
Arrays – VHDL Example
Create your own types using arrays.
Arrays are used in VHDL to create a group of elements of one data type. Arrays can only be used after you have created a special data type for that particular array. Below are some rules about arrays.
- Arrays can be synthesized
- Arrays can be initialized to a default value
- Array type definitions can be unconstrained (undefined length)
- Arrays of arrays are allowed (e.g. an array of std_logic_vector)
- Two-Dimensional (2D) arrays are allowed
- Signals and Variables can be declared as an array type
Creating An Array:
Initializing an array:, creating a two-dimensional (2d) array.
Learn Verilog
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
courses:system_design:vhdl_language_and_syntax:extended_data_types:arrays
More Arrays
- Constrained or unconstrained size
- Range specification necessary
- The index set can be of any type
Arrays are a collection of a number of values of a single data type and are represented as a new data type in VHDL.
It is possible to leave the range of array indices open at the time of definition. These so called unconstrained arrays can not be used as signals, however, i.e. the index range has to be specified in the signal declaration then. The advantage of unconstrained arrays is the possibility to concatenate objects of different lengths, for example, because they are still of the same data type.
This would not be allowed if each array length was declared as separate data type. VHDL does not put any restrictions on the index set of arrays, as long it is a discrete range of values. It is even legal to use enumeration types, as shown in the code example, although this version is not generally synthesizable.
Multidimensional Array
- Array of array
- Multidimensional array
- Different referencing
- Barely supported by synthesis tools
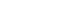
Multidimensional arrays can simply be obtained by defining a new data type as array of another array data type (1). When accessing its array elements, the selections are processed from left to right, i.e. the leftmost pair of brackets selects the index range for the “outermost” array. Thus ’MATRIX_3x8(2)’ selects the second ’INTEGER_VECTOR’ of ’MATRIX_A’.
The range enclosed in the next pair applies to the array that is returned by the previous slice selection, i.e. ’MATRIX_3x8(2)(4)’ returns the fourth integer value of this ’INTEGER_VECTOR’. Multiple dimensions can also be specified directly within a new array definition (2). The ranges of the different dimensions are separated by ’,’ symbols. If a whole row or column is to be selected, the range has to be provided in the slice selection. Multidimensional arrays are generally synthesizable up to dimension 2, only.
Aggregates and Multidimensional Arrays
- Aggregates may be nested
- Aggregates can be used to make assignments to all elements of a multidimensional array
The most convenient way to assign values to multiple array elements is via the aggregate mechanism. Aggregates can also be nested for this purpose. With an aggregate one can assign to all elements of an array a specific value in a clear fashion.
Chapters of System Design > VHDL Language and Syntax > Extended Data Types
- Introduction
- Standard Logic Type
- Enumeration Types
Chapters of System Design > VHDL Language and Syntax
- General Issues
- VHDL Structural Elements
- Process Execution
- Extended Data Types
- Sequential Statements
- Subprograms
- Subprogram Declaration and Overloading
- Concurrent Statements
VHDL Record, Array and Custom Types
In this post, we talk about the methods we can use to create our own custom data types in VHDL , including arrays and record types.
In the previous post we talked about the basic predefined types in VHDL . Whilst these are adequate for the majority of cases there are occasions when we require a custom data type in our code.
In VHDL, the most commonly used custom types are the enumerated types. These provide us with a technique for creating an entirely new type with custom values.
However, we can also create sub types which allow us to modify the range of values in one of the predefined VHDL types. In fact, the inbuilt VHDL positive and natural types are both example of subtypes which limit the range of values the integer can accept.
In addition to this, we can also use array and record types in our VHDL designs. This can provide us with a more structured design which is easier to maintain.
In the rest of this post we will at the methods we use to create all of these custom types in our VHDL code.
Creating Custom Types
When we write VHDL code, there are instances when the predefined types we wish to create a new type. One of the most common use cases is creating an enumerated type which we us to implement finite state machines (FSM) .
Actually there are two ways in which we can create a custom type in VHDL. We can either create an entirely new type or we can create a subtype .
Let's take a look at both of these methods.
- Type Declaration in VHDL
It is possible for us to create an entirely new type to use in our VHDL design. To do this, we must create a new name for our type and then associate some valid values with it.
The code snippet below shows the general syntax we use to create an new type.
The list of values is a comma separated list of all the values of our type can have.
When declaring a new type in VHDL we typically create an enumerated type. This means our list of values are just strings, or words, which we can assign to any instances of the type.
As an example, let's create a new type which we use to store the state of a small FSM. This is one of the most common reasons for creating a new type in VHDL.
For this example, our FSM will have just four states - idle, starting, runnning and stopping.
The code snippet below shows how we would create this type in VHDL. We can see that this is an enumerated type, meaning the list of values are simple strings.
Once we have created this type, we can create an instance of it in our code. We can then assign any value to it which we have listed in the declaration.
The code snippet below shows how we would create a signal using our custom type and assign it to the idle state.
- Subtype in VHDL
The second method we can use to create a custom type modifies one of the existing types. To do this, we use the subtype VHDL keyword and restrict the range of valid values which the new type can take.
The code snippet below shows the general syntax we use when creating a sub type.
One of the most common uses for the sub type keyword in VHDL is to restrict the number of bits in an integer type.
As an example, we may want to declare an integer which only uses 8 bits. In this case we can declare a new subtype and limit the maximum value to 255. The code snippet below shows how we would do this.
After we have created a new subtype, we can create instances of it to use in our VHDL design. We can then assign it any of the values we specified in the declaration.
The code snippet below shows how we would create a signal using our new type.
- Creating Array Types in VHDL
We can create our own array types in VHDL. To do this, we include the array keyword in the type definition. We must also declare the number of elements in the array.
The code snippet below shows the general syntax we use to declare an array type in VHDL.
The <type> field in the above construct can accept any VHDL type, including custom types we have declared. This means we can also build multidimensional arrays by using array types in this field.
The <range> field in the above example can be built using the downto and to VHDL keywords which we have seen before.
However, we can also use two special constructs which effectively create an unconstrained array type. This allows us to define the size of the array whenever we declare a port or signal which uses it.
To do this, we use the natural <range > or positive <range> keywords in the <range> field. The difference between the two is that the natural <range> option allows for zero based array numbering whereas positive <range> doesn't.
The VHDL code below shows the general syntax we use to create unconstrained array types.
Once we have declared a custom array type it can be used in an entity port, as a signal or a as a variable.
- An Example Array Type
To demonstrate how we declare a custom array type, lets consider a basic example. For this example we will create an array of 8 bit std_logic_vector types.
In addition, we will not constrain the array when we declare it. Instead, we will use the natural <range> construct so that we can change the size as we declare signals.
The code snippet below shows how we declare and use our custom array type.
Record Type in VHDL
We can create more complex data types in VHDL using a record. Records can contain any number of different signals which we want to group together. These signals don't need to be of the same type.
We can think of records as being roughly equivalent to structs in C.
We often use records to simplify the port list in a VHDL entity . If we have a number of common signals, we can group them together in a record. We can then use this record as part of the entity which reduces the number of ports we require.
Using record types in an entity can also improve the maintainability of our code. The main reason for this is that we only need to manage the contents of a record in the place it is declared. Therefore, we can change connections in our ports just by modifying the record type. If our design features multiple modules which use the same record, this can reduce the effort require to modify connections between entities.
- Declaring and Using a Record in VHDL
When we want to use a record in VHDL we must declare it as a type. We most commonly declare records inside a VHDL package . This allows us to use the record type in multiple different design files.
The code snippet below shows the general syntax we use to declare a record type in VHDL.
After we have declared a record type, we can use it in the exact same manner as any other port or signal in our VHDL design. We can assign data to individual elements in the record or to the entire array.
The code snippet below shows the two methods we can use to assign data to the record.
It is also possible for us to include records as elements in an array.
- An Example Record Type
Lets consider a basic example to better demonstrate how a record type works in VHDL. For this example, we will write a record which contains all the signals required in a UART interface.
The UART interface consists of 4 different signals. Each of these signals are a single bit which means we can use a std_logic type to model them.
The code snippet below shows how we would declare this record type.
After we have created the record, we can then use it in the type field for any port or signal in our VHDL design.
The code snippet below shows hows we would declare a signal which uses our UART record type.
Finally, we will obviously also want to drive data onto our record signal. The VHDL code snippet below gives some examples of how we can assign data to the record.
Write some VHDL code which creates an enumerated type for an FSM. The FSM has 4 states – idle, running, stopped and error
Create an integer subtype which can have a value between 5 and 200.
Write some VHDL code which declares an array of 8 32-bit std_logic_vectors
Write a record type which consists of an 8 bit unsigned type, a std_logic type and an unconstrained integer.
Table of Contents
Sign up free for exclusive content.
Don't Miss Out
We are about to launch exclusive video content. Sign up to hear about it first.
| Declaration | ---- used in ----> | Package Entity Architecture Process Procedure Function |
| Syntax |
| type_name (range) element_type; |
| Rules and Examples |
| An contains multiple elements of the same type. When an array object is declared, an existing array type must be used. |
| An array type definition can be , i.e. of undefined length. and are defined in this way. An object (signal, variable or constant) of an unconstrained array type must have it's index type range defined when it is declared. |
| Arrays with character elements such as and may be assigned a literal value using double quotes (see : |
| Arrays may also be assigned using (&), , , or a mixture. By default, assignment is made be |
| Arrays of arrays may be declared. These are useful for memories, vector tables, etc.: |
| True two (or more) dimensional arrays may also be declared: |
| Synthesis Issues |
Most logic synthesis tools accept one-dimensional arrays of other supported types. 1-D arrays of 1-D arrays are often supported. Some tols also allow true 2-D arrays, but not more dimensions.
Note that arrays are usually implemented using gates and flip-flops, not ROM's and RAM's.
| Whats New in '93 |
Array types have not changed in VHDL -93.
What is an array
In any software programming language, when we need to deal with a collection of elements of the same type we can take advantage of the dedicated data structures provided by the language. In VHDL such kind of structure is defined “ array “.
We can collect any data type object in an array type, many of the predefined VHDL data types are defined as an array of a basic data type.
An example is:
VHDL array declaration
The VHDL Arrays can be may both one-dimensional (with one index) or multidimensional (with two or more indices).
When we declare an array, we can decide if the array is
- Constrained
- Urnconstrained
In the constrained array, he bounds for an index are established when the array type is defined
In the unconstrained array, the bounds are established subsequently during the declaration of the variable or signal.
The BNF for declaring an array type is:
the subtype allows the values taken on by an object to be restricted or constrained subset of some base type.
Some examples of constrained array type declarations:
Accessing to the array object
An element of an array object can be referred to by indexing the name of the object.
Figure 1 reports an example of the signal vector and matrix addressing, here below the VHDL code for matrix and vector definition and addressing.
Implementing a MUX using an array in VHDL
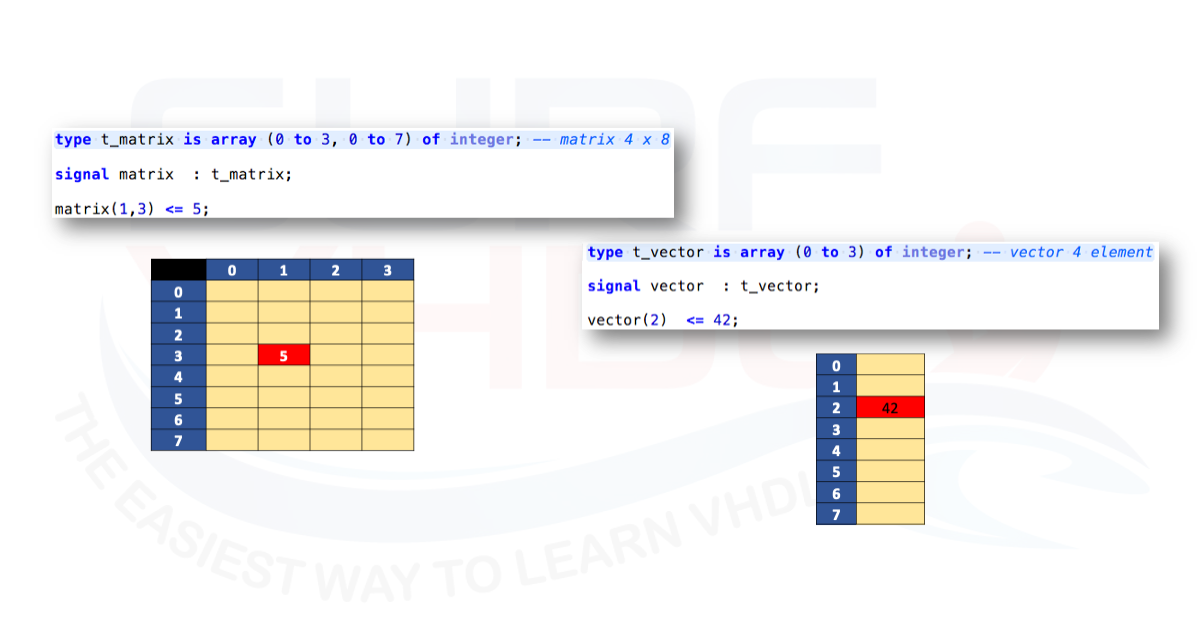
In this post, we describe the VHDL implementation of a MUX using the CASE-WHEN statement . Another compact and elegant way for describing a MUX architecture in VHDL is to use the array approach. In the VHDL code below is reported the VHDL code of the implementation of an 8-way MUX. We defined an array of the same type of data of the MUX then the array is referenced using the MUX selector. In a single VHDL line, we can implement an N-way MUX.
As example, Figure 2 shows the RTL view of the 8-way MUX implementation on Altera/Intel Cyclone II FPGA
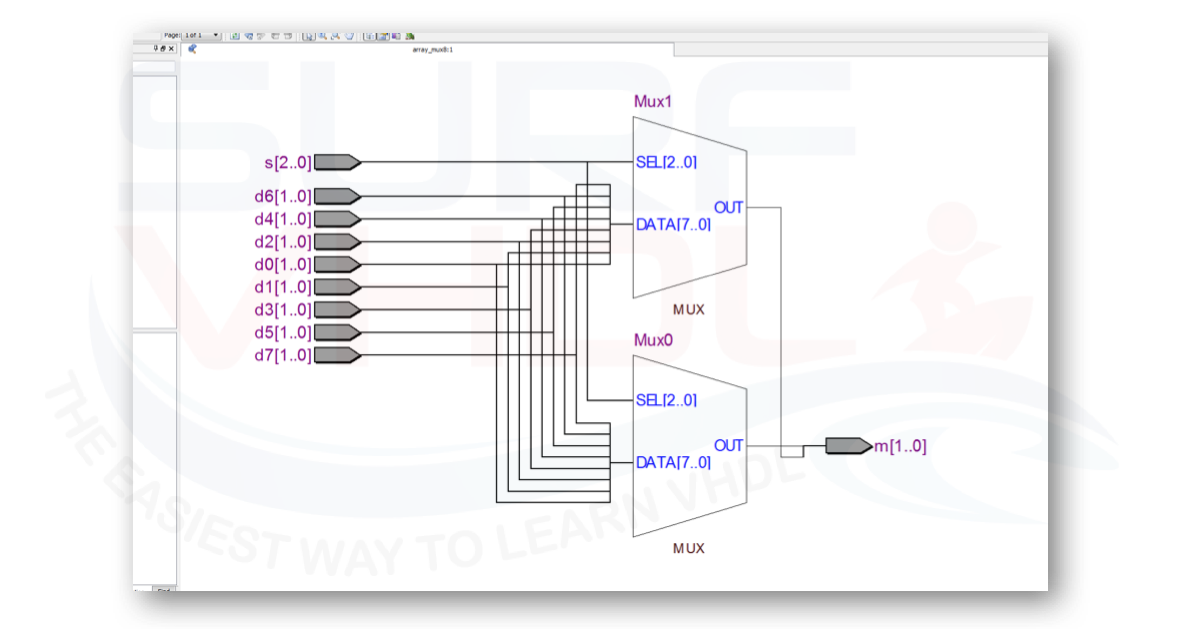
Implementing a LUT using an array in VHDL
A typical application of array in VHDL is the implementation of a LUT aka Look Up Table. In the example below is reported a vector of integer whose range is 0 to 15 i.e. 4 bit unsigned. The LUT is can be initialized in different ways as in the VHDL example below:
Figure 3 shows the technology view of the LUT implementation on Altera/Intel Cyclone II FPGA
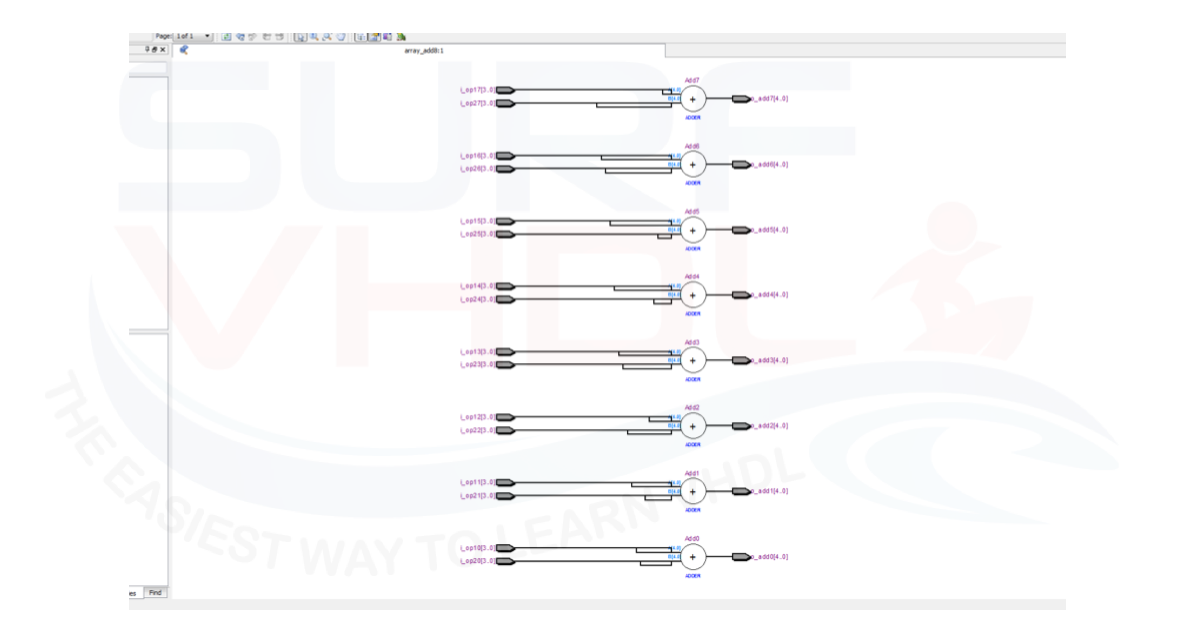
Implementing a Digital Signal Processing section using an array
Another typical example of array usage is when you need to perform the same operation on a large number of a signal. An example is adding two sets of input number in the code below:
Figure 4 shows the RTL view of the 8-adder implementation on Altera/Intel Cyclone II FPGA using the array approach.
As you saw in the previous example, using array allow you writing a very compact and elegant VHDL code. Moreover, using array approach you minimize the coding error since the VHDL code is more compact and simple to read and understand. After all these advantages, you should pay a great attention to your VHDL. Using the array coding style, you can fill a huge FPGA with only just few line of VHDL code! The rule is always the same:
Think hardware!
Every time you write a VHDL code, check the area report if it matches with your design intention and when you are not sure of the VHDL synthesis, check the RTL viewer and technology view.
[1] RTL HARDWARE DESIGN USING VHDL Coding for Efficiency, Portability, and Scalability
[2] VHDL Programming by Example 4th Ed Douglas – Perry
[3] The VHDL Cookbook
[4] Altera/Intel Cyclone II
[5] Altera Quartus II
12 thoughts to “VHDL Array”
How realize interleave array? Thanks.
Hi Valentin, can you explain better your needs?
I have a 1D array. I need to get 2 arrays: 1st – indexes 0,2,4,…, 2nd – indexes 1,3,5,…
you can use a single array and use the index (2*i) and (2*i+1)
Hello, Firstly thanks very much for your post and i found it very helpful. My questions is my input is an array of 13X13 8 bit vector and i feel wrong to simply type 169 lines for my input. Is there another way of easier definition in Entity regarding arrays as input or output?
Thanks in advance
You can use a package where define your input type. For instance:
type t_my_input_row is array(0 to 12) of std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); type t_my_input is array(0 to 12) of t_my_input_row;
your input/output port could be
my_input : in t_my_input;
Any hint on how to develop a square root synthesizable design? Thanks,
You can use a Cordic
In the first picture of the array example, vector(2)<=42 is on the 4rd element with index 3. Shouldn't it be 3rd element and index 2?
you are right, it is a typo, I’ll fix it thank you
In the Implementation of a LUT using an array in VHDL, you have written m1 <= std_logic_vector(to_unsigned(C_LUT1(to_integer(unsigned(s1))),4)); This statement I don't understand. Can you explain it more clearly?
the first type casting is “std_logic_vector” is related to m1 signal type to_integer(unsigned(s1) is related to convert to integer the signal s1
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Flexible and High-Quality VHDL programming
Array – basics
- October 18, 2019 December 26, 2019
- Keywords , VHDL Types
Array, a collection of values of the same type, is very useful representation of data in VHDL. It is helpful during creating memory blocks (FIFOs, shift registers, RAM, ROM) or in designs where exist duplicated data flows, pipes or blocks (many ADC channels, filters etc). They can be used in synchronous designs as well as in combinational. But using it in combinational parts, sometimes for specific solution, it is very important to be aware how the code will be interpreted and synthesized.
To use the array object in the code, we need to do following steps:
- declare a new type
- declare signal of a new type
- use it properly in the code
Array declaration
type array_type_name is array (elements_range) of elements_type;
array_type_name – name of a new array type, elements_range – number of elements in the array, elements_type – type of each element in the array.
Example of usage
This line creates a new array type with 4 elements, where every element is a 12-bit width std_logic_vector type:
type arr_adcin is array (0 to 4-1) of std_logic_vector (12-1 downto 0);
After declaring a new type, we can create signals of a new type:
signal signal_name : arr_adcin;
At the end, the new signal can be used in a project. Below, basic example shows how to do that.
As can be seen, it is much easier to create many identical data flows with an array type. Array usage is similar as in high-level languages. Every cell of an array is easily accessible by index value. Every cell can be used separately. With arrays, the code is much cleaner and more understandable.
Please, by aware that array itself does not optimize anything (timings or resources) but makes code much more readable and flexible (and that is what I always fight for). Array does not create any registers. It just groups similar single signals, which makes them easier to use.
*** *** ***
All source codes used in that post (with testbench) you can find on gitlab.com .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Cite this chapter

- Ben Cohen
422 Accesses
Arrays are important data structures in VHDL because they represent busses, registers, and memories. The language provides several rules regarding the manipulation of arrays. This section addresses many of those issues, including array operations, array initialization, use of constrained and unconstrained arrays, and mapping of arrays of different sizes. The application of arrays in synthesis is also addressed.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions

Copyright information
© 1998 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cohen, B. (1998). Arrays. In: VHDL Answers to Frequently Asked Questions. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5641-1_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5641-1_2
Publisher Name : Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN : 978-1-4613-7581-4
Online ISBN : 978-1-4615-5641-1
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Search forums
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
Welcome to EDAboard.com
Welcome to our site edaboard.com is an international electronics discussion forum focused on eda software, circuits, schematics, books, theory, papers, asic, pld, 8051, dsp, network, rf, analog design, pcb, service manuals... and a whole lot more to participate you need to register. registration is free. click here to register now..
- Digital Design and Embedded Programming
- PLD, SPLD, GAL, CPLD, FPGA Design
array assignment in vhdl with signed numbers
- Thread starter 214
- Start date Mar 22, 2016
- Mar 22, 2016
Junior Member level 2
i have to declare an array with numbers like (for eg. 4.344, 2.55, 0.56, 6.33) ... how to initialize this type of array.... TYPE buf_ary_d IS ARRAY (...????) OF SIGNED(7 DOWNTO 0); what to write inside bracket
amit.kumar11
Member level 5.
Hi, Inside bracket is the no of element in the array. ex: type array_type2 is array (0 to 3) of std_logic_vector(11 downto 0); Here array is of 4 element with each having 12 bits. Amit
TYPE buf_ary IS ARRAY(NATURAL RANGE <>) OF UNSIGNED(7 DOWNTO 0); what does NATURAL RANGE <> mean ?????
Super Moderator
Natural number range, any subrange of 0 to maxint or maxint downto 0. You are using this declaration to define a type without specifying the actual range. The range will be specified when referencing the type declaration. Like below: Code: TYPE buf_ary IS ARRAY(NATURAL RANGE <>) OF UNSIGNED(7 DOWNTO 0); SIGNAL buf1 : buf_ary(0 to 5); SIGNAL buf2 : buf_ary(13 downto 2);
Advanced Member level 4
'left and 'right are natual numbers -- the subset of VHDL integers that are not negative. ( n >= 0). The second part is that decimal values don't have a fully standard representation. VHDL2008 supports fixed point values, were indicies below 0 indicate "fractional bits". for example, bit index 0 represents 1. bit index -1 represents 0.5. index -2 represents 0.25. This is done with sfixed. In previous versions, you would need to use signed, but then keep track of where the fractional bits were.
sorry....can you make this explanation simpler.....i did not understand this
Numbers like 4.344, 2.55, 0.56, 6.33 are not unsigned. Unsigned can only take integer values. You can scale the numbers to unsigned by multiplying it with a factor of your choice, preferably 2^N, and rounding to nearest integer. Or read about IEEE fixed point package.
TYPE buf_ary_d IS ARRAY (NATURAL RANGE <>) OF SIGNED(7 DOWNTO 0); will it work for my case ???
I overlooked that you want signed, not unsigned. You could e.g. use a scaling factor of 16. Code: CONSTANT carray: buf_ary_d(0 to 3) := ( to_signed(integer(16.0*4.344),8), to_signed(integer(16.0*2.55),8), to_signed(integer(16.0*0.56),8), to_signed(integer(16.0*6.33),8)); - - - Updated - - - That's without rounding to nearest integer
TrickyDicky
Advanced member level 7.
vGoodtimes said: 'left and 'right are natual numbers -- the subset of VHDL integers that are not negative. ( n >= 0). The second part is that decimal values don't have a fully standard representation. VHDL2008 supports fixed point values, were indicies below 0 indicate "fractional bits". for example, bit index 0 represents 1. bit index -1 represents 0.5. index -2 represents 0.25. This is done with sfixed. In previous versions, you would need to use signed, but then keep track of where the fractional bits were. Click to expand...
my point on 'left and 'right was a response to "what is natural range <>". I had started the response before your reply to the same question. (also, you don't need to anchor to 0 on either side)
Member level 2
214 said: i have to declare an array with numbers like (for eg. 4.344, 2.55, 0.56, 6.33) ... how to initialize this type of array.... TYPE buf_ary_d IS ARRAY (...????) OF SIGNED(7 DOWNTO 0); what to write inside bracket Click to expand...
You can't use numbers with type "real" for synthesys, only in testbench. Click to expand...
Similar threads
- Started by KfirMaymon84
- Jun 14, 2024
- Started by KrishKrishnaa
- Aug 7, 2024
- Started by metamisers
- Aug 2, 2024
- Started by irfanraina1@123
- Feb 27, 2024
- Started by Xenon02
- Jan 21, 2024
- Replies: 18
Part and Inventory Search
Welcome to edaboard.com.
- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies. Accept Learn more…
| Declaration | ---- used in ----> | Package Entity Architecture Process Procedure Function |
| Syntax |
| type_name (range) element_type; |
| Rules and Examples |
| An contains multiple elements of the same type. When an array object is declared, an existing array type must be used. |
| An array type definition can be , i.e. of undefined length. and are defined in this way. An object (signal, variable or constant) of an unconstrained array type must have it's index type range defined when it is declared. |
| Arrays with character elements such as and may be assigned a literal value using double quotes (see : |
| Arrays may also be assigned using (&), , , or a mixture. By default, assignment is made be |
| Arrays of arrays may be declared. These are useful for memories, vector tables, etc.: |
| True two (or more) dimensional arrays may also be declared: |
| Synthesis Issues |
Most logic synthesis tools accept one-dimensional arrays of other supported types. 1-D arrays of 1-D arrays are often supported. Some tols also allow true 2-D arrays, but not more dimensions.
Note that arrays are usually implemented using gates and flip-flops, not ROM's and RAM's.
| Whats New in '93 |
Array types have not changed in VHDL -93.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Is there a way to use "others" as index when assigning to slices of VHDL array?
Is it possible to do something like this in VHDL?
Rather than what I do at present:
- \$\begingroup\$ If doing anything critical I usually prefer to make direct explicit assignments for all possibilities so there is no way the synthesizer could misinterpret what I intended. \$\endgroup\$ – Voltage Spike ♦ Commented Jul 26, 2021 at 21:20
- \$\begingroup\$ @user_1818839 That should be posted as answer :-) \$\endgroup\$ – Mitu Raj Commented Jul 26, 2021 at 21:22
Something like, using an array aggregate :
- \$\begingroup\$ I did this and I get this error: COMP96 ERROR COMP96_0597: "Aggregate with multiple choices has a non-static or null choice. Use -relax to compile aggregates composed of one non-static or null choice and choice others." \$\endgroup\$ – quantum231 Commented Jul 27, 2021 at 19:23
- 1 \$\begingroup\$ When you get an error message like that, it's always worth posting the toolchain and version. But as the message hints, if you want to do it this way, you'll need the -relax compile flag. \$\endgroup\$ – user16324 Commented Jul 27, 2021 at 19:58
- \$\begingroup\$ Note that ghdl, which is possibly one of the strictest VHDL compilers according to standards compliance, has no problem with this code (assuming a is declared in the same architecture and thus its length is static) \$\endgroup\$ – user16324 Commented Jul 27, 2021 at 20:04
- 2 \$\begingroup\$ However, take care to only use this in an assignment as the rules for ordering may produce unexpected results in an expression. OK, so using others in an expression is also a non-starter as the expression needs to be sized. \$\endgroup\$ – Jim Lewis Commented Jul 28, 2021 at 15:05
- \$\begingroup\$ @JimLewis Indeed, the assignment target provides the size and direction here, whether or not there are static values or just 'others'. \$\endgroup\$ – user16324 Commented Jul 29, 2021 at 15:10
Your Answer
Sign up or log in, post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged vhdl or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- The hidden cost of speed
- The creator of Jenkins discusses CI/CD and balancing business with open source
- Featured on Meta
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
Hot Network Questions
- DateTime.ParseExact returns today if date string and format are set to "General"
- What is the first work of fiction to feature a vampire-human hybrid or dhampir vampire hunter as a protagonist?
- How should I tell my manager that he could delay my retirement with a raise?
- Is it helpful to use a thicker gage wire for part of a long circuit run that could have higher loads?
- How high does the ocean tide rise every 90 minutes due to the gravitational pull of the space station?
- Visuallizing complex vectors?
- Is it a good idea to perform I2C Communication in the ISR?
- How do you tip cash when you don't have proper denomination or no cash at all?
- Can reinforcement learning rewards be a combination of current and new state?
- Hashable and ordered enums to describe states of a process
- How to Interpret Statistically Non-Significant Estimates and Rule Out Large Effects?
- Is there a non-semistable simple sheaf?
- Confusion about time dilation
- Are incomplete magic squares with some integral entries necessarily purely integral
- Fusion September 2024: Where are we with respect to "engineering break even"?
- help to grep a string from a site
- What is the nature of the relationship between language and thought?
- Wien's displacement law
- Remove an edge from the Hasse diagram of a finite lattice
- What is the optimal number of function evaluations?
- What other crewed spacecraft returned uncrewed before Starliner Boe-CFT?
- How to go from Asia to America by ferry
- Applying to faculty jobs in universities without a research group in your area
- Are others allowed to use my copyrighted figures in theses, without asking?
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
in VHDL, how to assign list of output ports to an array?
I have an entity that has hundreds of output such as tap0(15 downto 0), tap1(15 downto 0), ..., tap200(15 downto 0)
For each iteration, I would like to assign four of those outputs to a complex multiplier entity that has four inputs.
For example: on 1st iteration:
on 2nd iteration:
On 3rd iteration:
and so on...
How do I make the code above more efficient by having some kind of for loop and putting those output ports to an array? So that I can write the code as following:
Here is the code example
Then down below in some process I have the following:
Several questions: 1. Why did the following port assignment work? taps0x => sample_i(0) 2. How can I use for..loop or for..generate to simplify the following codes?
taps0x => sample_i(0), taps1x => sample_i(1), taps2x => sample_i(2), taps3x => sample_i(3), taps4x => sample_i(4), taps5x => sample_i(5), and so on.
- Yes you can. Look up for loop s and for generate s – JHBonarius Commented Feb 14, 2018 at 7:57
- 1 You need to show what code you have written to try to solve this problem, and explain what problems or errors you are seeing with it. – scary_jeff Commented Feb 14, 2018 at 8:07
- @scary_jeff I like this site for this kind of feedback.Example: idownvotedbecau.se/noattempt – JHBonarius Commented Feb 14, 2018 at 8:54
- Your edit makes no sense with regards to your earlier question plus it's not complete. It seems you're asking two questions. – JHBonarius Commented Feb 15, 2018 at 11:37
Well, you did good with type sample ... so why not use that on the interface?
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged vhdl or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- The hidden cost of speed
- The creator of Jenkins discusses CI/CD and balancing business with open source
- Featured on Meta
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- What does a new user need in a homepage experience on Stack Overflow?
- Feedback requested: How do you use tag hover descriptions for curating and do...
- Staging Ground Reviewer Motivation
Hot Network Questions
- How do you tip cash when you don't have proper denomination or no cash at all?
- How to go from Asia to America by ferry
- Confusion about time dilation
- Representing permutation groups as equivalence relations
- \ExplSyntaxOn problem with new paragraph
- How to connect 20 plus external hard drives to a computer?
- Is it helpful to use a thicker gage wire for part of a long circuit run that could have higher loads?
- An instructor is being added to co-teach a course for questionable reasons, against the course author's wishes—what can be done?
- Star Trek: The Next Generation episode that talks about life and death
- I'm not quite sure I understand this daily puzzle on Lichess (9/6/24)
- Wien's displacement law
- Is this host and 'parasite' interaction feasible?
- How to Interpret Statistically Non-Significant Estimates and Rule Out Large Effects?
- How can I play MechWarrior 2?
- do-release-upgrade from 22.04 LTS to 24.04 LTS still no update available
- Is there a problem known to have no fastest algorithm, up to polynomials?
- I'm a little embarrassed by the research of one of my recommenders
- Is it a good idea to perform I2C Communication in the ISR?
- What is the optimal number of function evaluations?
- Where is this railroad track as seen in Rocky II during the training montage?
- In a tabular with p-column, line spacing after multi-line cell too short with the array package
- Remove an edge from the Hasse diagram of a finite lattice
- DateTime.ParseExact returns today if date string and format are set to "General"
- Why is LiCl a hypovalent covalent molecule?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Arrays - VHDL Example Create your own types using arrays. Arrays are used in VHDL to create a group of elements of one data type. Arrays can only be used after you have created a special data type for that particular array. Below are some rules about arrays. Arrays can be synthesized; Arrays can be initialized to a default value
1. I have an array in VHDL of the form, type CacheArray is array(0 to 15) of std_logic_vector(33 downto 0); signal cache_array: CacheArray := (others => (others => '0')); I wish to assign values to this array such that only one bit of each index is initialized. I suspected something like this will work,
Arrays are a collection of a number of values of a single data type and are represented as a new data type in VHDL. It is possible to leave the range of array indices open at the time of definition. ... Aggregates can also be nested for this purpose. With an aggregate one can assign to all elements of an array a specific value in a clear ...
type foo is array (0 downto 0) of std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); with an example assignment to a constant of: constant cFoo : foo := ( x"00", x"11" ); Moreover consider that I try to assign index 0 with another constant. For example. type foo is array (0 downto 0) of std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); constant cBar : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
We must also declare the number of elements in the array. The code snippet below shows the general syntax we use to declare an array type in VHDL. type <type_name> is array (<range>) of <type>; The <type> field in the above construct can accept any VHDL type, including custom types we have declared.
An array contains multiple elements of the same type. When an array object is declared, an existing array type must be used. An array type definition can be unconstrained, i.e. of undefined length. String, bit_vector and std_logic_vector are defined in this way. An object (signal, variable or constant) of an unconstrained array type must have ...
In VHDL such kind of structure is defined " array ". We can collect any data type object in an array type, many of the predefined VHDL data types are defined as an array of a basic data type. An example is: type string is array (positive range <>) of character; type bit_vector is array (natural range <>) of bit; Figure 1 - example of VHDL ...
Array - basics. Array, a collection of values of the same type, is very useful representation of data in VHDL. It is helpful during creating memory blocks (FIFOs, shift registers, RAM, ROM) or in designs where exist duplicated data flows, pipes or blocks (many ADC channels, filters etc). They can be used in synchronous designs as well as in ...
Arrays are important data structures in VHDL because they represent busses, registers, and memories. The language provides several rules regarding the manipulation of arrays. ... Assignments Must be the same size and type. .-.-, <--RelaUonal Must be one-dimensional discrete arrays of the same type. < > " <= >= , Per LRM 7.2.2, ...
See LRM sections 7.3.2. Rules and Examples. Aggregates are a grouping of values to form an array or record expression. The first form is called positional association, where the values are associated with elements from left to right: signal Z_BUS : bit_vector (3 downto 0); signal A_BIT, B_BIT, C_BIT, D_BIT : bit; ...
[VHDL] how to assign array of records to another array? Hi All, I'm trying to assign an array of records (record elements are of the std_logic_vector type) to a signal of the std_logic_vector type. Something is going wrong... Here is the signals declaration: signal dbg_port0 : dbg_reg_t;
It doesnt specify what the numbers are. So using this, you can declare a signal or variable that is an array of signed numbers. Again, it doesnt specify what they are. - - - Updated - - -. vGoodtimes said: 'left and 'right are natual numbers -- the subset of VHDL integers that are not negative. ( n >= 0).
For the aggregate assignment you haven't specified the VHDL version, earlier than or -2008 type nybble_array is array (0 to 1) of std_logic_vector ... The new -2008 feature is that array aggregate association elements can be the type of the aggregate itself in addition to the aggregate element type. Prior revisions only support association ...
An array contains multiple elements of the same type. When an array object is declared, an existing array type must be used. An array type definition can be unconstrained, i.e. of undefined length. String, bit_vector and std_logic_vector are defined in this way. An object (signal, variable or constant) of an unconstrained array type must have ...
VHDL - assigning array signal in a loop generates side effects. 1. How to assign a hexadecimal value to integer type in VHDL? 0. Why can't I connect a std_logic_vector signal to a port of type signed or unsigned. 2. problem assigning a zero-length array port in vhdl. 2.
The init_array_func() is a VHDL function which initializes the big_array_s with data from the "test.dat" ascii file. The section where I'm stuck is assigning a portion of the big_array_s to the small_array_s. For example something like, small_array_s <= big_array_s(0 to 3); is what I need to achieve with the RTL.
I have an entity that has hundreds of output such as tap0(15 downto 0), tap1(15 downto 0), ..., tap200(15 downto 0) For each iteration, I would like to assign four of those outputs to a complex multiplier entity that has four inputs.
Hello everyone! I have a question about arrays. I have filled an array with some unsigned values and I would like to know if I can pass it to another entity as a whole, without sending one value of the array at a time ( in each cycle). Thanks in advance! Programmable Logic, I/O and Packaging. Liked Like. Answer. Share.