a column graph for the data and show the position of the measures of centre (mean, median and mode) on the horizontal axis.
c) Describe the distribution of the data.
d) why is the mean smaller than the median for this data ?
e) which measure of centre would be the most suitable for this data set ?
Problem 5 :
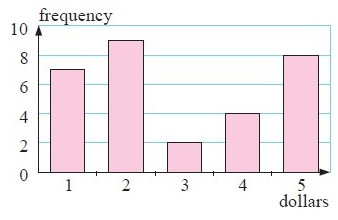
The frequency column graph alongside gives the value of donations for an overseas aid organisation, collected in a particular street.
a) construct the frequency table from the graph.
b) Determine the total number of donations.
c) For the donations find the : (i) mean (ii) median (iii) mode
d) which of the measures of central tendency can be found easily from the graph only ?
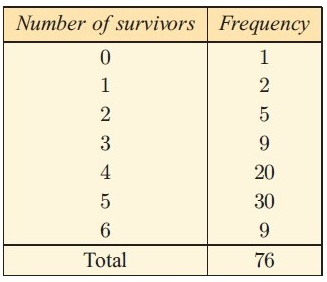
Problem 6 :
Hui breeds ducks. The number of ducklings surviving for each pair after one month is recorded in the table.
a) Calculate the : (i) mean (ii) median (iii) mode
b) Is the data skewed ?
c) How does the skewness of the data affect the measures of the middle of the distribution ?
Answers
| (1) | Mean | Median | Mode |
| (a) | 24 | 24 | No mode |
| (b) | 13.33 | 11.5 | 8 |
| (c) | 10.32 | 10 | 11.2 |
| (d) | 428.57 | 428 | 415 and 427 |
| Set A Mean = 7.73 Median = 7 | Set B Mean = 8.45 Median = 7 |
(c) the mean of A is less than the mean of B.
(d) median is the same.
(3) (a) Mean = 1.4 (b) median = 1 (c) mode = 1
(4)
(a) (i) Mean = 5.74 (ii) median = 7 (iii) mode = 8
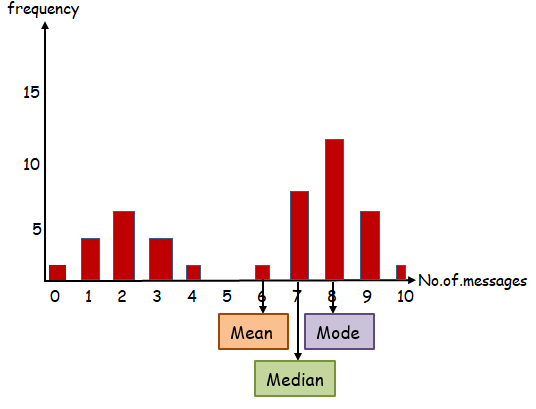
(c) bimodal data.
The mean takes into account the full range of numbers of text messages and is affected by extreme values. Also, the value which is lower than the median is well below it.
(e) The median
(5)
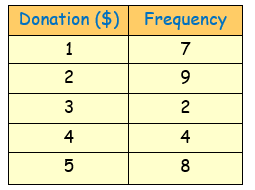
(b) ∑f = 30
(c) (i) Mean = $2.9 (ii) median = $2 (iii) mode = $2
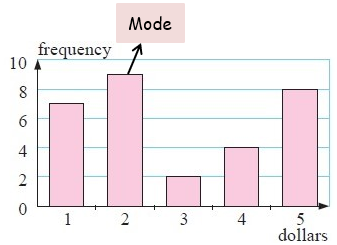
(6)
(a) (i) Mean = 4.25 (ii) median = 5 (iii) mode = 5
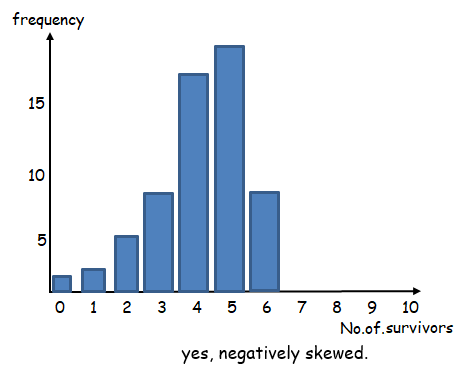
c) By observing the graph, the mean is less than the median and mode.

Apart from the stuff given above, if you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
Kindly mail your feedback to [email protected]
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
- Sat Math Practice
- SAT Math Worksheets
- PEMDAS Rule
- BODMAS rule
- GEMDAS Order of Operations
- Math Calculators
- Transformations of Functions
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Lines of symmetry
- Compound Angles
- Quantitative Aptitude Tricks
- Trigonometric ratio table
- Word Problems
- Times Table Shortcuts
- 10th CBSE solution
- PSAT Math Preparation
- Privacy Policy
- Laws of Exponents
Recent Articles
Sat math resources (videos, concepts, worksheets and more).
Aug 25, 24 08:56 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 34)
Aug 25, 24 08:51 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 33)
Aug 23, 24 11:59 PM
- Worksheet on Mean Median and Mode
In worksheet on mean median and mode the questions are based on finding the mean median and mode.
1. Find the mean of the following data.
(b) 16, 18, 19, 21, 23, 23, 27, 29, 29, 35
2. Find the mean of first ten whole numbers.
3. Find the mean of first 5 prime numbers.
4. The mean of 8, 11, 6, 14, x and 13 is 66. Find the value of the observation x.
5. The mean of 6, 8, x + 2, 10, 2x - 1, and 2 is 9. Find the value of x and also the value of the observation in the data.
6. Find the mean of the following distribution.
(a) The age of 20 boys in a locality is given below.
(b) Marks obtained by 40 students in an exam are given below.
(d) The daily wages of 50 employees in an organization are given below:
Find the mean daily wages.
(a) 12, 8, 4, 8, 1, 8, 9, 11, 9, 10, 12, 8
(b) 15, 22, 17, 19, 22, 17, 29, 24, 17, 15
(c) 0, 3, 2, 1, 3, 5, 4, 3, 42, 1, 2, 0
(d) 1, 7, 2, 4, 5, 9, 8, 3
8. The runs scored in a cricket match by 11 players is as follows:
7, 16, 121, 51, 101, 81, 1, 16, 9, 11, 16
Find the mean, mode, median of this data.
9. The weights in kg of 10 students are given below:
39, 43, 36, 38, 46, 51, 33, 44, 44, 43
Find the mode of this data. Is there more than 1 mode? If yes, why?
10. The marks obtained by 40 students out of 50 in a class are given below in the table.
Find the mode of the above data.
11. The number of rupee notes of different denominations are given below in the table.
12. Find the median of the following data.
(a) 27, 39, 49, 20, 21, 28, 38
(b) 10, 19, 54, 80, 15, 16
(c) 47, 41, 52, 43, 56, 35, 49, 55, 42
(d) 12, 17, 3, 14, 5, 8, 7, 15
13. The following observations are arranged in ascending order. The median of the data is 25 find the value of x.
17, x, 24, x + 7, 35, 36, 46
14. The mean of the following distribution is 26. Find the value of p and also the value of the observation.
Also, find the mode and the given data.
Answers for the worksheet on mean median and mode are given below to check the exact answers of the above questions.
5. 9, 11, 17
6. (a) 11.8
(d) no mode
8. Mean = 39 1/11;
Median = 16
● Statistics - Worksheets
- Worksheet on Frequency Distribution
- Worksheet on Bar Graph
- Worksheet on Pie Graph
- Worksheet on Line Graph
From Worksheet on Mean Median and Mode to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
New! Comments
Share this page: What’s this?
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy
| E-mail Address | |
| First Name | |
| to send you Math Only Math. |
Recent Articles
Data handling | data analysis | data processing | numerical data | def.
Aug 26, 24 06:02 PM

Construction of Angles by using Compass, Construction of Angles
Aug 25, 24 04:58 PM
Bisecting an Angle | Bisecting an Angle by Using a Protractor | Rules
Aug 24, 24 04:14 PM

Construction of an Angle using a Protractor | Drawing an Angle
Aug 24, 24 02:26 PM
Construction of Perpendicular Bisector of a Line Segment|Steps-by-Step
Aug 24, 24 11:35 AM
© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.

Averages and Range Textbook Exercise
Click here for questions.
means, modes, medians, mean, mode, median
GCSE Revision Cards

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024
- Inspiration
Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A)
Welcome to The Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A) Math Worksheet from the Statistics Worksheets Page at Math-Drills.com. This math worksheet was created or last revised on 2013-02-16 and has been viewed 106 times this week and 1,228 times this month. It may be printed, downloaded or saved and used in your classroom, home school, or other educational environment to help someone learn math.
Teacher s can use math worksheets as test s, practice assignment s or teaching tool s (for example in group work , for scaffolding or in a learning center ). Parent s can work with their children to give them extra practice , to help them learn a new math skill or to keep their skills fresh over school breaks . Student s can use math worksheets to master a math skill through practice, in a study group or for peer tutoring .
Use the buttons below to print, open, or download the PDF version of the Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A) math worksheet . The size of the PDF file is 35070 bytes . Preview images of the first and second (if there is one) pages are shown. If there are more versions of this worksheet, the other versions will be available below the preview images. For more like this, use the search bar to look for some or all of these keywords: math, statistics, data, management, mean, median, mode, range .
Print Full Version
Open Full Version
Download Full Version
Print Student Version
Open Student Version
Download Student Version
The Print button initiates your browser's print dialog. The Open button opens the complete PDF file in a new browser tab. The Download button initiates a download of the PDF math worksheet. Teacher versions include both the question page and the answer key. Student versions, if present, include only the question page.

Other Versions:
More Statistics Worksheets
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.

Core Math Worksheets
Addition worksheets, subtraction worksheets, multiplication worksheets, division worksheets, fact family worksheets, long division worksheets, negative numbers, exponents worksheets, order of operations worksheets, fraction worksheets, fractions worksheets, graphic fractions, equivalent fractions, reducing fractions, comparing fractions, adding fractions, subtracting fractions, multiplying fractions, dividing fractions, fractions as decimals, fraction decimal percent, word problems, pre-algebra word problems, money word problems, combining like terms, properties of multiplication, exponent rules, linear equations, one step equations, two step equations, factoring polynomials, quadratic equations, other worksheets, place value, percentages, rounding numbers, ordering numbers, standard, expanded, word form, mean median mode range, ratio worksheets, probability worksheets, roman numerals, factorization, gcd, lcm, prime and composite numbers, pre-algebra, geometry worksheets, blank clocks, telling analog time, analog elapsed time, greater than and less than, arithmetic sequences, geometric sequences, venn diagram, graph worksheets, measurement & conversions, inches measurement, metric measurement, metric si unit conversions, customary unit conversions, customary and metric, patterns and puzzles, number patterns, patterns with negatives, missing operations, magic square, number grid puzzles, word search puzzles, color by number, addition color by number, subtraction color by number, multiplication color by number, division color by number, color by number, holiday & seasonal, valentine's day, st. patrick's day, thanksgiving, early learning, base ten blocks, printable flash cards, number matching, number tracing, missing numbers, picture math addition, picture math subtraction, picture math multiplication, picture math division, multiplication chart, multiplication table, prime numbers chart, hundreds chart, place value chart, roman numerals chart, handwriting paper, graph paper, coordinate plane, spaceship math check-off, square root chart, fraction chart, probability chart, measurement chart, number line, comic strip template, calculators, age calculator, factoring calculator, fraction calculator, slope calculator, degrees to radians, percentage calculator, prime factorization calculator, roman numeral converter, long division calculator, multiplication calculator, math worksheets by grade, preschool math worksheets, kindergarten math worksheets, 1st grade math worksheets, 2nd grade math worksheets, 3rd grade math worksheets, 4th grade math worksheets, 5th grade math worksheets, 6th grade math worksheets, worksheet news, math worksheets for mean, median, mode and range.
Problem worksheets for finding the mean, median, mode and range given a set of numbers. These are basic problems suitable for 'by-hand' calculations. The data in earlier problems are pre-sorted.
Easy Sorted Mean Median Range
Sorted Mean Median Range - Single Digits

Easy Mean Median Range
Mean Median Range - Single Digits
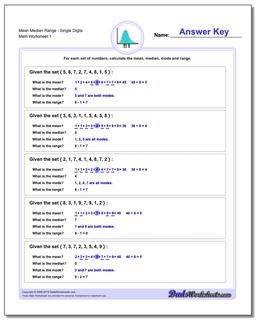
Mean Median Range 2

Mean Median Range 3

Getting Started with Mean, Median, Mode and Range Problems
The worksheets on this page require kids to calculate the mean, median, range and mode for small sets of numbers, all of which are easy enough to add up on paper without the aid of a calculator. These are great practice tools for introducing concepts like mean or median because the sets of numbers are small enough to focus on the techniques to compute these statistics without getting bogged down in the calculations themselves.
Computing the median requires summing all the values in the set, so working initially with a small group of numbers is advantageous for learning the technique. Similarly, finding the median and the mode requires looking at the numbers in order, so making this a bit more frustrating if the set of numbers is large. Because of these issues, starting with this set of worksheets will build confidence in student's ability to tackle mean, median, mode and range problems before moving on to larger sets of numbers in the following sections...

Copyright 2008-2024 DadsWorksheets, LLC
- Skills by Standard
- Skills by Grade
- Skills by Category
Go to profile
- Assignments
- Assessments
- Report Cards
- Our Teachers
Remove ads and gain access to the arcade and premium games!
Unlock harder levels by getting an average of 80% or higher.
Earn up to 5 stars for each level The more questions you answer correctly, the more stars you'll unlock!
Each game has 10 questions. Green box means correct. Yellow box means incorrect.
Need some help or instruction on how to do this skill?
Want a paper copy? Print a generated PDF for this skill.
Share MathGames with your students, and track their progress.
See how you scored compared to other students from around the world.
Learn Math Together.
Grade 7 - Statistics & Probability
Standard 7.SP.B.4 - Given the mean, median, mode or range, find the missing number of a sample.
Included Skills:
Use measures of center and measures of variability for numerical data from random samples to draw informal comparative inferences about two populations. For example, decide whether the words in a chapter of a seventh-grade science book are generally longer than the words in a chapter of a fourth-grade science book.
If you notice any problems, please let us know .
Mean, Median and Mode from Grouped Frequencies
Explained with Three Examples
The Race and the Naughty Puppy
This starts with some raw data ( not a grouped frequency yet ) ...

Alex timed 21 people in the sprint race, to the nearest second:
59, 65, 61, 62, 53, 55, 60, 70, 64, 56, 58, 58, 62, 62, 68, 65, 56, 59, 68, 61, 67
To find the Mean Alex adds up all the numbers, then divides by how many numbers:
Mean = 59 + 65 + 61 + 62 + 53 + 55 + 60 + 70 + 64 + 56 + 58 + 58 + 62 + 62 + 68 + 65 + 56 + 59 + 68 + 61 + 67 21 Mean = 61.38095...
To find the Median Alex places the numbers in value order and finds the middle number.
In this case the median is the 11 th number:
53, 55, 56, 56, 58, 58, 59, 59, 60, 61, 61 , 62, 62, 62, 64, 65, 65, 67, 68, 68, 70
Median = 61
To find the Mode , or modal value, Alex places the numbers in value order then counts how many of each number. The Mode is the number which appears most often (there can be more than one mode):
53, 55, 56, 56, 58, 58, 59, 59, 60, 61, 61, 62, 62, 62 , 64, 65, 65, 67, 68, 68, 70
62 appears three times, more often than the other values, so Mode = 62
Grouped Frequency Table
Alex then makes a Grouped Frequency Table :
| Seconds | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 51 - 55 | 2 |
| 56 - 60 | 7 |
| 61 - 65 | 8 |
| 66 - 70 | 4 |
So 2 runners took between 51 and 55 seconds, 7 took between 56 and 60 seconds, etc

Suddenly all the original data gets lost (naughty pup!)
Only the Grouped Frequency Table survived ...
... can we help Alex calculate the Mean, Median and Mode from just that table?
The answer is ... no we can't. Not accurately anyway. But, we can make estimates .
Estimating the Mean from Grouped Data
So all we have left is:
The groups (51-55, 56-60, etc), also called class intervals , are of width 5
The midpoints are in the middle of each class: 53, 58, 63 and 68
We can estimate the Mean by using the midpoints .
So, how does this work?
Think about the 7 runners in the group 56 - 60 : all we know is that they ran somewhere between 56 and 60 seconds:
- Maybe all seven of them did 56 seconds,
- Maybe all seven of them did 60 seconds,
- But it is more likely that there is a spread of numbers: some at 56, some at 57, etc
So we take an average and assume that all seven of them took 58 seconds.
Let's now make the table using midpoints:
| Midpoint | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 53 | 2 |
| 58 | 7 |
| 63 | 8 |
| 68 | 4 |
Our thinking is: "2 people took 53 sec, 7 people took 58 sec, 8 people took 63 sec and 4 took 68 sec". In other words we imagine the data looks like this:
53, 53, 58, 58, 58, 58, 58, 58, 58, 63, 63, 63, 63, 63, 63, 63, 63, 68, 68, 68, 68
Then we add them all up and divide by 21. The quick way to do it is to multiply each midpoint by each frequency:
| Midpoint x | Frequency f | Midpoint × Frequency fx |
|---|---|---|
| 53 | 2 | 106 |
| 58 | 7 | 406 |
| 63 | 8 | 504 |
| 68 | 4 | 272 |
| Totals: |
And then our estimate of the mean time to complete the race is:
Estimated Mean = 1288 21 = 61.333...
Very close to the exact answer we got earlier.
Estimating the Median from Grouped Data
Let's look at our data again:
The median is the middle value, which in our case is the 11 th one, which is in the 61 - 65 group:
We can say "the median group is 61 - 65"
But if we want an estimated Median value we need to look more closely at the 61 - 65 group.
We call it "61 - 65", but it really includes values from 60.5 up to (but not including) 65.5.
Why? Well, the values are in whole seconds, so a real time of 60.5 is measured as 61. Likewise 65.4 is measured as 65.
At 60.5 we already have 9 runners, and by the next boundary at 65.5 we have 17 runners. By drawing a straight line in between we can pick out where the median frequency of n/2 runners is:
And this handy formula does the calculation:
Estimated Median = L + (n/2) − B G × w
- L is the lower class boundary of the group containing the median
- n is the total number of values
- B is the cumulative frequency of the groups before the median group
- G is the frequency of the median group
- w is the group width
For our example:
- B = 2 + 7 = 9
Estimating the Mode from Grouped Data
Again, looking at our data:
We can easily find the modal group (the group with the highest frequency), which is 61 - 65
We can say "the modal group is 61 - 65"
But the actual Mode may not even be in that group! Or there may be more than one mode. Without the raw data we don't really know.
But, we can estimate the Mode using the following formula:
Estimated Mode = L + f m − f m-1 (f m − f m-1 ) + (f m − f m+1 ) × w
- L is the lower class boundary of the modal group
- f m-1 is the frequency of the group before the modal group
- f m is the frequency of the modal group
- f m+1 is the frequency of the group after the modal group
In this example:
Our final result is:
- Estimated Mean: 61.333...
- Estimated Median: 61.4375
- Estimated Mode: 61.5
(Compare that with the true Mean, Median and Mode of 61.38..., 61 and 62 that we got at the very start.)
And that is how it is done.
Now let us look at two more examples, and get some more practice along the way!
Baby Carrots Example

Example: You grew fifty baby carrots using special soil. You dig them up and measure their lengths (to the nearest mm) and group the results :
| Length (mm) | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 150 - 154 | 5 |
| 155 - 159 | 2 |
| 160 - 164 | 6 |
| 165 - 169 | 8 |
| 170 - 174 | 9 |
| 175 - 179 | 11 |
| 180 - 184 | 6 |
| 185 - 189 | 3 |
| Length (mm) | Midpoint x | Frequency f | fx |
|---|---|---|---|
| 150 - 154 | 152 | 5 | 760 |
| 155 - 159 | 157 | 2 | 314 |
| 160 - 164 | 162 | 6 | 972 |
| 165 - 169 | 167 | 8 | 1336 |
| 170 - 174 | 172 | 9 | 1548 |
| 175 - 179 | 177 | 11 | 1947 |
| 180 - 184 | 182 | 6 | 1092 |
| 185 - 189 | 187 | 3 | 561 |
| Totals: |
Estimated Mean = 8530 50 = 170.6 mm
The Median is the mean of the 25 th and the 26 th length, so is in the 170 - 174 group:
- L = 169.5 (the lower class boundary of the 170 - 174 group)
- B = 5 + 2 + 6 + 8 = 21
The Modal group is the one with the highest frequency, which is 175 - 179 :
- L = 174.5 (the lower class boundary of the 175 - 179 group)
Age Example
Age is a special case.
When we say "Sarah is 17" she stays "17" up until her eighteenth birthday. She might be 17 years and 364 days old and still be called "17".
This changes the midpoints and class boundaries.

Example: The ages of the 112 people who live on a tropical island are grouped as follows:
| Age | Number |
|---|---|
| 0 - 9 | 20 |
| 10 - 19 | 21 |
| 20 - 29 | 23 |
| 30 - 39 | 16 |
| 40 - 49 | 11 |
| 50 - 59 | 10 |
| 60 - 69 | 7 |
| 70 - 79 | 3 |
| 80 - 89 | 1 |
A child in the first group 0 - 9 could be almost 10 years old. So the midpoint for this group is 5 not 4.5
The midpoints are 5, 15, 25, 35, 45, 55, 65, 75 and 85
Similarly, in the calculations of Median and Mode, we will use the class boundaries 0, 10, 20 etc
| Age | Midpoint x | Number f | fx |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 - 9 | 5 | 20 | 100 |
| 10 - 19 | 15 | 21 | 315 |
| 20 - 29 | 25 | 23 | 575 |
| 30 - 39 | 35 | 16 | 560 |
| 40 - 49 | 45 | 11 | 495 |
| 50 - 59 | 55 | 10 | 550 |
| 60 - 69 | 65 | 7 | 455 |
| 70 - 79 | 75 | 3 | 225 |
| 80 - 89 | 85 | 1 | 85 |
| Totals: |
Estimated Mean = 3360 112 = 30
The Median is the mean of the ages of the 56 th and the 57 th people, so is in the 20 - 29 group:
- L = 20 (the lower class boundary of the class interval containing the median)
- B = 20 + 21 = 41
The Modal group is the one with the highest frequency, which is 20 - 29:
- L = 20 (the lower class boundary of the modal class)
- For grouped data, we cannot find the exact Mean, Median and Mode, we can only give estimates.
Estimated Mean = Sum of (Midpoint × Frequency) Sum of Frequency
- n is the total number of data
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Problem Solving Averages and Range
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
29 January 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Many thanks for your resources, extremely useful especially focusing on literacy in Maths.
Really helpful set of questions, thank you
JulieHallas
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Mean, Median, Mode, Range Calculator
Please provide numbers separated by comma to calculate.
Related Statistics Calculator | Standard Deviation Calculator | Sample Size Calculator
The word mean, which is a homonym for multiple other words in the English language, is similarly ambiguous even in the area of mathematics. Depending on the context, whether mathematical or statistical, what is meant by the "mean" changes. In its simplest mathematical definition regarding data sets, the mean used is the arithmetic mean, also referred to as mathematical expectation, or average. In this form, the mean refers to an intermediate value between a discrete set of numbers, namely, the sum of all values in the data set, divided by the total number of values. The equation for calculating the arithmetic mean is virtually identical to that for calculating the statistical concepts of population and sample mean, with slight variations in the variables used:
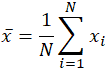
The mean is often denoted as x̄ , pronounced "x bar," and even in other uses when the variable is not x , the bar notation is a common indicator of some form of the mean. In the specific case of the population mean, rather than using the variable x̄ , the Greek symbol mu, or μ , is used. Similarly, or rather confusingly, the sample mean in statistics is often indicated with a capital X̄ . Given the data set 10, 2, 38, 23, 38, 23, 21, applying the summation above yields:
IMAGES
COMMENTS
averages, average, means, modes, medians, ranges. Practice Questions. Previous: Area of a Triangle Practice Questions. Next: Median from a Frequency Table Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on the Averages and Range.
These printable mean median mode range problem sheets will help your child to use and apply their skills to solve problems. The first problem sheet is more suitable for 5th grade and the second sheet is aimed at 6th graders.
Learn how to find the mean, find the median, find the mode, and find the range of data set using this complete step-by-step guide! Examples and a free practice worksheet are included.
These Mean Mode Median and Range Worksheets are perfect for mastering the math topic of means, modes, medians, and ranges of data set of numbers.
Mean, median, mode and range worksheets contain printable practice pages to determine the mean, median, mode, range, lower quartile and upper quartile for the given set of data. The pdf exercises are curated for students of grade 3 through grade 8. Interesting word problems are included in each section. Sample some of these worksheets for free!
Discover how to find the mean, median, mode, and range of a data set with eight examples and clear explanations. Improve your math skills with ChiliMath.
Mean, Median, Mode, and Range Notes, Examples, and Practice Exercises Topics include weighted average, data analysis, percentages, and more.
The mean takes into account the full range of numbers of text messages and is affected by extreme values. Also, the value which is lower than the median is well below it. Practice Problems on Mean Median Mode
Finding the Mean, Median, Mode Practice Problem ems. You may use a calculator if you would like. Study each of these problems carefully; you will se similar problems on the lesson knowledge check. You will need paper nd a pencil to complete the following exercises. You will be able to check your answers with the link provid
In worksheet on mean median and mode the questions are based on finding the mean median and mode.
The Corbettmaths Textbook Exercise on the Mean, Median, Mode and Range
Calculator Mean, Median, Range 16 Mean, Median, Mode and Range Worksheets Harder problems for determining the mean, median, mode and range from a larger set of numbers. You will probably want a calculator to solve these problems.
Learn how to find the mean, median, mode, and range of a data set in this free, interactive math lesson. Practice, get feedback, and have fun learning!
The Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A) Math Worksheet from the Statistics Worksheets Page at Math-Drills.com.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Find the mode of the following numbers. {33,60,33,60,33,57}, Find the range of the following numbers. {69,51,39,27,39}, Find the mean of the following numbers. {12,68,48,36} and more.
Getting Started with Mean, Median, Mode and Range Problems. Basic printable PDF worksheets for mean, median, mode and range calculations using smaller and shorter sequences of numbers.
Mean, Median, Mode and Range worksheets, questions and revision for GCSE Maths. All the revision you need in one place.
The mean, median, mode, & range are fundamental statistical calculations necessary to evaluate and comprehend the significance of a set of numbers. Learn how to calculate mean, medium, mode ...
Standard 7.SP.B.4 - Given the mean, median, mode or range, find the missing number of a sample. Included Skills: Use measures of center and measures of variability for numerical data from random samples to draw informal comparative inferences about two populations. For example, decide whether the words in a chapter of a seventh-grade science ...
Lesson 13: Mean, Median, Mode, and Range. Weekly Focus: central tendency. Skill: computation and real applicationLesson Summary: First, students. ill solve a problem about buying carpet. In Activity 1, the. will do a vocabulary matching activity. In Activity 2, they will d. some examples and computation practice. In Activity 3, they will.
Learn how to calculate the Mean, Median and Mode from grouped frequencies.
A mixed bag of problem solving style questions on mean, median, mode and range. Suitable for key stage 3 and key stage 4 student. Answers are included too.
This calculator determines the mean, median, mode, and range of a given data set. Also, learn more about these statistical values and when each should be used.