How to Write a Critical Response Essay With Examples and Tips
- Icon Calendar 20 July 2024
- Icon Page 5910 words
- Icon Clock 27 min read
A critical response essay is an important type of academic essay, which instructors employ to gauge the students’ ability to read, react, and respond critically and express their opinions. Firstly, this guide begins with a detailed definition of a critical response paper and an extensive walkthrough of source analysis and its format. Next, the manual breaks down the writing process into the pre-writing, writing, and post-writing stages and discusses each stage in extensive detail. Finally, the article provides practical examples of an outline and a paper itself, which implement the writing strategies and guidelines of critical response writing. After the examples provided, there is a brief overview of documentation styles for people to use in their papers. Hence, students need to learn how to write a perfect critical response essay to follow its criteria.

What Is a Critical Response Essay and Its Purpose
According to its definition, a critical response essay presents a writer’s reaction to the content of an article, text, book, story, film, artwork, play, performance, or any other piece of writing and the author’s strategy for achieving his or her intended purpose. Basically, this type of paper goes beyond mere summary and response, requiring the writer to engage deeply with the material to assess its merits and shortcomings (Wallace & Wray, 2021). The main purpose of writing a critical response essay is to develop a reasoned argument that expresses the writer’s analysis and critique. Moreover, a critical response to a piece of any text under review demands an analysis, interpretation, and synthesis of a reading (Ogbonnaya & Brown, 2023). These parts allow readers to develop their personal positions and reactions concerning the extent to which an author of a specific work creates a desired effect on the audience, establishing it implicitly or explicitly at the beginning. Mostly, students assume that a critical reaction revolves around the identification of flaws, but this aspect only represents one dimension of writing (Davies, 2022). In turn, a critical response in an essay should identify both the strengths and weaknesses of the work under analysis and present them without exaggerating their significance.
Source Analysis

1. Questions That Guide Source Analysis
Writers engage in textual analysis through critical reading. Hence, students undertake this reading to answer three primary questions:
- What does the author say or show unequivocally?
- What does the author not say or show outright but implies intentionally or unintentionally in the text?
- What do I think about responses to the previous two questions?
Readers should strive to comprehensively answer these questions with the context and scope of a critical response essay. Basically, the need for objectivity is necessary to ensure the student’s analysis does not contain any biases through unwarranted or incorrect comparisons (Ogbonnaya & Brown, 2023). Nonetheless, the author’s pre-existing knowledge concerning the topic is crucial in facilitating the process of critical reading. In turn, the generation of answers to three guiding questions occurs concurrently throughout the close reading of an assigned text or other topics.
2. Techniques of Critical Reading
Previewing, reading, and summarizing are the main methods of critical reading. Basically, previewing a text allows readers to develop some familiarity with the content of any paper, which they gain through exposure to content cues, publication facts, important statements, and authors’ backgrounds (Fort, 1971). In this case, readers may take notes of questions that emerge in their minds and possible biases related to prior knowledge. Then, reading has two distinct stages: first reading, rereading, and annotating. In this case, students read an assigned text at an appropriate speed for the first time with minimal notetaking. After that, learners reread a text to identify core and supporting ideas, key terms, and connections or implied links between ideas while making detailed notes (Lauritzen, 2021). Lastly, writers summarize their readings into the main points by using their own words to extract the meaning and deconstruct reaction papers into meaningful parts. As such, writers should avoid bias in a critical response essay because it undermines the objectivity and credibility of the entire analysis, and, before writing a paper, they should ask themselves the next minor guiding questions:
- What is the author’s background?
- What is the purpose of the source?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What is the main argument or thesis?
- What evidence does the author use to support their argument?
- How does the source fit into the broader context?
- What assumptions does the author make?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
- How does the author address counterarguments or alternative perspectives?
- What is the overall impact or significance of the source?
3. Creating a Critical Response
Up to this point, source analysis is a blanket term that represents the entire process of developing a critical response. Mainly, the creation of a reaction paper involves analysis, interpretation, and synthesis, which occur as distinct activities (Lauritzen, 2021). In this case, students analyze their readings by breaking down texts into elements with distilled meanings and obvious links to a thesis statement. During analysis, writers may develop minor guiding questions under first and second guiding questions, which are discipline-specific. Then, learners focus on interpretations of elements to determine their significance to an assigned text as a whole, possible meanings, and assumptions under which they may exist (Lauritzen, 2021). Finally, they create connections through the lens of relevant pre-existing knowledge, which represents a version of the element’s interconnection that they perceive to be an accurate depiction of a text. In turn, the length of a critical response essay varies by academic level and the specific requirements of the course or instructor. Here are general guidelines for the length of critical response essays at different academic levels:
High School
- Pages: 2-4 pages
- Words: 500-1,000 words
College (Undergraduate)
- Pages: 3-5 pages
- Words: 750-1,500 words
University (Upper Undergraduate)
- Pages: 5-8 pages
- Words: 1,500-2,500 words
Master’s
- Pages: 8-12 pages
- Words: 2,500-4,000 words
- Pages: 12-20 pages
- Words: 4,000-8,000 words
Critical Response Essay Format
| Introduction | Introduce the work under analysis with its title and author, including a brief summary in 1-2 sentences, to provide further context. | In a well-known novel “To Kill a Mockingbird,” Harper Lee explores sensitive themes of racial injustice among people and their moral growth. |
| Thesis Statement | Present your main argument or perspective on the work. | Lee uses Atticus Finch as one of the central characters to highlight the pervasive racial injustices of the American South. |
| Summary of the Work | Provide a concise summary of the work, focusing on key points relevant to your analysis. | The novel presents the main character of Scout Finch, a young girl, as she grows up in a racially divided town and witnesses that her father defends a Black man accused of rape. |
| Analysis: Theme | Discuss the main themes of the work and how they are developed. | The theme of racial injustice is central to the novel, and it is illustrated through the trial of Tom Robinson. |
| Analysis: Characters | Examine the main characters and their development. | Atticus Finch embodies moral integrity, serving as a role model for his children and the community. |
| Analysis: Techniques | Analyze some literary techniques used by the author (e.g., symbolism, imagery, narrative style). | Lee uses symbolism, such as the ‘mockingbird,’ to represent innocence and the destruction caused by evil. |
| Personal Reflection | Reflect on your personal response to the work and explain how it resonated with you and why. | The novel’s portrayal of justice and morality deeply impacted me, prompting me to reflect on my own beliefs. |
| Supporting Evidence | Provide specific examples and quotes from the work or other credible sources to support your analysis and reflections. | Finch says, “You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view… .” |
| Conclusion | Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and provide final thoughts on the work’s significance. | Through its strong themes and compelling characters, Lee’s “To Kill a Mockingbird” remains an outstanding example of literature concerning justice and human dignity. |
Note: Analysis sections can be added, deleted, or combined with each other in 1 paragraph depending on the type of the source under review and assignment requirements. Other sections must be provided to ensure writers follow the key rules of critical reading criteria.
Critical Response Essay Outline Template
I. Introduction
A. Summary of an article. B. Thesis statement.
A. First body paragraph
- The idea for the first paragraph.
- Evidence for the first point from an article.
- Interpretation of the evidence.
B. Second body paragraph
- The idea for the second paragraph.
- Evidence for the second point from an article.
C. Third body paragraph
- The idea for the third paragraph.
- Evidence for the third point from an article.
III. Conclusion
A. Summary of three points that form a body section. B. Closing remarks.
The presence of a summary in the introduction and an interpretation for each piece of evidence are defining features of a critical response essay. Typically, the introduction, being one of 5 parts of an essay, does not contain a succinct summary of a source that an author uses in body paragraphs (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). In this case, the incorporation of a summary and response in the introduction paragraph provides the audience with specific information concerning the target article. Specifically, such a work differs from other response papers because it emphasizes the provision of reasonable judgments of a text rather than the testing and defense of one’s evaluations or arguments (Wallace & Wray, 2021). In turn, writers do not provide evaluation for their judgments, which implies critical responses may be different but correct if a specific interpretation is reasonable to the audience.
Expanding an Outline Format Into a Critical Response Essay
1. introduction.
The introductory paragraph in a critical response essay consists of two primary sections: a summary of an article and a thesis statement. Firstly, a summary of an article consists of the text’s central argument and the purpose of the presentation of the argument (Davies, 2022). Basically, students should strive to distill the main idea and purpose of the text into a few sentences because the length of the introduction is approximately 10% of the essay’s word count. Then, a summary provides the audience with adequate background information concerning an article, which forms a foundation for announcing the student’s primary idea. In this case, writers may include an additional sentence between a summary and a thesis statement to establish a smooth flow in the opening paragraph (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). However, learners should not quote thesis and purpose statements because it results in a fragmented introduction, which is unappealing to readers and ineffective.
- All body paragraphs have in a critical response essay four main elements: the writer’s idea, meaningful evidence from a reading text, interpretation of the evidence, and a concluding statement.
A. Writer’s Idea
The writer’s idea for a paragraph appears in the first sentence of a paragraph, which is a topic sentence. For example, if students know how to write a topic sentence, they present readers with a complete and distinct idea that proves or supports a thesis statement (Davies, 2022). In this case, authors should carefully word their topic sentences to ensure there is no unnecessary generalization or spillovers of ideas from other paragraphs. Notably, all the topic sentences in the body of a critical response essay share a logical relationship that allows the audience to easily follow the development of the central idea of a paper.
B. Evidence
Students should provide evidence that supports the idea they propose in the topic sentence. Basically, the evidence for all body paragraphs is the product of critical reading of an article, which allows writers to identify meaningful portions of a text (Wallace & Wray, 2021). During the presentation of evidence, learners should ascertain that the contextual meaning of paraphrases or quotations is not lost because such a strategy will harm interpretations that follow after it. In turn, critical response essays must not contain lengthy or numerous quotations unless the meaning or intended effect of a quotation is not replicable upon paraphrasing.
C. Interpretation
Interpretation segments of paragraphs allow writers to explain the significance of the evidence to the topic sentence. In a critical response essay, the interpretation is the equivalent of an author revealing the possible assumptions behind a text paraphrase and commenting on whether or not he or she finds them reasonable (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Moreover, students make inferences concerning their meaning in the context of the entire narrative and its relation to the paragraph’s idea. In turn, learners should refrain from reading too much into a piece of evidence because it may result in false or unreasonable inferences.
D. Concluding Sentence
The concluding statement is the final sentence of any paragraph. In this case, the primary role of the concluding sentence is to emphasize the link between the topic sentence, evidence, interpretation, and the paper’s central idea (Davies, 2022). Besides, the concluding statement should not contain an in-text citation because it does not introduce new evidence to support the topic sentence. Therefore, authors use concluding sentences to maintain the unity between body paragraphs and a critical response essay in its entirety.
3. Conclusion
The conclusion comprises three core elements: a restatement of a thesis statement, a summary of the main points that writers present in body paragraphs, and closing remarks. In particular, the first sentence of the conclusion draws the attention of the audience to the central idea, which an author proposes in a thesis statement (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Then, students review the main points of their papers to demonstrate that written arguments in body paragraphs adequately support a thesis statement. Moreover, writers should summarize the main points of a paper in the same order they appear in the main part and guarantee logical patterns in the body are readily discernible in summary. Finally, learners make their closing remarks, which creates a sense of wholesomeness in a critical response essay or ties a paper to a larger relevant discourse.
Writing Steps of a Critical Response Essay
Step 1: pre-writing, a. analysis of writing situation.
Objective. Before a student begins writing a critical response essay, he or she must identify the main reason for communication to the audience by using a formal essay format. Basically, the primary purposes of writing reaction papers are explanation and persuasion, and it is not uncommon for two objectives to overlap (Davies, 2022). However, one of the purposes is usually dominant, which implies it plays a crucial role in the wording, evidence selection, and perspective on a topic. In turn, students should establish their purposes in the early stages of the writing process because the purpose has a significant effect on the essay writing approach. Beginning a critical response essay correctly also effectively sets an appropriate tone and provides a clear direction for the whole analysis (Fort, 1971). All opening sentences must introduce the subject, set the context, and hint at the writer’s perspective or main argument. Here are ten examples of starting sentences:
- The famous narrative of [Title] by [Author] shows [main theme], revealing [author’s message or argument].
- In [Title], [Author] masterfully employs [literary device] to explore [theme or issue], prompting readers to consider [related question or implication].
- The powerful depiction of [subject] in [Title] by [Author] challenges conventional views on [topic], offering a new perspective on [specific aspect].
- Through [Title], [Author] presents a compelling argument about [issue], using [specific elements] to underscore [main point or message].
- The thought-provoking themes of [Title] by [Author] allow readers to critically assess [related topic or issue], shedding light on [specific aspect].
- In [Title], [Author] explores the complexities of [subject], using [specific technique] to highlight [main idea or argument].
- The evocative imagery in [Title] by [Author] serves to illustrate [theme], encouraging readers to reflect on [related issue or question].
- By examining [specific aspect] in [Title], [Author] effectively critiques [related issue], providing valuable insights into [main point].
- The dynamic characters and intricate plot of [Title] by [Author] offer a rich exploration of [theme], challenging readers to think critically about [related topic].
- In [Title], [Author] uses [specific technique] to convey [main idea], ultimately arguing that [related point or implication].
Audience. Students should establish a good understanding of the audience’s expectations, characteristics, attitudes, and knowledge in anticipation of the writing process. Basically, learning the audience’s expectations enables authors to meet the organizational demands, ‘burden of proof,’ and styling requirements (Lauritzen, 2021). In college writing, it is the norm for all essays to attain academic writing standards. Then, the interaction between characteristics and attitudes forces students to identify a suitable voice, which is appreciative of the beliefs and values of the audience (Davies, 2022). Lastly, writers must consider the level of knowledge of the audience while starting a critical response essay because it has a direct impact on the context, clarity, and readability of a paper. Consequently, writing a critical response essay for classmates is quite different from a paper that an author presents to a multi-disciplinary audience.
Define a topic. Topic selection is a critical aspect of the prewriting stage to respond. Ideally, assignment instructions play a crucial role in topic selection, especially in higher education institutions. For example, when writing a critical response essay, instructors may choose to provide students with a specific article or general instructions to guide learners in the selection of relevant reading sources (Wallace & Wray, 2021). In this case, students may not have opportunities for independent topic selection in former circumstances. However, by considering the latter assignment conditions, learners may need to identify a narrow topic to use in article selection. Moreover, students should take adequate time to do preliminary research, which gives them a ‘feel’ of the topic, for example, 19th-century literature. Next, writers narrow down the scope of the topic based on their knowledge and interests, for example, short stories by black female writers from the 19 th century.
B. Research and Documentation
Find sources. Once a student has a topic, he or she can start the process of identifying an appropriate article. Basically, choosing a good source for writing a critical response essay is much easier when aided with search tools on the web or university repository (Davies, 2022). In this case, learners select keywords or other unique qualities of an article and develop a search filter. Moreover, authors review abstracts or forewords of credible sources to determine their suitability based on their content (Ogbonnaya & Brown, 2023). Besides content, other factors constrain the article selection process: the word count for a critical response essay and a turnaround time. In turn, if an assignment has a fixed length of 500 words and a turnaround time of one week, it is not practical to select a 200-page source despite content suitability.
Content selection. The process of selecting appropriate content from academic sources relies heavily on the purpose of a critical response essay. Basically, students must select evidence that they will include in a paper to support their claims in each paragraph (Wallace & Wray, 2021). However, writers tend to let a source speak through the use of extensive quotations or summaries, which dilutes a synthesis aspect of a critical reaction essay. Instead, learners should take a significant portion of time to identify evidence from reliable sources, which are relevant to the purpose of an essay (Davies, 2022). In turn, a student who is writing a critical response essay to disagree with one or more arguments will select different pieces of evidence as compared to a person who is writing to analyze the overall effectiveness of the work.
Annotated bibliography. An annotated bibliography is vital to the development of a critical response essay because it enables students to document useful information that they encounter during research. During research and documentation stages for a critical response essay, annotated bibliographies contain the main sources for a paper and other sources that contribute to the knowledge base of an author, even though these sources will not appear in reference lists (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Mostly, a critical response paper has only one source. However, an annotated bibliography contains summaries of other sources, which may inform the author’s response through the development of a deep understanding of a topic. In turn, an annotated bibliography is quite useful when an individual is writing a critical response to an article on an unfamiliar topic.
Step 2: Writing a Critical Response Essay
A. organization.
Thesis . A thesis statement sentence is a crucial component of a critical response essay because it presents the student’s purpose, argument, and the conclusion that he or she draws from the textual evidence. In this case, the thesis statement is the response to the thesis question, which an author creates from assignment instructions (Davies, 2022). After completing the research stage, students can develop a tentative thesis statement to act as a starting point for the writing stage. Usually, tentative thesis statements undergo numerous revisions during the writing stage, which is a consequence of the refinement of the main idea during the drafting. In turn, these examples of sentence starters can help writers to craft a strong thesis statement that clearly defines a critical response lens and the main argument or insight:
- In [Title], [Author] effectively/ineffectively uses [element] to convey [theme or message], prompting readers to … .
- Through [specific technique or element], [Title] by [Author] offers a compelling critique/endorsement of [issue or theme], illustrating that … .
- The portrayal of [character/element] in [Title] by [Author] serves as a powerful commentary on [issue or theme] because of … .
- In [Title], [Author] explores [theme or issue] through [specific technique or narrative], demonstrating … .
- The [specific element] in [Title] by [Author] highlights the complexities of [theme or issue], suggesting that … .
- By examining [element or aspect] in [Title], [Author] provides a better insight into [theme or issue], challenging readers to consider…
- In [Title], [Author] uses [literary device or technique] to address [theme or issue], ultimately arguing … .
- The narrative structure of [Title] by [Author] effectively/ineffectively conveys [theme or message], encouraging readers to … .
- Through the lens of [specific perspective], [Title] by [Author] reveals the intricacies of [theme or issue] and suggests that … .
- In [Title], [Author] employs [specific technique] to critique/celebrate [issue or theme], making a particular situation when … .
Weigh the evidence. Based on the tentative thesis, an author evaluates the relative importance of collected pieces of textual evidence to the central idea. Basically, students should distinguish between general and specific ideas to ascertain that there exists a logical sequence of presentation, which the audience can readily grasp (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Firstly, for writing a critical response essay, learners should identify general ideas and establish specific connections that exist between each general idea and specific details, which support a central claim. Secondly, writers should consider some implications of ideas as they conduct a sorting process and remove evidence that does not fit. Moreover, students fill ‘holes’ that are present due to the lack of adequate supporting evidence to conclude this stage.
Create an outline. An essay outline is a final product of weighing the significance of the evidence in the context of the working thesis statement. In particular, a formal outline is a preferred form of essay structure for a critical response paper because it allows for detailed documentation of ideas while maintaining a clear map of connections (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). During the formation of an outline, students use a systematic scheme of indentation and labeling all the parts of an outline structure. In turn, this arrangement ensures elements that play the same role are readily discernible at a glance, for example, primary essay divisions, secondary divisions, principle supporting points, and specific details.
Drafting. The drafting step involves the conversion of the one-sentence ideas in an outline format into complete paragraphs and, eventually, a critical reaction essay. In this case, there is no fixed approach to writing the first draft. Moreover, students should follow a technique they find effective in overcoming the challenge of starting to write a critical response essay (Davies, 2022). Nonetheless, it is good practice to start writing paragraphs that authors believe are more straightforward to include regardless of specific positions they hold on an outline. In turn, learners should strive to write freely and be open to new ideas despite the use of an outline. During drafting, the conveyance of meaning is much more important than the correctness of the draft.
Step 3: Post-Writing
Individual revision. An individual revision process focuses on the rethinking and rewriting of a critical response essay to improve the meaning and structure of a paper. Essentially, students try to review their papers from a perspective of readers to ensure the level of detail, relationship and arrangement of paragraphs, and the contribution of the minor ideas to the thesis statement attain the desired effect (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). In this case, the use of a checklist improves the effectiveness of individual revision. Moreover, a checklist contains 12 main evaluation categories: assignment, purpose, audience and voice, genre, thesis, organization, development, unity, coherence, title, introduction, and conclusion.
Collaborative revision. Collaborative revision is a revision strategy that covers subconscious oversight that occurs during individual revision. During an individual revision of a critical response essay, writers rely on self-criticism, which is rarely 100% effective because writers hold a bias that their works are of high quality (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Therefore, subjecting an individual’s work to peer review allows students to collect critique from an actual reader who may notice problems that an author may easily overlook. In turn, learners may provide peer reviewers with a checklist to simplify the revision process.
Editing . The editing step requires authors to examine the style, clarity, and correctness of a critical response essay. In particular, students review their papers to ascertain their conformance with the guidelines of formal essay writing and the English language (Davies, 2022). Moreover, sentence fragments, subject-verb agreement, dangling modifiers, incorrect use of punctuation, vague pronoun references, and parallelism are common grammar issues that learners eliminate during editing. Then, writers confirm that their critical reaction essays adhere to referencing style guidelines for citation and formatting, such as the inclusion of a title page, appropriate in-text citation, and proper styling of bibliographic information in the reference list (Wallace & Wray, 2021). In turn, students must proofread a critical response paper repeatedly until they find all errors because such mistakes may divert the audience’s attention from the content of a paper and consider the following criteria to ensure a comprehensive and reflective piece:
- Clear Thesis Statement: Present a clear and concise thesis statement that reflects your overall response to an assigned text or experience, outlining your main argument or perspective.
- Personal Connection: Describe your personal connection to the subject matter and explain how the text or experience resonates with your own experiences, feelings, or beliefs.
- Summary of the Source: Provide a brief summary of the source under analysis you are responding to, highlighting key points relevant to your response.
- Detailed Analysis: Analyze specific elements of the source that are important to you, including characters, themes, settings, or any other aspects that lead to a strong reaction.
- Supporting Evidence: Use quotes, examples, or references from the work under review or other credible sources to support your response and personal reflections on the actual content.
- Emotional and Intellectual Reflection: Balance your emotional reactions with intellectual analysis and reflect on why certain aspects make you feel a particular way and explore any deeper meanings or implications.
- Organization: Ensure your essay is well-organized, with a clear and strong introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs, and a conclusion that ties everything together.
- Clarity and Coherence: Write clearly and coherently, making sure your ideas flow logically from one point to the next, avoiding ambiguity, and ensure each paragraph transitions smoothly.
- Personal Voice: Maintain a personal and engaging tone throughout the entire composition, making your writing genuine and authentic.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your writing and reflect on the overall impact of the source on your thoughts and feelings or discuss any changes in perspective or insights gained.
Example of Writing a Critical Response Essay
Topic: American Capitalism: The New Face of Slavery
I. Sample Introduction
Capitalism is a dominant characteristic of the American economy. In this case, Matthew Desmond’s article “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation” discusses the role of slavery in shaping contemporary business practices. Specifically, the author attempts to convince the audience that the brutality of American capitalism originates from slavery. In turn, Desmond lays a strong but simple foundation for his argument, which ensures that the audience can conceptualize the link between plantation slavery and contemporary American capitalistic practices.
II. Example of Body Paragraphs
A. American Capitalism
Early in the article, Desmond informs readers of the high variability in the manifestation of capitalism in societies, which creates the impression that American capitalism is a choice. For example, Desmond (2019) argues that the brutality of American capitalism is simply one of the possible outcomes of a society built on capitalistic principles because other societies implement the same principles in a manner that is liberating, protective, and democratic. Moreover, Desmond begins his argument by eliminating a popular presumption that exploitation and oppression are unavoidable outcomes of capitalism. In turn, this strategic move to establish this fact is in the introductory section of the article because it invites the audience to rethink the meaning of capitalism. Furthermore, its plants doubt regarding the ‘true’ meaning of capitalism outside the context of American society.
B. Slavery and American’s Economic Growth
After establishing that the perception of capitalism through the lens of American society has some bias, Desmond proceeds to provide detailed evidence to explain the attempt to camouflage the obvious link between slavery and America’s economic growth. For instance, Desmond (2019) notes the role of Alfred Chandler’s book, The Visible Hand, and Caitlin Rosenthal’s book, Accounting for Slavery, in breaking the link between management practices in plantations and modern corporations by suggesting that the current business practices are a consequence of the 19th-century railroad industry. In this case, Desmond uses this evidence to make a logical appeal to the audience, which makes his argument more convincing because he explains the reason behind the exclusion of slavery in the discourse on modern industry. As a result, Desmond dismisses one of the main counterarguments against his central argument, which increases his persuasive power.
C. Input vs. Output Dynamic
Desmond emphasizes the link between slavery and American capitalism to readers by using the simple input vs. output dynamic throughout the article. For example, Desmond (2019) compares the Plantation Record and Account Book to the heavy digital surveillance techniques in modern workplaces because they collect data, which the employers use to maximize productivity while minimizing inputs. In particular, the comparison reveals that employers did not stop the practice of reducing laborers into units of production with fixed productivity thresholds. Moreover, the constant repetition of the theme of low input and high output dominates the body paragraphs, which makes it nearly impossible for readers to lose sight of the link between slavery and business practices under American capitalism. In turn, the simplification of the underlying logic in Desmond’s argument ensures its clarity to the audience.
III. Sample Conclusion
Desmond carefully plans the presentation of his argument to the audience, which allows readers to follow the ideas easily. In particular, the author starts with a call for readers to set aside any presumptions concerning capitalism and its origin. Then, Desmond provides the audience with an alternative narrative with support from seminal texts in slavery and economics. On the whole, Desmond manages to convince the audience that the American capitalistic society is merely a replica rather than an aberration of slavery.
Citing Sources in a Critical Response Essay
A critical response essay contains specific thoughts of the article’s author and direct words of the text’s author. In this case, students must conduct proper documentation to ensure readers can distinguish between these two types of ‘voices’ (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Moreover, documentation prevents incidents of plagiarism. Usually, instructors mention a referencing technique that students should use while writing a critical response paper. However, if assignment instructions do not identify a specific documentation style, writers should use a referencing technique that is acceptable for scholarly writing in their disciplines.
In-text citation:
- Parenthetical: (Desmond, 2019).
- Narrative: Desmond (2019).
- Desmond, M. (2019, August 12). In order to understand the brutality of American capitalism, you have to start on the plantation. New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html
- Parenthetical: (Desmond par. 1).
- Narrative: Desmond argues . . . (par. 1).
Works Cited:
- Desmond, Matthew. “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation.” New York Times , 14 Aug. 2019, www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html.
Harvard Referencing
- Parenthetical: (Desmond 2019).
Reference List:
- Desmond, M 2019, ‘In order to understand the brutality of American capitalism, you have to start on the plantation,’ New York Times . Available from: <https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html>. [06 June 2024].
Chicago/Turabian
In-text citation (footnote):
- 1. Matthew Desmond, “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation,” New York Times , August 14, 2019, https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html.
Bibliography:
- Desmond, Matthew. “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation.” New York Times . August 14, 2019. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html.
Final Provisions on a Critical Response Essay
- Adequate reading is a precursor for writing an effective critical response essay.
- Students must conduct adequate research on a topic to develop a proper understanding of a theme, even if only one article appears on the reference list.
- Notetaking or annotation is a good practice that aids students in extracting meaning from an article.
- Writers should plan for all activities in the writing process to ascertain they have adequate time to move through all the stages.
- An outline is an organizational tool, which learners must use to establish the sequence of ideas in such a paper.
- The purpose of a critical response essay has a significant impact on the selection of evidence and the arrangement of body paragraphs.
- Students should prioritize revision and editing, which represent opportunities to refine the content of composition and remove mechanical issues.
- Collaborative and individual revision are equally important because they play different roles in the writing of a good paper.
- Evidence selection is dependent on the purpose and thesis statement of a critical response essay.
Campbell, K. H., & Latimer, K. (2023). Beyond the five-paragraph essay . Routledge.
Davies, M. (2022). Writing critical reviews: A step-by-step guide. In S tudy skills for international postgraduates (pp. 194–207). Bloomsbury. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312965969
Fort, K. (1971). Form, authority, and the critical essay. College English , 32 (6), 629–639. https://www.jstor.org/stable/374316
Lauritzen, J. (2021). Read, write, and cite . Kendall Hunt Publishing Company.
Ogbonnaya, C., & Brown, A. D. (2023). Editorial: Crafting review and essay articles for Human Relations . Human Relations , 76 (3), 365–394. https://doi.org/10.1177/00187267221148440
Wallace, M., & Wray, A. (2021). Critical reading and writing for postgraduates . Sage.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

723 Informative Essay Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 8 September 2020
- Icon Page 6759 words

Character Analysis Essay: Student Guidelines
- Icon Calendar 6 September 2020
- Icon Page 6256 words
How to Write a Critical Response Essay: Step-by-Step Guide
Graduating without sharpening your critical thinking skills can be detrimental to your future career goals. To spare you the trouble, college teachers assign critical response tasks to prepare learners for making rational decisions.
Critical response papers also help professors assess the knowledge of each student on a relevant topic. They expect learners to conduct an in-depth analysis of each source and present their opinions based on the information they managed to retrieve.
This article aims to help students who have no idea how to write critical response essays. It offers insight into academic structuring, formatting, and editing rules. Here is our step-by-step recipe for writing a critical response essay.
What Is a Critical Response Essay?
The critical response essay displays the writer’s reaction to a written work. By elaborating on the content of a book, article, or play, you should discuss the author’s style and strategy for achieving the intended purpose. Ideally, the paper requires you to conduct a rhetorical analysis, interpret the text, and synthesize findings.
Instead of sharing somebody else’s solution on the subject matter, here you present your argumentation. Unlike a descriptive essay, this paper should demonstrate your strong expository skills. Often, a custom writing service can prove helpful if you find your evaluation essay time-consuming. Offering a value judgment about a specific topic takes time to acquire.
Another thing you should consider is not just focusing on the flaws. Though this is not a comparison and contrast essay, you must also reveal the strengths and present them without exaggeration. What matters is to develop your perspective on the work and how it affects the readership through implicit and explicit writing means.
Besides assessing your ability to develop coherent argumentation, professors will also grade your paper composition skills. They want to ensure you can critically reflect on various literature pieces. Hence, it’s essential to learn to analyze your topic thoroughly. This way, you gain a deep understanding and can organize a meaningful text.
Critical Response Essay & Other Essay Types
Standard essays contain three main segments: introduction, main body, and conclusion. But any other aspect beyond this vague outline differs depending on the assigned type. And while your critical response resembles an opinion essay since it expresses your viewpoint, you must distinguish it from other kinds.
For example, let’s consider a classification essay or a process essay. The first only lists the features of a particular object or several concepts to group them into categories. The second explains how something happens in chronological order and lists the phases of a concrete process. Hence, these variants are purely objective and lack personal reflection.
A narrative essay is more descriptive, with a focal point to tell a story. Furthermore, there’s the definition essay, an expository writing that provides information about a specific term. The writer, while showcasing their personal interpretation, must avoid criticism of the matter. Professional personal statement writers can provide assistance in creating the best essay that reflects the writer’s individual opinion.
Finally, though you can find some resemblances with an argumentative paper, critical responses comprise two parts. First, you quickly make an analytical summary of the original work and then offer a critique of the author’s writing. When drafting, it’s advisable to refrain from an informal essay format.
What Is the Structure of a Critical Response Essay?
The critical essay will have a typical structure consisting of five paragraphs. It is the most effective and easiest to follow. Here’s a brief demonstration of what you should include in each segment.
Introduction
The introductory paragraph reveals your main argument related to the analysis. You should also briefly summarize the piece to acquaint the reader with the text. The purpose of the introduction is to give context and show how you interpreted the literary work.
These paragraphs discuss the main themes in the book or article. In them, ensure you provide comments on the context, style, and layout. Moreover, include as many quotations from the first-hand text or other sources to support your interpretation.
However, finding memorable quotes and evidence in the original book can be challenging. If you have difficulties drafting a body paragraph, write your essay online with the help of a custom writing platform. These experts will help you show how you reached your conclusions.
This paragraph restates all your earlier points and how they make sense. Hence, try to bind all your comments together in an easily digestible way for your readers. The ultimate purpose is to help the audience understand your logic and unify the essay’s central idea with your interpretations.
Writing Steps of a Critical Response Essay

If you wonder how to write a critical response, remember that it takes time and proper planning. You will have to address multiple data, draft ideas, and rewrite your essay fast and efficiently. Follow the methods below to organize better and get a high grade without putting too much pressure on your shoulders.
1. Pick a Topic
Professors usually choose the topic and help you grasp the focus of the research. Yet, in some cases, you might be able to select a theme you like. When deciding, ensure the book can provide several arguments, concepts, or phenomena to review. You should also consider if there’s enough available data for analysis.
2. Research and Gather Information
This assignment means you cannot base your argumentation on personal beliefs and preferences. Instead, you must be flexible and accept different opinions from acknowledged scholarly sources. Moreover, ensure you have a reliable basis for your comments.
In short, avoid questionable resources and be accurate when referencing. Finding a single article claiming the concept or idea is correct and undisputable isn’t enough. You must read and consult various sources and conduct a meticulous examination.
3. Prepare the Outline
Define your claim or thesis statement and think of a “catch” sentence that will attract the reader’s attention. You must also consider titling an essay and giving background data and facts. At this stage, it’s also recommendable to establish the number of body segments. This step will help you get a more precise writing plan you will later reinforce with examples and evidence.
4. Start Rough Drafting
When writing your first draft, consider dedicating each section to a distinct argument or supporting evidence that proves your point. Cite and give credit as appropriate and ensure your text flows seamlessly and logically. Also, anticipate objections from opponents by including statements grounding your criticism.
5. Revise and Edit
Typically, your rough draft will require polishing. The best approach is to sleep on it to reevaluate its quality in detail. Check the relevance of your thesis statement and argumentation and ensure your work is free of spelling and grammatical mistakes. Also, your sentences should be concise and straight to the point, without irrelevant facts or fillers.
The Dos and Don’ts in Critical Response Essay Writing
Check your work against the following dos and don’ts for a perfect written piece.
- Pick an intriguing title.
- Cite each source, including quotations and theoretical information.
- Connect sentences by using transition words for an essay like “First,” “Second,” “Moreover,” or “Last” for a good flow.
- Start writing in advance because last-minute works suffer from poor argumentation and grammar.
- Each paragraph must contain an analysis of a different aspect.
- Use active verbs and dynamic nouns.
- Ask a friend or classmate to proofread your work and give constructive comments.
- Check the plagiarism level to ensure it’s free of copied content.
- Don’t exceed the specified word limit.
- Follow professional formatting guidelines.
- Your summary must be short and not introduce new information.
- Avoid clichés and overusing idioms.
- Add the cited bibliography at the end.
Related posts:
- Persuasive Essay: a Comprehensive Guide & Help Source
- How to Write a News Story
- How to Write an Autobiography Essay: Guide for College Students
- A Foolproof Guide to Creating a Causal Analysis Essay
Improve your writing with our guides

How to Write a Scholarship Essay

Definition Essay: The Complete Guide with Essay Topics and Examples

Critical Essay: The Complete Guide. Essay Topics, Examples and Outlines
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Writing the Critical Response Essay (CRE)
The Critical Response Essay is a multi-paragraph, multi-page essay that requires you to take one of your Critical Response Paragraphs and revise it to create a more complex and stronger argument. You should choose your best CRP or the one that most interests you. Focus on making it not only a longer argument, but also a better argument, using what you’ve learned since writing the original piece to improve the argument and the writing itself (argument form, paragraph form, and grammar). Also use what you’ve learned from my feedback and from our discussions in class and individual conferences. You must include confutation.
ARGUMENT FORM
CREs require that you use classical argument form. The parts of this kind of argument are as follow:
Key Takeaways
- Introduction Paragraph , ending with claim
- [ Confutation as first argument paragraph ?]
- Argument Paragraphs (two or three): Begin with a subclaim , then support it by providing textual evidence and analysis of evidence [including confutation within?]
- [ Confutation as final argument paragraph ?]
- Conclusion [confutation as conclusion?]
- Works Cited
Your title may not be simply the title of the story or the assignment. It must be a title that is specific to your argument.
INTRODUCTION PARAGRAPH with CLAIM
- Introduce the story and the author about which you are writing. If you’re writing about a film, identify the director.
- Call attention to the features of the story on which you will base your argument. This is the ONLY part of the essay in which you may summarize parts of the story.
- END the introduction with your CLAIM.
- If you have no claim, you have no argument, and therefore you may earn a disappointing grade.
- Likewise, if your claim does not appear in the introduction, your reader has no way of knowing what your subclaims and evidence are attempting to prove.
- It’s not like a joke where you save the punchline until last.
- It’s not mystery-writing, where you don’t identify the murderer until the end.
- It’s an argument. So for your reader to understand what is the point of all the evidence and analysis you’re working so hard to create, you must tell her, in the introduction, what you’re trying to argue and prove.
Writing an Arguable Claim
- Think in terms of theme .
- Theme cannot be expressed with just a word or even a short phrase, like sibling rivalry or fear of marriage. Those are interesting topics, but they are not yet themes.
- To turn a topic into a theme, you must be able to say what the story shows us about the topic , that relates to real life beyond the story.
“Beauty and the Beast” illustrates sibling rivalry.
This is an insufficient claim about theme because it doesn’t give me even a hint of what you think the story says about sibling rivalry. Unless you plan to tell me that in the next sentence, there’s a problem with your claim. By the way, a claim can be more than one sentence.
Jeanne-Marie Leprince de Beaumont’s “Beauty and the Beast” illustrates how sibling rivalry can be caused by unnecessary competition for mates, particularly in the case of sisters.
Now that’s an arguable claim because it includes author, title, a topic, and what the story says about the topic and how it relates to real life.
You can make this claim even stronger (and give yourself greater confidence that your argument will be persuasive) by including the main textual evidence you will cite.
Or you could revise this idea to discuss how cultural expectations play a role in this kind of rivalry and unhealthy competition. See the CRP Example for something like that.
If it helps, you can think of these components as part of a formula.
Let X be the story and some particular feature of it.
Let Y be the theme you are arguing.
Instead of an equal sign, we insert a verb that expresses the relationship between X and Y:
(=) illustrates, shows, portrays, dramatizes, suggests (etc.)
In this example:
Let X be the elder sisters’ resentment toward Beauty.
Let Y be how sibling rivalry can be caused by competition for mates.
Notice in the example below how this process creates an arguable claim.
(X) The elder sisters’ resentment toward Beauty in “Beauty and the Beast”
(Y) how sibling rivalry can be caused by competition for mates.
ARGUMENT PARAGRAPHS
- Support the claim with argument paragraphs.
- How many you need is up to you, but generally at least two, in some cases three or four.
- Begin EVERY argument paragraph with a TOPIC SENTENCE
- The topic sentence is like a mini-claim, the paragraph’s claim
- Tells me what you’ll argue in this paragraph
- And tells or shows how this point supports the main claim.
- Support the topic sentence with textual evidence and analysis
- Quotations and your analysis of them.
- See the Quotation Sandwich document for guidance.
- Vary the verbs you use to incorporate quotations into your sentences. DO NOT use the words “says,” “states,” or “writes” (or any forms of these verbs). See the document titled “Effective Verbs for Introducing Quotations in Canvas for many possible verbs that you may use.
- Use transitional terms—also called “signposts”—to show the relationships from one point to the next and from one paragraph to the next. The internet is full of lists of transitional terms. Here’s one good source: Transition Words.
CONFUTATION
Confutation makes an argument stronger by dealing with opposing points and evidence.
- Confutation includes the following parts:
- Presenting opposition fairly (opposing claims or ideas)
Remember that the opposition must not be a “straw man.” That is, you must engage with something that a careful reader would actually argue, not a simplistic, obviously erroneous reading.
Some readers might argue that the sisters are not abusive toward Beauty.
This example is a straw man statement. No one would seriously argue this point because the sisters actually plot to get Beauty killed, and what could be more abusive than that?
- Refuting the opposition: showing how it is incorrect or at least as correct as your reading.
- Directly after the introduction
- o Directly before the conclusion
- o As part of the conclusion
- o Within paragraphs, to deal with possible alternative interpretations of your textual evidence.
Consider a confutation involving the fairy who appears at the end of “Beauty and the Beast” and what she does to Beauty’s sisters. That is, she punishes the two sisters for their bad behavior. Some readers see this as fair because those mean girls get what’s coming to them. But others see it as a missed opportunity to promote sisterhood among all three of the girls. Here are examples of how to write these points as a complete confutation.
State the opposition, as fairly as possible: When the fairy punishes the two sisters for their bad behavior, some readers see this extreme punishment as fair because those mean girls finally get what is coming to them.
Refute the opposition: But by imposing this punishment, the fairy misses a chance to promote sisterhood among all three of the girls. But if she has such powerful magic, that she can turn young women to stone, shouldn’t she be able to teach them to love each other instead?
This refutation includes a rhetorical question; it is not meant for you to answer, but to leave the reader thinking about your ideas. You are not required to pose your refutation as a question; this is just one way to write your refutation.
What do you do with a conclusion? Do not just restate your claim, even if you change some of the wording. That’s not worth your reader’s time. So what is worth your reader’s time?
- A kind of wrap-up: What’s the point of this argument? What has been learned here and why does it matter? What do you want you and your reader to have learned or created together?
- And why is this important? Does it apply to real life now? How?
- Certainly the spirit of your claim will be here. But not just your claim reworded.
- o Because you’ve just been feeding it and exercising it,
- o So now it’s bigger and more interesting.
- o So you should be able to talk it about it with greater complexity and authority. Don’t go crazy and add new ideas—remember you’re wrapping things up.
- Confutation as Conclusion: You may be able to write a conclusion that includes confutation. Why might this be a useful strategy? Why might it be problematic?
Understanding the difference between claim and conclusion
- the conclusion is similar to the claim
- and yet more detailed and complete in meaning.
- Notice the relationship between the CLAIM and the Conclusion in this example:
The story of “The Frog King, or Iron Henry” illustrates and even promotes the importance of consent in relationships.
In this way, the story highlights the importance of understanding and respecting the value of consent. This tale teaches readers to stand up for themselves and refuse to give in to situations that will clearly cause discomfort or danger.
Keep this guidance and these examples handy as you draft your essay, and remember that I’m happy to answer questions and review drafts within the time constraints announced in class.
Introduction to Literature Copyright © by Judy Young is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
RMIT UP News
- RMIT Europe
- RMIT Global
- RMIT Vietnam
- Study online
- Courses by study area
- Undergraduate courses
- Postgraduate courses
- Vocational studies
- Pre-university studies
- Online courses and degrees
- Entry pathways
- Single courses
- Short courses and microcredentials
- Courses for international students
- How to apply
- Scholarships
- School leaver information
- Student services
- Student experience
- Frequently asked questions
- Career advisers
- Study experience
- Student life
- Support for students
- Global opportunities
- Industry connections
- Our strategy
- Governance & management
- Schools & colleges
- Respect for Australian Indigenous cultures
- Our locations and facilities
- Our heritage
- Our research
- Partnerships
- Centres and collaborations
- Research degrees
- Find researchers
- Recruit students and graduates
- Workforce development
- Collaborate with RMIT
- Research partnerships
- Facilities, equipment and services
- Contact Industry Engagement
- Giving to RMIT
- Study in Australia
- Apply to RMIT as an international student
- International student enquiries
- Fees and scholarships for international students
- International student services
- Key dates and intake information for international students

Latest news articles and blog posts

Introducing our new name - RMIT University Pathways (RMIT UP)
RMIT Training is changing its name to RMIT University Pathways, or RMIT UP – ushering in a new era of growth and connection with a dynamic, inviting, and vibrant refreshed identity.

Farewell to RMIT Training Board Chair Professor Julie Cogin
RMIT Training bids farewell to Deputy Vice Chancellor College of Business and Law and Vice-President Professor Julie Cogin, who is stepping down from her role as the RMIT Training Board Chair after 3 years.

RMIT Training Innovation Showcase
New ideas and creative business solutions were given the Shark Tank treatment at RMIT Training recently as the staff participants of our first ever Innovation Program pitched concepts to drive transformation across the organisation.

Libraries in Melbourne
Melbourne has some great libraries where you can study and find books to help you study.

Establishing good study habits
Create the best environment to maximise study time.

Medibank OSHC
If you have a student visa, you’ll have health insurance. We can help make it work for you.

Staying healthy
A healthy body equals a healthy mind! Here are some tips to help you to stay healthy and be your best.

Getting around Melbourne
Melbourne has an extensive network of public transport including trains, trams and buses. It’s also great for cyclists!
Get in touch with us
Need help or have more questions? Get in touch and we will help you with your enquiry.

Acknowledgement of Country
RMIT University acknowledges the people of the Woi wurrung and Boon wurrung language groups of the eastern Kulin Nation on whose unceded lands we conduct the business of the University. RMIT University respectfully acknowledges their Ancestors and Elders, past and present. RMIT also acknowledges the Traditional Custodians and their Ancestors of the lands and waters across Australia where we conduct our business - Artwork 'Luwaytini' by Mark Cleaver, Palawa.
RMIT University acknowledges the people of the Woi wurrung and Boon wurrung language groups of the eastern Kulin Nation on whose unceded lands we conduct the business of the University. RMIT University respectfully acknowledges their Ancestors and Elders, past and present. RMIT also acknowledges the Traditional Custodians and their Ancestors of the lands and waters across Australia where we conduct our business.
- Levels of study
- Applying to RMIT
- International students
- Careers advisers
- Research contacts
- Staff development and training
- Facilities and equipment services
- Governance and management
- Sustainability
- Schools and colleges
- Copyright © 2024 RMIT University |
- Accessibility |
- Website feedback |
- Complaints |
- ABN 49 781 030 034 |
- CRICOS provider number: 00122A |
- TEQSA provider number: PRV12145 |
- RTO Code: 3046 |
- Open Universities Australia
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Critical Response Essay

Students have to write different types of essays all the time. However, they face many problems when it comes to writing a critical response essay. Why is it so hard to manage? What are the main components of it? We will answer all these questions in our complete guide to help you learn how you can write this type of essays quickly and easily.
What Is a Critical Response Essay?
First things first – let’s find out what a critical response essay is and what components it includes.
It is an assignment that is based on your analytical skills. It implies the understanding of the primary source, such as literary work, movie or painting (its problematic, content, and significance), and the ability to perform critical thinking and reflect your opinion on the given subject.
The aim of critical response essay is to get familiarised with the subject, form your opinion (the agreement or disagreement with the author), reveal the problematic of the piece and support your claims with evidence from the primary source.
For example, your task might be to analyze the social structure in Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet.
How Is It Different From Other Essay Types?
Every essay you write has a very similar structure that consists of an introduction, the main body, and the conclusion. While this type is not an exception and is quite similar to an analytical essay , it still has differences. One of those is the fact that it contains two parts. The first part includes a quick summary of the analyzed work. The second part is a critique – a response to the author’s opinion, facts, examples, etc.
What Should You Pay Attention To?
Before we dive into the guide and the steps of crafting your critical essay, let’s take a look at some of the most common pitfalls that often occur during the writing process of a piece like this.
Not knowing what you are writing about.
This makes no sense, right? So, be sure to read the piece that your topic is based on and make sure you understand what it is about.
Not understanding what your task is.
Be attentive to the task and make sure you understand what is required from you. You would be surprised if you knew how many essays are written without even touching the main question or problematic.
Being in a hurry.
A lot of students start working on their essays at the very last moment and do it in haste. You can avoid a lot of mistakes if you are attentive, focused, and organized. If you have too little time to write a strong response essay yourself, you can always get the assistance of a professional writing service. This will help you to be on time with your assignment without sacrificing its quality.
And now let’s begin your journey of writing an essay.
Step 1. Examine the Primary Source
Before starting actually writing your critical essay, you need to get acquainted with the subject of your analysis. It might be an article, a book or any other type of text. Sometimes, this task is given for pieces of art, such as a painting or a movie.
So, the first step would be to gain as much information about the subject as possible. You might also search for some reviews or research papers on the subject. Be sure to examine the primary source thoroughly and read the complete text if it is a piece of writing.
Advice: make notes while you are working with your primary source. Highlight the main points that will build a basis for your analysis and which you can use to form your opinion on. Notes will also help you to structure your essay.
- Did you read the whole text or examined your primary source thoroughly?
- Did you find information on the topic of your assignment?
- Did you write down the key points that you are going to use for your essay?
Step 2. Analyze the Source and Your Notes
After you finished with your primary source, try to analyze and summarize all of your findings. Identify the problematic of the piece and find the appropriate notes that you have made to structure your future essay.
Formulate your opinion – are you agree or disagree with the author? Can you support your statements with evidence?
- Did you examine all the notes you have?
- Did you form your opinion on the subject?
- Did you find the arguments to support your main point?
- Did you succeed to define the strengths and weaknesses of the work?
Step 3. Write Your Essay
After you have all of the needed materials next to you, you can start working on the text of your essay.
- First of all, write a critical response essay rough draft.
- Reread your draft and make your edits.
- Proofread and edit your final version.
- Check for plagiarism, grammatical and punctuation errors.
- Write a Works Cited page or bibliography page (if required).
Now, we will look at each part of your essay in detail. Keep in mind that you have to follow the guidelines provided by your teacher or professor. Some critical response essay examples will come in handy at this step.
How to Write a Critical Response Introduction
Your introduction is the part where you have to provide your thesis statement. Once you have your opinion and your thoughts organized, it’s pretty easy to make them transform into a statement that all your essay will be built on. Express your agreement or disagreement with the author.
For example, your thesis statement might be:
“Romeo and Juliet” by Shakespeare is a masterpiece that raises the problem of social inequality and classes differentiation which aggravates the drama culmination.
Advice: make sure you have evidence to support your thesis statement later in the text. Make your introduction in the form of a brief summary of the text and your statement. You need to introduce your reader to the topic and express your opinion on it.
- Did you embed your thesis statement?
- Is your thesis statement complete and suitable for the topic?
- Can you support your thesis statement with evidence?
- Did you summarize the analyzed subject?
- Did you start your introduction with a catchy sentence – a powerful statement, fact, quote or intriguing content?
- Did you include a transition sentence at the end of your introduction?
How to Write Critical Response Paragraphs
Explain each of your main points in separate body paragraphs. Structure your text so that the most strong statement with the following supporting evidence is placed first. Afterward, explain your other points and provide examples and evidence from the original text.
Remember that each of your statements should support your main idea – your thesis statement. Provide a claim at the beginning of the paragraph and then develop your idea in the following text. Support each of your claims with at least one quote from the primary source.
For example:
To distinguish the division between classes and express the contribution of each social class Shakespeare used different literary methods. For example, when a person from a lower class speaks, Shakespeare uses prose:
NURSE I saw the wound, I saw it with mine eyes (God save the mark!) here on his manly breast— A piteous corse, a bloody piteous corse, Pale, pale as ashes, all bedaubed in blood, All in gore blood. I swoonèd at the sight. (3.2.58-62)
At the same time upper-class characters speak in rhymed verse:
MONTAGUE But I can give thee more, For I will raise her statue in pure gold, That while Verona by that name is known, There shall no figure at such rate be set As that of true and faithful Juliet. (5.3.309-313)
- Did you support your thesis statement with claims?
- Do your claims appeal to critical response questions?
- Did you provide evidence for each claim?
How to Write Critical Response Conclusion
The best way to conclude your essay is to restate your thesis statement in different phrasing. Summarize all of your findings and repeat your opinion on the subject. A one- or two-paragraph conclusion is usually enough if not requested more.
We’ve also prepared some critical response essay topics for you:
- Explain the changes of the character throughout the novel: Frodo from Lord of the Rings /Dorian Gray from The Picture of Dorian Gray .
- Examine a setting and the atmosphere in the novel Gone with the Wind/Jane Eyre .
- Investigate the cultural or historical background in Romeo and Juliet/Macbeth .
- Describe the impact of the supporting character: Horatio in Hamlet /Renfield in Dracula .
- Describe the genre of the work and its influence on the mood of the piece: To Build a Fire/ For Whom the Bell Tolls.
This was our step-by-step guide to writing your perfect critical response essay. We hope our tips will be useful to you!
Related posts

Critical Response Process


Role 1: Artist/Maker
Role 2: responder, role 3: facilitator.

Critique Is Creative: The Critical Response Process in Theory and Action
In this first in-depth study of CRP, Lerman and her long-term collaborator John Borstel describe in detail the four-step process, its origins and principles. The book also includes essays on CRP from a wide range of contributors.
With insight, ingenuity, and the occasional provocation, these practitioners shed light on the applications and variations of CRP in the contexts of art, education, and community life.
Book a workshop
With a focus on actual works in progress – a dance, a script, a lecture, visual art work, even a cake – your training will highlight participation, conversation, and the flexibilty of the Process. You will leave with a firm grasp of procedures and tools to apply in your professional and daily life.
Training programs are customized to suit the needs of our hosts and may last from two hours to four days. The Critical Response Process team has trained arts faculty, orchestra members, museum docents, acting companies, social science researchers, and nonprofit boards, as well as students and makers in almost every artistic discipline.
Book now >
“ In supporting the creation of new work, we have found Liz Lerman’s Critical Response Process to be the best tool we’ve ever encountered in assisting individual artists at the most vulnerable stages of creation. The Process empowers artists and invests responders with real responsibility as audience members. ”
– james c. nicola, artistic director, new york theatre workshop, critical response process certification.
In 2019 we launched the annual Critical Response Process Certification program, with cohorts planned through 2023. Graduating practitioners are deeply invested in the practice and possibilities of CRP, and you can work with them directly as facilitators for your needs.

Essay Writing 201: Critical Response Essay
- Class overview
Registration Details
More information.
- High School
There are currently no upcoming sessions scheduled for this class.
Artificial Intelligence can spit out a generic essay of regurgitated ideas pieced together from various public sources. In seconds.
Original voice? Something AI can’t do.
Personal reflection? Something AI can’t do.
Complex reasoning? Something AI can’t do.
Critical response essays are popular in college because they defy ChatGPT. Students will be required to apply those skills to specific assignment parameters, subjects, and texts. They’ll need to write about history, investigate science, or respond to current events.
We teach your teens how!
Class Overview
Made with you in mind.
Raising nuanced thinkers is increasingly difficult in the age of images, short ranty blurbs of text, and speedy delivery of new content that just races by.
In Essay Writing 201: Critical Response Essay , students
- get into the center of the reading and writing experience
- read purposefully, identifying main points and arguments
- decipher images in the news
- separate how a text is written from what it’s written about
- receive feedback showing that their thoughts and reactions matter
We revitalize your teen’s thinking, leading to more complex thoughts. Experience the satisfaction of transferring thinking to the page and seeing the reaction of other readers as they interact with those thoughts.
Bonus?
The skills taught here have maximum cross-curricular appeal. Use these exercises again in your history, art, or civics units! All great reasons to consider picking up this class.
Who should take this course?
This course is designed for high school students with essay writing experience.
Students should already be competent writers and have experience with academic formats. The Essay Writing 101: Analytic Essay and Essay Writing 102: Persuasive Essay classes are recommended preparatory courses, though not required.
If your teen has multiple essay writing experiences, knows how to formulate a thesis and offer their own analysis in writing, then you are ready for this course! If you have any questions about your student's eligibility for this class, don't hesitate to contact us with a writing sample and we'll point you in the right direction.
Week by Week
Students learn to wield tools that will help them develop sophisticated habits of thinking. The initial target of analysis: examination of a photograph.
Critical reasoning includes powerful reading habits. Students work on seeing texts from various points of view and offering a personal reflection on those texts.
Rhetorical analysis of a modern-day text is the focus this week in preparation for the final critical response essay.
Students draft, revise, and edit a critical response essay this week.
Word on the Street
I enjoyed getting another set of eyes on my writing projects from my teacher. We were able to toss some ideas back and forth until I found what I needed to do to the current assignment. Orson, 18
I like the flexibility of the class. The fact that there is no scheduled live class is nice. It gives me the opportunity to work on the assignments when it is most convenient. Samir, 17
This class was amazing! The weekly readings were excellent and were very helpful for the assignments, which were fun and creative, while also being challenging. Val, 17
You learn how to look at an image or a piece of writing and determine why the creator made certain choices (lighting, word choice, magazine article vs speech) in their work. You also learn how to analyze the pieces to see what effect those rhetorical choices had on the piece. Mike 16
Want to see how our classroom works? Test drive a sample class complete with real class readings, assignments, and instructor comments!
Follow these instructions:
- Navigate to class.bravewriter.com . If you are a current student, you’ll need to log out in the upper right corner before proceeding.
- Log in using these credentials: Username: [email protected] Password: Brave1
- Next, you will land on our Family Dashboard. You'll find a Parent icon and a Student icon to represent classes where the parent or the student is the primary participant. Click on Parent to view parent participation classes. To find classes with direct student-instructor interaction, click on Student.
- Click on the class name of interest and start reading posts!

Essay Writing 101: Analytic Essay
Ages 13 - 18

Essay Writing 102: Persuasive Essay

Essay Writing 202: Timed Essay

Essay Writing 301: Advanced Composition
Ages 15 - 18

Essay Writing 302: MLA Research Essay
Ages 16 - 18

Analyzing Lit: High School

Analyzing Lit: Shakespeare

Brave Writer® 201: Academic Revision
Ages 11 - 18

College Admissions Essay

Essay Prep: Dynamic Thinking

Essay Prep: Reading the Essay

Essay Prep: Research and Citation

Fan Fiction

High School Writing: Current Events

High School Writing: Historical Fiction
Ages 12 - 18

High School Writing: History Lab

Journaling Jumpstart

Movie Discussion Club
Ages 9 - 18

Nature Journaling

Passion for Fiction

Playing with Poetry: Discovery

Playing with Poetry: Exploration

Powerful Fiction Techniques

Scriptwriting

Songwriting

Songwriting: Poetry of Lyrics

Writing the Short Story
We’re reviewing our resources this spring (May-August 2024). We will do our best to minimize disruption, but you might notice changes over the next few months as we correct errors & delete redundant resources.
Critical Reflection
A Critical Reflection (also called a reflective essay) is a process of identifying, questioning, and assessing our deeply-held assumptions – about our knowledge, the way we perceive events and issues, our beliefs, feelings, and actions. When you reflect critically, you use course material (lectures, readings, discussions, etc.) to examine our biases, compare theories with current actions, search for causes and triggers, and identify problems at their core. Critical reflection is not a reading assignment, a summary of an activity, or an emotional outlet. Rather, the goal is to change your thinking about a subject, and thus change your behaviour.
Tip: Critical reflections are common in coursework across all disciplines, but they can take very different forms. Your instructor may ask you to develop a formal essay, produce weekly blog entries, or provide short paragraph answers to a set of questions. Read the assignment guidelines before you begin.
How to Critically Reflect
Writing a critical reflection happens in two phases.
- Analyze: In the first phase, analyze the issue and your role by asking critical questions. Use free writing as a way to develop good ideas. Don’t worry about organized paragraphs or good grammar at this stage.
- Articulate: In the second phase, use your analysis to develop a clear argument about what you learned. Organize your ideas so they are clear for your reader.
First phase: Analyze
A popular method for analyzing is the three stage model: What? So What? Now what?
In the What? stage, describe the issue, including your role, observations, and reactions. The what? stage helps you make initial observations about what you feel and think. At this point, there’s no need to look at your course notes or readings.
Use the questions below to guide your writing during this stage.
- What happened?
- What did you do?
- What did you expect?
- What was different?
- What was your reaction?
- What did you learn?
In the second So What? stage, try to understand on a deeper level why the issue is significant or relevant. Use information from your first stage, your course materials (readings, lectures, discussions) -- as well as previous experience and knowledge to help you think through the issue from a variety of perspectives.
Tip: Since you’ll be using more course resources in this step, review your readings and course notes before you begin writing.
Below are three perspectives you can consider:
- Academic perspective: How did the experience enhance your understanding of a concept/theory/skill? Did the experience confirm your understanding or challenge it? Did you identify strengths or gaps in your knowledge?
- Personal perspective: Why does the experience matter? What are the consequences? Were your previous expectations/assumptions confirmed or refuted? What surprised you and why?
- Systems perspective: What were the sources of power and who benefited/who was harmed? What changes would you suggest? How does this experience help you understand the organization or system?
In the third Now what? stage, explore how the experience will shape your future thinking and behaviour.
Use the following questions to guide your thinking and writing:
- What are you going to do as a result of your experiences?
- What will you do differently?
- How will you apply what you learned?
Second phase: Articulate
After completing the analysis stage, you probably have a lot of writing, but it is not yet organized into a coherent story. You need to build an organized and clear argument about what you learned and how you changed. To do so, develop a thesis statement , make an outline , write , and revise.
Develop a thesis statement
Develop a clear argument to help your reader understand what you learned. This argument should pull together different themes from your analysis into a main idea. You can see an example of a thesis statement in the sample reflection essay at the end of this resource.
Tip: For more help on developing thesis statements, see our Thesis statements resource
Make an outline
Once you have a clear thesis statement for your essay, build an outline. Below is a straightforward method to organize your essay.
- Background/Context of reflection
- Thesis statement
- Introduce theme A
- Writer's past position/thinking
- Moment of learning/change
- Writer's current/new position
- Introduce theme B
- Introduce theme C
- Summarize learning
- Discuss significance of learning for self and others
- Discuss future actions/behaviour
Write and revise
Time to get writing! Work from your outline and give yourself enough time for a first draft and revisions.
Even though you are writing about your personal experience and learning, your audience may still be an academic one. Consult the assignment guidelines or ask your instructor to find out whether your writing should be formal or informal.
Sample Critical Reflection
Below are sample annotated paragraphs from one student’s critical reflection for a course on society and privilege.
Introduction
Background/context of reflection : I became aware of privileged positions in society only in recent years. I was lucky enough, privileged enough, to be ignorant of such phenomena, but for some, privilege is a daily lesson of how they do not fit into mainstream culture. In the past, I defined oppression as only that which is obvious and intentional. I never realized the part I played. However, during a class field study to investigate privileged positions in everyday environments, I learned otherwise. Thesis: Without meaning to, I caused harm by participating in a system where I gained from others’ subtle oppression. In one of these spaces, the local mall, everything from advertisements to food to products, to the locations of doorways, bathrooms and other public necessities, made clear my privilege as a white, heterosexual male.
Body paragraph
Topic sentence : Peggy McIntosh describes privilege as an invisible knapsack of tools and advantages. This description crystalized for me when I shopped for a greeting card at the stationary store. There, as a white, heterosexual male, I felt comfortable and empowered to roam about the store as I pleased. I freely asked the clerk about a mother’s day card. Writer’s past position: Previously, I never considered that a store did anything but sell products. However, when I asked the sales clerk for same sex greeting cards, she paused for a few seconds and gave me a look that made me feel instantly uncomfortable. Some customers stopped to look at me. I felt a heat move over my face. I felt, for a moment, wrong for being in that store. I quickly clarified that I was only doing a report for school, implying that I was not in fact homosexual. Writer’s current position: The clerk’s demeanor changed. I was free to check, she said. It was the only time during the field study that I had felt the need to explain what I was doing to anyone. I could get out of the situation with a simple clarification. But what if I really was a member of the homosexual community? The looks and the silence taught me that I should be feared. I realized that, along with its products, the store was selling an image of normal. But my “normality” was another person’s “abnormality.” After I walked out of the store I felt guilty for having denied being homosexual.
Summary of learning: At the mall I realized how much we indirectly shame nonprivileged groups, even in seemingly welcoming spaces. That shame is supported every time I or any other privileged individual fails to question our advantage. And it leads to a different kind of shame carried by privileged individuals, too. Value for self and others: All of this, as Brown (2003) documents, is exacerbated by silence. Thus, the next step for me is to not only question privilege internally, but to publicly question covert bias and oppression. If I do, I may very well be shamed for speaking out. But my actions might just encourage other people to speak up as well.
Sample paragraphs adapted from James C. Olsen's Teaching Portfolio from Georgetown University .
Essay Papers Writing Online
Writing a comprehensive and engaging response essay – a step-by-step guide to mastering the art of crafting a well-structured and persuasive analytical essay.

When it comes to composing a coherent and engaging response piece, a few key principles can make all the difference. Whether you are tasked with providing commentary on a literary work, expressing your thoughts on a thought-provoking article, or formulating a response to a challenging question, these strategies will help you create an insightful and effective essay.
The first step in crafting a remarkable response is to thoroughly comprehend the stimulus material. Carefully read, watch, or listen to the source material, taking note of the main ideas, key arguments, and underlying themes. By gaining a firm grasp of the content, you will be better equipped to analyze and evaluate the text, and ultimately, construct a pertinent and well-informed response.
Once you have a comprehensive understanding of the stimulus, it is crucial to organize your thoughts in a coherent manner. Begin by outlining the main points you plan to address in your essay. This will provide structure and clarity, ensuring that your response flows logically and effectively communicates your message. Use strong topic sentences to introduce each idea, and provide appropriate evidence or examples to support your claims. Employing these techniques will not only enhance the credibility of your response, but also engage and captivate your readers.
Understand the Assignment

Before starting to write a response essay, it is crucial to fully comprehend the requirements and expectations of the assignment. By understanding the assignment, you will be able to approach the essay with a clear focus and direction.
Take the time to carefully read the essay prompt and any accompanying materials. Pay attention to key words and phrases that indicate what is expected from you, such as “analyze,” “compare,” or “evaluate.” Understanding these instructions will help you determine the appropriate approach to take in your response.
Additionally, consider the context and purpose of the assignment. Is it a formal academic essay or a casual personal reflection? Understanding the intended audience and purpose of the assignment will guide your writing style and tone.
It is also important to be aware of any specific guidelines or formatting requirements provided by your instructor. These may include page length, citation style, or specific sources to include. Following these guidelines will ensure that you meet the necessary criteria and present a well-structured and organized response.
In summary, understanding the assignment is the first step to writing an effective response essay. By carefully reviewing the prompt, considering the context and purpose, and following any specific guidelines, you can ensure that your essay meets the requirements and fulfills its intended purpose.
Analyze the Source Material
When writing a response essay, it is crucial to thoroughly analyze the source material provided. This process involves carefully examining and understanding the key ideas, arguments, and evidence presented by the author without bias or preconceived notions. By effectively analyzing the source material, you can ensure that your response essay is well-informed, well-supported, and engaging.
First and foremost, it is important to read the source material attentively. Take the time to fully comprehend the main points and arguments put forth by the author. Look for any evidence or examples the author provides to support these arguments. Pay attention to the language and tone used, as well as any rhetorical devices employed, such as metaphors or analogies.
Once you have a solid understanding of the source material, it is essential to critically evaluate it. Consider the strengths and weaknesses of the arguments presented. Are the ideas logical and coherent? Is there sufficient evidence to support the claims? Look for any biases or assumptions that may be present in the text, and assess how they may impact the overall credibility of the author’s argument.
Additionally, it is important to consider the context in which the source material was written. Take into account the author’s background, expertise, and any potential biases they may have. Understanding the context can provide valuable insights into the author’s perspective and intentions, helping you to formulate a more nuanced and well-rounded response to the source material.
Finally, don’t be afraid to engage with the source material on a personal level. Think about how the ideas presented resonate with your own experiences, beliefs, or values. Consider any emotional or intellectual responses the material evokes. This personal engagement can add depth and authenticity to your response essay.
In conclusion, analyzing the source material is a critical step in writing an effective response essay. By carefully examining the key ideas, arguments, and evidence presented by the author, critically evaluating the text, considering the context, and engaging with the material personally, you can craft a well-informed and engaging response that adds value to the ongoing conversation.
Formulate a Clear Thesis Statement
In order to craft an effective response essay, it is crucial to formulate a thesis statement that clearly conveys your main argument or perspective on the given topic. The thesis statement serves as the foundation for your entire essay, outlining the central point you will be addressing and guiding the reader through your analysis.
When formulating your thesis statement, it is important to be concise, specific, and focused. Avoid vague or general statements that do not provide a clear direction for your essay. Instead, use precise language to articulate your main argument and ensure that it is accessible to readers.
Additionally, your thesis statement should be debatable, meaning that it allows for differing opinions or interpretations. This encourages critical thinking and engagement with your essay, as readers may have different perspectives on the topic at hand.
To ensure the clarity and effectiveness of your thesis statement, consider the following tips:
| Clearly state the main point you will be arguing in your essay, avoiding vague or general statements. | |
| Choose words that are precise and easily understood by your audience, avoiding jargon or technical terms. | |
| Pose an argument or perspective that allows for different interpretations or opinions. | |
| Support your thesis statement with examples, facts, or quotes that strengthen your argument. | |
| Continuously evaluate and revise your thesis statement as you develop your essay, ensuring that it accurately reflects your analysis. |
By formulating a clear thesis statement, you establish a strong foundation for your response essay and provide readers with a clear roadmap of your analysis. Take the time to carefully craft your thesis statement, considering its clarity, specificity, and debatability, to ensure the effectiveness of your essay.
Develop Strong Supporting Arguments
Crafting compelling and convincing arguments is crucial when writing a response essay. Your arguments should serve as evidence to support your claims and effectively communicate your perspective on the given topic. Developing strong supporting arguments involves careful analysis, critical thinking, and the ability to provide relevant examples or evidence to back up your ideas.
When developing your supporting arguments, it’s essential to consider the main points or themes of the essay prompt. By understanding the key concepts, you can identify the most relevant evidence or examples to support your arguments. Additionally, it’s important to ensure that your arguments are logical, coherent, and well-structured to make your essay persuasive.
One effective way to develop strong supporting arguments is by conducting thorough research on the topic. This research could involve reading relevant books, articles, or studies, and gathering credible sources of information. By relying on factual evidence and expert opinions, you can strengthen the validity of your arguments and make your essay more convincing.
In addition to research, it’s beneficial to consider counterarguments. Anticipating opposing viewpoints and addressing them in your response essay demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of the topic and strengthens your own arguments. By addressing counterarguments, you can present a well-rounded and balanced perspective, which enhances the credibility of your essay.
| 1. Craft compelling and convincing arguments. |
| 2. Analyze the main points of the essay prompt. |
| 3. Conduct thorough research on the topic. |
| 4. Consider counterarguments and address them. |
Overall, developing strong supporting arguments is crucial to the success of your response essay. By carefully analyzing the essay prompt, conducting thorough research, considering counterarguments, and crafting well-structured arguments, you can ensure that your essay effectively communicates your perspective and convinces your readers of your viewpoint.
Use Evidence and Examples
In order to strengthen your response essay and effectively convey your ideas, it is essential to use evidence and examples to support your arguments. By providing evidence and examples, you can demonstrate the validity of your viewpoint and make your essay more persuasive and compelling.
Using evidence involves citing relevant sources such as articles, books, or studies to back up your claims. These sources can provide factual information, expert opinions, or statistical data that support your arguments. By incorporating these sources into your essay, you show that your ideas are not just based on personal opinion, but are grounded in reliable and credible information.
In addition to using evidence, it is also important to use examples to illustrate your points. Examples can take the form of anecdotes, case studies, or real-life situations that help to clarify and emphasize your ideas. By using specific examples, you make your arguments more concrete and relatable to your readers.
When using evidence and examples in your response essay, it is crucial to ensure that they are relevant and directly support your main points. Avoid using unrelated or weak evidence that does not add value to your argument. Instead, focus on using evidence and examples that are strong, compelling, and directly related to the topic at hand.
Using evidence and examples effectively can greatly enhance the persuasiveness and impact of your response essay. By providing solid evidence and using relevant examples, you can strengthen your arguments and engage your readers, making your essay more convincing and thought-provoking.
Organize Your Thoughts and Ideas
When writing a response essay, it is important to structure your thoughts and ideas in a clear and logical manner. Without proper organization, your essay may lack coherence and fail to effectively convey your argument or analysis.
One way to organize your thoughts and ideas is by creating an outline. This allows you to visually map out the main points you want to make and establish a logical flow for your essay. Start by identifying the main thesis or argument of your response, and then break it down into subtopics or key supporting points.
Once you have established your outline, you can start drafting your essay. Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea or argument of that particular section. This will help guide your reader and ensure that your essay remains focused and cohesive.
In addition to creating an outline and using topic sentences, it is also important to use transitional words and phrases to connect your thoughts and ideas. This helps to establish a smooth flow between paragraphs and allows your reader to easily follow your train of thought.
Furthermore, consider organizing your essay using a structured format, such as the traditional introduction-body-conclusion format. This provides a clear framework for your essay and ensures that you cover all necessary points in a logical order.
Remember, organizing your thoughts and ideas is crucial for writing an effective response essay. By creating an outline, using topic sentences, utilizing transitional words and phrases, and employing a structured format, you can ensure that your essay is well-organized and effectively conveys your arguments and analysis.
Edit and Proofread Your Essay
Once you have completed the writing process for your response essay, it is crucial to edit and proofread your work before submitting it. This final step allows you to refine and polish your essay to ensure that it is clear, concise, and error-free.
Editing involves reviewing your essay for clarity and coherence. Read through your essay carefully, paying attention to the flow of your ideas and the logical progression of your arguments. Make sure that each paragraph is focused and supports your thesis statement. Consider the overall structure of your essay and make any necessary changes to enhance the organization and flow of your ideas.
Proofreading, on the other hand, focuses on eliminating grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and punctuation errors. Carefully go through your essay sentence by sentence, identifying any errors and correcting them. Pay attention to commonly confused words and ensure that you are using them correctly. Double-check the spelling of proper nouns and technical terms.
It can be helpful to read your essay aloud during the editing and proofreading process. This allows you to hear any awkward or unclear phrasing and make necessary revisions. Additionally, consider seeking feedback from others, such as peers or instructors, who can provide fresh perspectives and identify any areas that may need improvement.
Remember that editing and proofreading are essential steps in the writing process that should never be skipped. By taking the time to carefully review and revise your essay, you can ensure that it is effective and professional. Don’t underestimate the importance of attention to detail – it can make a significant difference in the overall quality of your essay.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
Critical Response Essay: Topics, Examples & How to Write
If you’ve ever read an exhaustive review of a movie or a book, you already know what a critical response essay looks like. This assignment requires you to reflect on a writing piece, film, play, or other art product. The point is to analyze the work and express your attitude toward its content and form.
This article will teach you how to write a critical response essay on different texts. You’ll also find some topic ideas and an example of this paper type.
🔤 What Is a Critical Response Essay?
💡 response essay topics.
- ✍️ How to Write a Critical Response
📝 Critical Response Essay Example
📚 more critical response examples, 🔗 references.
A critical response essay is a written assignment in which you should analyze someone’s work. The subject of your analysis can be a book, a piece of poetry , a short story, a scholarly article, a film, a song, and many more.
You might wonder what the “critical” part of a critical response essay means. It doesn’t imply that you should harshly judge the writing piece. Rather, you need to evaluate a text, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. For example, you can analyze whether the author used enough convincing evidence to support the main point.
A critical response essay usually includes the following elements: an introduction, summary, analysis, response, and conclusion.
| , introduces the text you will respond to, and includes a thesis statement with your main argument. | |
| Briefly retells the main ideas of the analyzed work. | |
| Evaluates different features of the text, such as its , structure, and content; includes quotes from the original piece. | |
| Presents your opinion on the text, e.g., whether the author effectively accomplished the writing purpose or how the text could be improved. | |
| Sums up the discussed points and links them to your |
The first step in creating an essay is to decide what to write about. Below you’ll find a list of interesting topics to inspire you. However, if none of these ideas meets your demands, you can try our topic generator.
- Is Shakespeare’s King Lear insane?
- Is peace or success more critical in The Great Gatsby by F. S. Fitzgerald?
- Allegory and symbolism in “ Everyday Use” by Alice Walker.
- Women’s challenges in “The Story of an Hour.”
- Ravenscroft’s use of irony in Careless Lovers to reveal society’s wrongs.
- The symbolic meaning of the devil in Hawthorne’s “Young Goodman Brown.”
- How did Tim O’Brien express the theme of morality in The Things They Carried ?
- The meaning of “hero” in The Things They Carried by Tim O’Brien.
- The American Dream in The Death of a Salesman .
- A caretaker’s conflict in “Daddy Issues ” by Sandra Tsing Loh.
- Was Hamlet’s revenge the right decision?
- Shakespeare’s Macbeth as a reference to the Christian fall of man.
- How did Mark Twain depict racism in The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn ?
- Would Hucklebery Finn make a good man?
- What is the tragedy in Sophocles’ Oedipus Rex ?
- What is the most acute issue highlighted in Nella Larsen’s Passing ?
- The press and the government in The Making of a Quagmire by David Halberstam.
- The Thousand and One Nights as a reflection of Middle East culture.
- Poverty in Oliver Twist by Charles Dickens.
- Gender issues raised in Othello by Shakespeare.
- Can The Glass Menagerie be considered a classical tragedy?
- The Chinese and American female characters in Joy Luck Club .
- The Epic of Gilgamesh : Can the opposites be partners?
- Egocentrism in “A Good Man Is Hard to Find.”
- The fragility of the family institution in Williams’ The Glass Menagerie .
- Does the book The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People answer how to achieve success?
- Franz Kafka’s “Metamorphosis” : Does Gregor Zamza deserve pity or compassion?
- The issue of a social outsider in “A Rose for Emily” by William Faulkner.
- “The Story of an Hour” : Is every marriage doomed?
- The god complex in Frankenstein by Mary Shelley.
✍️ How to Write a Critical Response Essay
A critical response essay has the following format:
- Introduction.
- Conclusion.
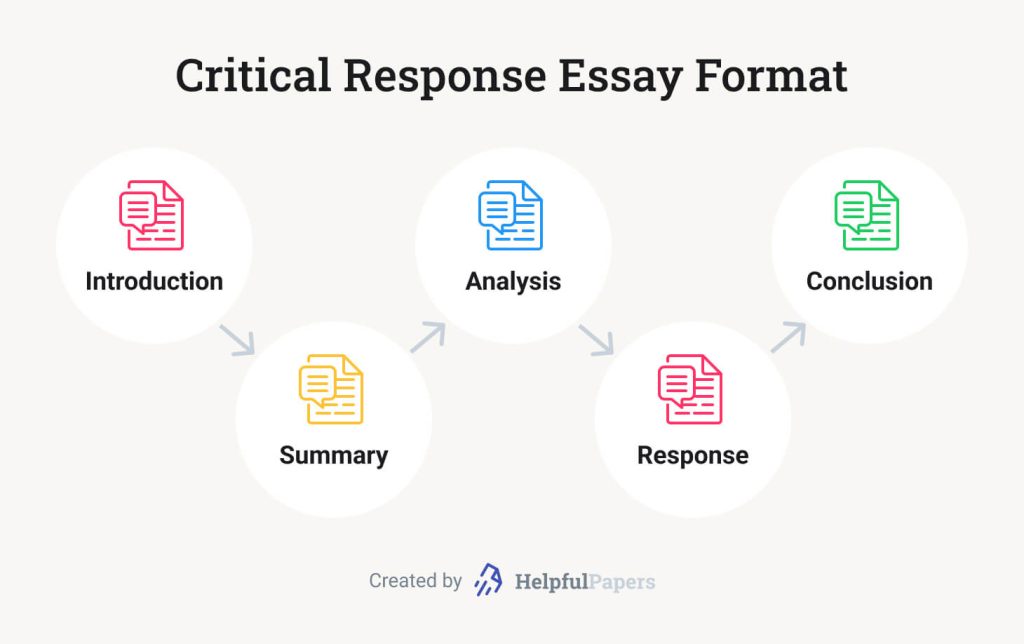
Below we will look at how to write a critical response essay step by step.
Critical Response Introduction
An introduction is your chance to make an excellent first impression on a reader. Here is a detailed breakdown of what it should include:
- Details about the analyzed work . In the first sentence, provide the author’s name and the title of the work you will write about.
- Relevant background information . Explain what the analyzed writing piece is about and provide the relevant context.
- The author’s thesis statement . Mention what argument the author makes and what key points are used to support it.
- Your thesis statement . The last sentence of your introduction should include your main argument about the analyzed work. Avoid simply agreeing or disagreeing with the author’s thesis. Instead, highlight the evaluated text’s strengths and weaknesses or focus on particular aspects, such as characters, style, literary devices, etc.
As the name implies, critical response summary part should summarize your selected work in a few paragraphs. Here are some tips for you to write this section:
- Explain the author’s purpose — why did they create this work?
- Summarize the author’s main points used to support the argument.
- Do not use direct quotes ; instead, paraphrase key points from the source.
- Do not provide your opinion — you’ll get a chance to do it in the later sections.
While the previous section looked at what the author wrote, this one will examine how the author expressed their point.
Here are some questions to guide your analysis. You should choose only those that fit your essay purpose and the analyzed piece:
- Has the author reached their writing goal (persuading, informing, explaining, etc.)?
- How unbiased and precise was the piece?
- What literary devices have you noticed?
- Were the author’s arguments strong enough?
- Are there any logical flaws in the writing?
- What is the author’s tone?
The analysis section should include direct quotes from the original text. They should be relevant to the point you make. After introducing a quotation, explain it and link it to your main argument.

Finally, you’ve reached the point where your opinion is required .
In this section, you should present your well-thought-out evaluation of the source. For example, if you’ve been analyzing an argumentative essay , explain whether you found it convincing enough and why. When assessing an informative article, say whether it gave you a good grasp of the topic and what particular text features made it simple for you to understand.
Consider these tips when writing a personal response section:
- Make sure you express your opinion to the fullest.
- Reflect on particular elements rather than an entire work.
- Use strong evidence to support your point of view.
- Organize your ideas in logical order.
- Tie your response to your thesis statement.
The conclusion of your critical analysis essay should include the following:
- Restated thesis. Start your final paragraph by paraphrasing your thesis statement.
- Summary of the points discussed. Remind the reader of your main ideas.
- Closing statement. Suggest a prompt that will make your readers think further about your argument.

Now, let’s look at a critical response essay example.
In his famous speech given at Stanford in 2005, Steeve Jobs gave valuable advice to Stanford graduates. The author’s main point is that if people want to accomplish their goals, they should be passionate. While I agree with this view, I will argue that one of the key themes permeating this speech is hope and faith.
The author shares three stories from his life. The first story is about dropping out of college. The second is about the lessons Jobs learned when he was fired from Apple. Finally, the third story deals with the author’s reflections on death.
While this talk is mainly about passion for one’s work, it also deals with the issues of hope and faith. This theme can be traced throughout the speech. For example, in the first story, Jobs says that people should “connect the dots.” It means that life is not a random sequence of events. Whatever difficulties arise, they serve some purpose, so people should never lose faith in a better future.
For me, this speech sounds hopeful and inspiring. I agree with Job’s view that passion is vital, but even more, I support his emphasis on the role of hope and faith. Jobs showed that his ability not to lose hope guided him through hard times. For example, Jobs’ dismissal was a devastating experience for him, but he realized that it was a new start for him, and he was able to move on.
In conclusion, hope and faith in a better future are one of the main themes of Jobs’ speech at Stanford. The speaker showed how being hopeful has helped him survive the darkest moments. Therefore, people should not give up whenever life throws challenges at them.
Do you want some more critical response examples? Below, we’ve included two sample responses to a non-fiction article and a fiction work. Check them out!
Critical Response to an Article Example
The following critical response example is based on an article published in Time. Check it out to learn how to respond to non-fiction.
In his article entitled "Conspiracy Theories, Class Tension, Political Intrigue," Maurice Samuels draws a parallel between the French government's mishandling of the cholera crisis in 1832 and the US government's response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Samuels believes that leadership failures increase societal tensions and create the way for political revolution. His analysis is a powerful reminder of the critical role that strong and united leadership plays in dealing with public health crises.
The article discusses the 1832 cholera outbreak in Paris, highlighting the government's ineffective response and the public's anger. It also examines the June Rebellion and the Duchesse de Berry's coup attempt, which failed because of public indifference. The author links the Paris cholera outbreak to the recent coronavirus pandemic in the US, arguing that leaders should prioritize transparency and openness to scientific advice.
On the one hand, the author emphasizes the importance of effective leadership and a unified response to public health crises, which makes this article relevant to the coronavirus situation in the US. On the other hand, the article could be more specific in analyzing the consequences of President Trump's actions, providing more examples of what a leader should do in a crisis.
I found the article both informative and thought-provoking. The author profoundly understands the history of epidemics and their impact on society. The article also raises important questions about leadership and public health policy. I agree with the author's conclusion that we need leaders who are willing to put the needs of their citizens first and who are not afraid to make tough decisions.
The article is a valuable contribution to discussing the pandemic and its broader societal implications. It highlights the importance of strong, united leadership in managing public health crises and preventing societal unrest. This article reminds us that even in an emergency, we must learn from our past mistakes to ensure a bright and healthy future.
Critical Response Paper Example for Fiction
Here, we have prepared a critical response essay to Fahrenheit 451 written by Ray Bradbury.
In Fahrenheit 451, Ray Bradbury outlines a dystopian future in which books are prohibited, and firemen are responsible for burning them. The novel warns about the dangers of censorship and the importance of freedom of speech. It raises questions about the role of government and the nature of knowledge and explores issues that are still relevant today.
The novel is about Guy Montag, a fireman who burns books for a living. Montag is a kind and polite man, but at the same time, he is unsatisfied with his job. He begins to doubt the government's policy of burning books and finally begins stealing and reading books secretly. He joins a group of rebels who teach him about the importance of books and the dangers of censorship. Eventually, Montag and the rebels defeat the government, establishing a society where books are allowed and people can think freely.
The novel effectively uses vivid imagery, symbols, and strong characters to create a suspenseful story. Bradbury's setting creates a familiar and strange world, with characters like Montag and others. However, the text still needs more depth and complexity in some characters, particularly the protagonist, Guy Montag.
I found Fahrenheit 451 an exciting and insightful novel since it allows the reader to rediscover the significance of reading through Montag's journey. I was particularly struck by the novel's depiction of censorship and the rebels' victory, which shows that it is possible to fight against censorship and preserve freedom of speech.
To summarize, Fahrenheit 451 is a well-written work that sends a message to humans about the value of knowledge and identity in a society that is easily corrupted by ignorance and censorship. The novel is still relevant in today’s world because it reminds us that the fight for free thought is an eternal one, waged not just on battlefields but in the quiet corners of every mind.
Other Critical Response Essay Examples
Find out other examples of critical responses below:
- Analysis of “Letter from Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King Jr. Essay Example
- “Why We Need Violent Video Games” by Gilsdorf Essay Example
- Mukherjee’s “Two Ways to Belong in America” Response Essay Example
- A Critical Appraisal of Two Qualitative Research Studies | Healthcare Paper Example
Now you know the secrets of writing an excellent critical response essay. So, feel free to start writing! Once you have done the assignment, listen to how your essay sounds with our text-to-speech tool. It will help you spot where your paper needs improvements.
- Guidelines for the Process for Critical Response | University of Michigan
- Writing a Response or Reaction Paper | Hunter College
- Writing Critical Analysis Papers | JSIS Writing Center
- Writing a Critical Response | University of Richmond
- Advice on Writing and Revising Critical Essays | Williams College
Film Analysis: Example, Format, and Outline + Topics & Prompts
Demoessays review: free political science essay samples.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Sample: Effective Response #1. The article could have been much more convincing if the author didn't begin most of his back-up arguments with "I", it gave the article a complaining and ranting tone, when an argument is explained like "a real course creates intellectual joy, at least in some.
Step by step tutorial on how to write a critical analysis essay with example thesis statement.
When developing your thesis statement, consider the following tips: 1. Identify the main topic or issue you will be responding to. 2. State your position or stance on the topic clearly and concisely. 3. Provide a brief preview of the key points or arguments you will present in your essay to support your thesis.
1. Introduction. The introductory paragraph in a critical response essay consists of two primary sections: a summary of an article and a thesis statement. Firstly, a summary of an article consists of the text's central argument and the purpose of the presentation of the argument (Davies, 2022).
The critical response essay displays the writer's reaction to a written work. By elaborating on the content of a book, article, or play, you should discuss the author's style and strategy for achieving the intended purpose. Ideally, the paper requires you to conduct a rhetorical analysis, interpret the text, and synthesize findings.
The Critical Response Essay is a multi-paragraph, multi-page essay that requires you to take one of your Critical Response Paragraphs and revise it to create a more complex and stronger argument. You should choose your best CRP or the one that most interests you. Focus on making it not only a longer argument, but also a better argument, using ...
A critical response essay can analyze a piece of nonfiction or fiction writing. For a fiction text, the writer could analyze features such as plot, characterization, setting, theme, point of view ...
It requires the highly valued academic skills of summarising and critical thought. It requires the ability to develop a clear and logical 'academic argument', which is extremely important for university and beyond. It is a relatively flexible genre, which is both challenging and useful for international students in terms of preparing them ...
Step 1. Examine the Primary Source. Before starting actually writing your critical essay, you need to get acquainted with the subject of your analysis. It might be an article, a book or any other type of text. Sometimes, this task is given for pieces of art, such as a painting or a movie. So, the first step would be to gain as much information ...
See all the different steps in action to make writing a response essay a breeze. Get an outline of the process for how to write a response essay from the prewriting to the final piece. See all the different steps in action to make writing a response essay a breeze. ... give it a critical listen, viewing, or read. For example, for a song, listen ...
work to help each other hone critical reading and writing skills. Peer response is particularly helpful in writing and speaking intensive courses. Contents: 1. Peer response on writing Benefits of peer response—1 Options for Peer Response—1 2. Preparing students for peer response The most effective peer response—2 Running an in-class ...
Critical response essays involved summarizing and analyzing another author's work. A specific format is used when writing such essays. The essay begins with an introduction to the text studies ...
Step 2. Artist as Questioner. The artist asks questions about the work. In answering, responders stay on topic with the question and may express opinions in direct response to the artist's questions. Step 3. Neutral Questions. Responders ask neutral questions about the work, and the artist responds.
This method is different from a reader-response method. While many workshops require the writer to remain quiet while the readers provide feedback, the goal of the Process for Critical Response is to foster a conversation centered around neutral questions and to give the writer more control of the workshop by requiring that the audience members ...
USING PEER REVIEW TO IMPROVE STUDENT WRITING . SUPPLEMENT 8: GUIDELINES FOR THE PROCESS FOR CRITICAL RESPONSE . Guidelines for the Process for Critical Response . This method of giving feedback was developed for the performance arts discipline. It promotes a dialogue-oriented workshop that helps writers to generate ideas for further developing ...
In Essay Writing 201: Critical Response Essay, students. get into the center of the reading and writing experience; read purposefully, identifying main points and arguments; decipher images in the news; separate how a text is written from what it's written about; receive feedback showing that their thoughts and reactions matter
Critical Reflection. A Critical Reflection (also called a reflective essay) is a process of identifying, questioning, and assessing our deeply-held assumptions - about our knowledge, the way we perceive events and issues, our beliefs, feelings, and actions. When you reflect critically, you use course material (lectures, readings, discussions ...
5. Revise and refine: Continuously evaluate and revise your thesis statement as you develop your essay, ensuring that it accurately reflects your analysis. By formulating a clear thesis statement, you establish a strong foundation for your response essay and provide readers with a clear roadmap of your analysis.
Critical Response Essays: To become a good writer of poetry, you must first be an informed and engaged reader of poetry. To that end, you will be asked to write four 750-word critical response essays. Your response should be a considered critique of the poem in question, paying particular attention to the poetic devices/strategies discussed in ...
Other Critical Response Essay Examples. Find out other examples of critical responses below: Analysis of "Letter from Birmingham Jail" by Martin Luther King Jr. Essay Example. "Why We Need Violent Video Games" by Gilsdorf Essay Example. Mukherjee's "Two Ways to Belong in America" Response Essay Example.
ENG 100 Instructor regarding your paper. You will receive personal responses and suggestions to help you develop and revise each essay and to help you grow as a writer. You will also be allowed time, in workshop, to write and revise. All of these activities are designed to give you more experience with writing, increasing your fluency, critical ...