- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.

General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.

100 Words and Phrases to use in an Essay
Thomas Babb
Writing a compelling essay involves much more than simply putting your thoughts on paper. It demands the use of a precise vocabulary that not only enriches your content but also structures it in a way that is both logical and engaging. The right words and phrases can transform your essay from a basic assignment to an insightful and persuasive piece of writing.
This guide introduces you to 100 essential words and phrases recommended by expert English tutors that will help you convey your ideas more effectively. From adding information to expressing contrasts, and from illustrating examples to summarising your points, these carefully selected terms will enhance the clarity and impact of your essays.
Adding Information
When crafting an essay, integrating additional details effectively can enrich the written content and present a well-rounded argument. Here's how you can use each phrase under this category:
1. Furthermore - Use this to add weight to a point already mentioned, providing further evidence without redundancy.
2. Moreover - Similar to "furthermore," it introduces information that not only adds to the argument but enhances it.
3. Similarly - This indicates that the upcoming point shares notable characteristics with the previous one, aiding in drawing parallels.
4. Additionally - Introduces extra information or arguments that augment the current discussion.
5. Also - A simpler form of "additionally" that integrates extra facts smoothly.
6. Likewise - Indicates similarity and supports points by showing how they relate to each other in terms of qualities or actions.
7. In addition - This phrase is useful for contributing additional supportive details in a clear manner.
8. As well as - Functions to include another subject or item into your discussion without diverging from the main topic.
9. Not only... but also - A powerful structure for emphasizing not just one, but two important points, enhancing the depth of the argument.
10. Alongside - Implies that the information being added runs parallel to the already established facts, reinforcing them.
These phrases, when used correctly, help to build a strong, cohesive narrative flow in your essays, guiding the reader through a logical progression of ideas. For more on enhancing your writing with effective information addition, explore resources like Oxford Royale's Essay Writing Tips .
Introducing Examples
Introducing concrete examples is crucial in illustrating and supporting your claims effectively in an essay. Here’s how to use each word or phrase linked to this category:
11. For instance - Introduces a specific example that illuminates a broader point, helping to clarify complex ideas.
12. For example - Functions similarly to "for instance," offering a direct illustration to support or demonstrate a claim.
13. Such as - Prepares the reader for an example that is part of a larger category, typically used to list items or concepts.
14. Like - Introduces comparisons or examples in a casual and relatable manner.
15. Particularly - Highlights an example that is especially relevant to the argument, focusing attention on significant details.
16. In particular - Similar to "particularly," but often used to introduce a standout example that underscores a critical point.
17. Including - Serves to add examples to a list that may already be understood to be part of the topic being discussed.
18. Namely - Specifies and introduces exact and often multiple examples or details directly related to the point.
19. Chiefly - Points to the most important or significant examples or reasons in support of an argument.
20. Mainly - Indicates that the examples provided are the primary ones to consider, focusing on the most relevant instances.
Effective use of these phrases not only clarifies your points but also strengthens your arguments by making abstract concepts tangible. For detailed guidance on how to incorporate examples effectively in your essays, refer to academic resources like Harvard College Writing Center .
Demonstrating Contrast
IB English tutors suggest that Using contrast effectively in your essays can highlight differences that clarify your points or show alternative perspectives. Here’s how to use each phrase to demonstrate contrast:
21. Conversely - Signals a stark contrast to what has just been discussed, often introducing an opposing viewpoint.
22. However - A versatile tool to introduce a contradiction or counterpoint, breaking from the previous line of reasoning.
23. Nevertheless - Indicates persistence of a stated fact or opinion despite the contrasting information that follows.
24. On the other hand - Used to present a different perspective or an alternative to the argument previously mentioned.
25. Although - Begins a sentence where the main clause contrasts with the lesser significant, conditional clause.
26. Even though - Similar to "although," but often emphasizes a stronger degree of contrast between the conflicting elements.
27. But - A simple and direct way to introduce a contradiction to the preceding statement.
28. Yet - Suggests a contrast that is surprising or unexpected based on the previous statements.
29. Instead - Introduces an alternative action or thought in response to what has been previously discussed.
30. Rather - Used to correct or propose a different idea from what was initially stated or understood.
These phrases are essential for essays where comparing and contrasting ideas, arguments, or perspectives is necessary to deepen understanding or enhance the argument’s complexity. To learn more about using contrast in writing, visit educational resources such as Purdue Online Writing Lab .
Showing Cause and Effect
A-Level English tutors point out that effectively indicating cause and effect relationships in your essays helps clarify the reasons things happen and the consequences that follow. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to illustrate these relationships:
31. Consequently - Signals a direct result from the action or situation mentioned, highlighting the effect or outcome.
32. Therefore - Used to introduce a logical conclusion or result that follows from the reasoning presented earlier.
33. Thus - Indicates a conclusion or result that is a natural consequence of the facts previously mentioned.
34. Hence - Similar to "thus," it conveys a consequence that is a logical extension from the argument or data presented.
35. Accordingly - Shows that an action or decision is a logical response to the circumstances or facts discussed.
36. As a result - Directly points out the outcome or effect resulting from a specific cause or set of conditions.
37. This leads to - Introduces a sequence where one event or fact causes another, often used to chain multiple effects.
38. It follows that - Used when deducing a conclusion that logically arises from the preceding argument or evidence.
39. Leading to - Connects an initial action or decision directly with its consequences, highlighting a progression of events.
40. Contributing to - Indicates that the action or event adds to a situation, leading to a particular result or effect.
Mastering the use of these phrases can enhance the persuasive power of your writing by clearly linking actions and their consequences.
Adding Emphasis
Effectively emphasising key points in your essays can make your arguments more compelling and memorable. Here’s how to appropriately use each word or phrase to add emphasis:
41. Significantly - Indicates that something is of great importance or consequence, drawing the reader's attention to the gravity of the point being made.
42. Importantly - Prioritises the following information as crucial for understanding the argument or situation.
43. Indeed - Reinforces the truth of a statement, often used to confirm and agree with a previously mentioned point that might be surprising or emphatic.
44. Absolutely - A strong affirmation that leaves no doubt about the veracity or importance of the statement.
45. Definitely - Communicates certainty about a fact or opinion, strengthening the author's stance.
46. Certainly - Similar to "definitely," it expresses a high degree of assurance about the information being provided.
47. Undoubtedly - Suggests that there is no doubt about the statement, reinforcing its truth and relevance.
48. Without a doubt - A more emphatic form of "undoubtedly," eliminating any ambiguity about the point’s validity.
49. Particularly - Highlights specific information as especially significant within a broader context.
50. Especially - Used to indicate that something holds more significance than other elements, often emphasizing exceptional cases or instances.
Using these expressions strategically can enhance the persuasive impact of your writing by underscoring the most critical elements of your argument. To see more words and further explore techniques for adding emphasis in academic writing, visit resources like Cambridge Dictionary Blog .
Explaining and Clarifying
In academic essays, clearly explaining and clarifying complex ideas is essential for effective communication. IGCSE tutors and GCSE tutors suggest that each of these phrases can be used to enhance understanding:
51. That is to say - Used to introduce a rephrasing or elaboration on something that has just been stated.
52. In other words - Helps clarify a statement by expressing it in different terms for better understanding.
53. To put it another way - Similar to "in other words," it offers an alternative explanation or perspective to ensure clarity.
54. To clarify - Directly states the intent to make something clearer or to resolve any misunderstandings.
55. To explain - Introduces a detailed explanation aimed at enhancing understanding of a complex issue or point.
56. This means that - Connects a statement or idea to its implications or necessary interpretations.
57. This implies - Suggests a deeper, often unspoken consequence or meaning behind the given information.
58. Put simply - Introduces a simpler or more straightforward version of what has been discussed, making it more accessible.
59. In simpler terms - Another phrase to ease comprehension by breaking down complex concepts into basic language.
60. Thus - Concludes an explanation by summarizing the logical result or conclusion derived from the argument made.
Using these phrases effectively can help articulate intricate arguments in a more digestible format, aiding the reader’s understanding and engagement.
Summarising and Concluding
Expert IB tutors and A-Level tutors recommend that effectively summarising and concluding your essays is crucial for reinforcing your main points and providing a satisfying closure to any persuasive essay. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to effectively wrap up your discussions:
61. In conclusion - Signals the beginning of the final summary, clearly stating that the argument is drawing to a close.
62. To sum up - Introduces a concise summary of the key points discussed, often used before the final conclusion.
63. Ultimately - Indicates a final, overarching conclusion derived from the arguments and evidence presented.
64. Finally - Marks the introduction of the last point or an additional important point that concludes the discussion.
65. Lastly - Similar to "finally," it is used to introduce the final argument or point in the list.
66. To conclude - Directly states the intent to wrap up the essay, leading into a summary of the main findings.
67. In summary - Offers a recap of the essential elements discussed, reinforcing the thesis without introducing new information.
68. All things considered - Provides an overall conclusion, taking into account all the points made throughout the essay.
69. In the final analysis - Suggests a thorough consideration of all aspects discussed, leading to a concluding viewpoint.
70. After all - Implies that the conclusion takes into account all arguments and evidences previously presented.
Mastering the use of these concluding phrases ensures that your essay ends on a strong note, summarising key points and reinforcing your argument.
Discussing Similarities
Highlighting similarities effectively can enhance your argument by showing connections and parallels between ideas or topics. Here’s how to use each phrase to discuss similarities in your essays:
71. Similarly - Indicates that what follows is in alignment with the previous statement, reinforcing the connection between two points.
72. Likewise - Also used to show agreement or similarity, it confirms that the upcoming point supports the previous one in terms of characteristics or outcomes.
73. Just as - Introduces a comparison, suggesting that the situation or argument is equivalent to another.
74. As with - Used before mentioning another example, indicating that it shares properties or conditions with what has been discussed.
75. Equally - Implies that two or more elements are on the same level in terms of importance, quality, or characteristics.
76. Analogous to - Introduces a more formal comparison, indicating that one situation is comparable to another, often used in more scientific or technical discussions.
77. Comparable to - Suggests that two things can be likened to each other, providing a basis for comparison.
78. In the same way - Confirms that the action, process, or idea mirrors another, reinforcing the similarity.
79. Just like - A more casual phrase used to draw a direct comparison, making the similarity clear and understandable.
80. Similarly important - Asserts that the importance or relevance of two or more aspects is equal, emphasising their comparative significance.
Utilising these phrases allows you to effectively link concepts and arguments, showing how they complement or mirror each other, which can strengthen your overall thesis. For further reading on comparing and contrasting ideas effectively, the University of North Carolina Writing Center offers excellent resources.
Providing Alternatives
Offering alternatives in your essays can demonstrate critical thinking by showing different possibilities or approaches. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to introduce alternative ideas:
81. Alternatively - Introduces a different option or suggestion, providing another route or perspective.
82. On the contrary - Used to present a direct opposition to the previously mentioned idea, emphasising a contrasting point.
83. Rather - Suggests a preference for one choice over another, typically used to propose a different approach or opinion.
84. Conversely - Indicates a reversal of what has been previously stated, introducing an opposing viewpoint.
85. Instead - Specifies a substitute or replacement, clearly stating that one option is to be considered in place of another.
86. On the flip side - Introduces a contrasting scenario or viewpoint in a more informal manner, often used in conversational or less formal writing.
87. Rather than - Presents a comparison between two choices, highlighting a preference for one over the other.
88. As an alternative - Explicitly states the introduction of a different option or method, providing variety to the discussion.
89. Either...or - Sets up a choice between two distinct options, forcing a decision that impacts the argument’s direction.
90. Neither...nor - Used to deny two possibilities simultaneously, often restructuring the argument by excluding common options.
Incorporating these phrases allows you to explore and present multiple facets of an issue, enriching the essay’s depth and persuasiveness. For tips on effectively presenting alternative arguments, visit Harvard College Writing Center .
Expressing Conditions
Effectively expressing conditions in your essays can help outline scenarios where certain outcomes or arguments hold true. Here’s how to use each word or phrase to specify conditions:
91. If - Introduces a conditional statement, setting up a scenario where a specific result depends on a preceding condition.
92. Unless - Specifies an exception to a general rule or statement, indicating that a condition will change the outcome if not met.
93. Provided that - Sets a stipulation or requirement for a scenario to occur, emphasizing that certain conditions must be satisfied.
94. Assuming that - Suggests a hypothesis or a precondition that needs to be accepted before proceeding with an argument or conclusion.
95. In case - Prepares for a situation that might occur, setting up precautions or actions based on potential scenarios.
96. Even if - Acknowledges that even under certain circumstances, the primary argument or conclusion still holds.
97. Only if - Restricts the conditions under which a statement or outcome is valid, narrowing down the scenarios to very specific ones.
98. Whether - Presents alternatives, usually offering a choice between possibilities within the condition stated.
99. As long as - Indicates that a condition is contingent upon the duration or continuation of a specified situation.
100. Given that - Introduces a premise as a fact, assuming its truth for the sake of argument or to advance the discussion.
Final Thoughts
In crafting compelling essays, the strategic use of specific words and phrases can significantly enhance both the clarity and persuasiveness of your writing. By mastering the use of these 100 essential terms, students can effectively structure their essays, convey complex ideas, and articulate contrasts and comparisons with precision. Each category of phrases serves a unique purpose, from adding information to providing alternatives, which empowers writers to construct well-rounded arguments and engage their readers more deeply.
As you continue to refine your essay-writing skills, remember that the power of your arguments often lies in the details—the precise words and phrases you choose to express your thoughts. The power of a well crafted essay introduction and precise essay conclusion should also not be overlooked. By integrating these tools into your writing repertoire, you are better equipped to present clear, persuasive, and engaging essays that stand out in academic settings.
How can I improve my essay planning process?
Effective essay planning begins with a clear understanding of the essay question. Break down the question to identify key terms and the required response. Create an outline to organise your main points and supporting arguments logically. Consider using a mind map to visually plot connections between ideas, which can spur creative thinking. Allocate time for research, writing, and revision within your plan. Practising essay plans for different questions can enhance your ability to organise thoughts quickly and efficiently, a crucial skill especially under exam conditions.
What makes an essay introduction effective?
An effective introduction grabs the reader's attention, sets the tone, and provides a clear thesis statement. Start with a hook such as a provocative question, a startling statistic, or a compelling quote. Provide some background information to set the context, ensuring it's directly relevant to the essay's question. The thesis statement should be concise and outline your main argument or response to the question. This setup not only intrigues but also informs the reader about the essay's focus, establishing your understanding and control of the subject.
How do I choose the best evidence for my essay?
The best evidence is relevant, credible, and supports your thesis directly. Use primary sources where possible as they provide first-hand accounts that you can analyse directly. When primary sources are not available, rely on peer-reviewed journals and reputable publications. Diversify your sources to avoid over-reliance on a single type of evidence, and critically evaluate sources for bias and reliability. Properly integrating this evidence into your argument involves summarising, paraphrasing, and quoting sources while always linking back to your main argument.
How can I make my essay arguments more persuasive?
To make your arguments more persuasive, begin with a clear, assertive thesis statement. Structure your essay so each paragraph introduces a single point supporting your thesis. Use credible evidence and explain how this supports your argument. Address potential counterarguments to show the depth of your understanding and strengthen your position by demonstrating why your approach is preferable. Employing a confident but respectful tone and precise language also enhances the persuasiveness of your essay.
What are common pitfalls in essay writing to avoid?
Common pitfalls in essay writing include poor structure, weak thesis statements, and lack of coherence. Avoiding these starts with a robust plan and clear outline. Stay on topic by linking each paragraph back to your thesis statement. Avoid plagiarism by properly citing all sources. Overly complex sentence structures can confuse readers, so strive for clarity and conciseness. Finally, neglecting proofreading can leave typographical and grammatical errors, which diminish the quality of your work, so always review your essay thoroughly.
How do I manage time when writing an essay under exam conditions?
Time management in exams is crucial. Allocate about 10% of your time for planning, 80% for writing, and 10% for revising. Quickly outline your main points to structure your essay from the start. Write your body paragraphs first, as these contain the bulk of marks, then your introduction and conclusion. Keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself to ensure you have enough time to adequately develop your arguments and conclude effectively.
What are the best practices for editing and proofreading essays?
After writing your essay, take a break before you start editing to give you a fresh perspective. Read your essay aloud to catch awkward phrasing and sentences that don't flow logically. Check for consistency in tense and point of view throughout the essay. Use spell-check tools, but do not rely on them solely—manually check for homophones and commonly confused words. Consider having someone else read your work to catch errors you might have overlooked and to provide feedback on the clarity of your arguments.
How can I develop a strong thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement is clear, concise, and specific. It should express one main idea that is debatable, meaning there is potential for argument. Reflect on the essay prompt and decide on your position regarding the topic. Your thesis should guide the reader through your arguments and indicate the rationale behind your viewpoint. It serves as the backbone of your essay, so ensure it is robust and directly linked to the question asked.
How do I handle counterarguments in my essays?
Handling counterarguments effectively involves acknowledging them and then refuting them with stronger evidence or reasoning. Present them fairly and objectively, then use logical, fact-based arguments to demonstrate why your position remains valid. This not only shows critical thinking but also strengthens your original argument by showing you have considered multiple perspectives.
What is the role of a conclusion in an essay?
The conclusion of an essay should effectively summarise the main arguments discussed while reaffirming the thesis statement. It should synthesise the information presented rather than introducing new ideas. Provide a final perspective on the topic or suggest implications, further research or practical applications to leave the reader with something to ponder. A strong conclusion can reinforce your argument and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
How can I ensure my essay flows logically?
To ensure logical flow, each paragraph should seamlessly connect to the next with clear transitions. Focus on structuring paragraphs around one main idea that supports your thesis. Use transitional words and phrases to show the relationship between paragraphs. Consistency in your argumentation style and maintaining a clear focus throughout the essay will help keep your writing coherent.
What techniques help maintain reader interest throughout an essay?
To maintain reader interest, start with a strong hook in your introduction and use engaging content like relevant anecdotes, striking statistics, or interesting quotes throughout your essay. Vary your sentence structure and use active voice to keep the narrative dynamic. Also, ensure your topic is relevant and your arguments are presented with passion and clarity.
How can I integrate quotes effectively in essays?
To integrate quotes effectively, introduce the quote with a sentence that sets up its relevance to your argument, then follow the quote with analysis or interpretation that ties it back to your main point. Do not rely heavily on quotes to make your points; use them to support your arguments. Ensure that every quote is properly cited according to the required academic style guide.
What are the differences between descriptive and argumentative essays?
Descriptive essays focus on detailing a particular subject to give the reader a clear image or understanding of the topic through vivid language and sensory details. In contrast, argumentative essays aim to persuade the reader of a particular viewpoint or position using evidence and reasoning. The former is more about painting a picture, while the latter is about convincing through argument.
How can I use feedback to improve my essay writing skills?
Feedback is invaluable for improving essay writing skills. Actively seek out feedback from teachers, peers, or tutors and focus particularly on recurring themes in their comments. Reflect on this feedback critically and apply it to your future essays. Regularly revisiting and revising your work based on constructive criticism allows you to develop a more refined and effective writing style over time.
Need help from an expert?
4.93 /5 based on 486 reviews
The world’s top online tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
Study and Practice for Free
Trusted by 100,000+ Students Worldwide
Achieve Top Grades in your Exams with our Free Resources.
Practice Questions, Study Notes, and Past Exam Papers for all Subjects!
Need Extra Help?
Stuck on your analytical essay? Connect with our English tutors for expert assistance in crafting a compelling analysis!

Professional tutor and Cambridge University researcher

Written by: Thomas Babb
Thomas is a PhD candidate at Oxford University. He served as an interviewer and the lead admissions test marker at Oxford, and teaches undergraduate students at Mansfield College and St Hilda’s College. He has ten years’ experience tutoring A-Level and GCSE students across a range of subjects.
Related Posts

How to Write a Narrative Essay

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Persuasive Essay

Hire a tutor
Please fill out the form and we'll find a tutor for you
- Select your country
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bouvet Island
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei Darussalam
- Burkina Faso
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Congo, The Democratic Republic of the
- Cook Islands
- Cote D'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Guinea-Bissau
- Heard Island and Mcdonald Islands
- Holy See (Vatican City State)
- Iran, Islamic Republic Of
- Isle of Man
- Korea, Democratic People'S Republic of
- Korea, Republic of
- Lao People'S Democratic Republic
- Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Liechtenstein
- Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Moldova, Republic of
- Netherlands
- Netherlands Antilles
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territory, Occupied
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia and Montenegro
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Taiwan, Province of China
- Tanzania, United Republic of
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Virgin Islands, British
- Virgin Islands, U.S.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara

Alternatively contact us via WhatsApp, Phone Call, or Email

100+ Useful Words and Phrases to Write a Great Essay
By: Author Sophia
Posted on Last updated: October 25, 2023
Sharing is caring!
How to Write a Great Essay in English! This lesson provides 100+ useful words, transition words and expressions used in writing an essay. Let’s take a look!
The secret to a successful essay doesn’t just lie in the clever things you talk about and the way you structure your points.
Useful Words and Phrases to Write a Great Essay
Overview of an essay.

Useful Phrases for Proficiency Essays
Developing the argument
- The first aspect to point out is that…
- Let us start by considering the facts.
- The novel portrays, deals with, revolves around…
- Central to the novel is…
- The character of xxx embodies/ epitomizes…
The other side of the argument
- It would also be interesting to see…
- One should, nevertheless, consider the problem from another angle.
- Equally relevant to the issue are the questions of…
- The arguments we have presented… suggest that…/ prove that…/ would indicate that…
- From these arguments one must…/ could…/ might… conclude that…
- All of this points to the conclusion that…
- To conclude…
Ordering elements
- Firstly,…/ Secondly,…/ Finally,… (note the comma after all these introductory words.)
- As a final point…
- On the one hand, …. on the other hand…
- If on the one hand it can be said that… the same is not true for…
- The first argument suggests that… whilst the second suggests that…
- There are at least xxx points to highlight.
Adding elements
- Furthermore, one should not forget that…
- In addition to…
- Moreover…
- It is important to add that…
Accepting other points of view
- Nevertheless, one should accept that…
- However, we also agree that…
Personal opinion
- We/I personally believe that…
- Our/My own point of view is that…
- It is my contention that…
- I am convinced that…
- My own opinion is…
Others’ opinions
- According to some critics… Critics:
- believe that
- suggest that
- are convinced that
- point out that
- emphasize that
- contend that
- go as far as to say that
- argue for this
Introducing examples
- For example…
- For instance…
- To illustrate this point…
Introducing facts
- It is… true that…/ clear that…/ noticeable that…
- One should note here that…
Saying what you think is true
- This leads us to believe that…
- It is very possible that…
- In view of these facts, it is quite likely that…
- Doubtless,…
- One cannot deny that…
- It is (very) clear from these observations that…
- All the same, it is possible that…
- It is difficult to believe that…
Accepting other points to a certain degree
- One can agree up to a certain point with…
- Certainly,… However,…
- It cannot be denied that…
Emphasizing particular points
- The last example highlights the fact that…
- Not only… but also…
- We would even go so far as to say that…
Moderating, agreeing, disagreeing
- By and large…
- Perhaps we should also point out the fact that…
- It would be unfair not to mention the fact that…
- One must admit that…
- We cannot ignore the fact that…
- One cannot possibly accept the fact that…
Consequences
- From these facts, one may conclude that…
- That is why, in our opinion, …
- Which seems to confirm the idea that…
- Thus,…/ Therefore,…
- Some critics suggest…, whereas others…
- Compared to…
- On the one hand, there is the firm belief that… On the other hand, many people are convinced that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 1

How to Write a Great Essay | Image 2

Phrases For Balanced Arguments
Introduction
- It is often said that…
- It is undeniable that…
- It is a well-known fact that…
- One of the most striking features of this text is…
- The first thing that needs to be said is…
- First of all, let us try to analyze…
- One argument in support of…
- We must distinguish carefully between…
- The second reason for…
- An important aspect of the text is…
- It is worth stating at this point that…
- On the other hand, we can observe that…
- The other side of the coin is, however, that…
- Another way of looking at this question is to…
- What conclusions can be drawn from all this?
- The most satisfactory conclusion that we can come to is…
- To sum up… we are convinced that…/ …we believe that…/ …we have to accept that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 3

- Recent Posts
- Plural of Process in the English Grammar - October 3, 2023
- Best Kahoot Names: Get Creative with These Fun Ideas! - October 2, 2023
- List of Homophones for English Learners - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- How to Write a Letter: A Guide to Informal and Formal English
- How to Write Informal Letters in English (with Examples)
- Most Commonly Used English Phrases on the Phone
- Asking for Help, Asking for Opinions and Asking for Approval
Nur Syuhadah Zainuddin
Friday 19th of August 2022
thank u so much its really usefull
12thSeahorse
Wednesday 3rd of August 2022
He or she who masters the English language rules the world!
Friday 25th of March 2022
Thank you so so much, this helped me in my essays with A+
Theophilus Muzvidziwa
Friday 11th of March 2022
Monday 21st of February 2022

Useful Academic Expressions & Phrases For Essay Writing
These useful academic expressions , words, vocabulary and phrases will help you to write a top-notch essay. Writing an essay can be a challenging task. However it becomes simpler if it is divided into manageable pieces. There are three main parts in an essay: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. You can easily overcome your essay writing task with these academic phrases and vocabulary for essay writing.

Phrases to Finish an Introduction Paragraph
In this essay, I will look at some of the arguments for This essay will discuss different ways of … This essay outline some of the reasons why… Let us examine both views before reaching a concrete decision. The following essay takes a look at both sides of the argument.
Vocabulary for Opinion Essay
In my opinion, I strongly agree with the idea that … I strongly disagree with the idea that … I strongly opine that… I strongly believe that… In my view… As far as I am concerned… It seems to me that… However, I strongly believe that… I oppose the view and my reasons will be explained in the following paragraphs. I will support this view with arguments in the following paragraphs. I personally believe that… Thus the advantages far outweigh the disadvantages…
Useful Expressions For Listing Your Ideas
First… First of all… Firstly… First and foremost… Initially… To begin with… To start with… In the first place…
On the one hand… Second(ly)… (do not use ‘Second of all’) Third(ly)… Then… Next… After that… And… Again… Also… Besides… Likewise… In addition… Consequently… What’s more… Furthermore… Moreover… Apart from that…
Finally… Last but not the least…
Check Also: Vocabulary for Starting Your Essay How to Write The Best Essay Ever!
Phrases to Show a Comparison in Your Essay
In the same way… Likewise… Similarly… Like the previous point… Similar to… Also… At the same time… Just as…
Useful Vocabulary and Phrases to Show Contrast
On the other hand… On the contrary… However… Nevertheless…/ Nonetheless… But… Nonetheless/ Nevertheless… Oppositely… Alternatively… Unlike… While… Whilst… Although… Though… Even though… Despite… / In spite of… In spite of the fact that… Alternatively… In contrast to this… Then again… On the other hand… Despite the fact that… Even so… Yet… Meanwhile…
Vocabulary For Expressing Condition
If… Provided that… Because of that… For this reason… Unless… Providing that… So that… In case… Whether…
Phrases for Expressing Certainty in Your Essay
Certainly… Definitely… No doubt… Of course… Doubtlessly… Without any doubt… Undoubtedly…
Vocabulary for Adding Further Information
In addition… And… Moreover… Similarly… Furthermore… Also… As well as… Besides… Even… Too… What’s more… Again… In a similar fashion… Likewise…
Expressions for Agreement & Disagreement in Your Essay
While writing your essay, as a writer you are required to show whether you agree & disagree or partially agree with a given statement or opinion.
Vocabulary for Expressing Agreement
I strongly agree… I completely agree that… I totally agree with the given idea that… I agree with the opinion that… I am quite inclined to the opinion that… I accept that… I accept the fact that… I am in agreement… I consent that…
Vocabulary for Expressing Disagreement
I disagree with the opinion that… I strongly disagree… I completely disagree with… I totally disagree with the given idea that… I disagree with the statement… I quite oppose the opinion that… I disapprove that… I totally do not accept the fact that… My own opinion contradicts… I disagree with the group of people… However, my opinion is different from…
Vocabulary for Expressing Partial Agreement
To some extent… In a way… I agree with the given statement to some extent… Up to a point, I agree… More or less… So to speak…
Essay Writing Expressions PDF
Essay Expression PDF – (download)
You May Also Like

12 Tenses in English Grammar with Examples (PDF)
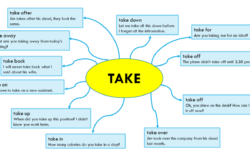
Phrasal Verbs with TAKE – Exercise (PDF)

20+ Funny English Jokes. 99% English Speakers Won’t Understand!
Tower Language
Foreign Language Lessons, In-Company Classes, Translation

60 Useful Words and Phrases for Outstanding Essay Writing
General explaining.
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage : “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument.
Example : “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage : Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point.
Example : “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage : This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance.
Example : “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage : “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise.
Example : “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage : Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”.
Example : “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage : Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making.
Example : “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage :This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information.
Example : “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage : This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”.
Example : “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage : Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned.
Example : “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage : Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”.
Example : “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage : Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”.
Example : “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage : Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”.
Example : “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage : This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information.
Example : “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage : Used when considering two or more arguments at a time.
Example : “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage : This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other.
Example : “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage : “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis.
Example : “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage : Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said.
Example : “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”

18. On the other hand
Usage : Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion.
Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage : Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”.
Example : “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage : Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence.
Example : “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage : Use this to cast doubt on an assertion.
Example : “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage : This is used in the same way as “then again”.
Example : “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage : Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea.
Example : “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage : Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence.
Example : “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage : Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else.
Example : “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage : This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing.
Example : “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage : These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else.
Example : “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage : This is similar to “despite this”.
Example : “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage : This is the same as “nonetheless”.
Example : “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage : This is another way of saying “nonetheless”.
Example : “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example : “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example : “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage : Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent.
Example : “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage : This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it).
Example : “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage : Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”.
Example : “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage : Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview.
Example : “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage : Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay.
Example : “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage : This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing.
Example : “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage : Use in the same way as “persuasive” above.
Example : “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage : This means “taking everything into account”.
Example : “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below!
Additional Information ( more examples)
+20 examples of important transition words, additional information.
There are many linking words which can lead us into additional information and while it is useful to vary your vocabulary beyond ‘ and ,’ these words are not mere replacements for ‘ and .’ They have nuanced differences, thus, by these particular meanings, we can offer a more delicate illustration of the relationships between our ideas.
- ‘Furthermore’ is used to add information that expands upon the previous point. It precedes information that expands upon that already given. It usually occurs at the beginning of an independent clause.
- ‘Moreover’ and ‘More so’ are both similar to ‘furthermore’ while giving special emphasis to the greater importance of the following clause.
- “Despite cutting back on other staff, her father gave her a position, furthermore , he gave her an enviable office while still not having a role for her.”
- Writers also sequence additional information. ‘Firstly,’ ‘secondly’ and ‘thirdly’ are obvious options used to achieve this, however, there are others. For example, we can look into the past with ‘previously,’ ‘until the present’ or ‘preceded by.’
- “Present growth in the company was *preceded by several quarters of stagnation”*
- ‘Meanwhile’ and ‘simultaneously’ talk about things which are happening at the same time as another, while ‘concurrently’ does this while emphasising that the two ideas have played out in conjunction with one another.
- Usually, ‘incidentally’ is used to add relevant information while downplaying its significance compared with that of other ideas.
- “The priority of the zoo had been to protect species’ from extinction. The panda breeding program was enjoying some rare success, while simultaneously , other programs to increase the numbers of endangered species were being trialled. Meanwhile , the zoo was being visited by an influx of tourists who were, incidentally , able to enjoy seeing the young animals.”
- ‘Subsequently’ and ‘afterward’ lead into information after the fact.
Compare and Contrast
When writers need to illustrate similarity they can employ words such as ‘in like manner,’ ‘comparatively,’ and ‘correspondingly.’ Whereas , when they wish to highlight difference they have phrases like ‘on the contrary,’ ‘however,’ ‘notwithstanding,’ ‘nevertheless’ and ‘on the other hand.’
Notwithstanding the vehement opposition to online education programs being made available to inmates, considerable improvements were made to the re-employment prospects of many offenders who benefited from the trial. On the contrary, prisoners who were not able to access education while incarcerated were found to be more likely to reoffend and return to prison.
Clarification
When it comes time to clarify an argument or point, some of the transitional phrases which are used are, ‘to reiterate,’ ‘specifically,’ or ‘inasmuch as.’
Consequence and Conclusion
When we have lead our reader through our flow of logic, there might be nothing more rewarding than driving our point home by showing consequence or concluding our arguments. There are a lot of strong phrases such as ‘accordingly,’ ‘hence,’ ‘thus’ and ‘thereupon’ which can do this.
I hope you will feel encouraged, by this article, to continue to further your understanding of how transitional words can work to guide your reader through your flow of logic. When used well, they add power and order to your argument and can add to the result you see from your work.
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- How Homework Builds Good Study Habits for University Students
How to Write an Article Review in Simple Steps
- Understanding Content Validity: Definition & Examples
- 10 Tips for Writing Assignments
- Easy Steps to Write a History Essay: Tips and Tricks
- How To Select the Perfect CV Writing Service
- What Is an Adjective: Types, Uses, and Examples
- How to Write a Reflective Essay
- Abstract vs. Introduction: What’s the Difference?
- How Do AI detectors Work? Breaking Down the Algorithm
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips
Essay Phrases & Essay Words for Academic Writing Success
(Last updated: 10 October 2024)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
For the vast majority of students, essay writing doesn't always come easily. Writing at academic level is an acquired skill that can literally take years to master – indeed, many students find they only start to feel really confident writing essays just as their undergraduate course comes to an end!
If this is you, and you've come here looking for words and phrases to use in your essay, you're in the right place. We’ve pulled together a list of essential academic words you can use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essays .
Whilst your ideas and arguments should always be your own, borrowing some of the words and phrases listed below is a great way to articulate your ideas more effectively, and ensure that you keep your reader’s attention from start to finish.
It goes without saying (but we'll say it anyway) that there's a certain formality that comes with academic writing. Casual and conversational phrases have no place. Obviously, there are no LOLs, LMFAOs, and OMGs. But formal academic writing can be much more subtle than this, and as we've mentioned above, requires great skill.
So, to get you started on polishing your own essay writing ability, try using the words in this list as an inspirational starting point.
Words to use in your introduction
The trickiest part of academic writing often comes right at the start, with your introduction. Of course, once you’ve done your plan and have your arguments laid out, you need to actually put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard) and begin your essay.
You need to consider that your reader doesn’t have a clue about your topic or arguments, so your first sentence must summarise these. Explain what your essay is going to talk about as though you were explaining it to a five year old – without losing the formality of your academic writing, of course! To do this, use any of the below words or phrases to help keep you on track.
1. Firstly, secondly, thirdly
Even though it sounds obvious, your argument will be clearer if you deliver the ideas in the right order. These words can help you to offer clarity and structure to the way you expose your ideas. This is an extremely effective method of presenting the facts clearly. Don’t be too rigid and feel you have to number each point, but using this system can be a good way to get an argument off the ground, and link arguments together.
2. In view of; in light of; considering
These essay phrases are useful to begin your essay. They help you pose your argument based on what other authors have said or a general concern about your research. They can also both be used when a piece of evidence sheds new light on an argument. Here’s an example: The result of the American invasion has severely impaired American interests in the Middle East, exponentially increasing popular hostility to the United States throughout the region, a factor which has proved to be a powerful recruitment tool for extremist terrorist groups (Isakhan, 2015). Considering [or In light of / In view of] the perceived resulting threat to American interests, it could be argued that the Bush administration failed to fully consider the impact of their actions before pushing forward with the war.
3. According to X; X stated that; referring to the views of X
Introducing the views of an author who has a comprehensive knowledge of your particular area of study is a crucial part of essay writing. Including a quote that fits naturally into your work can be a bit of a struggle, but these academic phrases provide a great way in.
Even though it’s fine to reference a quote in your introduction, we don’t recommend you start your essay with a direct quote. Use your own words to sum up the views you’re mentioning, for example:
As Einstein often reiterated, experiments can prove theories, but experiments don’t give birth to theories.
Rather than:
“A theory can be proved by experiment, but no path leads from experiment to the birth of a theory.” {Albert Einstein, 1954, Einstein: A Biography}.
See the difference?
And be sure to reference correctly too, when using quotes or paraphrasing someone else's words.
Adding information and flow
The flow of your essay is extremely important. You don’t want your reader to be confused by the rhythm of your writing and get distracted away from your argument, do you? No! So, we recommend using some of the following ‘flow’ words, which are guaranteed to help you articulate your ideas and arguments in a chronological and structured order.
4. Moreover; furthermore; in addition; what’s more
These types of academic phrases are perfect for expanding or adding to a point you’ve already made without interrupting the flow altogether. “Moreover”, “furthermore” and “in addition” are also great linking phrases to begin a new paragraph.
Here are some examples: The dissociation of tau protein from microtubules destabilises the latter resulting in changes to cell structure, and neuronal transport. Moreover, mitochondrial dysfunction leads to further oxidative stress causing increased levels of nitrous oxide, hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxidases.
On the data of this trial, no treatment recommendations should be made. The patients are suspected, but not confirmed, to suffer from pneumonia. Furthermore, five days is too short a follow up time to confirm clinical cure.
5. In order to; to that end; to this end
These are helpful academic phrases to introduce an explanation or state your aim. Oftentimes your essay will have to prove how you intend to achieve your goals. By using these sentences you can easily expand on points that will add clarity to the reader.
For example: My research entailed hours of listening and recording the sound of whales in order to understand how they communicate.
Dutch tech companies offer support in the fight against the virus. To this end, an online meeting took place on Wednesday...
Even though we recommend the use of these phrases, DO NOT use them too often. You may think you sound like a real academic but it can be a sign of overwriting!
6. In other words; to put it another way; that is; to put it more simply
Complement complex ideas with simple descriptions by using these sentences. These are excellent academic phrases to improve the continuity of your essay writing. They should be used to explain a point you’ve already made in a slightly different way. Don’t use them to repeat yourself, but rather to elaborate on a certain point that needs further explanation. Or, to succinctly round up what just came before.
For example: A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between phenomena. In other words, there is no treatment effect.
Nothing could come to be in this pre-world time, “because no part of such a time possesses, as compared with any other, a distinguishing condition of existence rather than non-existence.” That is, nothing exists in this pre-world time, and so there can be nothing that causes the world to come into existence.
7. Similarly; likewise; another key fact to remember; as well as; an equally significant aspect of
These essay words are a good choice to add a piece of information that agrees with an argument or fact you just mentioned. In academic writing, it is very relevant to include points of view that concur with your opinion. This will help you to situate your research within a research context.
Also , academic words and phrases like the above are also especially useful so as not to repeat the word ‘also’ too many times. (We did that on purpose to prove our point!) Your reader will be put off by the repetitive use of simple conjunctions. The quality of your essay will drastically improve just by using academic phrases and words such as ‘similarly’, ‘as well as’, etc. Here, let us show you what we mean:
In 1996, then-transport minister Steve Norris enthused about quadrupling cycling trips by 2012. Similarly, former prime minister David Cameron promised a “cycling revolution” in 2013…
Or Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI) aims to bridge the gap of access to electricity across the continent (...). Another key fact to remember is that it must expand cost-efficient access to electricity to nearly 1 billion people.
The wording “not only… but also” is a useful way to elaborate on a similarity in your arguments but in a more striking way.
Comparing and contrasting information
Academic essays often include opposite opinions or information in order to prove a point. It is important to show all the aspects that are relevant to your research. Include facts and researchers’ views that disagree with a point of your essay to show your knowledge of your particular field of study. Below are a few words and ways of introducing alternative arguments.
8. Conversely; however; alternatively; on the contrary; on the other hand; whereas
Finding a seamless method to present an alternative perspective or theory can be hard work, but these terms and phrases can help you introduce the other side of the argument. Let's look at some examples:
89% of respondents living in joint families reported feeling financially secure. Conversely, only 64% of those who lived in nuclear families said they felt financially secure.
The first protagonist has a social role to fill in being a father to those around him, whereas the second protagonist relies on the security and knowledge offered to him by Chaplin.
“On the other hand” can also be used to make comparisons when worded together with “on the one hand.”
9. By contrast; in comparison; then again; that said; yet
These essay phrases show contrast, compare facts, and present uncertainty regarding a point in your research. “That said” and “yet” in particular will demonstrate your expertise on a topic by showing the conditions or limitations of your research area. For example:
All the tests were positive. That said, we must also consider the fact that some of them had inconclusive results.
10. Despite this; provided that; nonetheless
Use these phrases and essay words to demonstrate a positive aspect of your subject-matter regardless of lack of evidence, logic, coherence, or criticism. Again, this kind of information adds clarity and expertise to your academic writing.
A good example is:
Despite the criticism received by X, the popularity of X remains undiminished.
11. Importantly; significantly; notably; another key point
Another way to add contrast is by highlighting the relevance of a fact or opinion in the context of your research. These academic words help to introduce a sentence or paragraph that contains a very meaningful point in your essay.
Giving examples
A good piece of academic writing will always include examples. Illustrating your essay with examples will make your arguments stronger. Most of the time, examples are a way to clarify an explanation; they usually offer an image that the reader can recognise. The most common way to introduce an illustration is “for example.” However, in order not to repeat yourself here are a few other options.
12. For instance; to give an illustration of; to exemplify; to demonstrate; as evidence; to elucidate
The academic essays that are receiving top marks are the ones that back up every single point made. These academic phrases are a useful way to introduce an example. If you have a lot of examples, avoid repeating the same phrase to facilitate the readability of your essay.
Here’s an example:
‘High involvement shopping’, an experiential process described by Wu et al. (2015, p. 299) relies upon the development of an identity-based alliance between the customer and the brand. Celebrity status at Prada, for example, has created an alliance between the brand and a new generation of millennial customers.
Concluding your essay
Concluding words for essays are necessary to wrap up your argument. Your conclusion must include a brief summary of the ideas that you just exposed without being redundant. The way these ideas are expressed should lead to the final statement and core point you have arrived at in your present research.
13. In conclusion; to conclude; to summarise; in sum; in the final analysis; on close analysis
These are phrases for essays that will introduce your concluding paragraph. You can use them at the beginning of a sentence. They will show the reader that your essay is coming to an end:
On close analysis and appraisal, we see that the study by Cortis lacks essential features of the highest quality quantitative research.
14. Persuasive; compelling
Essay words like these ones can help you emphasize the most relevant arguments of your paper. Both are used in the same way: “the most persuasive/compelling argument is…”.
15. Therefore; this suggests that; it can be seen that; the consequence is
When you’re explaining the significance of the results of a piece of research, these phrases provide the perfect lead up to your explanation.
16. Above all; chiefly; especially; most significantly; it should be noted
Your summary should include the most relevant information or research factor that guided you to your conclusion. Contrary to words such as “persuasive” or “compelling”, these essay words are helpful to draw attention to an important point. For example:
The feasibility and effectiveness of my research has been proven chiefly in the last round of laboratory tests.
Film noir is, and will continue to be, highly debatable, controversial, and unmarketable – but above all, for audience members past, present and to come, extremely enjoyable as a form of screen media entertainment.
17. All things considered
This essay phrase is meant to articulate how you give reasons to your conclusions. It means that after you considered all the aspects related to your study, you have arrived to the conclusion you are demonstrating.
After mastering the use of these academic words and phrases, we guarantee you will see an immediate change in the quality of your essays. The structure will be easier to follow, and the reader’s experience will improve. You’ll also feel more confident articulating your ideas and using facts and examples. So jot them all down, and watch your essays go from ‘good’ to ‘great’!
Essay exams: how to answer ‘To what extent…’
How to write a master’s essay.
- academic writing
- writing a good essay
- writing essays
- writing tips
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- Professional CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Writing Service Examples
- Editing Service Examples
- Marking Service Examples
- Tutoring Service Examples
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.

Using Creative Words and Phrases for Composition Writing & Essays
- Primary School Composition Writing

Using Creative Words and Phrases for Composition Writing & Essays
How to use creative words and phrases for composition writing & essays.
This blog post will teach you how to use creative and inspired phrases for composition writing. It will also give you examples and ideas of Idioms, Similes, Metaphors or Personification that you can use in your compositions.
But first, here’s a Free Ebook – 80 Awesome Phrases to Wow your Teacher !
(Tip: You can print out the free ebook for your child to read.)

Do You Really Need Good Phrases for Composition Writing?
No, you don’t. Your child should not use good phrases just for the sake of impressing the reader. Your child should concentrate on using the RIGHT PHRASE for the RIGHT SITUATION . (In fact, our collection of Model Compositions for Primary School Students does not contain pompous, bombastic words or phrases.)
And to do so, your child needs to have a broad knowledge of a variety of phrases. That way, he will be well-equipped with an arsenal of words to express himself fluently and smoothly.
Many parents misunderstand the use of good vocabulary words for essays. They force their child to memorise bombastic words and phrases. This should not be the case as memorisation does not equal application. Students tend to memorise the phrases and then use them in the wrong context when writing. This causes the students’ writing to become stilted and mechanical. Some may even become addicted to the use of bombastic vocabulary and end up writing overly-complicated sentences or phrases to look smart.
Now which is smarter – expressing yourself in a short and sweet manner, or, writing a whole bunch of fancy and pompous words just to narrate a simple thought?
Instead of “good phrases”, focus on using – EFFECTIVE PHRASES.
It’s okay to use simple phrases! Keep your sentences short, concise, and straight to the point. Use the right words at the right time. Express your ideas fluently.
Remember – You are writing to let the reader read for the sake of enjoyment. You are not writing to IMPRESS the reader.
Bonus Video – How To Use Good Expressions in Composition Writing:
Here’s an online lesson I conducted some time back on how to use Good Expressions in your compositions. It is very similar to what I address in the article later on How to Write Good Phrases.
It’s about 1 hour long so you may want to set aside some time to watch it. (You can also fast forward to 6:09 to skip straight to the introduction and then the lesson.)
Types of Descriptive Phrases
“Good Phrases” can be broken down into:
Personification
An idiom is an expression of words whose meaning is not predictable from the usual meanings of its constituent elements. (Definition taken from dictionary.com )
In other words, an idiom is a quirky series of words combined to form a special meaning.
Idioms should be used sparingly in a composition. Do not overuse them as it may make your overall composition sound very cheesy or old-fashioned. Some idioms are also not commonly used in our everyday speech. Hence, over-usage of the less well-known idioms might make reading awkward.
Some Useful Idioms
1. An arm and a leg – Very expensive or costly.
E.g: Dining at this high-class restaurant cost me an arm and a leg ! I will never return here again.
2. Blessing in disguise – something good that was not recognized at first.
E.g: Missing that field trip turned out to be a blessing in disguise as the school bus met with an accident.
3. Piece of cake – used to describe something that is very easy to do.
E.g: This assignment was a piece of cake . I completed in less that fifteen minutes
4. Not to make head or tail of something – unable to decipher or understand the meaning
E.g: The teacher was talking so fast that I could not make head or tail of what he was saying.
5. See eye to eye – to agree with someone
E.g: Jack and Diane kept on quarreling as they could not see eye to eye with each other.
For more useful idioms, you check out our LIST of 88 AWESOME IDIOMS that you can learn and apply immediately. Boost your language marks for compo writing and WOW your teacher!
Click the button below to download this free ebook for your child!

- Simple & Easy-to-use
- Minimal Memory Work
- Examples provided
- Learn the meaning of these idioms!
It is a figure of speech where one thing is compared with another thing of a different kind.
It is used to make a description more vivid or to draw out a particular quality of the subject being mentioned.
Similes are used with the words “like” or “as…as”.
Similes are best used when they are original, creative, relevant and logical. A simile which has been used too many times – “as fast as a cheetah” or “as fast as lightning” – will not score you extra points.

Some Useful Similes
1.The students were chattering like monkeys .
2. The winner of the race paraded around the track like a peacock .
3. We tried to carry him but he was as heavy as an elephant .
4. The signboards were as bright as daylight .
5. When she heard someone call her name in the dark, she turned as pale as a sheet .
6. Filled with rage, the bully charged towards me like a bull .
7. The boys were laughing like hyenas when they pulled off the prank.
8. Don’t worry about her. She can handle it herself. She is as tough as nails !
9. When the exams commenced, the classroom became as silent as a grave .
10. On the last day of school, Jimmy dashed out of the school gates feeling as free as a bird .
A metaphor is a figure of speech in which a term or phrase is applied to something that is not literally applicable to suggest a resemblance. (definition taken from dictionary.com ).
In other words, it is almost like a simile, except you are not using the words ‘like’ or ‘as…as’.

Simile: He was as angry as a bull.
Metaphor: He was an angry bull.
Metaphors are slightly more difficult to use than similes. But when they are used right, they can give an extremely vivid portrayal of a character or a situation in the story.
A metaphor applied correctly can be a very powerful tool in writing.
Some Useful Metaphors
1. She felt a whirlwind of emotions passed through her. ( overwhelmed by emotions)
2. Don’t believe that fortune-teller. He is selling you snake oil . (metaphorical idiom, fake promises, products or services that fail to live up to expectations, something fraudulent)
3. Mr Tan is a teacher with a heart of gold . ( very kind or generous)
4. Stay away from him. He is a loaded gun . (dangerous)
5. When the basketball team got off the bus, we could smell the stench of defeat on them. ( they acted in such a way that it was easy to deduce that they have lost)
6. After failing her exams, Shirley wallowed in a sea of self-pity . ( metaphorical idiom, overwhelmed by self-pity)
7. He was so sad that he was crying rivers . (a lot of tears)
8. Sean’s stomach was a bottomless pit . ( extremely hungry, describe someone who cannot stop eating.)
9. Completing this assignment was a breeze . ( very easy to complete)
10. Hearing her laughter was music to my ears . (a pleasant sound)
Personification is done by attributing human characteristics to something non-human.
This is used to give a clearer picture of whatever that’s being described. It enables the reader visualise and see the imagery in their minds.
Personification can be done by simple usage of verbs or action words.
Just like metaphors, personification can count as good vocabulary words for essay writing.

Some Useful Ideas for Personification
1. The thunderstorm raged on outside my window.
2. The soft, cool sand caressed my feet.
3. The sun peeked out from behind the clouds.
4. I could hear the faint wail of the ambulance in a distance.
5. The moment I stepped out into the streets, I was greeted by the strong diesel fumes.
6. The trees shadowed the soldiers as they trekked through the forest.
7. The sports car roared with ferocity as it zoomed past the spectators.
8. The road was treacherous and unforgiving .
9. The expensive handbag seemed to call out to her. “Buy me!”
10. By the time the firemen arrived, the flames were already dancing on the roof.
How to come up with your own phrases?
The best descriptions are often ones that you come up with on the spot, that can fit the scenario or context that you are describing perfectly.
Coming up with good phrases for composition writing is not that hard. All you need is an inquisitive mind that is able to draw comparisons between 2 unrelated objects.
You need to be creative – a trait that is inherent in most children.
You need to be able to come up with fresh ideas and fresh perspectives.
Some questions to ask yourself when coming up with good vocabulary words for essays:
- How can I better depict this character/scene/object by comparing it with something else?
- What’s a better verb I can use to personify this object?
- How can I make this phrase or sentence more interesting for the reader?
- How can I better convey my point across to the reader?
- How can I help the reader to visualise better?
How to write a good essay in English?
DON’T be so preoccupied with employing gargantuan words in your expositions that your sentence ends up reading like this. See what I did there?
Often students pepper their essays with “smart-sounding” words to impress their examiners. This has the opposite effect; readers are left scratching their heads, wondering what message the student is trying to convey.
The best way to resist this impulse is to replace bombastic words with effective ones. “Bombastic”, according to Oxford Languages, means “high-sounding but with little meaning”. When you use bombastic words, you may just end up using words in the wrong context . You also tend to make errors of repetition by force-fitting all the words you know into your compo.
Consider this sentence: “The enraptured onlookers were jolted and entranced by the spine-tingling sight of the sunset.”
Did you spot the errors?
1. “Enraptured” and “entranced” mean the same thing. (Repetition)
2. “Jolted” means “shocked”. (Wrong context. This is a sunset, not a horror movie!)
3. “Spine-tinging” means “scary”. (Again, wrong context.)
Here’s the revised sentence: “The onlookers were left mesmerised by the breathtaking sunset.”
By replacing bombastic words with effective ones, you’re well on your way to writing a good essay in English.
Good vocabulary words for essays

Good vocabulary forms the bedrock of an essay, so it is important to use vocabulary that is appropriate, yet not overused and therefore, cliched. Let’s begin with the introduction.
Introduction
The introduction is where you set the scene for your reader. Use descriptive phrases that vividly describes the setting. Word of caution: do not overdo the setting descriptions, especially when the setting plays no role in your story plot.
- Use vivid vocabulary instead of vague adjectives :
For instance, replace vague adjectives like “beautiful” with more precise vocabulary. If you’re describing places like a quiet beach or park, “ serene ” and “tranquil ” can be used instead.
If you’re describing greenery, “verdant” is more appropriate and paints a more vivid picture in your reader’s mind:
e,g, “My parents and I were at the Bukit Timah Nature Reserve, enjoying a peaceful afternoon amidst the verdant expanse of lush trees and vibrant flower beds, blissfully unaware that things would soon take an unexpected turn.”
- Use creative phrases instead of cliches :
It’s high time we ditch cliched phrases about how “fluffy clouds dotted the azure sky”. This does not impress your reader!
Consider this other cliched phrase: “The smell of buttery popcorn wafted into my nostrils.”
What a yawn! Let’s improve by rewriting it as follows: “The smell of buttery popcorn beckoned to me, tantalising my senses.” You have effectively personified the smell of the popcorn and in doing so, you convey just how tempted you were by it!
Rising Action

Things are heating up here and if you want to keep your readers on their toes, use suspenseful language to plant clues. This is especially useful if your story is about an unfortunate event or something unexpected.
When something seems a little amiss, hint at the impending problem using phrases such as:
1. Something gnawed at the back of my mind, but I brushed it off.
2. I could not shake the feeling of…
3. I could feel it in my bones; something was not right.
4. I felt a tug of apprehension in my gut, subtle but persistent.
5. The birdsong abruptly ceased, as if nature itself were holding its breath.
This is where the main conflict or action occurs and where vocabulary should be impactful . Once again, stand out from the crowd by using high-intensity words (and avoid using “very”) to create excitement!
- Use impactful, highly charged vocabulary instead of dull phrases :
| Instead of this … | Try this! |
| scared/ terrified/ petrified
| with terror by the icy grip of fear |
| determined | resolve in my pursuit |
| a challenge | a trying a of my resolve a |
| ran towards the finishing line | towards the finishing line himself towards the finishing line |
| surrounded by fans | by screaming fans of fans descended upon him |
| winning the game | the game displaying skill |
- Use “show, not tell” instead of stating the facts :
This means showing, not telling , the reader what your character is thinking and feeling. In doing so, you engage the reader and make your writing a whole lot more immersive! When the reader can picture your character, you evoke a deeper emotional response.
Consider these two descriptions:
- Jane was devastated but determinedly continued on.
- Hastily wiping her tears away, Jane bit her lip and marched ahead.
Ask yourself: which one is more impactful? Which description draws you in and allows you to feel Jane’s pain?
Falling Action

Here’s the part where the dust settles. Common emotions experienced by characters include relief (usually after negative events) and happiness (for positive outcomes).
- Use body language to convey emotions like relief or joy
Your characters don’t always have to ‘heave/ breathe a sigh of relief”. There are plenty of other “show, not tell” or body language phrases we can use to convey relief:
1. Unclenching my fists, I…
2. Marcus slumped in his chair in relief .
3. She let out a long breath , thankful for the brief reprieve.
4. A soft smile played on her lips as worry washed away.
5. He wiped his brow as anxiety finally ebbed away
- Explore using new idioms and metaphors to convey emotions
While “jumped for joy” and “over the moon” do show happiness, it’s time to retire these and adopt some new lingo! Try these instead:
1. Benjamin was walking on air after winning the championship.
2. The blushing bride graced us with a smile that could light up a room .
3. I was tickled pink after being personally invited to Taylor Swift’s birthday bash.
Belle walked up on stage with a spring in her step .
- Capture complexity of emotions to create round (not flat) characters
More advanced writers might want to play around with describing more nuanced feelings because human emotions are complex! We often experience bittersweet emotions like joy tinged with melancholy.
Consider descriptions that capture this complexity. For instance, if describing a graduation, you can try: “The valedictorian gave the graduating class a wistful smile as he prepared to throw up his mortarboard for the final hurrah.”
This lends more depth to your characters; this makes your characters three-dimensional, rounded … and real.

Leave the reader with a thought-provoking statement as you wrap up your final scene. You do your essay no favours by ending with crutch phrases about how “this memory will always be etched in his mind”.
- Use reflective vocabulary and words that convey closure:
1. Mulling over the day’s events, she…
2. Sandra was lost in a pleasant reverie as the jubilant cheers of her teammates faded into the backdrop.
3. Cristopher kept turning things over in his mind until he finally concluded that…
- Use vivid descriptions to end with imagery:
1. Rain pattered against the window, washing away the dust of the day.
2. I stared at my reflection in the gleaming medal and saw, for the first time, a champion.
Remember, the best conclusions should leave the reader satisfied, bring closure, and create a lasting impression. And that’s how you end with a bang.
See other related articles on Writing Samurai:
- Proverbs are Phrases Commonly Used in Compositions
- 6 Tips On How to Write a Good Composition For Primary School Students
- Great Phrases To Use For Composition Writing & Essays
- Situational Writing For Primary School Students
Still need more help?
Here’s an ebook of good phrases that your child can use to describe emotions, $15 free for a limited time only.
More than 28,437 students have benefited from this book!
Click or Tap on the button below to download!

Follow Writing Samurai on Telegram for the latest tips and strategies for English, Chinese, and Creative Writing! Pssst... We will also share the latest compo topics during test or exam season!
Click this link to follow our channel >>> https://t.me/writingsamurai
Free Test Papers for Primary School English Compositions Exams
Key tips on writing good compositions for primary school.
Writing Samurai is an online platform dedicated to nurturing children’s creative writing skills. Our courses are designed to be engaging and effective, without resorting to traditional teaching methods.
Subscribe for latest news & English tips:
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy
2024 Copyright Writing Samurai
PRIMARY ENGLISH
- Model Compositions
- Situational Writing Tips
- PSLE English Oral Exam Tips
- PSLE Chinese Oral Exam Tips
- 50 Meaningful Proverbs
- Composition Writing
- PSLE Marking Scheme
SECONDARY ENGLISH
- Past Year's O-Level Essays
- Discursive Essay Writing
- Argumentative Essay Writing
- Secondary English Writing Tips (O-Levels)
- Exam Tips for Secondary English
- 7 Exam Tips for Language Editing (O-Levels)

POPULAR TOPICS
- English Oral
- Chinese Oral
- Situational Writing
- Secondary School Writing
- Essay Writing Lower Secondary
- Synthesis & Transformation
- Calculate AL PSLE Score
TOP FREE RESOURCES
- Free English Writing Resources List
- Free Model Compositions Examples
- Video - Proverbs Composition Writing
- Video - How to Write A Powerful Introduction
- Video - How to Use Good Expressions in your Compositions
- Free Online Writing Course - Kick Start Your Writing
TOP COURSES
- Junior Writers Masterclass - P1 / P2
- Little Writers Masterclass - P3 / P4
- Creative Writing Masterclass - P5 / P6
- Chinese Composition Writing - P5 / P6
- Essay Writing Masterclass - S1 / S2
- Essay Writing - Expository & Argumentative Crash Course
- Grammar Editing Crash Course for Secondary School
- Model Composition Examples
- Free Model Compositions

Supercharge Your English Essays with Idioms

Image by Annie Spratt
What Are Idioms?
Every language has its own sayings and expressions. In English, these are called idioms.
Idioms are used to convey figurative meanings that are different from their literal meanings. For example, one famous idiom for your essay that you may have encountered in school is ‘to kill two birds in one stone’ which of course does not involve any actual killing of birds. It simply means to solve two problems or tasks with one action or solution.
Idioms can be an interesting way to learn English especially if you try to find out the story behind the phrase. For example, ‘bite the bullet’ means to force yourself to do something you dislike. This phrase likely originated from injured soldiers who were biting down on bullets to avoid screaming during war operations in the past. Today, we continue to use the phrase in various contexts.
Why Use Idioms For Your Essays?
You’re encouraged to use idioms for your essays to:
allow you to convey thoughts and messages in a concise but figurative manner
make your essay interesting and help enhance the quality of your essay
further develop your writing skills by using stylistic devices
You can start by trying to use 1 idiom for each essay and then increase the number if appropriate. However, avoid overpopulating your essay with idioms unnecessarily as they should only be used intentionally and purposefully.
When using idioms for your essay, make sure that it fits the context and that the right pronouns and tenses are used. One way to get a grasp on how to use idioms properly is to read more English stories. Click here for a list of English stories that can help you improve your English.
List Of Common Idioms For Your Essays

Image by Debby Hudson
1) a blessing in disguise
Meaning: Something unfortunate that eventually proves to be fortunate.
“It was a blessing in disguise that Sarah couldn’t go for the trip. Everyone who went ended up falling really sick.”
2) a fish out of water
Meaning: To be out of place, someone who is in an unfamiliar setting.
“Tom felt like a fish out of water at the party because he was the only one who did not dress up according to the theme.”
3) give someone the cold shoulder
Meaning: To intentionally ignore someone or treat someone in an unfriendly way.
“After his sister pulled the prank on him, Amir gave her the cold shoulder.”
4) get off on the wrong foot
Meaning: Make a bad start at something.
“We might have gotten off on the wrong foot when we first met the other day.”
5) pulling your leg
Meaning: Kidding or joking with someone in a friendly way.
“My mum was just pulling my leg when she said I had to cook for everyone.”
6) caught red-handed
Meaning: Caught in the act of committing something wrong.
“The thief was caught red-handed by the security guard who was monitoring the CCTV at the time.”
7) in the limelight
Meaning: Center of public attention and interest.
“Lily loves being in the limelight especially when there are boys around.”
8) take something with a pinch of salt
Meaning: To not completely believe something that you are told because you think it is unlikely to be true
“These are some of the predicted questions for the exam tomorrow that I found on the internet. Take it with a pinch of salt.”
9) spill the beans
Meaning: To tell a secret.
“I didn’t want to tell anyone about this but I have to spill the beans now so that no one gets hurt.”
10) beating around the bush
Meaning: Avoiding the main topic, not speaking directly about the issue.
“Stop beating around the bush and tell me what it is that you want!”
11) not out of the woods
Meaning: Not yet free from difficulties or problems.
“While the doctors say she is in recovery, she is not out of the woods yet.”
12) burn the candle at both ends
Meaning: To work or do other things from early in the morning until late at night with very little rest
“Jia Sheng was burning the candle at both ends when he decided to take up a full-time job while studying.”
13) right-hand man
Meaning: The most helpful and important assistant or employee.
“When Mr Ravi is not around, you should look for Steven as he is Mr Ravi’s right-hand man in the company.”

Image by Zac Ong
14) hit the road
Meaning: To leave, to set out on a journey.
“It's time to hit the road so that we can arrive there on time”
15) call it a day
Meaning: To stop what you are doing because you do not want to do any more or think you have done enough.
“Qistina was feeling sleepy so she decided to just call it a day and continue writing her essay tomorrow.”
16) fit as a fiddle
Meaning: In good health.
“Grandpa was looking as fit as a fiddle when we last visited him.”
17) under the weather
Meaning: Not feeling well.
“Mrs Tan is feeling under the weather so she did not come to school today.”
18) through thick and thin
Meaning: If you support or stay with someone even if there are problems or difficulties.
“Lisa has been with me through thick and thin since our college days.”
19) bite off more than you can chew
Meaning: To attempt more than one can manage or take on a project that you cannot finish.
“This race is for professional athletes, Don’t bite off more than you can chew!”
20) see eye to eye
Meaning: Agreeing with someone.
“We may not always see eye to eye but I still respect him.”
21) once in a blue moon
Meaning: Something that rarely happens.
“We only go to the cinema once in a blue moon.”
22) butterflies in my stomach
Meaning: To be nervous.
“Priya had butterflies in her stomach before she went on stage to sing.”
23) finding a needle in a haystack
Meaning: Virtually impossible to find.
“Trying to find my dad among all those people who were waiting outside the stadium was like trying to find a needle in a haystack.”
24) costs an arm and a leg
Meaning: Very expensive.
“The new Macbook Pro costs an arm and a leg!”
25) a piece of cake
Meaning: Something easy.
“I was well prepared for the test so it was a piece of cake.”

Image by Aaron Burden
Best Movies To Learn English: GuruLab’s Top 10 Picks
Learning how to read with phonics - a simple guide.
Words to Use in an Essay: 300 Essay Words

By Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
Words to use in the essay introduction, words to use in the body of the essay, words to use in your essay conclusion, how to improve your essay writing vocabulary.
It’s not easy to write an academic essay .
Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way.
To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life.
If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay.
The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write.
You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay.
That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay.
Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases:
To use the words of X
According to X
As X states
Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.”
Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper.
If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases:
In this essay, I will…
The purpose of this essay…
This essay discusses…
In this paper, I put forward the claim that…
There are three main arguments for…

Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students.
After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea.
When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words:
First and foremost
First of all
To begin with
Example: First , consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers.
All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on.
The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence.
It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research.
Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay.
It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random.
Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional.
The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea:
Additionally
In addition
Furthermore
Another key thing to remember
In the same way
Correspondingly
Example: Additionally , public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces.
Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words:
In other words
To put it another way
That is to say
To put it more simply
Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words , over half the students wanted more dormitory options.”
Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words:
For instance
To give an illustration of
To exemplify
To demonstrate
As evidence
Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance , engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward.
Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said.
When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words:
As a result
Accordingly
As you can see
This suggests that
It follows that
It can be seen that
For this reason
For all of those reasons
Consequently
Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus , the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”

When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words:
What’s more
Not only…but also
Not to mention
To say nothing of
Another key point
Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover , it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct.
Often, you'll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words:
On the one hand / on the other hand
Alternatively
In contrast to
On the contrary
By contrast
In comparison
Example: On the one hand , the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand , it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived.
Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases:
Having said that
Differing from
In spite of
With this in mind
Provided that
Nevertheless
Nonetheless
Notwithstanding
Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that , I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century.
Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay.
Strong Verbs for Academic Writing
Verbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb.
You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb.
For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change , because they give the reader more descriptive detail.
Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine.
Verbs that show change:
Accommodate
Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something:
Verbs that show increase:
Verbs that show decrease:
Deteriorate
Verbs that relate to parts of a whole:
Comprises of
Is composed of
Constitutes
Encompasses
Incorporates
Verbs that show a negative stance:
Misconstrue

Verbs that show a positive stance:
Substantiate
Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence:
Corroborate
Demonstrate
Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis:
Contemplate
Hypothesize
Investigate
Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format:
Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic Essays
You should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences.
However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay.
Sometimes you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis:
Significant
Other times, you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis:
Controversial
Insignificant
Questionable
Unnecessary
Unrealistic
Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays:
Comprehensively
Exhaustively
Extensively
Respectively
Surprisingly
Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis.
In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words:
In conclusion
To summarize
In a nutshell
Given the above
As described
All things considered
Example: In conclusion , it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever.
In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought.
To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words:
Unquestionably
Undoubtedly
Particularly
Importantly
Conclusively
It should be noted
On the whole
Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure.
These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way.
There are many useful essay words out there that we didn't include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics.
If you're writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you're writing about literature.
So how do you improve your vocabulary skills?
The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words.
One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading.
Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays.
You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay.
Don't be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible.
Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives.
There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay . Good luck!

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Hannah Yang
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:

COMMENTS
40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays. To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered. Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write ...
The right words and phrases can transform your essay from a basic assignment to an insightful and persuasive piece of writing. This guide introduces you to 100 essential words and phrases recommended by expert English tutors that will help you convey your ideas more effectively.
This lesson provides 100+ useful words, transition words and expressions used in writing an essay. Let’s take a look! The secret to a successful essay doesn’t just lie in the clever things you talk about and the way you structure your points.
These useful academic expressions, words, vocabulary and phrases will help you to write a top-notch essay. PDF also available
General explaining. Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points. 1. In order to. Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.” 2. In other words.
Learn essential essay phrases, words to start paragraphs, and critical analysis terms. Elevate your academic writing with our comprehensive guide.
How to Use Creative Words and Phrases for Composition Writing & Essays? This blog post will teach you how to use creative and inspired phrases for composition writing. It will also give you examples and ideas of Idioms, Similes, Metaphors or Personification that you can use in your compositions.
Words To Use In Essays. Using a wide range of words can make your essay stronger and more impressive. With the incorporation of carefully chosen words that communicate complex ideas with precision and eloquence, the writer can elevate the quality of their essay and captivate readers.
List Of Common Idioms For Your Essays. Image by Debby Hudson. 1) a blessing in disguise. Meaning: Something unfortunate that eventually proves to be fortunate. “It was a blessing in disguise that Sarah couldn’t go for the trip. Everyone who went ended up falling really sick.” 2) a fish out of water.
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. Contents: Words to Use in the Essay Introduction. Words to Use in the Body of the Essay. Words to Use in Your Essay Conclusion. How to Improve Your Essay Writing Vocabulary.