

The Peak Performance Center
The pursuit of performance excellence, thinking skills.
Thinking skills are the mental activities you use to process information, make connections, make decisions, and create new ideas. You use your thinking skills when you try to make sense of experiences, solve problems, make decisions, ask questions, make plans, or organize information.
Everybody has thinking skills, but not everyone uses them effectively. Effective thinking skills are developed over a period of time. Good thinkers see possibilities where others see only obstacles or roadblocks. Good thinkers are able to make connection between various factors and be able to tie them together. They are also able to develop new and unique solutions to problems.
Thinking refers to the process of creating a logical series of connective facets between items of information. Often times, thinking just happens automatically. However, there are times when you consciously think. It may be about how to solve a problem or making a decision. Thinking enables you to connect and integrate new experiences into your existing understanding and perception of how things are.
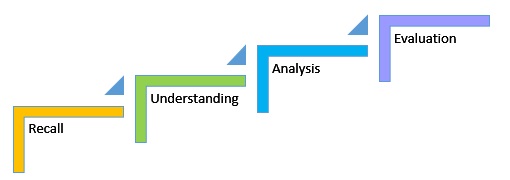
The simplest thinking skills are learning facts and recall, while higher order skills include analysis, synthesis, problem solving, and evaluation .
Core Thinking Skills
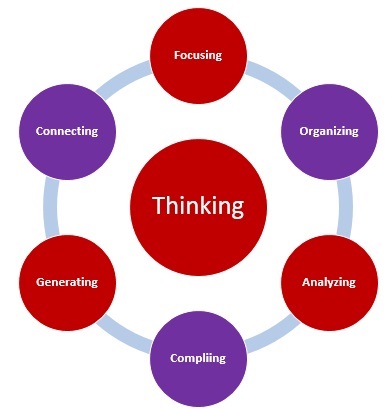
Thinking skills are cognitive operations or processes that are the building blocks of thinking. There are several core thinking skills including focusing, organizing, analyzing, evaluating and generating.
Focusing – attending to selected pieces of information while ignoring other stimuli.
Remembering – storing and then retrieving information.
Gathering – bringing to the conscious mind the relative information needed for cognitive processing.
Organizing – arranging information so it can be used more effectively.
Analyzing – breaking down information by examining parts and relationships so that its organizational structure may be understood.
Connecting – making connections between related items or pieces of information.
Integrating – connecting and combining information to better understand the relationship between the information.
Compiling – putting parts together to form a whole or building a structure or pattern from diverse elements.
Evaluating – assessing the reasonableness and quality of ideas or materials on order to present and defend opinions.
Generating – producing new information, ideas, products, or ways of viewing things.
Classifications and Types of Thinking
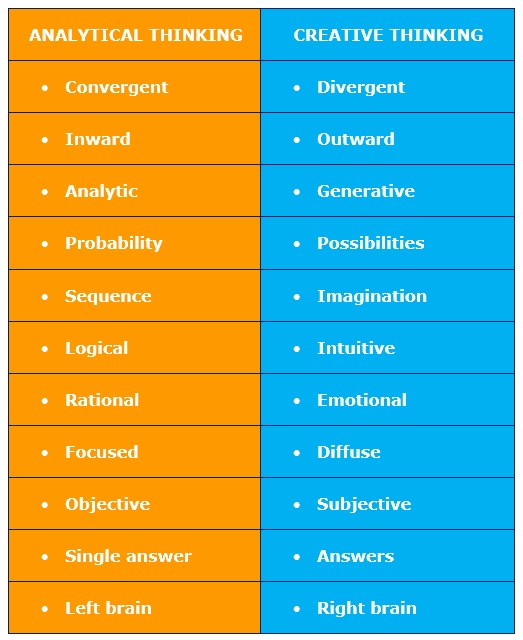
Convergent or Analytical Thinking: Bringing facts and data together from various sourc es and then applying logic and knowledge to solve problems or to make informed decisions.
Divergent thinking: Breaking a topic apart to explore its various components and then generating new ideas and solutions.
Critical Thinking: Analysis and evaluation of information, beliefs, or knowledge.
Creative Thinking: Generation of new ideas breaking from established thoughts, theories, rules, and procedures.
Metacognition
Thinking about thinking is called Metacognition. It is a higher order thinking that enables understanding, analysis, and control of your cognitive processes. It can involve planning, monitoring, assessing, and evaluating your use of your cognitive skills.
In the simplest form, convergent thinking or deductive reasoning looks inward to find a solution, while divergent or creative thinking looks outward for a solution.
Both thinking skills are essential for school and life. Both require critical thinking skills to be effective. Both are used for solving problems, doing projects and achieving objectives. However, much of the thinking in formal education focuses on the convergent analytical thinking skills such as following or making a logical argument, eliminating the incorrect paths and then figuring out the single correct answer.
Standardized tests such as IQ tests only measure convergent thinking. Pattern recognition, logic thought flow, and the ability to solve problems with a single answer can all be tested and graded. Although it is an extremely valuable skill, there are no accurate tests able to measure divergent or creative thinking skills.
Types of thinking
Critical thinking
Blooms Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy Revised
Mind Mapping
Chunking Information
Brainstorming
Critical Thinking skills
Divergent and Convergent thinking skills are both “critical thinking” skills.
Critical thinking refers to the process of actively analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating and reflecting on information gathered from observation, experience, or communication and is focused on deciding what to believe or do. Critical thinking is considered a higher order thinking skills, such as analysis, synthesis, and problem solving, inference, and evaluation.
The concept of higher order thinking skills became well known with the publication of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. Bloom’s Taxonomy was primarily created for academic education; however, it is relevant to all types of learning.
Often times when people are problem solving or decision making, he or she flips back and forth between convergent and divergent thinking. When first looking at a problem, people often analyze the facts and circumstances to determine the root cause. After which, they explore new and innovative options through divergent thinking, then switch back to convergent thinking to limit those down to one practical option.
Author: James Kelly, September 2011

Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

What is Coaching?
Types of Coaching
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

How to develop critical thinking skills

Jump to section
What are critical thinking skills?
How to develop critical thinking skills: 12 tips, how to practice critical thinking skills at work, become your own best critic.
A client requests a tight deadline on an intense project. Your childcare provider calls in sick on a day full of meetings. Payment from a contract gig is a month behind.
Your day-to-day will always have challenges, big and small. And no matter the size and urgency, they all ask you to use critical thinking to analyze the situation and arrive at the right solution.
Critical thinking includes a wide set of soft skills that encourage continuous learning, resilience , and self-reflection. The more you add to your professional toolbelt, the more equipped you’ll be to tackle whatever challenge presents itself. Here’s how to develop critical thinking, with examples explaining how to use it.
Critical thinking skills are the skills you use to analyze information, imagine scenarios holistically, and create rational solutions. It’s a type of emotional intelligence that stimulates effective problem-solving and decision-making .
When you fine-tune your critical thinking skills, you seek beyond face-value observations and knee-jerk reactions. Instead, you harvest deeper insights and string together ideas and concepts in logical, sometimes out-of-the-box , ways.
Imagine a team working on a marketing strategy for a new set of services. That team might use critical thinking to balance goals and key performance indicators , like new customer acquisition costs, average monthly sales, and net profit margins. They understand the connections between overlapping factors to build a strategy that stays within budget and attracts new sales.
Looking for ways to improve critical thinking skills? Start by brushing up on the following soft skills that fall under this umbrella:
- Analytical thinking: Approaching problems with an analytical eye includes breaking down complex issues into small chunks and examining their significance. An example could be organizing customer feedback to identify trends and improve your product offerings.
- Open-mindedness: Push past cognitive biases and be receptive to different points of view and constructive feedback . Managers and team members who keep an open mind position themselves to hear new ideas that foster innovation .
- Creative thinking: With creative thinking , you can develop several ideas to address a single problem, like brainstorming more efficient workflow best practices to boost productivity and employee morale .
- Self-reflection: Self-reflection lets you examine your thinking and assumptions to stimulate healthier collaboration and thought processes. Maybe a bad first impression created a negative anchoring bias with a new coworker. Reflecting on your own behavior stirs up empathy and improves the relationship.
- Evaluation: With evaluation skills, you tackle the pros and cons of a situation based on logic rather than emotion. When prioritizing tasks , you might be tempted to do the fun or easy ones first, but evaluating their urgency and importance can help you make better decisions.
There’s no magic method to change your thinking processes. Improvement happens with small, intentional changes to your everyday habits until a more critical approach to thinking is automatic.
Here are 12 tips for building stronger self-awareness and learning how to improve critical thinking:
1. Be cautious
There’s nothing wrong with a little bit of skepticism. One of the core principles of critical thinking is asking questions and dissecting the available information. You might surprise yourself at what you find when you stop to think before taking action.
Before making a decision, use evidence, logic, and deductive reasoning to support your own opinions or challenge ideas. It helps you and your team avoid falling prey to bad information or resistance to change .
2. Ask open-ended questions
“Yes” or “no” questions invite agreement rather than reflection. Instead, ask open-ended questions that force you to engage in analysis and rumination. Digging deeper can help you identify potential biases, uncover assumptions, and arrive at new hypotheses and possible solutions.
3. Do your research
No matter your proficiency, you can always learn more. Turning to different points of view and information is a great way to develop a comprehensive understanding of a topic and make informed decisions. You’ll prioritize reliable information rather than fall into emotional or automatic decision-making.

4. Consider several opinions
You might spend so much time on your work that it’s easy to get stuck in your own perspective, especially if you work independently on a remote team . Make an effort to reach out to colleagues to hear different ideas and thought patterns. Their input might surprise you.
If or when you disagree, remember that you and your team share a common goal. Divergent opinions are constructive, so shift the focus to finding solutions rather than defending disagreements.
5. Learn to be quiet
Active listening is the intentional practice of concentrating on a conversation partner instead of your own thoughts. It’s about paying attention to detail and letting people know you value their opinions, which can open your mind to new perspectives and thought processes.
If you’re brainstorming with your team or having a 1:1 with a coworker , listen, ask clarifying questions, and work to understand other peoples’ viewpoints. Listening to your team will help you find fallacies in arguments to improve possible solutions.
6. Schedule reflection
Whether waking up at 5 am or using a procrastination hack, scheduling time to think puts you in a growth mindset . Your mind has natural cognitive biases to help you simplify decision-making, but squashing them is key to thinking critically and finding new solutions besides the ones you might gravitate toward. Creating time and calm space in your day gives you the chance to step back and visualize the biases that impact your decision-making.
7. Cultivate curiosity
With so many demands and job responsibilities, it’s easy to seek solace in routine. But getting out of your comfort zone helps spark critical thinking and find more solutions than you usually might.
If curiosity doesn’t come naturally to you, cultivate a thirst for knowledge by reskilling and upskilling . Not only will you add a new skill to your resume , but expanding the limits of your professional knowledge might motivate you to ask more questions.
You don’t have to develop critical thinking skills exclusively in the office. Whether on your break or finding a hobby to do after work, playing strategic games or filling out crosswords can prime your brain for problem-solving.

9. Write it down
Recording your thoughts with pen and paper can lead to stronger brain activity than typing them out on a keyboard. If you’re stuck and want to think more critically about a problem, writing your ideas can help you process information more deeply.
The act of recording ideas on paper can also improve your memory . Ideas are more likely to linger in the background of your mind, leading to deeper thinking that informs your decision-making process.
10. Speak up
Take opportunities to share your opinion, even if it intimidates you. Whether at a networking event with new people or a meeting with close colleagues, try to engage with people who challenge or help you develop your ideas. Having conversations that force you to support your position encourages you to refine your argument and think critically.
11. Stay humble
Ideas and concepts aren’t the same as real-life actions. There may be such a thing as negative outcomes, but there’s no such thing as a bad idea. At the brainstorming stage , don’t be afraid to make mistakes.
Sometimes the best solutions come from off-the-wall, unorthodox decisions. Sit in your creativity , let ideas flow, and don’t be afraid to share them with your colleagues. Putting yourself in a creative mindset helps you see situations from new perspectives and arrive at innovative conclusions.
12. Embrace discomfort
Get comfortable feeling uncomfortable . It isn’t easy when others challenge your ideas, but sometimes, it’s the only way to see new perspectives and think critically.
By willingly stepping into unfamiliar territory, you foster the resilience and flexibility you need to become a better thinker. You’ll learn how to pick yourself up from failure and approach problems from fresh angles.

Thinking critically is easier said than done. To help you understand its impact (and how to use it), here are two scenarios that require critical thinking skills and provide teachable moments.

Scenario #1: Unexpected delays and budget
Imagine your team is working on producing an event. Unexpectedly, a vendor explains they’ll be a week behind on delivering materials. Then another vendor sends a quote that’s more than you can afford. Unless you develop a creative solution, the team will have to push back deadlines and go over budget, potentially costing the client’s trust.
Here’s how you could approach the situation with creative thinking:
- Analyze the situation holistically: Determine how the delayed materials and over-budget quote will impact the rest of your timeline and financial resources . That way, you can identify whether you need to build an entirely new plan with new vendors, or if it’s worth it to readjust time and resources.
- Identify your alternative options: With careful assessment, your team decides that another vendor can’t provide the same materials in a quicker time frame. You’ll need to rearrange assignment schedules to complete everything on time.
- Collaborate and adapt: Your team has an emergency meeting to rearrange your project schedule. You write down each deliverable and determine which ones you can and can’t complete by the deadline. To compensate for lost time, you rearrange your task schedule to complete everything that doesn’t need the delayed materials first, then advance as far as you can on the tasks that do.
- Check different resources: In the meantime, you scour through your contact sheet to find alternative vendors that fit your budget. Accounting helps by providing old invoices to determine which vendors have quoted less for previous jobs. After pulling all your sources, you find a vendor that fits your budget.
- Maintain open communication: You create a special Slack channel to keep everyone up to date on changes, challenges, and additional delays. Keeping an open line encourages transparency on the team’s progress and boosts everyone’s confidence.

Scenario #2: Differing opinions
A conflict arises between two team members on the best approach for a new strategy for a gaming app. One believes that small tweaks to the current content are necessary to maintain user engagement and stay within budget. The other believes a bold revamp is needed to encourage new followers and stronger sales revenue.
Here’s how critical thinking could help this conflict:
- Listen actively: Give both team members the opportunity to present their ideas free of interruption. Encourage the entire team to ask open-ended questions to more fully understand and develop each argument.
- Flex your analytical skills: After learning more about both ideas, everyone should objectively assess the benefits and drawbacks of each approach. Analyze each idea's risk, merits, and feasibility based on available data and the app’s goals and objectives.
- Identify common ground: The team discusses similarities between each approach and brainstorms ways to integrate both idea s, like making small but eye-catching modifications to existing content or using the same visual design in new media formats.
- Test new strategy: To test out the potential of a bolder strategy, the team decides to A/B test both approaches. You create a set of criteria to evenly distribute users by different demographics to analyze engagement, revenue, and customer turnover.
- Monitor and adapt: After implementing the A/B test, the team closely monitors the results of each strategy. You regroup and optimize the changes that provide stronger results after the testing. That way, all team members understand why you’re making the changes you decide to make.
You can’t think your problems away. But you can equip yourself with skills that help you move through your biggest challenges and find innovative solutions. Learning how to develop critical thinking is the start of honing an adaptable growth mindset.
Now that you have resources to increase critical thinking skills in your professional development, you can identify whether you embrace change or routine, are open or resistant to feedback, or turn to research or emotion will build self-awareness. From there, tweak and incorporate techniques to be a critical thinker when life presents you with a problem.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
What is lateral thinking? 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas
Critical thinking is the one skillset you can't afford not to master, how divergent thinking can drive your creativity, what’s convergent thinking how to be a better problem-solver, the power of professional learning communities, 8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems, how different learning styles make a difference at work, what are analytical skills examples and how to level up, can dreams help you solve problems 6 ways to try, betterup named a 2019 “cool vendor” in human capital management: enhancing employee experience by gartnerup your game: a new model for leadership, 7 critical teamwork skills and how to develop them, what is creative thinking and how can i improve, 6 big picture thinking strategies that you'll actually use, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case studies
- ROI of BetterUp
- What is coaching?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Briefing
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Related Articles
How to Spot Fake News
Information Gathering
Business Reports
Good Charts and Good Charts Workbook
How to Use Gantt Charts
Article • 8 min read
Critical Thinking
Developing the right mindset and skills.
Written by the Mind Tools Content Team
We make hundreds of decisions every day and, whether we realize it or not, we're all critical thinkers.
We use critical thinking each time we weigh up our options, prioritize our responsibilities, or think about the likely effects of our actions. It's a crucial skill that helps us to cut out misinformation and make wise decisions. The trouble is, we're not always very good at it!
In this article, we'll explore the key skills that you need to develop your critical thinking skills, and how to adopt a critical thinking mindset, so that you can make well-informed decisions.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well.
Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly valued asset in the workplace. People who score highly in critical thinking assessments are also rated by their managers as having good problem-solving skills, creativity, strong decision-making skills, and good overall performance. [1]
Key Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinkers possess a set of key characteristics which help them to question information and their own thinking. Focus on the following areas to develop your critical thinking skills:
Being willing and able to explore alternative approaches and experimental ideas is crucial. Can you think through "what if" scenarios, create plausible options, and test out your theories? If not, you'll tend to write off ideas and options too soon, so you may miss the best answer to your situation.
To nurture your curiosity, stay up to date with facts and trends. You'll overlook important information if you allow yourself to become "blinkered," so always be open to new information.
But don't stop there! Look for opposing views or evidence to challenge your information, and seek clarification when things are unclear. This will help you to reassess your beliefs and make a well-informed decision later. Read our article, Opening Closed Minds , for more ways to stay receptive.
Logical Thinking
You must be skilled at reasoning and extending logic to come up with plausible options or outcomes.
It's also important to emphasize logic over emotion. Emotion can be motivating but it can also lead you to take hasty and unwise action, so control your emotions and be cautious in your judgments. Know when a conclusion is "fact" and when it is not. "Could-be-true" conclusions are based on assumptions and must be tested further. Read our article, Logical Fallacies , for help with this.
Use creative problem solving to balance cold logic. By thinking outside of the box you can identify new possible outcomes by using pieces of information that you already have.
Self-Awareness
Many of the decisions we make in life are subtly informed by our values and beliefs. These influences are called cognitive biases and it can be difficult to identify them in ourselves because they're often subconscious.
Practicing self-awareness will allow you to reflect on the beliefs you have and the choices you make. You'll then be better equipped to challenge your own thinking and make improved, unbiased decisions.
One particularly useful tool for critical thinking is the Ladder of Inference . It allows you to test and validate your thinking process, rather than jumping to poorly supported conclusions.
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
Combine the above skills with the right mindset so that you can make better decisions and adopt more effective courses of action. You can develop your critical thinking mindset by following this process:
Gather Information
First, collect data, opinions and facts on the issue that you need to solve. Draw on what you already know, and turn to new sources of information to help inform your understanding. Consider what gaps there are in your knowledge and seek to fill them. And look for information that challenges your assumptions and beliefs.
Be sure to verify the authority and authenticity of your sources. Not everything you read is true! Use this checklist to ensure that your information is valid:
- Are your information sources trustworthy ? (For example, well-respected authors, trusted colleagues or peers, recognized industry publications, websites, blogs, etc.)
- Is the information you have gathered up to date ?
- Has the information received any direct criticism ?
- Does the information have any errors or inaccuracies ?
- Is there any evidence to support or corroborate the information you have gathered?
- Is the information you have gathered subjective or biased in any way? (For example, is it based on opinion, rather than fact? Is any of the information you have gathered designed to promote a particular service or organization?)
If any information appears to be irrelevant or invalid, don't include it in your decision making. But don't omit information just because you disagree with it, or your final decision will be flawed and bias.
Now observe the information you have gathered, and interpret it. What are the key findings and main takeaways? What does the evidence point to? Start to build one or two possible arguments based on what you have found.
You'll need to look for the details within the mass of information, so use your powers of observation to identify any patterns or similarities. You can then analyze and extend these trends to make sensible predictions about the future.
To help you to sift through the multiple ideas and theories, it can be useful to group and order items according to their characteristics. From here, you can compare and contrast the different items. And once you've determined how similar or different things are from one another, Paired Comparison Analysis can help you to analyze them.
The final step involves challenging the information and rationalizing its arguments.
Apply the laws of reason (induction, deduction, analogy) to judge an argument and determine its merits. To do this, it's essential that you can determine the significance and validity of an argument to put it in the correct perspective. Take a look at our article, Rational Thinking , for more information about how to do this.
Once you have considered all of the arguments and options rationally, you can finally make an informed decision.
Afterward, take time to reflect on what you have learned and what you found challenging. Step back from the detail of your decision or problem, and look at the bigger picture. Record what you've learned from your observations and experience.
Critical thinking involves rigorously and skilfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions and beliefs. It's a useful skill in the workplace and in life.
You'll need to be curious and creative to explore alternative possibilities, but rational to apply logic, and self-aware to identify when your beliefs could affect your decisions or actions.
You can demonstrate a high level of critical thinking by validating your information, analyzing its meaning, and finally evaluating the argument.
Critical Thinking Infographic
See Critical Thinking represented in our infographic: An Elementary Guide to Critical Thinking .

This premium resource is exclusive to Mind Tools Members.
To continue, you will need to either login or join Mind Tools.
Our members enjoy unparalleled access to thousands of training resources, covering a wide range of topics, all designed to help you develop your management and leadership skills
Already a member? Login now
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Key Management Skills
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Pain Points Podcast - Fearless Feedback

NEW! Pain Points - Data Stories
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Creating successful strategic plans.
The Context of Strategic Planning Key Ideas for Creating a Good Strategic Plan Today
The Psychological Contract
Meeting your team's unspoken expectations
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Managing poor performance.
A view from an expert panel
Expert Interviews
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Member Newsletter
Introducing the Management Skills Framework
Transparent Communication
Social Sensitivity
Self-Awareness and Self-Regulation
Team Goal Setting
Recognition
Inclusivity
Active Listening

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In short, the ability to think critically is the art of analyzing and evaluating data for a practical approach to understanding the data, then determining what to believe and how to act.
Critical thinking is important for making judgments about sources of information and forming your own arguments. It emphasizes a rational, objective, and self-aware approach …
There are six main critical thinking skills you can develop to successfully analyze facts and situations and come up with logical conclusions: 1. Analytical thinking. Being able to properly analyze information is the most …
Critical thinking is a kind of thinking in which you question, analyse, interpret, evaluate and make a judgement about what you read, hear, say, or write. The term critical comes from the Greek word kritikos meaning “able to judge or …
Here’s how to develop critical thinking, with examples explaining how to use it. What are critical thinking skills? Critical thinking skills are the skills you use to analyze information, imagine scenarios holistically, and create rational solutions.
What is critical thinking and why is it important? Discover key thinking skills that enable you to test assumptions and make better decisions.