Thesis vs. Topic Sentence
What's the difference.
A thesis statement and a topic sentence are both essential components of academic writing, but they serve different purposes. A thesis statement is a concise and arguable claim that presents the main idea or argument of an essay or research paper. It provides a roadmap for the entire piece of writing and guides the reader on what to expect. On the other hand, a topic sentence is a statement that introduces the main idea of a paragraph. It acts as a mini-thesis within the larger context of the thesis statement, focusing on a specific aspect or supporting point. While a thesis statement is typically found at the end of an introduction, a topic sentence is usually the first sentence of a paragraph.
| Attribute | Thesis | Topic Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A statement or theory that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. | A sentence that expresses the main idea or focus of a paragraph or essay. |
| Placement | Usually found in the introduction or conclusion of an essay. | Typically appears at the beginning of a paragraph. |
| Function | Provides a clear and concise summary of the main argument or point of view in an essay. | Introduces the main idea of a paragraph and sets the tone for the following sentences. |
| Scope | Encompasses the entire essay or research paper. | Focuses on a specific point within a paragraph. |
| Length | Usually consists of one or two sentences. | Varies in length but is typically shorter than a thesis statement. |
| Content | States the main argument or claim and provides a roadmap for the essay. | Introduces the main idea of the paragraph and supports the overall thesis statement. |

Further Detail
Introduction.
When it comes to academic writing, two essential components that play a crucial role in structuring an essay or research paper are the thesis statement and the topic sentence. Both the thesis statement and the topic sentence serve as guiding principles for the entire piece of writing, providing a clear focus and direction. While they share similarities in their purpose, they also have distinct attributes that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of both the thesis statement and the topic sentence, highlighting their importance and differences.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a concise and declarative sentence that presents the main argument or claim of an essay or research paper. It is typically found in the introductory paragraph and sets the tone for the entire piece of writing. The thesis statement is often considered the backbone of the paper, as it provides a roadmap for the reader and guides the writer's thought process.
One of the key attributes of a thesis statement is its specificity. It should clearly state the main point or argument of the paper, leaving no room for ambiguity. A well-crafted thesis statement is focused and precise, allowing the reader to understand the writer's stance on the topic from the very beginning.
Furthermore, a thesis statement should be arguable. It should present a claim that can be supported or refuted through evidence and logical reasoning. This attribute distinguishes a thesis statement from a mere statement of fact. By presenting an arguable claim, the writer invites the reader to engage with the topic and consider different perspectives.
In addition, a thesis statement should be concise and to the point. It should capture the essence of the writer's argument without unnecessary elaboration. This brevity ensures that the thesis statement remains clear and impactful, avoiding confusion or ambiguity.
Lastly, a thesis statement should be placed at the end of the introductory paragraph. This positioning allows it to serve as a transition between the introduction and the body paragraphs, providing a smooth flow of ideas and setting the stage for the subsequent discussion.
Topic Sentence
Similar to a thesis statement, a topic sentence plays a vital role in structuring a paragraph within an essay or research paper. While a thesis statement encompasses the entire paper, a topic sentence focuses on a specific paragraph or section. It serves as a mini-thesis, summarizing the main idea of the paragraph and connecting it to the overall argument.
One of the primary attributes of a topic sentence is its clarity. It should clearly state the main point of the paragraph, allowing the reader to understand its purpose and relevance. A well-crafted topic sentence provides a concise preview of the information that will be discussed in the paragraph, guiding the reader through the writer's thought process.
Furthermore, a topic sentence should be unified. It should address only one main idea or argument, avoiding the inclusion of unrelated or extraneous information. This attribute ensures that the paragraph remains focused and coherent, enhancing the overall clarity and effectiveness of the writing.
In addition, a topic sentence should be placed at the beginning of the paragraph. This positioning allows it to serve as a clear transition from the previous paragraph and provides a logical flow of ideas throughout the essay or research paper. By starting with a strong topic sentence, the writer sets the stage for the subsequent discussion and helps the reader navigate through the content smoothly.
Lastly, a topic sentence should be supported by evidence and examples. It should not only present the main idea but also provide sufficient information to validate or illustrate the point being made. By including supporting details, the writer strengthens the argument and enhances the overall persuasiveness of the paragraph.
In conclusion, both the thesis statement and the topic sentence are essential components of academic writing that provide structure and coherence to essays and research papers. While the thesis statement encompasses the entire paper and presents the main argument, the topic sentence focuses on individual paragraphs and summarizes their main ideas. Both the thesis statement and the topic sentence should be clear, specific, and supported by evidence. The thesis statement is placed in the introductory paragraph, while the topic sentence starts each paragraph. By understanding the attributes of both the thesis statement and the topic sentence, writers can effectively convey their ideas and engage readers in their writing.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences
Learning objectives.
- Identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts
We’ve learned that a thesis statement conveys the primary message of an entire piece of text. Now, let’s look at the next level of important sentences in a piece of text: topic sentences in each paragraph.
A useful metaphor would be to think of the thesis statement of a text as a general: it controls all the major decisions of the writing. There is only one thesis statement in a text. Topic sentences, in this relationship, serve as captains: they organize and sub-divide the overall goals of a writing into individual components. Each paragraph will have a topic sentence.
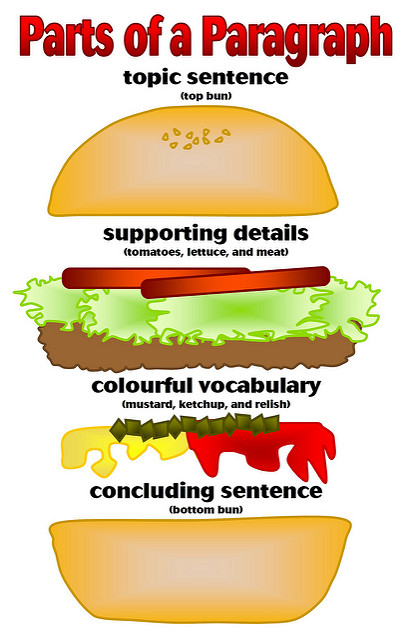
It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay’s thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself. For example, consider the following topic sentence:
Many characters in Lorraine Hansberry’s play A Raisin in the Sun have one particular dream in which they are following, though the character Walter pursues his most aggressively.
If this sentence controls the paragraph that follows, then all sentences in the paragraph must relate in some way to Walter and the pursuit of his dream.
Topic sentences often act like tiny thesis statements. Like a thesis statement, a topic sentence makes a claim of some sort. As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove it in some way. Topic sentences make a point and give reasons or examples to support it.
The topic sentence is often, though not always, the first sentence of a paragraph.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Topic Sentences. Authored by : Ms. Beardslee. Located at : http://msbeardslee.wikispaces.com/Topic+Sentences?showComments=1 . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of Parts of a Paragraph. Authored by : Enokson. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/ak9H3v . License : CC BY: Attribution

Home | Literary Movements | Timeline | American Authors | American Literature Sites | Bibliographies | Site Updates
- Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences
- Key to Comments
- Analytical Research Paper Checklist
- Test-Yourself Quiz on Commonly Confused Words
- Citing Sources
- Formatting Guidelines for Papers
- General Grading Criteria
Thesis Statements
A thesis statement defines the scope and purpose of the paper. It needs to meet three criteria: 1. It must be arguable rather than a statement of fact. It should also say something original about the topic. Bad thesis: Lily Bart experiences the constraints of many social conventions in The House of Mirth . [Of course she does. What does she do with these social conventions, and how does she respond to them? What's your argument about this idea?] Better thesis: Lily Bart seeks to escape from the social conventions of her class in The House of Mirth , but her competing desires for a place in Selden's "republic of the spirit" and in the social world of New York cause her to gamble away her chances for a place in either world. [You could then mention the specific scenes that you will discuss.] 2. It must be limited enough so that the paper develops in some depth. Bad thesis: Lily Bart and Clare Kendry are alike in some ways, but different in many others. [What ways?] Better thesis: Lily Bart and Clare Kendry share a desire to "pass" in their respective social worlds, but their need to take risks and to reject those worlds leads to their destruction. 3. It must be unified so that the paper does not stray from the topic. Bad thesis: Lily Bart gambles with her future, and Lawrence Selden is only a spectator rather than a hero of The House of Mirth . [Note: This is really the beginning of two different thesis statements.] Better thesis: In The House of Mirth, Lawrence Selden is a spectator who prefers to watch and judge Lily than to help her. By failing to assist her on three separate occasions, he is revealed as less a hero of the novel than as the man responsible for Lily's downfall. [Note: Sometimes thesis statements are more than one sentence long.] 4. Statements such as "In this essay I will discuss " or "I will compare two stories in this paper" or "I was interested in Marji's relationship with God, so I thought I would talk about it in this essay" are not thesis statements and are unnecessary, since mentioning the stories in the introduction already tells the reader this. Topic Sentences Good topic sentences can improve an essay's readability and organization. They usually meet the following criteria: 1. First sentence. A topic sentence is usually the first sentence of the paragraph, not the last sentence of the previous paragraph. 2. Link to thesis . Topic sentences use keywords or phrases from the thesis to indicate which part of the thesis will be discussed. 3. Introduce the subject of the paragraph. They tell the reader what concept will be discussed and provide an introduction to the paragraph. 4. Link to the previous paragraph. They link the subject of the present paragraph to that of the previous paragraph. 5. Indicate the progression of the essay. Topic sentences may also signal to the reader where the essay has been and where it is headed through signposting words such as "first," "second," or "finally." Good topic sentences typically DON'T begin with the following. 1. A quotation from a critic or from the piece of fiction you're discussing. The topic sentence should relate to your points and tell the reader what the subject of the paragraph will be. Beginning the paragraph with someone else's words doesn't allow you to provide this information for the reader. 2. A piece of information that tells the reader something more about the plot of the story. When you're writing about a piece of literature, it's easy to fall into the habit of telling the plot of the story and then adding a sentence of analysis, but such an approach leaves the reader wondering what the point of the paragraph is supposed to be; it also doesn't leave you sufficient room to analyze the story fully. These "narrative" topic sentences don't provide enough information about your analysis and the points you're making.
Weak "narrative" topic sentence: Lily Bart next travels to Bellomont, where she meets Lawrence Selden again. Stronger "topic-based" topic sentence: A second example of Lily's gambling on her marriage chances occurs at Bellomont, where she ignores Percy Gryce in favor of Selden. [Note that this tells your reader that it's the second paragraph in a series of paragraph relating to the thesis, which in this case would be a thesis related to Lily's gambling on her marriage chances.]
3. A sentence that explains your response or reaction to the work, or that describes why you're talking about a particular part of it, rather than why the paragraph is important to your analysis.
Weak "reaction" topic sentence: I felt that Lily should have known that Bertha Dorset was her enemy. Stronger "topic-based" topic sentence: Bertha Dorset is first established as Lily's antagonist in the train scene, when she interrupts Lily's conversation with Percy Gryce and reveals that Lily smokes.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Thesis Statement or Topic Sentence?
- High School

Occasionally at IEW our customer service team will receive questions about the differences between topic sentences and thesis statements. Hopefully this blog post will dispel any confusion between the two and empower you to help your students assail the essay in style!
Thesis statements summarize the central position of an entire essay and typically appear at the end of the introductory paragraph. Think of them as guideposts for the entire essay. They provide the reader of the essay an idea of the direction it will take. While beginning essay writers will typically write a single-sentence thesis statement, the thesis can be more than one sentence.
Depending upon the type of essay being written, a thesis statement’s emphasis will vary. In an expository essay, an essay that explains or informs, the thesis will narrow what is being explained. Thesis statements in narrative essays, which are essays that relate a story, paint an overall picture of the story that is being described and as such tend to be more personal in nature. Another type of essay, the argumentative essay, features thesis statements that underscore the writer’s opinion. In contrast, persuasive essays employ a somewhat different approach. In a persuasive essay, the thesis statement is oftentimes replaced with a question. This question serves to entice the reader to continue reading the essay in order to learn the writer’s position.
While you can think of thesis statements as guideposts for an entire essay, think of topic sentences as guideposts for individual paragraphs. Topic sentences appear in the body of the essay and are the first sentence in the paragraph. Not only do topic sentences focus the content in the paragraph, they also support the thesis statement made in the introduction.
So what might thesis statements and topic sentences look in a real-life example? Let’s consider a narrative essay prompt that asks the writer to describe someone who challenged him or her to work hard. A thesis statement might look something like this: “My gym teacher, Mr. Hernandez, never stopped encouraging me to do ‘hard things’ in high school.” This thesis statement helps the reader prepare to read some of the ways that Mr. Hernandez encouraged the writer. The topic sentences would support the thesis. Consider the following potential topic sentences:
- Mr. Hernandez encouraged me to enroll in an honors English class my senior year in high school.
- When he learned of an opportunity to help a family who had fallen on hard times, Mr. Hernandez reached out to me to help organize a clothing drive.
- Once I began to apply to colleges, Mr. Hernandez encouraged me to apply to a selective college and even offered to write a reference letter on my behalf.
These topic sentences all support the thesis of the paper by showing how Mr. Hernandez supported the writer of the essay. In the conclusion of the essay, the writer would reiterate the topics one more time before finishing the paper by emphasizing the most important point that underscores the thesis. That point might be something like this:
Mr. Hernandez saw something in me that I didn’t recognize in myself. He helped me to grow in confidence and take on challenges I would never have considered on my own. I’m excited to say that this next fall I’ll be attending ____________ University as an honors student majoring in English. And I even received an academic scholarship thanks in part to his letter of recommendation. I am so thankful he took the time to help me on my path!
|
| has always loved reading and writing and received a B.A. in English from the University of Kansas in 1991. Once she and her husband had children, they decided to homeschool, and she put all her training to use in the home. In addition to homeschooling her children, Jennifer teaches IEW classes out of her home, coaches budding writers via email, and tutors students who struggle with dyslexia. |

What's the difference between a thesis statement and a topic sentence?
4 answers by expert tutors.

Brooke J. answered • 01/05/21
Helping Students Shine for Over 17 Years!
Both thesis statements and topic sentences help your audience understand the structure and main ideas of your essay. They differ in a few ways.
1) The thesis statement belongs in the introductory paragraph , while topic sentences belong at the beginning of body paragraphs . An essay will have just one thesis statement, but the number of topic sentences depends on the number of body paragraphs.
2) A thesis statement provides an overview of your entire essay. It contains your claim and your reasons .
Thesis statement = claim + "because" + reasons
Example: Capital punishment should be outlawed because it is immoral and does not deter crime.
claim : Capital punishment should be outlawed
reason #1 : it is immoral
reason #2 : it does not deter crime
3) A topic sentence tells your reader what the paragraph is about. Each reason in your thesis should correspond to a body paragraph.
Example: Capital punishment is immoral.
I know from reading this topic sentence that the paragraph will discuss how capital punishment is immoral.
Bonus Tip: Always revisit your thesis statement before submitting your essay. Make sure the reasons in your thesis match the reasons in your body paragraphs! Often writers will include reasons in their thesis statement only to find that their reasons evolve as they research and write their body paragraphs. If the reasons in your thesis statement don't match the reasons in your essay, your audience will become puzzled and frustrated.

Reza A. answered • 01/08/21
Persian/English Teacher
A good way to start a paragraph is with a short, simple sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Teachers often call this a ‘ topic sentence".
A thesis statement, on the other hand, carries the main idea of your whole essay & therefore your stance for/ against the topic along with only mentioning your reasons.

Rachel P. answered • 01/05/21
Legal Professional Tutoring Law, Writing, etc.
Topic Sentence - usually at the beginning of every paragraph
Thesis Statement - usually at the end of the first/intro paragraph only
Topic Sentence - gives a glimpse as to what the paragraph will discuss
Thesis Statement - gives a glimpse as to what the entire paper will discuss

Karen B. answered • 01/05/21
ESL/ESOL, English Literature, TOEFL, Reading, Writing, and more
In my opinion, a topic sentence just states what the topic of your essay is. For example " The subject of my essay is on how the fashion and beauty industry influences women's body image." With a thesis statement, you need to present a stance on the topic and theory that you are trying to prove or options on how to change the situation. An example of this would be " The subject of my essay is on how the beauty industry negatively impacts women's body image and possible ways that the industry can adopt a more positive image."
Still looking for help? Get the right answer, fast.
Get a free answer to a quick problem. Most questions answered within 4 hours.
Choose an expert and meet online. No packages or subscriptions, pay only for the time you need.
RELATED TOPICS
Related questions, what specific resources willyou use to make sure this area is well presented and covered.
Answers · 11
How do you write a newspaper Article?
Answers · 12
I need a scary sentence story starter! I'm stuck on this for hours! Fast, I need Help!
Answers · 18
How do write an epilogue for an autobiography?
Answers · 7

how can i write a letter
Answers · 10
RECOMMENDED TUTORS

Marianne B.
find an online tutor
- Writing tutors
- College Essay tutors
- Dissertation Writing tutors
- Creative Writing tutors
- Research Paper Writing tutors
- Speech tutors
- SAT Writing tutors
- Grammar tutors
related lessons
- SAT Writing Test Format and Strategies
- How to Write an Essay
- Need help with something else? Try one of our lessons.
- CT Học bổng Vingroup
- TT Học tập Xuất sắc
- Cựu Sinh viên

Thesis statement là gì? Hướng dẫn viết trong Writing Task 2
Thesis statement là gì là câu hỏi được nhiều người quan tâm khi thi IELTS Writing. Đây cũng là phần gây không ít khó khăn cho các bạn học khi ôn luyện. Trong bài viết này, bạn hãy cùng VinUni tìm hiểu về Thesis statement và cách viết bài luận hay nhé!
Thesis statement là gì?
Thesis statement là gì ? Cụm từ này được tạm dịch là tuyên bố luận điểm hoặc được gọi là luận đề. Đây là một câu văn ngắn giúp tóm tắt ý chính của bài luận. Thông thường, câu luận điểm thường nằm ở đoạn mở đầu để giới thiệu chủ đề chính. Đây cũng là câu đóng vai trò làm trọng tâm cho việc phát triển ý tưởng và lập luận của bạn sau đó.
Nhìn chung, một Thesis statement hiệu quả cần đảm bảo 3 tiêu chí sau:
- Súc tích (Concise) : Một câu luận điểm hay cần ngắn gọn và đi thẳng vào vấn đề. Bạn không cần dài dòng quá mức cần thiết. Khi viết essay, bạn cần thể hiện quan điểm của mình rõ ràng và trực tiếp trong 1 – 2 câu.
- Có nội dung tranh luận (Contentious) : Luận điểm của bạn không nên là tuyên bố đơn giản về sự thật hiển nhiên mà ai cũng đều biết. Một Thesis statement tốt cần phải có bằng chứng hoặc lập luận phân tích.
- Mạch lạc (Coherent) : Nội dung được đề cập trong tuyên bố luận điểm cần được trình bày và giải thích trong phần còn lại của bài viết.

Thesis statement là tuyên bố luận điểm hoặc được gọi là luận điểm
Vì sao bạn cần viết Thesis statement?
Trong IELTS Writing Task 2, Thesis statement đóng vai trò là ý chính, ý chủ đạo của bài viết. Bằng cách đầu tư vào nghiên cứu và phát triển luận đề, bạn có thể:
- Xác định trọng tâm và hướng triển khai của nội dung cho bài viết.
- Giúp người đọc nhanh chóng hiểu được ý chính mà bạn sẽ trình bày bên dưới.
- Nếu không có tuyên bố luận điểm rõ ràng, bài luận của bạn có thể trở nên lan man. Điều đó khiến người đọc dễ bị “lạc trôi” và khó nắm bắt nội dung.
Ví dụ về Thesis statement trong Writing Task 2
Đề Writing Task 2 như sau:
“In some countries, children have very strict rules of behavior, while in other countries they are allowed to do almost anything they want. To what extent should children have to follow rules?”
Vậy Thesis statement mẫu có thể viết như sau: “In my opinion, children should have some rules to follow in order to ensure their safety and proper development, but overly strict rules can hinder their creativity and independence. Therefore, it is important to strike a balance between discipline and freedom for children.”
Trong Thesis statement này, bạn đã trình bày quan điểm về đề bài và tóm tắt ý chính trong bài viết. Bài viết nói về trẻ em cần có một số quy tắc để đảm bảo sự an toàn và phát triển cá nhân. Tuy nhiên, có quá nhiều quy định có thể tác động đến sự sáng tạo và tư duy của trẻ nhỏ. Do đó, chúng ta cần phải duy trì sự cân bằng giữa kỷ luật và tự do cho trẻ em.

Thesis statement đóng vai trò là ý chính, ý chủ đạo của bài viết
Sự khác biệt giữa Thesis statement và Topic sentence
Nhiều bạn thường hay nhầm lẫn giữa hai khái niệm “Thesis statement” và “Topic sentence“. Về cơ bản, hai thuật ngữ này khá tương đồng, song lại không hề giống nhau. Cụ thể, Thesis statement thể hiện luận điểm chính của cả bài luận. Còn topic sentence chỉ là câu ý chính của một đoạn văn nhất định trong bài.
| Thesis Statement (Câu luận điểm) | Topic Sentence (Câu chủ đề) |
Thesis statement nên nằm ở đâu?
Thesis statement thường xuất hiện ở cuối phần giới thiệu trong bài luận. Ví dụ:
The internet has had an immense impact on education, revolutionizing the way students learn and teachers teach. Through online access to educational materials and resources, students are now exposed to a variety of perspectives and can explore a range of topics at their own pace. Despite some valid worries about potential harms associated with internet use, it is clear that its various benefits far outweigh any negatives.
Cách viết Thesis statement trong IELTS Writing Task 2
Khi tìm hiểu Thesis statement là gì, mọi người thường thắc mắc cách viết chủ đề này ra sao trong Writing Task 2. Thesis statement được xem là một trong những phần quan trọng nhất trong IELTS Wring Task 2. Sau đây là một số bước giúp bạn viết luận đề hiệu quả:
- Bước 1: Đọc kỹ đề bài và xác định chủ đề chính của đề bài.
- Bước 2: Xác định ý chính của bản thân về chủ đề bằng cách phác thảo ý tưởng, tình huống.
- Bước 3: Lựa chọn một ý kiến chính để bao quát toàn bộ bài viết của bạn.
- Bước 4: Sắp xếp các ý kiến, tình huống. Ví dụ thành một cụm từ, câu hoặc đoạn văn ngắn để diễn đạt ý chính của bạn về chủ đề của bài.
Trong quá trình này, bạn cần lưu ý đảm bảo Thesis statement phải rõ ràng và ngắn gọn. Một tuyên bố luận điểm trình bày tốt sẽ giúp bài viết của bạn đạt điểm cao hơn.
5 lưu ý về cách viết Thesis statement trong Writing IELTS Task 2
Sau đây là 5 lưu ý chính về cách viết câu luận điểm để có hiệu quả cao nhất:
Mạch lạc và súc tích
Thesis statement cần phải được viết rõ ràng và ngắn gọn. Từ đó để người đọc có thể nhanh chóng nắm được quan điểm và lập luận của bạn. Bạn nên tránh sử dụng ngôn ngữ mơ hồ, biệt ngữ hoặc các cấu trúc phức tạp, dễ gây nhầm lẫn.
Ví dụ, bạn nên tránh sử dụng các thuật ngữ mơ hồ và chung chung như “some,” “many,” hay “a lot”. Thay vào đó, bạn hãy sử dụng cách diễn đạt cụ thể để minh họa sâu sắc cho lập luận của mình.
Ví dụ: Some people believe that social media has a negative impact on mental health. -> The excessive use of social media can lead to depression and anxiety among adolescents.
Nêu ra quan điểm chính
Thesis statement cần thể hiện quan điểm xuyên suốt và đóng vai trò là “lộ trình” cho xuyên suốt toàn bộ bài. Từ đó giúp người đọc có thể hình dung về những ý tưởng mà họ có thể chờ đợi trong các phần tiếp theo. Hãy đảm bảo rằng bạn tuyên bố luận điểm của mình một cách cụ thể, có tính tranh luận và được hỗ trợ bằng dẫn chứng hoặc ví dụ.
Ví dụ minh họa:
Topic : Should schools teach financial management to students?
Thesis Statement : Schools should teach financial management to students as it will help them make informed financial decisions, cultivate responsible spending habits, and reduce the risk of debt in adulthood.
Như bạn thấy, câu luận điểm trên đây đã nêu rõ quan điểm chính của người viết về trường học nên dạy kỹ năng quản lý tài chính cho sinh viên. Có 3 điểm hỗ trợ như sau:
- Giúp sinh viên đưa ra quyết định tài chính sáng suốt
- Nuôi dưỡng thói quen chi tiêu có trách nhiệm và
- Giảm rủi ro mắc nợ khi trưởng thành.
Nó có tính tranh luận. Vì có thể có nhiều ý kiến khác nhau về việc trường nên ưu tiên dạy quản lý tài chính hay tập trung các môn khác cho sinh viên. Cuối cùng, luận điểm của bạn có thể được hỗ trợ bằng bằng chứng hoặc ví dụ. Vì đã có những nghiên cứu thực tế về lợi ích của giáo dục tài chính đối với sinh viên.
Sử dụng từ ngữ mạnh mẽ
Thesis statement nên được sử dụng ngôn ngữ mạnh mẽ, rõ ràng để truyền đạt quan điểm của bạn một cách hiệu quả nhất. Tránh sử dụng những cụm từ như “I think”, “In my opinion” vì nó sẽ làm suy yếu lập luận của bạn. Ngoài ra, sử dụng động từ chủ động sẽ thể hiện ý tưởng của bạn một cách chắc chắn hơn.
Topic : Should college education be free for everyone? Weak : In my opinion, I think that college education should be free for everyone. Strong : College education should be free for everyone as it is a basic human right and promotes equal opportunities for all individuals to access higher education.
Trong ví dụ ban đầu, việc bạn sử dụng cụm từ “I think” và “In my opnion” khiến luận điểm của bạn trở nên kém thu hút và mang tính chủ quan. Ngược lại, ví dụ thứ hai sử dụng các động từ tích cực và rõ ràng để truyền đạt quan điểm thu hút hơn. Bên cạnh đó, người viết cũng bao gồm lập luận hỗ trợ, rằng giáo dục đại học là quyền cơ bản của con người, góp phần thúc đẩy các cơ hội bình đẳng.
Tránh sử dụng đại từ nhân xưng
Trong bài viết IELTS Academic, bạn nên tránh sử dụng các đại từ nhân xưng như “I” hoặc “my”. Thay vào đó, bạn hãy sử dụng ngôn ngữ trung lập để trình bày lập luận. Điều này sẽ đảm bảo tính khách quan và xác thực cho luận điểm thể hiện trong bài.
Đảm bảo bám sát yêu cầu đề bài
Thesis statement cần liên quan trực tiếp đến câu hỏi trong đề thi IELTS Writing Task 2. Hãy đảm bảo rằng câu luận điểm của bạn đã đề cập đến câu hỏi cụ thể được đặt ra. Để làm điều này, bạn hãy đọc lại câu hỏi nhiều lần để đảm bảo nội dung của bạn đang đi đúng chủ đề.
Some people think that social media has more disadvantages than advantages. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
Lạc đề: Social media is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the way we communicate and interact with each other.
Trong ví dụ này, câu luận điểm không đề cập đến câu hỏi. Người viết nêu được chủ đề mạng xã hội (social media). Nhưng họ không đề cập đến những lợi thế và bất lợi của việc sử dụng mạng xã hội. Cũng như họ không đưa ra quan điểm rõ ràng về chủ đề này.
Đúng đề: While there are some disadvantages to using social media. The advantages outweigh them as it allows for easy communication and connection with others, provides access to information and resources. And it can be used for educational and professional purposes.
Với ví dụ này, câu luận điểm đề cập trực tiếp đến câu hỏi qua việc người viết thừa nhận rằng có những bất lợi khi sử dụng mạng xã hội. Nhưng đồng thời có những lợi ích to lớn hơn bù lại. Ngoài ra, người viết cũng đề cập 3 luận cứ chính sẽ được giải quyết trong bài luận này.

Bài viết trên đã giải thích cho bạn biết Thesis statement là gì . Bạn hãy nhớ rằng, câu luận điểm chính là xương sống của toàn bộ bài luận. Vì vậy, bạn hãy cố gắng luyện tập thật nhiều để tăng cường kỹ năng viết. Ngoài ra, VinUni có khoá học Pathway English giúp cho sinh viên có thể rèn luyện và nâng cao 4 kỹ năng trong tiếng Anh. Qua đó, sinh viên có thể tự tin sử dụng ngôn ngữ trong việc học và công việc trong tương lai hơn!
Có thể bạn thích

Chiến lược trình bày quan điểm IELTS Speaking Part 3

8 cách học tiếng Anh giỏi bạn nên tham khảo

Cách trả lời IELTS Speaking Part 2 và chiến thuật làm bài

Tổng hợp các dạng bài Listening IELTS: Bí quyết đạt điểm cao

Bảng quy đổi điểm TOEIC sang IELTS chi tiết

Hướng dẫn cách học tiếng Anh giao tiếp hiệu quả cho người mới bắt đầu

Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách phân biệt THAT và WHAT trong mệnh đề danh từ

Chia sẻ các cách học từ vựng tiếng Anh nhanh thuộc và nhớ lâu

Phương pháp học ngữ pháp tiếng Anh hiệu quả nhanh chóng

Tiếng Anh căn bản cho người mất gốc nên bắt đầu từ đâu?

IMAGES
COMMENTS
**Thesis s •A thesis statement can appear as one sentence (see examples C and D) or several sentences (see examples A and B); this is dependent on the requirements of your rhetorical context. ** Note: these are general guidelines for constructing a strong thesis statement and topic sentences in a thesis driven essay; always refer to your ...
With the prompt as a guide, here are the topic sentences for each body paragraph: Topic Sentence #1: The repeated characterization of Lilith as "too spirited" highlights her tenacity and pride, which are unusual traits for the enslaved characters to possess. Topic Sentence #2: The term "spirited" also connects Lilith to the spiritual ...
A thesis statement is a concise and arguable claim that presents the main idea or argument of an essay or research paper. It provides a roadmap for the entire piece of writing and guides the reader on what to expect. On the other hand, a topic sentence is a statement that introduces the main idea of a paragraph.
As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove it in some way. Topic sentences make a point and give reasons or ...
A thesis statement is written to state the main purpose or argument of your writing. That means that your thesis statement will be supported through all of the body paragraphs that make up your essay. A topic sentence is the first sentence of a body paragraph. This sentence indicates for your reader how the paragraph will support your thesis.
A topic sentence is one part— just one element— of our thesis statement. Our thesis statement, then, should be present or emphasized within our topic sentence in order to show relevance and cohesion throughout our paper. A topic sentence consists of: Reference to thesis + one specific idea for paragraph. (order doesn't matter, but we must ...
This video explains the difference between the Thesis Statement and the Topic Sentence. After you watch this, you will clearly understand what each one is. H...
To make sure every topic sentence and paragraph serves your argument, follow these steps. Step 1: Write a thesis statement. The first step to developing your topic sentences is to make sure you have a strong thesis statement. The thesis statement sums up the purpose and argument of the whole paper.
Thesis Statements. A thesis statement defines the scope and purpose of the paper. It needs to meet three criteria: 1. It must be arguable rather than a statement of fact. It should also say something original about the topic. Bad thesis: Lily Bart experiences the constraints of many social conventions in The House of Mirth.
5. A troublesome thesis is a fragment; a good thesis statement is expressed in a complete sentence. Example: How life is in New York after September 11th. Better: After September 11th, the city of New York tends to have more cases of post-traumatic disorder than other areas of the United States and rightfully so.
What you'll learn to do: identify, analyze, and create effective thesis statements. Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text while you're reading it takes practice, but it is an essential skill to successful writing. Powerful thesis statements are an effective and important element of almost every writing assignment in college.
Adaptions: Reformatted, some content removed to fit a broader audience. 5.2: Identifying Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Topic sentences and thesis statements are similar to main ideas. This section discusses those similarities and the differences ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
The thesis is a specific argument that will be involved in every paragraph of the paper whether one is introducing it, defending it, or reinforcing it. It is the sole reason for the paper's existence and should be one written as a well-constructed sentence that acts as a map for how the paper will unfold. Here are a few examples of topics and ...
The main idea, thesis statement, and topic sentences all provide structure to an essay. It is important for both readers and writers to understand the roles of each of these in order to maintain ...
Explains the differences between Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences with examples of how to improve each.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Thesis statements summarize the central position of an entire essay and typically appear at the end of the introductory paragraph. Think of them as guideposts for the entire essay. They provide the reader of the essay an idea of the direction it will take. While beginning essay writers will typically write a single-sentence thesis statement ...
the rest of the sentences explained the topic sentence. Look at the following chart to see how the thesis statement and topic sentences are connected. Thesis Statement (big idea) ^ 3 Topic Sentences explain the thesis statement. Each begins a new paragraph and tells the reader what the paragraph will be about. (smaller reasons) ^
After being introduced during the K-12 years of a student's education, academic writing is a mainstay in college and higher education. With proper format and technique being a major aspect of academic writing, it is essential for students to understand the differences between a topic sentence and a thesis ...
The following video, Thesis Statements vs Topic Sentences created by Worldwide Speak is a step by step guide to writing thesis statements and topic sentences. This page titled 2.3: Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Sravani Banerjee, ...
The thesis statement is the fundamental stand the writer takes. It incorporated the generalized idea of the essay, including the author's perspective of the topic and the key points included in the text. Striving to make this part influential, the learner should fixate on the topic, limit it, and narrow it down, presenting only the most ...
They differ in a few ways. 1) The thesis statement belongs in the introductory paragraph, while topic sentences belong at the beginning of body paragraphs. An essay will have just one thesis statement, but the number of topic sentences depends on the number of body paragraphs. 2) A thesis statement provides an overview of your entire essay.
Sự khác biệt giữa Thesis statement và Topic sentence. Nhiều bạn thường hay nhầm lẫn giữa hai khái niệm "Thesis statement" và "Topic sentence". Về cơ bản, hai thuật ngữ này khá tương đồng, song lại không hề giống nhau. Cụ thể, Thesis statement thể hiện luận điểm chính của ...