A Fine Parent
A Life Skills Blog Exclusively For Parents

9 Simple Tips for Teaching Kids How to Focus on Homework
by Cate Scolnik . (This article is part of the Positive Parenting FAQ series. Get free article updates here .)

Five minutes into my daughter starting it, she’s asked 4 irrelevant questions and walked across the room twice – for no reason .
She had a break when she first got in from school, and had a snack. Then we agreed to a little outside time before starting homework.
She’s got the book open and a pencil in her hand, but that’s the sum total of her achievement so far.
Her mind doesn’t seem to want to sit still – preferring to bounce all around the place. It’s like her mind is a magnet, and when it’s put near homework, it repels away from it.
When she was 5, I thought she would grow out of it; but at 8 years old I was beginning to worry.
As someone who likes to get in and get things done, it drives me nuts .
Don’t get me wrong, I love my daughter dearly. But the way she gets distracted every 5 minutes during homework time is enough to make anyone go crazy.
She’s highly intelligent, has loads of positive energy and is warm and engaging. She can focus long and hard on anything she is interested in. But getting her to focus on homework she isn’t keen on? Damn near impossible.
I just couldn’t sustain parenting positively unless I got this under control. I wanted to take some action.
At one point when her distraction was driving me nuts, I had started to wonder if I should get her tested for attention deficit disorder (ADD). My research on this topic led me to discover some behavioral techniques used with ADD kids, that are also applicable to any child having difficulty focusing.
I decided to try them for teaching my daughter how to focus on homework. Some worked better than others but overall it has been a great success. Here are the ones that worked for us –

#1 Keep It Short
When it came to doing homework, we kept it short and broke it down. Generally, that meant one ten-minute stint a day, instead of one 30-40 minute block each week.
Each time she wandered off task (mentally or physically), I would gently guide her back to the homework.
I kept the focus light and pointed out the fun parts of her work. And I bit down hard on my tongue every time I felt like screaming “If you just stuck to the task and focused you could be done already!”
#2 Use A Timer

So, if I estimated a task could be completed in about 2 minutes, I’d set the timer for 5 minutes. Each time she started chatting about something, I’d say something like “I hope you beat the timer!” or “Don’t forget – you want to beat the timer!”
#3 Wear Them Out
My daughter has loads of physical energy, so I made sure she got lots of exercise . Even now she needs to do lots of running around, or physical activity to wear her out a bit.
I’m not talking about making her run a marathon every day. Just encouraging and supporting her to move her body.
I worked with her natural rhythms as much as possible. I realized she had more energy in the afternoon, so we often went on outings in the morning.
If she’d been to school for the day and we were going to spend a few minutes on homework, I’d encourage her to go and jump her jiggles out on the trampoline before we sat down to focus.
#4 Kept It Positive
I focused on her positive outcomes as much as possible. Whenever she breezed through an activity I would give her positive feedback .
“Look how quickly you finished writing out your words! You stayed focused and you finished that in no time. Well done!”
We’d always start homework early and allow extra time to get things done, so I had to be organized and plan ahead. This meant I could sometimes say, “Wow! You finished your homework the day before it’s due. Great effort!”

If we’d been working on a homework task for a long time and she was just getting less and less focused, I’d call a stop to it. When a five-minute task is only half done after 25 minutes, and there’s no momentum, there really isn’t any point continuing.
This is a tricky one, and I didn’t use it often. She’s a bright girl and she knew she hadn’t finished what she set out to do that day. But if we kept trying and getting nowhere, we would both become very frustrated and dejected – no good ever comes out of that.
So, I’d suggest we leave it for now and come back to the task when we were fresher. This way she wasn’t failing, it just wasn’t the right time.
#6 Eat More Fish
Crazy as it might sound, eating more fish or taking fish oil supplements , is apparently helpful.
Now, I’m not a nutritionist and I understand that the fish oil theory is unproven. But there seems to be research to support the fact that fish oil high in EPA (rather than DHA) can help improve focus.
I figured it was something that couldn’t hurt, so I did it. It seemed to me that each time her fish oil consumption dipped, she became less focused.
I’ve no real evidence to support that – it may just be in my head. 😉
#7 Encourage Self-Management

The Tools of the Mind program produces brighter children who are classified as gifted more often, but more importantly, it also produces kids with better behavior, greater focus and control.
Classes involve role play and each child creates their own detailed plan of their part. If a child gets off track, the teacher refers them back to their plan.
One of the ways the program helps is through encouraging planning and time management by setting weekly goals. This helps to wire up the part of the brain responsible for maintaining concentration and setting goals.
The Tools of the Mind philosophy is that every child can become a successful learner, with the right support. Children learn by using the skills they currently have – such as drawing and play. They think through their play plan, then draw a detailed record of it, then carry it out.
Using their skills in this way teaches children to set achievable goals, work out how to reach them, and stay on track. They learn they can be responsible for their own outcomes. We’ve been using this to teach my daughter self-management .
#8 Work Together
My daughter is nearly eleven now and has matured a lot over the last year. And I’ve just started using self-management techniques to help her set goals and plan how she’ll achieve them.
Earlier this year she said she really wanted to improve her grades, which I said was a great goal. Then she said she wanted to be involved in band, which means taking some band lessons in class time.
I asked her to plan how she intended to achieve both goals, given she has other extra-curricular activities she wants to keep up.
She created a plan to practice her instrument regularly and do more homework than she has previously. We’re at week 7 of our school year here in Australia, and so far she’s on track.
She dives into homework without being reminded and gets it done early. She’s also completing homework tasks to a higher standard, rather than madly (and messily) rushing through them .
Since starting band she’s been practicing twice a day, every day – without being asked. I know that if she loses momentum, or strays off track, I can direct her back to her own plan.
#9 Understand The Scale

We all have different strengths and weaknesses. And attention and focus can vary wildly, particularly in the early years.
It partly depends on the environment, and partly the child.
Try and take the pressure off, and work with your child’s strengths.
Break tasks down and keep them fun.
Aim for a balance between physical and mental focus, and remember it’s OK to give up if the timing isn’t right.
Have realistic expectations, and know that your child’s focus will improve with age.
Don’t be scared to quit when things really are not working. Not doing a perfect job on the homework once in a while is not the end of the world. If it comes to a choice between quitting for the moment or screaming and yelling at your kids through the task, choose love and call it quits.
And finally, hang in there. It’s all going to be OK.

The 2-Minute Action Plan for Fine Parents
Take a moment to consider your child’s behavior.
- How does it compare to other children? Either their siblings or a number of other kids of a similar age? (Try to compare them with a range of other kids – rather than one or two)
- Does your child seem to have age-appropriate behavior and focus? If you’re concerned, do you need to seek help?
- How can you start breaking down big tasks into manageable (snack-sized) sections?
- Is your child able to focus on things they like doing? Can you use that in your favor?
- Are your kids distracted by things that could be controlled?
- What strategies can you put in place to keep your kids focus?
The Ongoing Action Plan for Fine Parents
- Brainstorm some roles that you can use to elicit certain behavior. If you need your child to be quiet and still for a few minutes, what can they pretend to be? A King or Queen on a throne? A soldier on guard? Good posture during homework is a good idea, but if the only way to get your child to do it without a fuss is to let them pretend to sit on a throne or stand at attention, go for it!
- Think back over the things that your child struggles to focus on. How can you get them to use self-management techniques to improve?
- If it seems impossible to get your child to focus and pay attention ask yourself this: “If it were possible, how would it be achieved?” Make some notes.
- Take a moment to check out why Tools of the Mind works so well and think about how you might use their strategies at home.
About Cate Scolnik
Cate is on a mission to help parents stop yelling and create families that listen to each other. She does this while imperfectly parenting two boisterous girls of her own and learning from her mistakes. Download her free Cheat Sheet to Get Your Kids from "No" to "Yes" in Three Simple Steps and reduce your yelling today.
May 16, 2016 at 6:21 am
This is a great article and there is some mention of it but I feel it has to be emphasized- that no homework should ever trump connection with your child. If homework struggles are causing you to butt heads time to re-think! Your child needs you in their side ALWAYS, there have long difficult days in School where social interactions and the system challenge their resources all day long. The need to come home to an ally. Here in Canada we are seeing tons of research that shows that homework before high school produces little increase in assessment scores – I imagine education philosophy will move toward reducing or almost eliminating primary homework! So don’t sacrifice your living connected relationship at home iver homework
May 16, 2016 at 2:35 pm
Totally agree with you on the point that “no homework should ever trump connection with your child”, Kim.
I’ve read some of the research about homework, but I’m not entirely convinced. To me, even if homework does little to increase assessment scores, it builds the habit and discipline of getting things done on your own outside the classroom… So IMO there is some merit to it. The question for me is more of how to teach our kids to focus and build this habit in a kind and gentle manner without butting heads…
May 16, 2016 at 11:29 pm
You’re right that we shouldn’t let homework damage relationships. I’m fortunate that our school has homework as an optional thing, but we do opt in. Like Sumitha, I think it’s more about getting a routine established.
Thanks for your comment. 😉
May 10, 2017 at 3:50 pm
Agree with #Cate. I asked school to increase the home work for my daughter to help her develop the habit of focus, responsibility, self – discipline and also prepare them for high school where they should not get shocked with the name of home work thinking it as a monster.
Apart from this, these tips are life saving and work word by word. Thank you so much for sharing and I liked these so much that I shared the page with my facebook friends.
May 16, 2016 at 1:35 pm
My child’s PRE-SCHOOL had homework. It was age-appropriate (“Color the baby chicks yellow”) but surprise, surprise–my daughter didn’t want to do it. She wanted to run around the playground and then jump on the sofa. I mentioned this to another parent (of a typically developing child) and she said, “Oh, we don’t do the homework. It’s not developmentally appropriate at this age.” Boy, did my life improve when I followed her advice and ignored the homework! I told the school, nicely, that I got home from work too late in the evening to do homework. And that was the end of it! Now, in elementary school, we don’t do the homework every night. It is BORING (math worksheets) and turns her off to everything related to school!
May 16, 2016 at 2:42 pm
Wendy, homework in preschool is probably pushing it too much… but as kids grow older, I do believe there is some merit to homework in terms of building habits and discipline of doing things on your own outside the classroom and being accountable for something that is assigned to you.
I personally feel that telling kids you don’t have to do something because it is boring sends the wrong message (listening to any grownup is boring for a kid… so if they can skip doing homework because it is boring, why not also skip listening to what grownups tell them?) To me, building the habits of accountability and sticking to a task even if it is sometimes boring and learning tricks to focus even when you sometimes don’t want to are important life skills… Homework is one of the ways to do this, and I would rather look for kind and gentle ways to do this than give up on homework entirely.
June 29, 2024 at 8:25 pm
I teach at a local nursery in order to have something to do. In addition I give them two tasks each week. For example a upcoming task will involve pumpkins. They recently as a entire preschool class painted a picture of a sunflower. They are little so I do the research for them instead. In the past we have focused on music, gardening and cooking. Best wishes. Planning a October visit to a pumpkin patch.
We also once did baking. From time to time we study animals and learn about other people. If it is hot we either do gardening or ride child friendly bikes. Recently we have gone on picnics and tried tennis. Each task has a theme. Drawing is fun.
Considering a museum trip and so on. In terms of future tasks, I’m planning one that is wholly based on Halloween. I’ve also got a idea for Christmas. Other activities include pond dipping and farm outings. Yet more such fun activities in consideration will involve poster design and card making. I’m keen on easy sports like table tennis. I believe that they have a sports day. Have a nice day.
Last week I decided on a whim to try sand art and water play. I also want to teach them to cook. Two weeks before we rode bikes and assisted in the garden at the nursery. Once or twice a day we do singing and reading in question. I’m also keen on classic board games and stencilling. I want to try out new activities like pottery and face painting. We do a lot of reading. I love origami.
Bingo wouldn’t fail either. They have never played simple games like Monopoly Deal or Scrabble. Additionally I love the idea of introducing them to other classic games. We have previously tried creative writing and poetry. I really do like to focus on basic skill development as far as possible. This includes story telling and independence building. For example making friends and being healthy.
Snap is cool. So is making fresh lemonade and the like. I’ve never tried either activity. I love to play UNO. Coding is hard work. One day in the near future I’m organising a class trip to a library and a zoo. In the past I’ve shown them how to use a shape sorter toy and puppets. We use the puppets to tell a simple story. And we have a sensory room.
May 16, 2016 at 7:49 pm
I don’t believe in most homework and glad it’s not generally a part of Montessori. At my kids’ school they don’t start handing out homework until 4th grade, and even then it’s a packet they have all week to complete so they can choose their own pace for finishing it. I like that no homework leaves time for other things like piano and violin and volleyball and Latin, not to mention the chance for my kids to help me cook, etc. When my oldest got to the adolescent program and we started to struggle with homework, we realized in her case the best approach was to back off and leave her to fail or succeed on her own. I think for many children there is much more value in unstructured time to play and explore. They have to be disciplined at school all day. I don’t see why they have to extend that into home time. I love watching my kids come up with their own projects which are often far more interesting than anything a teacher would send home as an assignment. Most homework is busy work. Life is too short for that.
May 16, 2016 at 9:20 pm
If the homework was long and unending, I would likely agree with you (at least to a certain extent ;)), Korinthia. Fortunately, my daughter’s home work assignments usually take just 10 – 15 minutes which she actually finishes up in school. It is busy work, but it reinforces the facts that she has learnt that day in school. Her teacher’s take is that it helps her gauge if the kids are grasping what they learn, and lets her know if she should repeat any concepts or slow down the pace etc. I love that idea of using homework (and tests) as a feedback loop. Her school also specifically tells parent not to get involved unless the child asks for clarifications. This also helps the homework serve as a mini-token of responsibility and self-management… which is all good in my book.
I love how every time this discussion comes up, we come at it from such opposite perspectives 🙂
May 16, 2016 at 10:14 pm
I think one of the trickiest things in parenting is realizing people can do the opposite of what you do and still not be wrong. We’re all so vulnerable in this area that people get defensive fast! I love that you are so thoughtful with every response, and that there is more than one way to be right. And I keep coming back here because I feel it’s a safe place to voice a different perspective without people taking it as a challenge to their own parenting decisions. That’s a rare and wonderful thing and you should be proud of this site. (For that and many reasons!)
May 16, 2016 at 10:23 pm
Thanks, Korinthia. I needed to hear that today (for a reason unrelated to this site and the comments here). And of course I lapped up the compliments about the site too. I never tire of that 🙂
And you stretch my thinking more than anyone I know and I learnt a lot about writing responses from studying your responses… so thanks right back at ya!
May 16, 2016 at 11:35 pm
Hi Korintha,
You’re right that we can use homework as a valuable learning experience. For years my older daughter (now 11) has ‘hoped’ for straight As, but hasn’t achieved them. She’s getting better for years she did the bare minimum with homework, and did it rather … messily too! While I don’t push her too much, I do make the point that A grades are the result of hard work. They’re achievable for anyone who puts in the effort – including her. But getting As means you’ve done the best you possible can, almost all the time.
It doesn’t stop her hoping every time her report comes home, but she knows she can set goals and strive to meet them (they’re just usually in non-academic areas!).
Anyway, your point about homework being a mutli-faceted learning opportunity is a great one. 😉
May 17, 2016 at 7:27 am
Grades are a weird measure of things, though, because they aren’t universal. Does getting an A mean it’s the best you as an individual can do, even if it’s not great? Does getting an A mean there is some objective level of excellence that few people can reach? Does getting an A mean the grade was on a curve and you are simply the best in this particular crowd? A’s on a single report card can mean all of those things or none of them.
I remember in college I was upset one semester because my perfect 4.0 was marred by a B in tennis which I was simply taking for fun. I felt I should get an A for showing up and doing my best every time. Apparently the teacher had a different measure. And how do you grade music (which was my major)? One person can play every note perfectly and leave you feeling cold with their performance, and another can make mistakes but be electrifying. In orchestra it was pure participation–you started with an A and every class you missed you went down one letter grade. The A says nothing about if you did well or even improved. (You could get worse and still get an A.) When I was in 6th grade I used to alternate between A’s and failing grades in reading based on if I handed in the book reports. Those grades said nothing about my reading ability.
Grades do say something, but I’m skeptical about what. And every time I get worried about grades I remember my grandma telling me that nobody ever asked her her GPA once she graduated. No one has ever asked me mine, either. People only care what I can actually do, and that I try to prove every day, and that’s what I tell my kids to aim for. They may or may not get the grades they deserve to reflect that, but they need to mentally grade themselves to stay honest.
May 20, 2016 at 8:19 pm
Your points are spot on, as always. Grades are an arbitrary measure.
I think it’s far more important that my daughter is satisfied that she’s done her best, and that she’s proud of her efforts. Having said that, I do think it’s useful to learn that you can set goals and strive towards them.
Arbitrary or not, we spend most of our lives being assessed. Either at school or university or in the workplace. It’s usually one person’s opinion of certain traits or activities, and it’s often arbitrary.
Whilst I’ve certainly been the victim of a manager who’s had their own agenda – and rated me accordingly – I think that’s the exception. I also think it’s important that my kids feel that they have some control over the assessment. If they put in greater time and effort, they will usually get greater results.
It’s important to know that grades and assessments are only one person’s opinion and that they may be flawed. That is, we need to keep it in perspective. But given we’ll have these assessments throughout our lives, we need to learn to feel we have some control over them and we need to learn how to handle them. How to digest them, how to cope with them, and how to use them too.
It’s a complicated, complex, multi-faceted issue! And I certainly appreciate your perspective. Thanks for commenting 😉
June 29, 2024 at 8:44 pm
I played table tennis once a week in order to keep fit. I also had to assist with the gardening and cooking. At only five years old I had to learn five new simple numbers and words each week. At Christmas we went to a local church. There were many family beach picnics. Best wishes. My parents loved to recite four line poems each night at bedtime.
As a entire family we played table tennis early on a Saturday afternoon once a week. I was expected to know first aid and learn how to fix a broken down car. Once a year we grew a pumpkin at home. On the warm beach we sang and read storybooks. And we went on Sunday nature walks. I even did the food shop and mastered the rather basic one times table in addition. I learnt how to cook, prepare a hot cocoa plus make the beds.
On a weekly trip to a farm shop at a nearby garden centre I had to count up or down in fives. I had a short numbered list of things to buy. I had to teach myself to play the guitar and how to use a camera. That was fun.
At home I washed the car and babysat at church. Other activities and skills included washing up and making bookmarks. On family days out we soaked up the sun on a cycling trip or a walk. We did woodland walks. I learned how to prepare a entire tray of scones and tasty biscuits. I also discovered how to make cakes and identify the trees and flowers.
May 17, 2016 at 4:28 pm
Thanks for this article! We are in our last week of kindergarten homework before the summer hits. That first sentence! So funny and spot on. Like “where are you going sit back down!” I find my self saying frequently. My son gets a packet of homework on Monday that he has to complete and turn in by Friday. I like the idea of using the timer! I’m not sure about play before homework.. I see the need for a break. My issue is that after eating and a play break its already so late then he’s not focused because he’s just getting tired. Also other than getting a 5 year old to focus on homework is doing the homework correctly. He will speed through it sometimes brag about how many pages he completed but he sometimes just writes down whatever to make it look like its complete! This has been driving me crazy, I have to erase so much! I’m trying to find the balance between getting him to work independently and me sitting there for every question. They do homework time in after school too and this is also when he makes it look like he’s doing homework and sometimes just draws pictures on the back of his homework pages. I think the amount of homework for kindergarten is a bit much, but I don’t think that not doing it is an option. I want to encourage him and be proud of him for completing his homework and also try to only let him play on the tablet after the whole packet is done… which also kinda leads to him speeding through it. Ugh and this is just year ONE! OMG!
May 18, 2016 at 3:57 am
Hi Amber, You’re right – you need to find what works for you. And if your kids are in after school care, it’s a bit too late to get them to concentrate when you get home. When I get my kids home it’s nearly 6pm, and there’s no way I can get them to focus on homework.
I’m lucky that I have two days a week where I don’t work late, so they are our ‘homework days’. The other option for us is to do a few minutes in the morning, before school, when the girls are fresh. Of course, this depends on what mornings look like in your house.
You say you want to be proud of him, but it’s also important that he’s proud of himself. That’s why I often ask my girls if they’re proud of their homework. It’s a great technique to get them to reflect on their efforts. 🙂
January 23, 2018 at 9:41 pm
Thanks for the tips for getting kids to do homework better. My son struggles with math, and he never wants to do his homework. I really like your idea to set a timer. That way, he knows exactly how long he needs to work before he can take a break to play. We will definitely give this a try.
April 7, 2018 at 9:49 am
Yes!! I totally agree with Korinthia! I have 5 kids from high school to a 2 yr. Old and it frustrates us as a family when we cannot take a walk, go out and play, or do any sports or extracurricular activity or even help with dinner because they have so much homework! How can kids get their 60 min. Of physical activity or eat healthier or spend time with family if we barely have time to eat a rushed meal to do homework? Including on weekends and vacation!
July 16, 2018 at 6:07 am
Homework is one word that makes every school child – and many parents – cringe. Follow these handy tips, and soon, homework related tension will become a thing of the past. https://www.parentcircle.com/article/exclusive-tips-to-make-homework-easy-for-your-child/
August 8, 2018 at 3:21 am
Awesome post!!! Homework is very important for students to get great results in academic. It is also essential to complete your homework on time. Thanks for sharing this information.
September 4, 2018 at 12:25 am
Good tips and very informative. Homework is a very important thing to get good grades n academic. Today, Focus on Homework is very essential. So, Students must do homework on time.
June 24, 2019 at 6:52 pm
October 15, 2019 at 7:55 am
It’s really useful tips for many parents and their kids. I think that right focus on homework is an important part to stay productive for a whole year in school.
January 7, 2020 at 11:13 am
Learning to focus is extremely important especially with the distractions that surrounds us in today’s world. Your article has been tremendously helpful and I am grateful so Thank you for sharing .
September 30, 2020 at 5:13 am
Nice!! I agree with the fine parent/this website.I tried all of them and almost all of them worked.Keep it up.👍👌👋
January 14, 2022 at 6:55 am
Nice tips, I’ll be sure to remember them. So I can try them out when I become a parent. Or I could just tell some parents around me.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Looking for Something Specific? Search Here…
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Raising-independent-kids
Evidence-based parenting tips and resources
10 Evidence-backed Tips to Teach Kids Focus and Concentration
May 29, 2017 by Sanya Pelini, Ph.D. 17 Comments

This post contains affiliate links for your convenience.
After years spent in different sectors of the education system, one thing I know for sure is that concentration in children doesn’t always come easy. Lack of focus and concentration is one of the issues most teachers struggle with; It is also one of the issues many parents struggle with.
Before I begin, here’s an outline of what this article will cover:
– Signs of poor concentration in children
– How to help your child learn to focus and concentrate better
– Some of the common causes of children’s inattention
– 18 easy tips to improve your child’s focus, concentration and self-regulation skills
– Toys and games that can help improve your child’s attentiveness
– Alternative natural options to increase your child’s focus and concentration
Help kid focus: What does poor concentration look like in children
If you are dealing with a child who is unable to concentrate, then you know what lack of focus and concentration looks like. Your child may:
– Be unable to or struggle to follow through on things (homework, tasks, etc.). A child who lacks concentration is also likely to have mastered the art of procrastination.
– Quickly lose interest in games and activities
– Rarely finish or take too long to finish assignments (you may hear frequent complaints from their teacher about their inattentiveness)
– Constantly need to be stimulated. For example, a child with low focus and concentration may be unable to stay concentrated on one activity for even brief moments and may keep changing activities at dizzying speeds.
– Be a daydreamer
– Be disorganized and unable to find their things
– Be easily distracted. The may set off to do something then end up doing something completely different because they forgot what they were supposed to be doing
– Appear to suffer from memory-loss
– Appear to never put in any effort
– Be unable to remember even the simplest instructions
– Have learning difficulties due to their inability to adapt to the school setting

Starting school is a major transition and although it can be an exciting moment for both your and your child, it is also a moment that has its fair share of challenges.
We now know that how well your child can navigate this transition largely depends on self-regulation. Several studies have found that a child’s ability to develop self-regulation skills determines their ability to create successful social interactions.
Self-regulated learners:
– are better able to resist distractions and remain focused on the task at hand
– demonstrate a higher sense of self-efficacy
– are more likely to be school ready
– have a greater sense of well-being
– encounter greater academic achievement even beyond the childhood years.
Help children focus, follow instructions, keep rules in mind and practice self-control
Adele Diamond, a well-known Professor whose studies have focused on self-regulation, argues that children should be taught to:
1. Develop self-control , i.e., they should learn to do what is appropriate rather than what they want to do.
2. Develop the working memory , i.e., they should be helped to hold information in memory while mentally incorporating new information.
3. Develop cognitive flexibility , i.e., they should learn to think outside the box.
Diamond believes that teaching self-regulation skills can help improve children’s concentration and focus. These skills can help your child learn to follow instructions and persist even when they encounter enormous challenges.
Other studies have found that self-regulated children are able to listen, pay attention, think, then act.

Everything you need to know if your child can’t focus
“My child can’t focus” is a rather common parenting complaint. While a child’s inability to focus is usually a common cause of concern, all children are easily distracted and generally have shorter attention spans than adults.
They are more curious and more easily distracted when they feel little interest for the tasks and activities they are asked to do.
Children’s concentration tends to improve as they grow older and develop their self-control skills .
That said, some children struggle more with focusing and resisting distractions. The problem with children’s lack of attention is that it contributes to their learning and to their day to day lives.
So first let’s look at what may be behind your child’s inability to pay attention.
Some of the common causes of children’s lack of focus and concentration
1) anxiety may be the reason your child can’t focus.
Anxiety is a common but often ignored cause of inattention among children described as “unfocused”, and this actually makes perfect sense.
It is not uncommon for anxiety to “block” your child, meaning that listening to and following instructions may be more complicated for such a child.
Your child’s separation anxiety or worry about doing something wrong at school or even embarrassing or humiliating themselves may mean that they are more likely to have difficulty paying attention.
2) Insufficient sleep has an impact on your child’s ability to concentrate
It is a well-known fact that poor sleeping habits have a negative impact on children’s focus and concentration.
If you think that your child’s lack of sleep may be behind their inability to focus, ensure that they are getting the appropriate number of hours of sleep every night or taking a mid-day rest if they need to.
The sleep foundation recommends that:
– 1 to 2 year olds need 11 to 14 hours of sleep
– 3 to 5 year olds need 10 to 13 hours of sleep
– 6 to 13 year olds need 9 to 11 hours of sleep
– 14 to 17 year olds need 8 to 10 hours of sleep
3) Lack of routines
Routines are very important in childhood because they provide your child with “a certain way of doing things”. A lack of routine brings uncertainty, and this may be responsible for their lack of concentration.
Adopting even a simple routine such as “ as soon as you get home, you take your snack, do your homework for 20 minutes, then watch TV for 20 minutes ” helps give your child a framework than can help reduce their lack of focus.
4) Inappropriate diet
While it is impossible to accurately determine how sugar (candy, sodas, cereals, snacks, etc.) impacts your child’s behavior, we now know that a moderate consumption of sugar is better for children.
This means paying attention to what your child eats and privileging the most natural diets possible and those that are high in fiber and low in sugar.
5) Excessive screen usage may lead to attention problems in children
Although the studies about screen time are inconclusive about “the right amount” and the “real impact” of screens on children, most screen-use researchers agree that too much screen time can have a negative impact on your child’s development.
There have been suggestions that screens overstimulate your child and therefore reduce their ability to focus.
Monitoring your child’s screen use and setting screen-use rules, establishing screen-free zones and forbidding screen use just before bedtime are easy ways that may help reduce their distraction.
It is not uncommon for children who have experienced traumatizing experiences to have a harder time paying attention.
Stressors may include issues such as bullying or peer pressure, major changes affecting the family (divorce, homelessness, changing schools) or even negative thoughts.
Age-appropriate resources can help your child learn to deal with strong emotions and reduce their lack of focus.
The good news is that many self-regulation strategies can be easily applied at home. In other words, each parent has the tools to help increase their child’s focus and concentration. Here’s how you can get started.

18 easy tips to improve your child’s focus, concentration and self-regulation skills
1 | Play Head-Toes-Knees-Shoulders
Everyone knows the Head, Shoulders, Knees and Toes song. Turns out it’s a great resource for teaching kids to learn about focus and concentration.
The natural tendency with the Head, Shoulders, Knees and Toes song is to touch the part of the body mentioned. However, research has shown that asking children to do the opposite of what they are told (for example touch their toes when they are asked to touch their head) helps develop their concentration.
2 | Play Simon says
Having trouble with your child’s concentration? Play Simon says. Simon says helps kids concentrate and follow directions and is thus a perfect game to develop self-regulation and concentration skills.
3 | Help your child train their mind to concentrate
The most effective way to improve your child’s concentration is to help them practice. We now know that the mental process of focusing one’s mind on a single activity can be learned.
Games and activities such as puzzles, mazes , find the missing number/object, pattern games, and so on have been proven to boost focus and concentration in children.
Age-appropriate Executive Function Kits are great because they help your child to work on different skills that can help improve not only their concentration, but also other skills such as organization, visual perception, memory retention, and much more.
Here are high-quality Executive Function Kits for children between the ages of four and six, and age-appropriate kits for kids between the ages of seven and nine .

4 | Try the day-night task
The day-night task involves showing a child a card (or picture) and asking them to say the opposite of what is on the card. For example, a child is expected to say “day” when shown a dark card with stars.
This tool has been used for years by researchers to improve children’s concentration.
5 | Propose picture sudoku puzzles
Picture sudoku puzzles are great for kids because they teach them about focus and concentration, help them practice their visual perception skills, and promote balance and harmony.
Picture sudoku puzzles are also an excellent art therapy activity to calm stressed kids and increase concentration. You can get high-quality picture sudoku puzzles here (for kids between the ages of 4 and 6) or here (for kids between the ages of 7 and 9).

6 | Make your child play a more active role
The more your child feels involved in choosing their activities, the more likely they are to focus and concentrate.
Several researchers have found that asking kids to plan their activities in advance helps increase their interest, concentration and creative skills because it makes them feel personally responsible for managing their time and activities.
Our Executive Function Kits are filled with activities and worksheets to help children play a more active role in planning activities as well as their play time.
7 | Reducing distractions can help increase your child’s concentration
One of the main reasons that explains children’s lack of focus is their inability to resist distractions.
Even the most disciplined adults struggle with distractions sometimes, so it is logical that dealing with distractions can be difficult for your child. Setting aside a specific space without distractions (no screens, silent) can make it easier for them to concentrate.
8 | Adopt a routine
Routines can help increase your child’s concentration by helping them get on a schedule. A predictable routine can help them feel secure, reinforce consistency, and give them a sense of comfort and control over their environment.
For example, scheduling homework for a set time each day and being consistent can help improve their focus.
If your child is struggling with attentiveness, starting homework early and privileging short homework sessions every day, at a set time, can be more effective in helping tackle inattentiveness.
9 | Encourage make-believe play
Many researchers and educationists argue that intentional make-believe play is an important aspect of learning. It is a central element in children’s cognitive development
Charles Schaefer, the play therapy expert, argues that role-playing helps a child learn to think ahead and reflect on appropriate responses to frustrating situations.
When kids engage in role-playing, they are more thoughtful, flexible and creative in the face of everyday problems.
10 | Encouraging your child to participate in household chores can help increase concentration
Science says doing chores is good for your kids. Some of the benefits associated with chores include:
– Better social, emotional and academic outcomes
– An increase in your child’s sense of worth and confidence
– Increased autonomy and self-reliance
– The development of important skills such as responsibility, self-reliance and accountability
Simple tasks that show your child that they are capable of success reinforce their ability to concentrate. The more your child feels confident in their ability to achieve expectations, the easier it will be for them to focus.
Letting them choose the tasks to perform also makes it more likely for them to follow through. Here are 70 age-appropriate chore cards to encourage your child to begin or continue doing household chores.
11 | Encourage your child to read
Reading can help develop your child’s focus and concentration skills because it requires their brain to focus on both the words and the story line.
Good children’s books captivate them, open up their world, and are presented in an age-appropriate manner (number of difficult words, use of colors and illustrations, etc.).
Talk to your local librarian if you are unsure about a great book that would suit your child. Or subscribe to a book box (this is a great gift idea) and let your child receive age-appropriate books according to a schedule that you feel is right for you.
The award-winning Bookroo Box and The Reading Bug Box are great subscriptions if this is something you want to try out.

12 | Try play planning
Play planning involves asking kids to determine what they would like to do (or will do) during a specific moment (for instance when they are bored).
This can be achieved by asking them to draw a picture or write about what they will do at that particular moment.
This tool gives you the resources you need to help even the youngest kids practise play planning.
13 | Play the freeze game
The freeze game was successfully used by McClelland and Tominey in a study to develop children’s concentration. The freeze game involves asking everyone to dance to music and then freeze when the music stops.
You can also ask your child to dance slowly to slow songs and quickly to fast songs. When this is mastered, ask them to dance slowly when fast songs are played, and quickly when slow songs are played.
The Freeze game teaches your child to listen attentively and to follow instructions.
14 | Focus on positive behavior
The more you focus on your child’s positive behavior, the more likely they are to repeat that behavior. Setting simple concentration goals that they can achieve and then reinforcing positive behavior can help improve their focus and concentration.
That said, positive reinforcement used the wrong way can cause more harm than good.
The Positive Behavior Kit gives you a step-by-step approach to using positive reinforcement appropriately in order to reduce specific negative behavior.
It outlines the pitfalls to avoid and gives you practical tips to avoid turning this discipline strategy into some form of “bribery”.
15 | Avoiding multiple instructions can reduce your child’s difficulty with concentration
Kids struggling with concentration often have a harder time processing information. The more your child receives multiple instructions, the harder it will be for them to follow through.
Breaking down instructions can therefore make it easier for them to understand expectations. Asking them to repeat what they have understood can also make it easier to keep focused.
Simple questions such as “ What will you do first? And then? What will you do next? ” can also help them get a good mental picture of what they are expected to do.
16 | Use a timer
A timer is a great tool to help your child keep track of how long they can stay focused. You can use it for homework or for any other tasks, and slightly increase the time set as they get better with focus and concentration.
17 | Help your child practice mindfulness
Several studies have shown that mindfulness can help children learn to keep still and focused. For instance, one study found that teaching seven- to eight-year-olds breathing exercises greatly reduced their anxiety levels and increased their focus.
Some easy ways to get started include encouraging your child to practice deep breathing, practicing walking meditation, or even using safe and age-appropriate essential oils .
18 | Be receptive to your child’s needs
Different people need different environments to concentrate. Some require calm and others can only concentrate if they can hear some background noise. Identifying what works best for your child can help reduce their inattentiveness.
Using toys to help children focus
Some toys can prove helpful if your child is struggling with attention problems. Here are two categories of toys that may help increase their concentration.
Remember that not all kids will respond to the same strategies, and not all toys or tools will have the same impact on your child. The best strategy is to test different tools and see which one is best able to help your child focus and concentrate.
Category 1: Fidget toys
Fidget toys help children concentrate by keeping their hands busy and therefore allowing them to focus on something else. It is important to avoid trends and to choose appropriate fidget toys to increase your child’s concentration.
Many positive things and many negative things have been said about fidgets. The truth is, fidgets are good at helping kids focus, but only if those kids need them.
In other words, if your child is not struggling with issues such as lack of concentration or anxiety, then a fidget toy may actually distract them.
The good news is that fidgets can help your child become more focused, but the bad news is that there are so may fidgets out there, it may be difficult choosing a quality fidget toy that doesn’t actually distract your child (for example too visually stimulating).
Below are ten examples of good (and classroom-friendly) fidget toys you may want to check out:
1) A fidget spinner

This Metal Fidget Spinner is a solidly built and attractive spinner that will help occupy your child’s hands. If you prefer a different fidget spinner, Innoplus has several other designs that might catch your eye or you can get a pack of a few fidget spinners to keep on hand.
2) A fidget band
If your child finds it difficult to keep their feet still, a fidget band that you can attach to their chair or desk can help keep their feet busy and therefore allow them to concentrate on the task at hand.

3) Focusing putty
Focusing putty is great for kids who need to squeeze things to reduce their stress.

4) Bubble pop fidgets
I bet you’ve already noticed these latest fidgets that are great for keeping your child’s hands busy!

5) Marble Fidgets
I love Marble Fidgets because of their size which means that your child can take them absolutely everywhere!

6) Infinity cube
The infinity cube has eight small cubes that your child can rotate from any direction and any angle. It’s small, not too heavy, and is suitable for kids from age eight. The JOEYANK Fidget Cube is more durable, but plastic models also exist.

7) Tangle toys
Tangle toys are simple but effective fidget toys that will keep your child’s hands busy and help them focus on the task at hand.
8) Monkey noodles
Your child can do absolutely anything with Monkey Noodles – stretch them, pull them, squeeze them, wrap them… What’s more, they are strong, safe and durable!

9) The smiley stretchy men
If you’re looking for a small fidget toy your child can take anywhere, then the smiley stretchy men are for you, and your child can use them from age three.

Other great fidgets your kid can put in their pocket include keychain bubble wrap pop fidgets and Fidget Bean Toy s.
10) Squishy balls
Squishy balls are great for reducing stress and keeping your child hands busy. They can also take them everywhere!

Category 2 – Focus games
Certain games can help your child improve their focus and concentration skills. Any game that can help them pay attention to small details, spot hidden objects, think, plan and use their memory are great options to help them become more attentive.
There’s no need to worry if they seem to struggle when you first begin – they more you play, the more accurate they should get!
Here are a few good games that may help with your child’s focus
1) Where’s Wally?
This activity book will provide your child with hours of fun and help them work on their concentration as they try to spot hidden objects.

2) Jigsaw puzzles
Puzzles are good toys for helping children learn to focus and concentrate, but not if they are too difficult for your child. Start will small puzzles or large puzzles , and don’t hesitate to help if your child is looking frustrated.
3) Memory card games
Memory games can help improve your child’s attentiveness by teaching them about focus and concentration.
How the game works
1) Get memory cards and ensure that there are only matching pairs.
2) Shuffle the cards and place them face down.
3) Each player picks any two cards. If the cards match, they keep them and take another turn. If the cards don’t match, they place them back exactly where they were. 4) The person who matched the most pairs wins.
Memory card games are great for developing your child’s focus and concentration because they force them to pay attention to remember where they last saw the images. Here are colorful and high-quality printable memory cards that your child will enjoy.

4) The Perplexus Rookie
If you’re looking for a great gift idea for a child who need help concentrating, The Perplexus Rookie is the toy for you. It has obstacles that your child must overcome and they must plan ahead and manipulate the sphere with care to achieve the end goal.
Jenga is a classic game that is also a great gift idea for a child struggling with attention. Your child is expected to pull out a block without crashing the stack. This is also a fun game to play as a family but your child can also play by themselves.

6) Hidden Pictures Scratch Art Book
Melissa and Doug’s hidden picture scratch art books are great tools to help boost your child’s concentration power and you have so many options to choose from!
They are also great for developing their hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills.
7) Rory’s Story Cubes
These educational story cubes provide endless opportunities for your child’s imagination and creativity and would also make a perfect gift.
Your child rolls the dice then has to make a story using the pictures from the dice. And the best part is that you have different styles so you’ll be able to find something if your kid is a Harry Potter fan, a “Heroes” fan, a “Mysteries” fan…

8) Pop and catch games
Pop and catch games use movement to help your child focus. They are expected to focus on the ball to catch it before it hits the ground. You can also try this game sitting down if it is too difficult for your child when they first begin.

9) Spot it!
Who doesn’t love Spot It! ? This game is great for helping your child improve their visual attention and learn to disregard distractions. Better still, the entire family will enjoy playing it!

Alternative natural options to help kids focus
1) natural supplements.
While undertaking the research on improving children’s focus and attention, I came across parents who spoke of amazing improvement in their kids’ attention after using natural focus supplements.
Here are a few supplements you can check out. Don’t forget to read the reviews to see what other parents think:
2) Essential oils
Not all essential oils are safe to use with kids. I have spoken in length about the precautions to take when using these oils with kids. That said, certain essential oils, used the right way, can help your kid calm down and can also boost their focus and attention.
If you are already an essential-oil fan or want to try using essential oils to help boost your child’s attentiveness, here are a few ready-made 100% pure blends you can start with:
Remember you can also easily make your own recipes using kid-friendly essential oils.
Should you worry about your child’s inability to focus and concentrate?
Most focus and attention problems in childhood tend to get better as your child grows older and develops their self-control and self-regulation skills.
However, for some parents, child inattention issues are more of a long-term than a short-term challenge. Here are a few of the learning difficulties associated with inattention in children:
ADHD – One of the most common symptoms of ADHD is the inability to regulate one’s attention span. If your child has the inattentive type of ADHD, they are more likely to struggle with focus and concentration.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder – If your child has this disorder, they will be focused on other things that prevent them from paying attention to what is going on around them.
For example, in a classroom situation, such a child may pay more attention to lining up all their pens and pencils on their desk and therefore will appear as a child unable to pay attention.
Other learning disorders – learning disorders mean that your child’s brain doesn’t process information quite in the same way as other children. They are therefore more likely to have trouble with focus because they feel unable to achieve what other kids can.
While they may be viewed as “easily distracted”, their behavior may be an attempt to cover up their frustration and embarrassment at “not being good enough”.
Hearing problems – A child with auditory processing problems may be mistaken for a child lacking focus. If your child cannot hear instructions, it is normal that they will be unable to follow through on those instructions.
Lack of attention and focus has a direct impact on how your child learns and develops. If your child is finding it hard to concentrate, please discuss your concerns with your family doctor who will point you in the right direction.
It may also be helpful to consult with your child’s teacher to better understand their attention and concentration level at school.
When your child won’t focus in school
Unfortunately, your child’s inability to focus in school has a direct impact on what and how they learn. The first step if you are concerned about their trouble with focus is to have a discussion with their teacher. Teachers can provide solutions such as:
- Reduce distractions within the classroom: For example, the teacher can change their sitting position to ensure that they can keep their eye on your child or keep them away from classmates who are likely to distract them (or even away from windows!)
- Ensure that your child has understood instructions before beginning a task
- Provide assistance.
Scientific resources
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17605527
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7805351
http://people.oregonstate.edu/~mcclellm/ms/Ponitz_McClelland_Matthews_Morrison_DP09.pdf
http://www.unco.edu/cebs/psychology/kevinpugh/motivation_project/resources/dweck_leggett88.pdf
https://self-regulationintheclassroom.wikispaces.com/file/view/Perry+mentoring+student+teachers+for+srl.pdf
http://psycnet.apa.org/psycinfo/1994-98882-000https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21898897

<a href=”http://selz.co/4JyaZp-5M” target=”_blank”>Buy now</a>
About Sanya Pelini, Ph.D.
Sanya Pelini holds a Ph.D. in Education. Her work has been published on Motherly, ParentMap, The Goffman Institute and Psych Central, among others. She lives in the south of France with her husband and three children.
Reader Interactions
March 29, 2023 at 11:50 pm
What an excellent array of techniques and suggestions!Thank you!
March 31, 2023 at 7:37 am
Thank you for your lovely comment 🙂
January 27, 2023 at 12:02 pm
January 27, 2023 at 3:13 pm
Thank you 🙂
August 9, 2021 at 3:35 pm
These are so many great ideas in one place. I would like to share in my weekly column (SUPPORTING SUPER STUDENTS) giving parents ideas about how to help their child focus as they prepare their children for school. I cite the source of my information in my column. So, I ask your permission to direct parents to your website. Thank you in advance.
August 9, 2021 at 4:19 pm
Thank you for your lovely comment. I’d be honored to have my article about improving children’s focus and concentration cited in your column 🙂
February 8, 2021 at 11:38 pm
This worked as a nice primer for someone like me who entered a relationship involving kids and silently asking myself why a 8&9 yr old can’t just “act more like adults” knowing that is unfair to them but wanting to better understand myself.
February 15, 2021 at 2:53 pm
This is such a lovely comment – and so true – we often forget that kids aren’t adults. Thank you Michael
March 18, 2020 at 5:23 pm
II thought it was so fun that you suggested playing Simon says with your child since it can help them develop self-regulation, as well as coloring mandalas to help them destress. I am now a stay-at-home mom and want to find ways to interact with and help my 4-year-old grow. I’d love to find a child health book with more activities like these for us to do together.
October 10, 2019 at 11:59 am
Outstanding and revealing….!!! About to go on an adventure with these…already… Thanks a lot.
October 10, 2019 at 4:14 pm
Thanks Ahmad. Glad you appreciate these tips on increasing your child’s focus and concentration 🙂
August 14, 2019 at 4:51 pm
Valuable information
August 17, 2019 at 11:02 pm
I appreciate the comments!
January 6, 2019 at 1:56 am
Thank you very much! My 7 y.o. son has problems concentrating. I will definitely try your suggestions! Again, thank you.
January 6, 2019 at 7:50 pm
So glad you found it helpful 🙂
August 9, 2018 at 1:37 pm
Thanks for sharing such a helpful article. Really story telling is a very effective way to to develop concentration among children.
August 13, 2018 at 7:19 am
Glad you enjoyed it 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Affiliate disclosure
Legal mention
Privacy policy
Recent Posts
- The Surprising Effects of Negative Discipline on Kids (and a Better Approach to Try)
- 20 Activities to Do With a 9-Month-Old Baby
- Science says this one thing alone can improve your teen’s emotional well-being
- 10 signs of anxiety that are often mistaken for something else
- Why every child needs to connect with nature every day, regardless of their environment
As an Amazon Associate , I earn from qualifying purchases.
This blog doesn’t offer professional advice. It is written and edited by me. It may contain affiliate links. Click here to read the full disclosure.
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Internet Explorer is no longer supported
Please upgrade to Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Firefox .
Lo sentimos, la página que usted busca no se ha podido encontrar. Puede intentar su búsqueda de nuevo o visitar la lista de temas populares.
Get this as a PDF
Enter email to download and get news and resources in your inbox.
Share this on social
Strategies to make homework go more smoothly.
Routines and incentive systems to help kids succeed
Writer: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP
Clinical Experts: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP , Karol Espejo, LCSW
Here is the best guide to helping kids do homework successfully that we’ve seen, published by the National Association of School Psychologists on their website, NASPonline.org . Our thanks to NASP for sharing it with us.
There are two key strategies parents can draw on to reduce homework hassles. The first is to establish clear routines around homework, including when and where homework gets done and setting up daily schedules for homework. The second is to build in rewards or incentives to use with children for whom “good grades” is not a sufficient reward for doing homework.
Homework Routines
Tasks are easiest to accomplish when tied to specific routines. By establishing daily routines for homework completion, you will not only make homework go more smoothly, but you will also be fostering a sense of order your child can apply to later life, including college and work.
Step 1. Find a location in the house where homework will be done. The right location will depend on your child and the culture of your family. Some children do best at a desk in their bedroom. It is a quiet location, away from the hubbub of family noise. Other children become too distracted by the things they keep in their bedroom and do better at a place removed from those distractions, like the dining room table. Some children need to work by themselves. Others need to have parents nearby to help keep them on task and to answer questions when problems arise. Ask your child where the best place is to work. Both you and your child need to discuss pros and cons of different settings to arrive at a mutually agreed upon location.
Step 2. Set up a homework center. Once you and your child have identified a location, fix it up as a home office/homework center. Make sure there is a clear workspace large enough to set out all the materials necessary for completing assignments. Outfit the homework center with the kinds of supplies your child is most likely to need, such as pencils, pens, colored markers, rulers, scissors, a dictionary and thesaurus, graph paper, construction paper, glue and cellophane tape, lined paper, a calculator, spell checker, and, depending on the age and needs of your child, a computer or laptop. If the homework center is a place that will be used for other things (such as the dining room table), then your child can keep the supplies in a portable crate or bin. If possible, the homework center should include a bulletin board that can hold a monthly calendar on which your child can keep track of longterm assignments. Allowing children some leeway in decorating the homework center can help them feel at home there, but you should be careful that it does not become too cluttered with distracting materials.
Step 3. Establish a homework time. Your child should get in the habit of doing homework at the same time every day. The time may vary depending on the individual child. Some children need a break right after school to get some exercise and have a snack. Others need to start homework while they are still in a school mode (i.e., right after school when there is still some momentum left from getting through the day). In general, it may be best to get homework done either before dinner or as early in the evening as the child can tolerate. The later it gets, the more tired the child becomes and the more slowly the homework gets done.
Step 4. Establish a daily homework schedule. In general, at least into middle school, the homework session should begin with your sitting down with your child and drawing up a homework schedule. You should review all the assignments and make sure your child understands them and has all the necessary materials. Ask your child to estimate how long it will take to complete each assignment. Then ask when each assignment will get started. If your child needs help with any assignment , then this should be determined at the beginning so that the start times can take into account parent availability. A Daily Homework Planner is included at the end of this handout and contains a place for identifying when breaks may be taken and what rewards may be earned.
Incentive Systems
Many children who are not motivated by the enjoyment of doing homework are motivated by the high grade they hope to earn as a result of doing a quality job. Thus, the grade is an incentive, motivating the child to do homework with care and in a timely manner. For children who are not motivated by grades, parents will need to look for other rewards to help them get through their nightly chores. Incentive systems fall into two categories: simple and elaborate.
Simple incentive systems. The simplest incentive system is reminding the child of a fun activity to do when homework is done. It may be a favorite television show, a chance to spend some time with a video or computer game, talking on the telephone or instant messaging, or playing a game with a parent. This system of withholding fun things until the drudgery is over is sometimes called Grandma’s Law because grandmothers often use it quite effectively (“First take out the trash, then you can have chocolate chip cookies.”). Having something to look forward to can be a powerful incentive to get the hard work done. When parents remind children of this as they sit down at their desks they may be able to spark the engine that drives the child to stick with the work until it is done.
Elaborate incentive systems. These involve more planning and more work on the part of parents but in some cases are necessary to address more significant homework problems. More complex incentives systems might include a structure for earning points that could be used to “purchase” privileges or rewards or a system that provides greater reward for accomplishing more difficult homework tasks. These systems work best when parents and children together develop them. Giving children input gives them a sense of control and ownership, making the system more likely to succeed. We have found that children are generally realistic in setting goals and deciding on rewards and penalties when they are involved in the decision-making process.
Building in breaks. These are good for the child who cannot quite make it to the end without a small reward en route. When creating the daily homework schedule, it may be useful with these children to identify when they will take their breaks. Some children prefer to take breaks at specific time intervals (every 15 minutes), while others do better when the breaks occur after they finish an activity. If you use this approach, you should discuss with your child how long the breaks will last and what will be done during the breaks (get a snack, call a friend, play one level on a video game). The Daily Homework Planner includes sections where breaks and end-of-homework rewards can be identified.
Building in choice. This can be an effective strategy for parents to use with children who resist homework. Choice can be incorporated into both the order in which the child agrees to complete assignments and the schedule they will follow to get the work done. Building in choice not only helps motivate children but can also reduce power struggles between parents and children.
Developing Incentive Systems
Step 1. Describe the problem behaviors. Parents and children decide which behaviors are causing problems at homework time. For some children putting homework off to the last minute is the problem; for others, it is forgetting materials or neglecting to write down assignments. Still others rush through their work and make careless mistakes, while others dawdle over assignments, taking hours to complete what should take only a few minutes. It is important to be as specific as possible when describing the problem behaviors. The problem behavior should be described as behaviors that can be seen or heard; for instance, complains about h omework or rushes through homework, making many mistakes are better descriptors than has a bad attitude or is lazy.
Step 2. Set a goal. Usually the goal relates directly to the problem behavior. For instance, if not writing down assignments is the problem, the goal might be: “Joe will write down his assignments in his assignment book for every class.”
Step 3. Decide on possible rewards and penalties. Homework incentive systems work best when children have a menu of rewards to choose from, since no single reward will be attractive for long. We recommend a point system in which points can be earned for the goal behaviors and traded in for the reward the child wants to earn. The bigger the reward, the more points the child will need to earn it. The menu should include both larger, more expensive rewards that may take a week or a month to earn and smaller, inexpensive rewards that can be earned daily. It may also be necessary to build penalties into the system. This is usually the loss of a privilege (such as the chance to watch a favorite TV show or the chance to talk on the telephone to a friend).
Once the system is up and running, and if you find your child is earning more penalties than rewards, then the program needs to be revised so that your child can be more successful. Usually when this kind of system fails, we think of it as a design failure rather than the failure of the child to respond to rewards. It may be a good idea if you are having difficulty designing a system that works to consult a specialist, such as a school psychologist or counselor, for assistance.
Step 4. Write a homework contract. The contract should say exactly what the child agrees to do and exactly what the parents’ roles and responsibilities will be. When the contract is in place, it should reduce some of the tension parents and kids often experience around homework. For instance, if part of the contract is that the child will earn a point for not complaining about homework, then if the child does complain, this should not be cause for a battle between parent and child: the child simply does not earn that point. Parents should also be sure to praise their children for following the contract. It will be important for parents to agree to a contract they can live with; that is, avoiding penalties they are either unable or unwilling to impose (e.g., if both parents work and are not at home, they cannot monitor whether a child is beginning homework right after school, so an alternative contract may need to be written).
We have found that it is a rare incentive system that works the first time. Parents should expect to try it out and redesign it to work the kinks out. Eventually, once the child is used to doing the behaviors specified in the contract, the contract can be rewritten to work on another problem behavior. Your child over time may be willing to drop the use of an incentive system altogether. This is often a long-term goal, however, and you should be ready to write a new contract if your child slips back to bad habits once a system is dropped.
Click here to download the homework planner and incentive sheet .
Frequently Asked Questions
To help homework go more smoothly, e stablish a routine that includes a time and place where it will be done, a planner that lists each assignment, scheduled breaks when some of the work is done, and a reward system for kids who are not motivated by good grades alone.
Set a good homework routine following these steps: Find a location in the house where homework will be done. Set up a homework center stocked with needed materials . Establish a homework time. Use a daily homework planner so that your child has everything in writing.
One tool that can make homework go more smoothly i s a Daily Homework Planner , which lists each assignment, how long it should take to complete, and what rewards may be earned for completing each assignment.
Was this article helpful?
Explore popular topics, subscribe to our newsletters.
" * " indicates required fields
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Join Our Community of Parents
Get expert advice on parenting, resources to help kids thrive, and much more.
Don’t Help Your Kids With Homework
Focus on prioritization and process, not the assignment itself.

So much of the homework advice parents are given is theory-based, and therefore not entirely helpful in the chaos of day-to-day life. People are told that students should have “ grit .” They should “ learn from failure .” But it’s hard to know how to implement these ideas when what you really need is to support a kid who has a chemistry test and two papers due in the next 48 hours but seems to be focused only on Instagram.
Some parents manage to guide their kids through these moments with relative ease. Others hire tutors. The large majority of us, however, are stuck at home alone, trying to stave off our own breakdowns in the face of our children’s.
While reprimanding your child for not having started her homework earlier may be your natural instinct, in the midst of stress, it will only make her shut down or lash out. In our experience as teachers, tutors, and parents, the students who feel terrible about procrastinating are more likely to have anxiety and negative feelings that will only fuel their continued procrastination. So instead of admonishing your procrastinator, take a deep breath and try to figure out how she’s going to manage the tasks at hand. Help her make a realistic plan to manage her time. Try to model understanding, even when you’re upset.
Having tolerance for challenges will allow her to approach future frustrations from a more positive perspective. Easier said than done, to be sure, but try to work with your child to identify not only how but why her homework habits are suffering. This understanding will be crucial to helping her transform these habits into more effective ones.
Read: The cult of homework

Because most of us are programmed to focus on present rather than future fulfillment, it’s easy to put off something we dread. Kids who procrastinate almost always do so because they have negative associations with or feelings about a particular task. Unfortunately, avoiding assignments usually lowers students’ self-esteem and makes them dislike the topic that much more, resulting in a vicious cycle of procrastination. Therefore, it’s important both to address why students are procrastinating—what’s upsetting them about the work at hand—and to give them practical tools to manage their time and set priorities.
If you’re worried that your child is the only one in her class who takes ages to get started on her homework, fear not. Students in our classes—and our own kids too, just like many of us adults—have found every which way to put off sitting down to tackle the one thing they know they need to get done. There are all kinds of reasons kids avoid doing their homework. Maybe they’re concerned about what a teacher will think, or that their work won’t measure up to a friend’s. Maybe they’re distracted by something that happened in school that day.
Whatever the case may be, the first step here is determining out what’s stressing your child out in the first place.
If your child fears what her teacher will think if she makes mistakes: She should start off by independently reviewing the material that she feels unsure of, and then reach out to her teacher for further help if she needs it. Assure her that asking questions and making an effort are important to her teacher. Take it from us: Teachers see questions as a sign of an engaged, conscientious, and curious student. No matter the teacher’s temperament or reputation, she will respond positively to your child coming to her with sincere questions and hard work.
If your child fears parental judgment due to bad grades: Remember that although high marks may be important to you, focusing on process and effort is key to your child’s success, not to mention that putting too much pressure on her can lead to resentment. Help your child create a process she can rely on for her work. Better effort will help your child engage with the material and yield better results in the long run.
If your child fears her best friend’s judgment: Start by encouraging your child not to discuss grades with her friends. Middle schoolers in particular tend to share their marks with one another, and it usually just makes kids feel lousy. The “What did you get?” question is tough for all students, especially in the middle grades, when they are looking for affirmation from their peers. Your child’s grades are no one else’s business. While her best friend may do well in history, he may have more trouble with math than your child does. Or maybe he seems great at everything now, but he actually struggles in art class, and in the future he’ll be a terrible driver or have an awkward first date. In other words, we all have subjects—or areas of our lives—that come more or less easily than others. Challenges are inevitable. What matters most is how we approach them.
If your child fears she isn’t capable: First acknowledge how painful this feeling must be. Then reassure her that she is capable and give concrete anecdotes so she doesn’t roll her eyes. Share with her a moment when you thought you couldn’t do something, but you learned to conquer the task. And be honest! Your kid will know that you didn’t really wrestle that champion alligator. Emphasize the importance of determination, effort, and persistence in whichever example of your successes you choose to share.
If your child is exhausted: Prioritize only what’s really essential. Try to help your child go to bed earlier. She can always wake up early to complete smaller assignments if need be. Getting major work done while exhausted is a losing battle for everyone. Help her plan ahead. Create a schedule for completing small portions of a larger assignment over the course of several days or weeks to make overwhelming work seem more manageable.
Read: My daughter’s homework is killing me
Once you figure out what’s driving your child’s procrastination, you can strategize with her about logistics. Start by removing temptation when possible. Of course she’d rather see where her friends went this afternoon than stare at a blinking cursor, and if all it takes is a simple click or swipe for your child to access social media, it’s going to take her eons to finish an assignment. It will be almost impossible for her to develop an argument that flows if she’s tempted by her phone. So all possible impediments to success should be removed. Disabling social-media and messaging apps and having a conversation about the purpose of setting technology limits is an important first step. Putting her phone aside will also help her compartmentalize time so that she can get her work done more thoroughly and then have free time afterward. Technological boundaries may lead to major pushback—especially now, when kids rely on technology for most forms of socializing—but this temporary misery is undoubtedly worth it in the long run.
And emphasize that short-term pleasure equals long-term pain. Empathize with children who do not want to do something that’s hard. Then remind them that the immediate instinct to procrastinate and play video games will make life miserable later. While they may resist and grumble, helping establish rules will ultimately prevent suffering tonight, tomorrow, and next week. Kids thrive in the comfort, reliability, and safety of a structured, focused work environment. It’s never easy, but on evenings when you want to tear your hair out because your child won’t sit down to work, reinforce the message that short-term gratification will only get in the way of long-term goals.
Finally, explain the relevance of the assignment. If kids don’t understand why they’re doing the work, they’re more likely to be frustrated. For example, your child might ask, “Why do I need to know algebra? I’ll never use it when I’m older.” You can tell the truth: “You probably won’t need to know about variables in everyday life, but learning algebra will give you a framework for understanding how to break down and solve complex tasks down the road.”
Learning to work independently, without a teacher’s direct counsel, is key to building academic and personal autonomy. So when your child is overwhelmed, help her figure out why, and then model strategies that foster independence, confidence, and well-being.
This piece is adapted from Freireich and Platzer’s new book, Taking the Stress out of Homework . Every Tuesday, they answer education-related questions . Have one? Email them at [email protected].
About the Authors
Homework challenges and strategies

By Amanda Morin
Expert reviewed by Jim Rein, MA

At a glance
Kids can struggle with homework for lots of reasons.
A common challenge is rushing through assignments.
Once you understand a homework challenge, it’s easier to find solutions.
Most kids struggle with homework from time to time. But kids who learn and think differently may struggle more than others. Understanding the homework challenges your child faces can help you reduce stress and avoid battles.
Here are some common homework challenges and tips to help.
The challenge: Rushing through homework
Kids with learning difficulties may rush because they’re trying to get through what’s hard for them as fast as possible. For kids with ADHD, trouble with focus and working memory may be the cause.
Rushing through homework can lead to messy or incorrect homework. It can also lead to kids missing key parts of the assignment. One thing to try is having your child do the easiest assignments first and then move to harder ones.
Get more tips for helping grade-schoolers and middle-schoolers slow down on homework.
The challenge: Taking notes
Note-taking isn’t an easy skill for some kids. They may struggle with the mechanical parts of writing or with organizing ideas on a page. Kids may also find it hard to read text and take notes at the same time.
Using the outline method may help. It divides notes into main ideas, subtopics, and details.
Explore different note-taking strategies .
The challenge: Managing time and staying organized
Some kids struggle with keeping track of time and making a plan for getting all of their work done. That’s especially true of kids who have trouble with executive function.
Try creating a homework schedule and set a specific time and place for your child to get homework done. Use a timer to help your child stay on track and get a better sense of time.
Learn about trouble with planning .
The challenge: Studying effectively
Many kids need to be taught how to study effectively. But some may need concrete strategies.
One thing to try is creating a checklist of all the steps that go into studying. Have your child mark off each one. Lists can help kids monitor their work.
Explore more study strategies for grade-schoolers and teens .
The challenge: Recalling information
Some kids have trouble holding on to information so they can use it later. (This skill is called working memory. ) They may study for hours but remember nothing the next day. But there are different types of memory.
If your child has trouble with verbal memory, try using visual study aids like graphs, maps, or drawings.
Practice “muscle memory” exercises to help kids with working memory.
The challenge: Learning independently
It’s important for kids to learn how to do homework without help. Using a homework contract can help your child set realistic goals. Encourage “thinking out loud.”
Get tips for helping grade-schoolers do schoolwork on their own.
Sometimes, homework challenges don’t go away despite your best efforts. Look for signs that kids may have too much homework . And learn how to talk with teachers about concerns .
Key takeaways
Some kids have a hard time doing schoolwork on their own.
It can help to tailor homework strategies to a child’s specific challenges and strengths.
Sometimes, there’s too much homework for a child to handle. Talk to the teacher.
Explore related topics
- Toddler Milestones
- How Your Preschooler Grows
- School-Age Children
- The Tween Years
- Teens and Young Adults
- Behavior & Discipline
- Child Safety
- Healthy Habits
- View Full Guide
How to Help Kids With Homework

Helping your child with their homework is an opportunity to connect with them and improve their chances of academic success. As a parent, you can reinforce concepts taught in the classroom and nurture good study habits . Helping with homework shows your child that you believe their education is important.
What Is the Best Way I Can Help My Child With Homework?
You don’t need to be a certified teacher or an expert in a subject in order to help with homework. You can help by developing your child's time management skills, introducing strategies to stay organized, and offering words of encouragement.
Here are some homework tips for parents:
- Know their teacher . Attending parent-teacher conferences, getting involved in school events, and knowing how to get in touch with your child’s teacher can help you better understand homework expectations.
- Family study time. Set aside time every day for homework. Some kids do best by jumping into homework right after school, while others need a break and will be better focused after dinner.
- Set a good example. Family study time gives you the opportunity to model studious behavior. Demonstrate the importance of organization and diligence by paying bills or planning your family’s budget during this shared time. Reading while your child completes their homework instills the idea that learning is a lifelong and enjoyable pursuit. Your example will be far more impactful than your lectures.
- Designate a homework space. Having a designated space for homework can help your child stay on task. It should be well lit and have extra school supplies within reach.
- Help with time management. If your student has a lot of homework, encourage them to break the workload into smaller and more manageable tasks. Create a schedule for the evening to ensure they get through their long to-do list , including opportunities for breaks.
- Don’t do the homework for them. Helping your child with homework isn’t the same as doing your child’s homework. You can make suggestions, but your child must do the work for meaningful learning to take place. Have patience, allow them to struggle a little, and resist the urge to simply give them the answers.
How Do I Help a Child Struggling With Homework?
Struggling through challenges is an important part of learning. Research shows that something called “productive struggle” is essential to learning new concepts. Too much struggle, however, can be demoralizing and counterproductive. So where's the line drawn between productive struggling and counterproductive struggling? You know your child better than anyone, so trust your instincts and step in before your student becomes overwhelmed.
Consider these tips if your child's struggling with homework:
- If your child's already stressed out or frustrated, start with taking a break.
- Engage your child in a conversation so you can understand where they're stuck
- Offer hints or guidance to help them move forward
- Resist the urge to do their homework or give them the answers
- As soon as your child understands how to resolve the issue, step back and let them continue without your direct assistance
- Avoid stressful cramming and last-minute panic by helping your student plan ahead for tests and long-term assignments.
- Offer your child encouragement and praise them for their perseverance.
- Work on your own paperwork or read nearby as your child completes their homework to help them stay on task.
- Reach out to the teacher if additional assistance is needed and remind your child to ask questions at school when they're confused
Should I Help My Child With Math Homework?
Math is taught differently now than it was twenty or thirty years ago. The Common Core Standards are used in 41 states, and most other states follow the same principles even if they don’t call them the Common Core. Instead of memorizing specific ways to solve math problems, students today are asked to solve problems in several different ways and explain the strategy they used.
For many parents, their child’s math homework seems complicated and confusing. The goal of this newer method, however, is a deeper understanding of mathematics. Just because you learned math in a different way doesn’t mean you can’t help with math homework.
- Focus on non-academic help . You can help your student by offering encouragement, tracking assignments, and helping with time management. Create a distraction-free time and place for them to focus on their math homework.
- Learn how it’s taught. Understand how math is taught at your child’s school. Some school districts offer parents a math night or online resources to help them better understand the way math is taught at schools.
- Reach out to the teacher. Ask the teacher for insight on how you can support your student at home. They might point you towards resources that align with their curriculum or offer additional help to your student at school.
At What Age Do You Stop Helping With Homework?
Some research has shown that the connection between student achievement and parental involvement in schoolwork is strongest in the elementary years but declines in middle school. By the time your child enters middle school, parents helping with homework can do more harm than good. At this stage, parental help with homework is associated with lower student achievement.
While you should be helping a lot less with homework, middle school isn't the time to retreat from your child's education. Non-homework forms of parent involvement are strongly associated with higher academic achievement. There are many ways you can support your middle schooler’s success.
- Monitor assignments and test scores
- Attend school events
- Participate in parent-teacher conferences
- Ask questions about classes and what your child is learning
- Continue to encourage a regular study time and place at home
Ideally, you laid the groundwork in the elementary years and good study habits are well established by middle school. While your child will outgrow the need for your direct homework assistance, they'll never outgrow the need for your support and encouragement.

Top doctors in ,
Find more top doctors on, related links.
- Pregnancy Home
- Pregnancy News
- Pregnancy Medical Reference
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor & Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Pregnancy Topics
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Calendar
- Pregnancy Related Topics
- Baby Medical Reference
- Child Development
- All Parenting Topics
- Children's Health
- Children's Vaccines
- Parenting Home
- Parenting News
- Find a Pediatrician
- More Parenting Topics
How to help your child with homework
by: The GreatSchools Editorial Team | Updated: June 13, 2023
Print article

Here are ways to best help your child when she’s doing homework:
Have your child settle into a good study space.
Help your child focus., keep school supplies close at hand., set up a regular time for homework., stay close by while your child does homework., review the work when your child says he’s finished..

Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

The best way to study for tests, according to science

4 things that make kids more likely to succeed

40 up-and-coming careers that don’t require a 4-year college degree (and 9 to avoid)
42 up-and-coming careers that don’t require a 4-year college degree (and 10 to avoid)
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
- Boarding Pass
- 866-354-8302
- Virtual Academy
- Career Technical Education
- Advanced Academics
- Field Trips
- Learning Labs
- Board & Leadership
- Faculty & Staff
- Elite Academic Academy and Downey Unified
- Student & Parent Portal
- Military Families
- Staff Portal
- Find a Partner
- COVID Updates
How to Get Your Child to Focus on Homework and Stop Procrastinating

It happens every day. There’s the ever-piling list of things to do, usually accompanied by the not-so-willing student who needs help staying motivated.
As a parent, you know too well that every decision in school impacts your student’s future. Better grades mean more opportunities, after high school and even in elementary school.
Getting your child to focus on homework can be stressful, but it doesn’t have to be. There are a few easy changes you can implement now to start seeing improvements today. Check out the tips below.
Tips to Help Your Child Focus on Homework
Tip 1: start with a small exercise.

Studies show that cardio-based exercises boost memory and thinking skills. Cardio based means doing something that accelerates the heart rate.
If you get your child moving before starting schoolwork, it will get the blood flowing. This will help the brain become more active and ready to focus on homework.
Some exercises could be jogging, riding a bike, playing a sport or even just dancing a bit to some fun music. Anything your student likes to do that’s fast-paced can certainly help the motivation and focus.
Tip 2: Help set a routine
In Elite’s homeschooling and virtual academies, there is the added benefit of a more flexible schedule. With that added benefit comes the need for discipline.
To be successful in courses, it’s best to create a daily schedule for your child. Ideally, your child would put this schedule together with your help where needed. Keep the schedule realistic, including breaks where necessary.
Once a schedule is in place, there’s less guessing. Routines can also lead to reduced stress, as some studies have shown .
This is a custom heading element.
1. Get a planner, or use a free online application
Some tool for your child easily view the daily schedule is important. This can be a physical planner or an app, but either way, it’ll make sticking to a schedule much simpler.
2. Think about the week; include every plan
Have your student list everything they plan to do that week. Does she like to fit in some time to skateboard? Great! Schedule it in. Besides, it might be best to do that skateboarding right before homework. 😉
3. Be Realistic
If your child is more of a night owl, you don’t have to force them to be an early bird and vice versa. Adjust free time and homework time accordingly. Your student might be one who needs frequent breaks in order to work efficiently. If that’s the case, then set a timer for 30 minutes of work with a 15-minute break immediately following.
Whatever works best with your child’s learning style will be a routine you both can stick to. You’ll be able to figure that out as you try new things and test them out.
Tip 3: Gather the necessary items before starting homework
Small disruptors go a long way (we’ll explain that more later).
If your child stops homework to grab a snack or a notebook, he’s going to get distracted.
Make sure your student has all the necessary materials ready to go before starting schoolwork.
If your student is an independent learner or homeschooler, keep a list of teacher’s and guidance counselor’s phone numbers on hand. Also having note-taking materials, the daily schedule and a glass of water will help your child be better prepared to focus.
Tip 4: Establish a workspace
We’re not saying you have to go to the store right now and drop hundreds on a desk, chair and supplies. The workspace doesn’t have to be traditional. But it should be a designated place in order to better focus on homework.
Maybe that place is an office in your home. Or perhaps your child has a fuzzy bean bag in your room that she loves. Whatever you both decide, make it a habit, and make sure it’s a place that’s comfortable to work. After all, that bean bag might be comfy to relax in, but might not be best once your student has a laptop and notebook to juggle.
It can be a good idea to incorporate some fun items to the workspace to help your child be excited to work there. These can be items like photos, music, lotion, candles or a favorite drink.
Whatever is decided, it’s a great idea to separate the workspace from sleep space.
If your child does homework in your bed where she sleeps, it’s likely going to make her want to take a nap rather than do homework. Make sure she studies somewhere you know he won’t get distracted until she finishes homework.
Tip 5: Remove all distractions

A distraction includes anything that deters your student from focusing on homework. This can range from music to a loud sibling.
Let’s take a moment to talk about those smartphones. They’re more detrimental to homework than you might think.
A study showed that having the phone on silent isn’t enough. Small disturbances like a screen notification could increase errors in your work. It also could prolong the time it takes to complete assignments. Here’s why:
As a researcher from the study stated, “Although these notifications are generally short in duration, they can prompt… mind-wandering, which has been shown to damage task performance,” ( PsychCentral ).
Even just being aware of a missed call, an unread text or another notification causes the brain to lose focus on homework. It knows there is something else to do, and it diverts attention.
We recommend setting all smart devices (phone, tablet, etc) in another room. If your child is able to forget about it, he will likely finish his homework quicker with fewer mistakes.
Tips to Help Your Child Stop Procrastinating
Tip 1: create rewards for motivation.
If you know your student has six assignments to complete in a day, then set aside a small reward for each.
Know your student’s weaknesses and turn them into rewards. If she likes to surf YouTube videos or SnapChat with friends, then allow these activities AFTER she’s completed schoolwork, but not until then.
Tip 2: If your child gets bored easily, incorporate more breaks
If your student has a hard time staying focused (like most students), it can cause stress or negative associations if she thinks he has to do his homework all in one sitting. And if your child experiences high stress before starting homework, he’s probably going to have a difficult time not procrastinating.
If that sounds like your child, then implement short breaks. Let him take a short break and color, or turn on a favorite YouTube music video and have a dance fest.
Getting the blood circulating will help your child’s brain and spirit. Nothin’ like rockin’ out to a favorite tune!
Now this is the way to do homework, right?!
By breaking up coursework with small, fun tasks, her brain will have more positive associations. This might help your child dread starting homework less.
Tip 3: Reach out to your guidance counselor
It’s often a forgotten fact that your guidance counselor’s job is to help your student with any academic struggles. If your child has trouble starting her coursework, reach out to your counselor for help. They are state-certified and dedicated to you.
Elite is also readily available to develop personalized learning plans for your child.
Helping your child stay on track with homework is never easy, we know. But by following the tips above, it can become less stressful, and your child will hopefully be able to stay more focused. Learn more about Elite’s faculty and staff here .
We’ll leave you with one last quote:
“You have the power to be as successful as you want to be. Never let others dictate who you are destined to become!” – Brent Woodard, Elite CEO
Add comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
GRADES 10-12 (by Invite & Induction Only)
National Honors Society for high school students is for students who have maintained a 3.0 GPA. It is open for grades 10-12. The idea behind being a part of NHS is that students have modeled excellent leadership, service, and scholarship.
Club Advisor: Ms. Yazdani | [email protected]
Club Dates : Every 3rd Wednesday of the Month
National Junior Honor Society (NJHS) is for students in grades 6-8 that value and exhibit traits, such as service, leadership, character, and citizenship.
Host : Ms. Ramirez
Visit Parent Square for the Zoom link and more information
Be a part of our student lead podcast team. Mr. Smith guides this student lead podcast teaching students interviewing techniques, audio fundamentals, live video framing, and promotion of the podcast.
Host: Mr. Smith
Visit Parent Square for the Zoom link and more information.
Meetings are Wednesdays at 3pm, which alternate between meetings and episode recordings.
Subscribe to our #BeElite Podcast on Spotify
Grades 6-12
Be a part of history as we launch our school record label in its inaugural year! Learn about distributing music as you release original songs written and created by Elite students on major streaming services like Spotify and Apple Music. Participate in recording sessions and go behind the scenes in Mr. Derik’s Virtual Recording Studio, collaborating to bring tracks to life. This hands-on experience will immerse you in the world of music production and how to record and release your own music.
Host: Mr. Nelson
The Math Club is a group where students with a love for math can come together and express their enjoyment of math in a supporting environment.
Hosts: Mr. Bunn & Mrs. Moore
This is a 6-8 week counseling group that will focus on self-confidence, motivation, and stress management for middle school students. This co-ed group is an opportunity for students to learn new skills to manage stress, increase their self-worth, and improve regulatory skills focused on supporting the student’s personal, social, and academic success.
Host: Ms.Lammers
Grades 5-12
STEM Club for Girls, a vibrant and supportive community dedicated to inspiring young women to explore the fascinating worlds of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM). Our club is a place where curiosity meets creativity, and where girls are empowered to dream big, experiment boldly, and achieve their full potential.
Host: Ms. Bobczynski
GRADES 6-12
Student Lead: Antonella Cavazos A space for all people who love or want to learn more about k-pop and k-dramas. We will listen to music, watch dramas, discuss, scrapbook, play games, and more as we dive into the world of Korean entertainment.
Host: Mrs. Kim
GRADES: 6-12
Join Elite’s Esports club, where casual gamers can connect and have fun at our lively social meetings and those seeking a thrilling challenge can join Elite’s championship caliber competitive teams! If you are looking to make new friends through gaming or to compete against other schools in the upcoming Fall season I encourage you to join!
Hosts: Mr. Keeley
The Quest Crew is an Elite enrichment program centered on introducing a life outdoors to our students and families. New to nature? Tenderfoot or seasoned trekker, all are welcome to join on Quest Crew outings. The natural world is a giant classroom full of endless opportunities to learn something new. Let’s get outside, Eagles!
Host: Mr. Olson
Join Elite’s Songwriting Club! Learn songwriting tips & tricks, write your own unique songs, and collaborate with other student musicians. This is a positive, supportive, and uplifting place to share new music, get inspired, and build confidence. Participate in performances and special events, guided by an award-winning pro musician (Mr. Derik)!
If you enjoy watching and talking about anime with your peers this is the club for you. We also create our very own anime storylines and explore the creativity of the world of anime.
Host: Mr. Thomas
GRADES TK-12
Join us as we learn more about art, share our own art, and take virtual in in-person field trips to art museums!
Host: Ms. Fleming
Grades Tk-12
The purpose of Elite Athletics Club is to foster a culture of excellence and personal growth, providing students with opportunities to develop their physical and mental abilities, build lifelong skills, and become well-rounded individuals who excel both on and off the field. This club aims to empower studentathletes to reach their full potential, cultivate a sense of community and teamwork, and develop a lifelong passion for fitness and athletic competition.
Host: Mrs. McCormick
Grades 3-8th
Our club is designed for students in grades 3 through 8 who love to explore the world through letters. Whether you’re interested in sharing stories from your hometown, learning about different cultures, or simply making a new friend from another part of the country (or the world!), this club is for you.
Hosts: Ms. Alder (Claar) & Mrs. Hernandez
GRADES: 5, 7, 9
Weekly PE Class to meet California Standrds that introduce a variety of sports and offer in-person opportunities, ie pickleball, horseback riding, golf etc….
Host: Coach Andy
Welcome to my Scrapbooking and Journaling Club! This club is a creative and friendly space where students can come together to preserve their cherished memories in beautiful, personalized scrapbooks, or produce imaginative pages to scribe their thoughts on. Whether you want to document your travels, celebrate family milestones, or simply enjoy a creative hobby, the Petal Pages Club is the perfect place to do it. Join us to turn your photos and memories into treasured keepsakes.
Host: Ms. Jackson
Grades 7-12
The purpose of the ASL Club is to promote the learning and use of American Sign Language (ASL) within our community. We aim to foster an inclusive environment where members can practice ASL, enhance their understanding of Deaf culture, and build connections with the Deaf and hard-of-hearing community. Through various activities, the ASL Club strives to create awareness, support linguistic diversity, and celebrate the rich cultural heritage of the Deaf community.
Host: Mrs. Smith
GRADES: 6-8
A space for students in grades 6-8 to make friends and participate in fun games and activities
Host: Ms. Ramirez
K-5TH GRADE
Kindness is the Way! The Kindness Club believes in the power of kindness and that we, our families, our school, our communities and the world can be changed one kind act at a time. The Kindness Club unites and empowers students who want to spread kindness. We create and host fun school activities and participate in local, national and worldwide events that promote kindness – Elite Kindness Rallies, Great Kindness Challenge, World Kindness Day, and many more. As you design your life journey, join us and let Kindness lead the way.
Host: Miss. Reeves & Mrs. Sims
If you are in 3-6th grade and want a positive place to share and socialize, join the Good Vibes Group. You are invited and welcome to join us every other
Host : Ms.Lammers
The Poetry Club is a welcoming space for students to express themselves while writing and sharing original poems, learn about and discuss famous poets, or simply listen to great poetry. At the end of the semester, we’ll host a Poetry Slam, where students can read their poems or cheer on their peers.
Host: Ms. Beckton
Lunch Bunch is open to all 1st-5th grade students. They will have the opportunity to make new friends and chat with old friends through fun games and activities.
Hosts: Ms. Lively
TK-8TH GRADE
The Filmmakers Fellowship is a dedicated group of students who are passionate about the art of filmmaking. The club is a sphere of support for members to get advice on filmmaking and exchange new ideas with one another.
Host : Mr. Hasper
FOR MORE INFORMATION CLICK HERE .

Mrs. Amrit Kaur
[email protected]

Mr. Tom Olson

Mr. Justin Diaz
[email protected]
SOAR SUMMER PROGRAM DATES
- NXTLVL – 4th-8th grade
- 6/3/24 – 8/23/24
July 3rd-Aug. 2nd K-3rd
- DMA (Digital Media Academia) Re-Inventing Machines (STEM class)
- Co-Author & Publish Class book
4th – 8th
- Written Out Loud
- Up to 5 cohorts
- Coding – Interactive Book Covers
- Coding – Simulating a Marine Ecosystem
VIDEO PLACEHOLDER
Elite is committed to providing direct intentional actions to support our student-athletes in the growth and development of their academics and athletics. Ms. Baker takes time to work with our student-athletes on these actions in her Peak Performance Huddle on Friday afternoons. They will work on Finding the balance skills and actions to help ensure student-athletes have successful weeks and continue to excel in both athletics and academics. Come find out what the new excitement is about! All Elite middle school student-athletes, no matter what their academy, are encouraged to join at 12pm and high school student-athletes at 12:30pm. Zoom meeting links are in Parent Square or contact Ms. Baker at [email protected] for a Google invite to your calendar.
Hosts: Kristy Baker
Club Dates: Every Friday: 12pm Middle School 12:30am High School
Peak Performance Coaches spend 2 sessions through a Zoom Meet & Greet to introduce students to different sports and get them connected with community partners in their areas. These community partners will be where they learn and play in person. Tennis, Jhu Jitsu, soccer, baseball, softball and so much more!
Hosts: Kristy Baker & Andy Allanson
Club Dates: Mondays and Tuesdays and Wednesdays at 1pm September 18th and 25th – Soccer, Baseball, and Softball September 19th and 26th – Golf, Tennis and Equestrian (this will replace the Clubs) September 20th and 27th – Wrestling, MMA and Boxing October 2nd and 9th- Cheer and Gymnastics October 3rd and 10th- Basketball and Football
Hosts: Kristy Baker and Andy Allanson
Club Dates: Starts after the Winter Break
GRADES: 9-12
High School students get together to find fellow elite students that are taking similar classes, can help with studying material and get helpful tips from Mrs. Makkai. There is a group chat going with all students in order to encourage a good academic schedule and hold everyone accountable for their projects.
Hosts: Cindy Nowland Medina & Karen Makkai
Club Dates: The Club starts on September 14th, we are closed November 23rd, December 21st, 28th, January 4th, February 15th, March 14th, The last date is June 6th.
GRADES: 1- 6
Do you want to be better at drawing? Have you given painting a try? Does sculpture and carving intrigue you? Have you ever knit, or crocheted? These are the kinds of things we will be doing in the Elite CreativeSpace Club!
Host/Email: Lena Olson [email protected]
Club Dates: 3rd Wednesday of the month @ 4pm
GRADES K-5
Rad Readers is a book club for all students! In our meetings we have discussions, games, and it is a great way to connect with other book lovers. Throughout the semester, the club will be reading a book and then discussing it in the Zoom meetings every 2 weeks. This club is student lead and teacher supported. We hope to host another Rad Reader field trip this year.
**Note: books are typically geared towards 3rd-5th graders. If you have a younger student then a family member can read the book with them so they can engage in the story.
Host/Email: Sarah O’Connor, Solana Gregg and Ava Maturo [email protected]
Club Dates: Tuesdays at 3pm bi weekly
GRADES: 9-12
The goal would be to connect with other Elite High School Students who have had the experience of taking classes at the community college. We would talk about our experience, share helpful tips and strategies, and offer Zoom study sessions for accountability. Being a high school student at a community college can also be scary or can cause some anxiety, so I have a community college counselor to an EAA high school counselor who is willing to provide general support and strategies from time to time.
Host/Email: Amanda Bobczynski & Eliana Hellon [email protected]
Club Dates: Friday at 12:00 noon once a month
Learning Labs are designed to be engaging and intentionally use strategies to increase students’ growth mindset and build academic confidence.
Students meet with their coach via zoom for 1 hour a week for a period of at least 10 weeks. , each session will target a specific ela or math skill. some will also provide an opportunity for students to practice their individual skills on their iready personalized pathway, labs are conducted by highly qualified, experienced and trained lab coaches, students are nominated for participation by their teacher of record. , student progress is monitored and shared with their teacher of record and families weekly. at the end of each semester, a progress report is provided. .
All Elite 6-12 students are welcome to join a reading club led by student host. Students read a selected book each semester and discuss!
Host/Email: Danielle Gregus
Club Dates: 1 PM First Wednesday on the month
For current equestrian members and any one interested in learning about becoming a part of the team! Coach Andy will be reviewing the components of Elite equestrian, and team members will get to recap their riding experience over the last month with fellow team members. Come and learn about Elite Equestrian & Riding Club and discuss your latest ride!
Host/Email: Andy Allanson
Club Dates:
Equestrian Club All Times are at 1 PM
3rd Thursday
Join your fellow bakers with Ms. Steele and Ms. Wright in participating in up to three monthly baking challenges! You will enjoy the company of like-minded students while exchanging recipes, learning new baking techniques in live demos, and practicing making everything from cookies and cakes to ice cream and pies!
Host/Email: Ashly Steele
Club Dates: All Times are at 1 PM
Every other Friday
Which Academy should I choose?
Step 1 of 5.
- My student's grade level: * TK-8 K-5 6-12

- My student prefers to learn via: * Print-based curriculum Online curriculum A mixture of both

- I plan on being involved by: * Collaborating with a Credentialed Elite Educator to educate my child Supporting the Credentialed Elite Educator who is educating my child

- When learning with an Elite Educator, we prefer: * In-Person meetings at a public location Virtual meetings scheduled online

- My student: * Is self-motivated, self-disciplined, and sticks to a schedule Would benefit from staff support in developing study skills

Repair Your Relationship With Your Child In Less Than 17 Seconds!

How to Easily Get Your Kids to Focus on Homework
You’re Frustrated.
You feel like you have to spend every single minute with your child,
Constantly asking them to sit down and pay attention,
Sometimes they’re breaking down in tears,
And sometimes you’re breaking down with them.
All in an attempt to get your kids to focus on homework.

I get it, I’ve been there too.
I remember my daughter’s 2nd-grade year so well. There were so many tears, thrown pencils, stomping feet, and tears when it came to her math homework.
Pulled my hair out.
Even hired a private tutor.
In the end, it was a matter of her not believing in herself, not trusting her skills. And a lot of me, not taking a step back to really look at what was causing this sudden breakdown during homework. However, once I was able to do a few things differently, it made a world of difference.
The tears ended, the frustration was so little and few between, it was like a whole new world!
I want that for you, so here are some tips on how to easily get your kids to focus during homework.
Kids want to feel in control over their own lives. But they are kids. We know that isn’t possible for them to be in control of everything in their life. However, we can give them some space on a few things. One of those includes how they do their homework.
Recently, I read Duct Tape Parenting by Vicki Hoefle and man did it change my perspective!
The main takeaway I had was to take a step back and just observe my child and gather data.
Take a chance on this. Take a step back. Remove yourself from your child’s homework for a few days (or even better a couple of weeks if you can handle it!).
No reminders.
No looking over their shoulder.
Just observe.
You can communicate to them by saying, “I’ve realized I’ve made a mistake. I’ve taken over responsibility over you doing your homework, but it’s your responsibility. I’m not going to remind you.I believe that you can do it without me.”
Just quietly watch and see what happens.
Give your kid permission to take breaks
When we’re mad, we don’t learn. If something is frustrating, no amount of redirection is going to help us calm down quickly and start learning.
If you ever need proof of that…come watch me trying to program my garage door remote. I often yell, stomp and do a lot of deep breathing. Trying to regain my composure to think through the problem. But I can do that because I have worked on controlling my upstairs brain and downstairs brain and self regulation. In “ The Whole-Brain Child: 12 Revolutionary Strategies to Nurture Your Child’s Developing Mind ” by Daniel J. Siegel & Tina Payne Bryson, they talk about the importance of being able to bridge the (upstairs brain) that houses our logic and our emotional (downstairs) brain.
Giving our kids permission to take breaks is huge! Kids often look to us for guidance, so verbally telling them it’s okay to take a break until they can feel comfortable making that call for themselves, is key.
They can work through the frustration from their homework struggles and come back calmer and with a brain that is ready to work and problem solve.
READ: 5 Tips to Help Your Kid Laser Focus on Homework
Let kids set a reward.
Ask your kids to take the lead on this one.
Trust me on this.
Ask them to decide on something they get when homework is done.
There are some guidelines to this though. Discuss the reward with your child so that you know what it is and you are able to be on board. Also, remind your kid that it needs to be a reward that doesn’t require you. So no money or taking them places.
This is a reward that they are in total control of!
Here are a few examples of ones your kids may like to use:
- Watching Roblox videos
- Playing outside
And that’s it! These simple and easy tips will help get your kids to focus on homework in no time!
Also, you can check out our Homework 911 and Homework Mastery courses for kids that helps your kids do homework independently and gives them step-by-step support!
Resources We Shared:
Homework Simplified
Homework 911
Homework Mastery
Download the transcripts HERE
The best mom is a happy mom. To better take care of you, download our No Guilt Mom mindset here . These reminders will help you second guess less, and feel more confidence every day in your parenting.
Recommended Posts

5 Tips to Help Your Kid Laser Focus on Homework

What to do when your kid gives up too easily

Homework is NOT Wrecking our Kids. The Four Skills Kids Master in Elementary School Homework.

How do you know if your kid’s homework is appropriate?

3 Things to Do When Your Kid Cries over Homework

The one tip you need to master your kid’s homework organization

What is Homework 911?

3 Simple Ways to Make Homework Fun

3 Simple Ways to Stop the Homework Power Struggle

10 Ways to Stop the Homework Hassle

5 Mistakes Every Parent Makes with Homework

How to Know What’s the “Right” Amount of Homework

When you have no clue how to help your child with their math homework

How to Stay Calm and Win the Homework Battle

Overwhelmed? Homework Help for your Middle School Student

Episode 003: The Four Homework Personalities

Podcast Episode 135: How to Easily Teach Your Kids to Cook for the Entire Family with Katie Kimball

Podcast Episode 167: How to Get Your Kids to Listen to You More

How to Stop the Homework Battle Even If You Kid Outright Refuses to Do the Work

3 Quick and Easy Steps to Get Your Family To Help Out More
Article info, popular posts.
- Brie Tucker
COO/ Podcast Producer at No Guilt Mom
- No Guilt Mom Podcast
- Podcast Episode 293: Is Your Kid a Mastermind Manipulator or Just Being a Kid Transcripts
- Podcast Episode 293: Is Your Kid a Mastermind Manipulator or Just Being a Kid?
- Podcast Episode 292: Lies You’ve Been Told About Being the Good Girl with Elise Loehnen
- Podcast Episode #146: How to Parent Like a Spy with Christina Hillsberg
- Podcast Episode 112: What is Social Justice Parenting?
- Podcast Episode #98: Talking about the Birds and the Bees with Brittany McBride
- Podcast Episode 86: Parenting on the Same Page with Amy McCready
- Podcast Episode 72: How to Reclaim Your Joy as a Mom
- How to Calm Down When Stressed
- One Simple Skill Your Kids Should Master to Deal with Mean Kids
- Podcast Episode 028: Why Don’t Our Kids Listen Anymore?
- 5 Tips to Calm Your Anxiety
Similar Posts

Queen Creek Olive Mill
When I look for a fun family activity in the Phoenix area, I want somewhere not too expensive, unique and that brings me happiness. Usually food…

3 Simple Tips on How to Take Control of Your Wardrobe
As moms, we often put our family ahead of us…even with our wardrobe. We share 3 simple tips on how to take control of your wardrobe.

Podcast Episode 137: What To Do When Your Kid Lies To You
What should you do when your kid lies to you? Whenever your kid lies, you probably feel like you’re the only one. But kids tell lies for many reasons! We’ll share with you the most common reasons kids lie, what you can do to stop the lying, and to strengthen your relationship with your kid in the process.

Podcast Episode 218: The B Word: Setting Boundaries to Help You Survive December (and the rest of the year too!)
Setting boundaries is key – during the holiday season and all year long. We’re sharing easy tips for setting boundaries for moms with kids of all ages and stages, to make December truly a wonderful time of year, for everyone in your family!

Podcast Episode 193: How Technology Can Help You Find Your Community (and more) with Jenny Wu
Over 70 million Americans face special needs, learning, and thinking differences and need resources to help them reach their full potential. We share a free online resource that can help get you the resources you need and find your community!


Podcast 175: How Unicorn Space Will Bring You Back to Life with Eve Rodsky
As moms, we can get lost in the identity of being a mom and spouse and that can have some pretty serious consequences for both their physical and mental health. Find out what unicorn space is and how it can help you get your life back.
Home / Expert Articles / Child Behavior Problems / School & Homework
10 Ways to Motivate Your Child to Do Better in School
By debbie pincus, ms lmhc.

How do you motivate a child who doesn’t seem to want to do his school work?
As parents, we are invested in our child’s academic life because we know how important it is for their future. Unfortunately, our kids don’t always seem to share our concern about their future. We know this because they continue to prioritize watching YouTube, gaming, and hanging out with their friends over their school work.
Why aren’t our kids motivated to do well in school? After all, it’s in their self-interest to do well. Why don’t they want to succeed as much as we want them to succeed?
Here’s the problem. School is an aspect of life that requires discipline and work, and kids need to learn to buy into the value of doing well. Your child must own the importance of doing well himself. Motivation can’t be forced. And if you try to force your child to be motivated, it almost always makes things worse.
Nevertheless, there are positive steps that you can take to help your child motivate himself to do better in school. Most of these steps involve setting up a structure to enable him to have better discipline and follow-through. This structure improves your child’s chance of success, and the taste of success is often what drives motivation.
In my work with parents and kids over the years, I have found the following 10 tips to help put your child in the best position to succeed and be motivated in school.
1. Stay Positive
Keep a relationship with your child that is open, respectful, and positive. Remind yourself that you and your child are on the same team. This will allow you to be influential, which is your most important parenting tool.
Punishing, preaching, and threatening will get you nowhere and will be detrimental to your relationship and their motivation. Your feelings of anxiety, frustration, and fear are normal and understandable. But reacting to your kids out of these emotions is ineffective and makes things worse.
Remember, your child is not behaving this way on purpose to make your life miserable. When you feel yourself getting worked up, try saying to yourself, “My child is just not there yet.”
And remind yourself that your job is to help him learn how to be responsible. If you get negative and make this a moral issue, then your child might become defiant, reacting to you instead of thinking through things himself.
2. Incorporate the “When You” Rule
One of life’s lessons is that we get paid after we do the work. So start saying things like:
“When you finish studying, you are welcome to go to your friend’s house.”
“When your homework is completed, we can discuss watching that movie you wanted to see on Netflix.”
Enforce this rule and stick to it. If your child does not yet have the necessary discipline, this will help to create it.

Indeed, by enforcing the “when you” rule, you are helping her learn how to do what her brain is not yet equipped to do, which is to be disciplined and to delay gratification.
3. Create Structure for Your Child
If your child is not studying and his grades are dropping, you have a right to get involved, whether he wants you there or not. Again, you’re not there to do the work for him. Instead, you are there to help set up the structure that he cannot create for himself.
The structure might include scheduled study times, having the computer out in a public place in your home, and saying, “No video games or electronics until after your homework is done.”
You might decide that he must devote a certain amount of hours to study time. During this time, no electronics or other distractions are allowed. You might make the rule that even if he finishes all his homework, he must complete study time by reviewing, reading, or editing.
Some kids do better listening to music while they study, and that’s okay. But keep in mind that this can be tricky because their music is usually integrated with their phones. This means YouTube, Twitter, Reddit, and instant messaging will all be at their fingertips.
If you can’t effectively keep them off those apps, then no phone and no music until their work is done. Just say:
“You can listen to music when you finish your homework.”
Think of it this way: schools don’t allow phones in class, and neither should you.
Understand that this structure is not a punishment. Rather, it is a way to help him to develop a good work ethic and to focus on his school subjects.
4. Meet With the Teacher
If your child’s grades and work habits are not up to par, you can set up a plan by sitting down with him and his teachers.
Have your child check with his teacher each day before coming home to ensure that he has all his homework assignments.
Also, you can ask him each morning to ensure that he brings his homework back to school. For me, nothing was more frustrating than my son doing his homework but then forgetting to bring it to school.
Once your child gets better at managing his time, completing his work, and getting organized, then it’s time for you to back off. Let him do it on his own. Only step in if he is consistently having a problem.
5. Identify a Study Spot
Your child may need a quiet location away from brothers and sisters to study. Or she may do better in a room near others. You can help her experiment, but once you find what works best, keep her in that location.
To keep your child focused, you may need to sit with her while she does her homework. You can read a book or newspaper while she works. At a minimum, be nearby to help ensure that she stays on track.

It’s okay to help her with her homework if she is stuck, but don’t do her work for her. For example, it’s okay to review her work and ask her if a certain paragraph makes sense to her. But it’s not okay to write every sentence or work on every math problem with her. Give just enough help to get her over the hump. Remember, learning how to struggle through difficult material is one of the skills your child needs to learn.
6. Break Assignments Into Manageable Pieces
Decide together whether you need to help him break down his assignments into smaller pieces and organize on a calendar what he should get done each day.
You can get him a big wall calendar or a whiteboard. It could be electronic if that is preferable, but I prefer written tools because electronics can be distracting.
7. Be Firm and Consistent with Homework Rules
You want to be positive and helpful to your child. At the same time, though, you have to be firm. You have to consistently enforce the rules you establish.
Being firm and consistent sends the message to your child that you know he can succeed.
Being firm also means that you enforce the rules with effective consequences. If he doesn’t follow the rules you set up, apply the consequences. And don’t try to shield him from the natural consequences of not doing his work, even if that means bad or failing grades.
In being firm, stay positive. For every negative interaction with your child, try to create ten positive ones. Try to put the focus on supporting and encouraging him instead of worrying and nagging.
And don’t take his performance personally. When you start to believe his grades are a reflection of you or your parenting, then you will be on his case, and it will make things worse.
8. Be Aware of His Anxiety Level
Recognize that much of your child’s lack of motivation (or what looks like irresponsibility) might be his anxiety or shame about academics and schoolwork. Kids may not be able to explain all of this to you because it’s not always on a conscious level for them.
Anxiety can be misinterpreted as a lousy attitude, lack of motivation, and irresponsibility. Often, the cover-up for these vulnerable emotions can take the form of acting out, shutting down, avoidance, or defiance.
While a little anxiety can motivate, too much blocks your child’s ability to think and to have access to the part of the brain that helps him with motivation.
Keep your emotions in check by recognizing that it may be your child’s anxiety at play rather than his laziness. Calmly help to give him a better structure to get his work done, and it will help reduce his anxiety.
And remember that what is happening now may look very different as your child matures and develops.
9. Don’t Over-Function For Your Child
It’s nerve-wracking and frustrating to see your child struggle and not meet his potential. You may feel that your child’s lack of motivation is a poor reflection on your parenting. In response, you react and shift into overdrive to get your child to succeed so that your feelings of shame, embarrassment, failure, or fear go away.
In the process, you may be tempted to over-function by helping to complete his work for him. But don’t do it. Resist the temptation. The more you over-function for your child, the more he will react to your anxiety, which causes things to go further and further downhill. Just set up the structure to help him succeed, but let him do the work and bear the consequences, good or bad.
Be your child’s coach. Set the strategy and give direction, but stay on the sidelines and let your child play the game—Root for him to win and praise him when he does. But don’t be afraid to let him fail. It’s all part of growing up and learning to take responsibility.
10. Don’t Obsess About the Future
When your child seems to have no interest in his life, it’s easy to start fast-forwarding into the future. When he acts like he doesn’t care about anything except video games and his friends, you worry that he won’t be successful or even function on his own. This heightens your anxiety and fear.
But none of us have a crystal ball or can see into the future. Focusing on the negative things your child is doing will only bring the spotlight on them and may set you both up for a power struggle. Instead, focus on your child’s positive traits and help him work on those in the present.
Is he outgoing? Helpful? A good cook? Good with cars or electronics? Focus on all the things that go into a developed, successful person, not just academics and grades. Help your child develop in social, creative, and emotional ways. Remember to always keep the big picture in mind.
For all of these tips, start from where your child is. What I mean is that, in many cases, your child may have a long way to go, and you don’t want to overwhelm him by trying to work on too many issues at once.
Expect that your child won’t like the structure at first, but he will get used to it. Be patient. Don’t expect improvement overnight, but don’t underestimate your child either. Be confident that he will come around and will improve with the structures you have put in place.
Related content: Sinking Fast at School: How to Help Your Child Stay Afloat “My Child Refuses to Do Homework” — How to Stop the Nightly Struggle Over School Work
Empowering Parents Podcast: Apple, Spotify
About Debbie Pincus, MS LMHC
For more than 25 years, Debbie has offered compassionate and effective therapy and coaching, helping individuals, couples and parents to heal themselves and their relationships. Debbie is the creator of the Calm Parent AM & PM™ program and is also the author of numerous books for young people on interpersonal relations.
You must log in to leave a comment. Don't have an account? Create one for free!
Mom of Senior Although these comments are great, currently all homework is online for my highschool senior. during the pandemic, all of his school was online, and now, he's in a brick and mortor school for the first time since 9th grade. i think encouraging kids to seek friends at this point is More helpful, but it has to be on his terms. i haven't heard of many other parents with kids in this situation, but i do believe we aren't the only ones at a new school for senior year. the other situation is how much my senior dislikes school. he hates the entire structure of the school day, and feels there's no opportunity to truly learn when forced to cram everything into a 45 minute class period. we struggle often, with all of this.
BW RC I agree with you.
Parents most definitely need to stay involved in making sure their kids are on track academically. Here are some tips, parent to parent, from someone who has raised kids who have had success in school:
(1) Understand each of your child's capabilities and set expectations at home. Keep in mind that every child is different and outcomes will vary. The one commonality is that every child needs to achieve to the best of his/her own ability. Establishing work ethic is key in the early academic years.
(2) Help your child with organizational tools. Many kids struggle early on because they miss due dates or don't know how to manage their time because of poor organization. Buy them agendas to write down assignments and talk to them at the beginning of each week about upcoming tests and projects.
(3) Create a quiet, stress-free environment at home where kids can focus without distraction.
(4) Self esteem and confidence are extremely important. Always try to focus on positive reinforcement rather than taking a punitive approach. Verbally acknowledge improvements, even if the grade isn't where you would like it to be. If a child scores a low C on a test one week, and brings it up to a mid C the next, focus on the improvement, not on the disappointment that the grade isn't an A.
(5) Teach your child to communicate directly with his/her teachers and take advantage of study halls and other opportunities to seek instruction. Only get involved directly if all other avenues have been exhausted.
RC These suggestions are great for those with children, who have little defiance and will react to consequences, by changing their behavior. But, for our kid, nothing seems to work, either positive or negative. Unfortunately, I find this information much too basic and general. We’ve tried all of this and nothing More has stuck. The only suggestion I can see as potentially beneficial is number nine. Focus on what the kid is good at and hope for the best. But, until kids can stop lying to everyone, especially themselves, it’s all for nothing...
Responses to questions posted on EmpoweringParents.com are not intended to replace qualified medical or mental health assessments. We cannot diagnose disorders or offer recommendations on which treatment plan is best for your family. Please seek the support of local resources as needed. If you need immediate assistance, or if you and your family are in crisis, please contact a qualified mental health provider in your area, or contact your statewide crisis hotline.
We value your opinions and encourage you to add your comments to this discussion. We ask that you refrain from discussing topics of a political or religious nature. Unfortunately, it's not possible for us to respond to every question posted on our website.
- 1. The Homework Battle: How to Get Children to Do Homework
- 2. What to Do When Your Child or Teen is Suspended or Expelled From School
- 3. "My Child Refuses to Do Homework" — How to Stop the Nightly Struggle Over Schoolwork
- 4. Acting Out in School: When Your Child is the Class Troublemaker
- 5. Young Kids in School: Help for the Top 4 Behavior Problems
- 140,000+ Subscribers Subscribe
- 50,000+ Fans Follow
- 10,000+ Followers Follow
- 6,000+ Followers Follow
Disrespect... defiance... backtalk... lack of motivation...
Frustrated and exhausted by your child's behavior?
Get your FREE Personal Parenting Plan today.
Does your child exhibit angry outbursts , such as tantrums, lashing out, punching walls, and throwing things?
Would you like to learn about how to use consequences more effectively?
Backtalk... complaints... arguments... attitude... just plain ignoring you
Do you struggle with disrespect or verbal abuse from your child?
Has your child been diagnosed with oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)?
Or does your child exhibit a consistent and severe pattern of anger, irritability, arguing, defiance, and vindictiveness toward you or other authority figures?
Intimidation... aggression... physical abuse and violence ...
Are you concerned that your child may physically hurt you or others?
You must select at least one category to create your Personal Parenting Plan:
We're just about finished! Create a secure account with Empowering Parents to access your Personal Parenting Plan.
- New Parent Support Group Community
- Baby Led Weaning Forum
- Raising Kids
- Mom's Corner - Chat Room for Moms
- Single Moms Chat Group
- All Ages & Stages
- Newborn (0-6wks)
- Baby (1st year)
- Toddler (1-2yrs)
- Little kid (3-5yrs)
- Big kid (6-9yrs)
- Tween (10-12yrs)
- Teen (13-18yrs)
- All Parentlife
- All Kidspiration
- Arts + Crafts
- Learning Fun
- Packed Lunches
- Family Meals
- Kids Activities Email Signup
- Sign In | Register

You are here:
10 hacks to help kids focus and study from home.

One of the biggest challenges we face when homeschooling, is helping our kids focus at home.
School is set up for learning: the classroom, the rituals, the structure. And the fact that there is a teacher and learning assistant to engage and motivate pupils.
When home is your classroom there are all sorts of things can become distractions.
From small things like the washing machine whirring or the dog wandering around. To the big things like having toys, TV and the garden nearby.
All more appealing than tackling times tables or tricky spellings.
So how on earth do you keep your child focused when they are learning from home?
Here are 10 creative and easy hacks to help kids study from home more effectively.
Be Purposeful When Creating Your Own Family Schedule
A schedule is often the key to making homeschooling work. , to create your own schedule it helps to divide the day into chunks of time, each one with its own activity or purpose. , if you have any particular goals, think about what you want to achieve in that week or month. then plan out how you can reach these goals., the beauty of learning at home is that you can create entirely your own schedule. it can be based based around your particular child’s or family’s needs. , this is an example of what a daily homeschool schedule might look like. it’s just a guide, yours may look completely different..
| 7-8 am | Breakfast / Getting dressed |
| 8-9:30 am | Learning activities |
| 9:30-11 am | Free play / Outdoor time / Exploring |
| 11-12:30 pm | Learning activities |
| 12:30-1 pm | Lunch |
| 1-3 pm | Quiet time / Reading / Stories / Snack |
| 3-4 pm | Creative activity |
| 4-5:30 pm | Free play / Outdoor time / Exploring |
| 5:30 pm | Dinner |
| 6-7:30 pm | Relax, bath and bedtime routine |
You could also write more details about what you want to achieve each week on your schedule.
For toddlers and young kids it helps to pin up little cards with drawings to let them know what their day will look like.
Give Kids Permission to Plan Their Day
It can often become a battle of the wills between parent and child to get kids to study at home.
We take on the traditional role of teacher, and child must take on the role of obedient student.
However we’re not teachers, we’re parents, so get a lot more attitude in return.
It can help a great deal to allow our child to control their day. They still have to do certain learning activities like maths, english or science, but let them decide which one they want to begin with.
What do they want to do next? How would they like to plan their day.
They can write out their own ‘schedule’ if they would like, as long as it includes the subjects they need to do.
Give them control over their environment and their learning. And they may become more passionate about what they’re studying.

Create a Quiet and Inspiring Work Space
It’s difficult for anyone to work in a messy or cluttered space. Or if they’re slouching on the sofa or writing on the floor.
Set up a space on a desk or table with enough room to spread out books, worksheets and perhaps a laptop.
Ideally have it in a quiet part of the house away from enticing TV screens or toys.
Add something beautiful for them there like a family photograph, a flower or a craft they’ve made. It all makes starting homework a lot more appealing.
Organise pencils, rubbers and stationery where your child can reach them so that they can get supplies for themselves.
They can even take ownership of labelling and decorating their exercise books and organising their own workspaces.
Start with Learning Games
We’re understanding more and more the importance of play in engaging children and helping them learn.
Before they get stuck into a black-and-white worksheet of maths sums or written task, let them play a learning game.
It could be a simple activity like a word search, a logic game or a printable reading game with dice.
There are a number of fantastic learning board games that you can purchase and keep on hand for study sessions.
These games are still learning-based but the fact that they’re fun, can help your child to sit down and engage with learning more easily and willingly.
Break up the Day with Physical Activity
If your child has lots of pent up energy or a short attention span then planning some outdoor time can help.
Any teacher will tell you that lessons after a rainy day playtime are much tougher as kids have had to stay cooped up indoors.
They learn much better when they’ve been allowed out to rush around and play outside.
You could break up learning sessions with some kind of physical activity. Anything that gets your child active and moving.
A bounce on the trampoline, a walk or scoot or bike ride at lunchtime or even a boogie in your living room.
The more chances your child gets to move, the easier they’ll find it to sit and focus on work afterwards.

Let Siblings Learn Together
Don’t be afraid to do learning activities for more than 1 child, even if they’re different ages.
They don’t all need to do separate ‘classes’ of the same subject.
For example they can do scientific experiments or art activities together as these can be done across age groups.
You could even combine some core subjects like Maths and English to an extent.
Your 3 year old may not understand the sums and adding that your 5 year old is learning.
But she can still absorb the numbers and counting that you’re doing as part of teaching your older child how to add.
You can also let older siblings teach younger ones.
It’s an incredible way to empower them and let them feel valued as a member of your ‘homeschool’.
They feel grown up and have a sense of achievement when they are given the responsibility to teach what they know.
Use Calming Tools
Some children benefit from having a ‘calming tool ‘ on their desk when they sit down to study at home.
You could give them a stress ball or a car they can move back and forth.
Fidget spinners have also become wildly popular in recent years.
Although many articles praise fidget spinners for helping kids focus (particularly those with ADHD) this is yet to be proven through scientific evidence.
Some parents love them, others feel they are a distraction. So it’s entirely up to you if you want to give the fidget-spinning craze a try.
Alternatively something as simple as having a small snack while working can help. It makes starting homework more appealing.
Learn Through Play and Exploration
Not all learning has to take place at a desk with a paper and pen in hand. Some of the best learning can happen away from the home ‘classroom’.
If your child is tired of studying indoors, why not move it outside? You could study in the garden or in a local outdoor space.
Go out and explore and learn in different environments.
History can be brought to life through trips to museums, or castles.
Especially when the interest it sparks is followed up by research through books or online.
Science can be understood by doing hands-on experiments.
So many other physical activities , such as baking, sewing and gardening, can teach valuable skills.
Your child might be fascinated by special topics like space. At school there might not have been much chance to really explore this. Now’s your opportunity.
You could visit an observatory and see the stars. You could read books and watch documentaries about life on a space rocket.
You could make models at home of rockets and planets in the solar system…
Take your chance to escape the traditional idea of learning at a desk.

Put Some Music On
Remember as a teenager that your parents used to get mad at you when you played music while you studied?
And you insisted it helped you focus? Turns out you were right.
A Stanford study found that music engages the parts of the brain involved with attention and memory.
It can really help some children focus on the task at hand.
If your child is easily distracted then try playing some classical or calm music through headphones to help them concentrate.
Offer Rewards for Good Work
At school your child would get their work marked and lots of feedback and rewards for doing it well.
They might have been made ‘Star of the Week’ or had their story read out to the class. They might have had their artwork hung up in the school entrance hall.
This praise goes a long way to building a child’s self esteem. It motivates them to continue working hard to achieve their goals.
During homeschooling, your child needs this kind of praise and reward too.
You can buy stamps and stickers to mark work.
You can hang up amazing artwork on the fridge.
You can be overheard telling Grandma how proud you are of how well your child has worked on a certain task.
You can also offer tangible rewards like treats or a movie night with pizza or a family trip out.
Incentives are a part of everyday life and it’s OK to reward your child for working hard and focusing well.
The beauty of homeschooling is that it’s flexible. You can decide how to make it work best for both you and your child.
You might not get everything right the first time. But, as you go along, you’ll learn what works best and how to keep your child engaged.
In the meantime you might find that you explore new things together, that you wouldn’t otherwise have been able to do.
Free resources for homeschooling:
Here are some of the best sites to get ideas, activities, videos, games and worksheets for homeschooling.
Many are offering their resources for free during the school closure period due to the coronavirus outbreak.
BBC Bitesize
The School Run
BBC History for Kids
Khan Academy
Teach Your Monster to Read
The 24 Hour Museum
The Kids Should See This
Big History Project
Online learning resources and curriculum for older children
There are a number of virtual learning platforms for older children.
If you want your child to follow a school based curriculum at home to work towards exams then these could be useful.
You do have to pay but you get access to a structured curriculum of work, set out in modules with assessments to check their progress.
You also get access to textbooks, videos and resources online as well as an online tutor.
Your child can work towards sitting nationally recognised exams (such as IGCSE, A levels and Highers) at a local college or centre that accepts private candidates:
Wolsey Hall
Cloud Learn
My Online Schooling
Interhigh
Celeb ‘school’ during the corona quarantine
At the time of publishing, the UK is in lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Celebrities have gone out of their way to set up online sessions for kids to learn everything from maths to music.
Here are some of the ways your child can attend online ‘celeb school’:
Daily P.E with Joe Wicks
The Great Indoors with Bear Grylls
Daily Stories with David Walliams
Myleene Klass’s Music Class
Carol Vorderman – The Maths Factor
Jamie Oliver – Keep Calm and Keep Cooking On
- Normal attention span expectations by age, Brain Balance Centers.com
- Music moves brain to pay attention, Stanford study finds, Stanford Medicine News Center
- Fidget Spinner Benefits, Gadget World
- Here’s the Science behind the fidget spinner craze, Forbes

You might like

How to Master Working From Home with Toddlers and Kids
Working from home with toddlers and kids around can be challenging. Here are 10 tactics to help make balancing the two, a little easier for you.

10 Best News Sites for Kids
Kids news websites are a great way to get children involved in current affairs. Here are 10 of the best trusted news sites for kids.

25 genius school lunch box hacks for busy moms
Making a school lunch box is one more thing to squeeze into a busy morning. Discover our 25 awesome lunch box hacks to save you time and stress on school mornings.
Not registered yet? Create an account
Only fill in if you are not human
Join Mas & Pas
Already Registered? Sign In
I want to create an account that's:
All your details are private and only your username and avatar photo are publicly visible
Your personal details are private. You can add a Business Listing to your account which will be Public.
Personal Account
Your chosen username and avatar (round) image are publicly viewable. Your profile page and personal information are all private.
Business Account
You will have a Personal Account as above with an additional option to add a Business Listing which will be publicly visible.
Please provide a username
Please provide a valid email
Please set a strong password
Please accept Terms & Conditions
Only fill in if you are human
Join this group to like, post and reply.
If you join, we’ll send you alerts about activity in the group to ensure that you stay up-to-date. You can turn these alerts off in your settings at any time.
If you join, we’ll send you alerts about activity in the group to ensure that you stay up-to-date.
Verify your account
Please enter the 4-digit code we've sent you.
Please enter a valid code
Didn't receive our email ?
Resend Activation Code
Please enter a valid email
We have resent your email
We have resent your verification code to the email address you provided. Please check your inbox and spam folder.
If your email hasn't arrived or you have trouble activating your account please feel free to contact us here

Get FREE Phonics Flashcards
Grab our phonics letter pack today!
Join our weekly newsletter and get the best of our fun learning activities delivered straight to your inbox

- 15 first letter sounds
- Initial sounds
- Learn to read first words
- How we help
- Individuals with ADHD
- Care Teams & Providers
- Our Coaches
- Testimonials
- Join Our Team
- Infographics & guides
- Events & webinars
- Case studies

ADHD Child Refuses to Do Schoolwork: Top Tips to Help | Beyond Booksmart
By Sean Potts and Jackie Hebert
Let’s be honest… No student loves homework - and for good reason. When we consider the full school day, extracurriculars, and various social components that are all part of a typical school week, it’s no wonder why students want to relax and recharge when they finally get home. However, part of growing up is learning to roll up our sleeves and do those essential things we might not want to do - and for students, this means working through that algebra worksheet or history reading despite being drained from the 10+ hour day they just had.
.png?width=341&height=258&name=Untitled%20design%20(32).png)
In this blog, we’re going to explore homework refusal and what you can do as a parent to nudge your student toward a healthier relationship with their homework. We’ll organize this exploration through four key questions:
- What is homework refusal?
- What causes homework refusal?
- How do you overcome homework refusal?
- What outside support is there for homework refusal?
Let’s dive right in.
1. What is homework refusal?
Homework refusal is when a student develops a strong avoidance of homework to the point of regularly refusing to complete their school work. A typical student who struggles with homework refusal may procrastinate to start their assignments, freeze up when they sit down to work, struggle to resist distractions after school, and release outbursts of anger or frustration when confronted about homework.
Over time, these issues often devolve into worsening grades, frequent conflicts at home, and increased stress levels for caregivers and students. As a result, the parent-child relationship can become strained due to nightly battles over homework that make time at home increasingly unpleasant for the whole family. So now that we understand what homework refusal is, how does it develop in the first place?
2. What causes homework refusal?
Homework refusal is a pattern of avoidance that’s developed to cope with the stress of completing homework. Understanding the core cause of homework refusal starts with identifying what exactly about homework is so stressful for your child. We’ll explore a few common reasons for this stress so you can identify which is most relevant to your situation. It’s also important to remember that attributing homework refusal solely to inherent character flaws (like laziness or apathy) is almost always counterproductive. Homework refusal can develop around the same age that other latent challenges around learning or mental health do. In other words, what may seem like laziness at the surface may simply be the tip of a much deeper iceberg with a core problem that exists outside of your student’s control. Let’s explore some of those potential underlying causes. (Note: It’s possible that more than one of these causes is relevant to your student - many can and do coexist.)
Learning Differences & Disorders
If homework feels overwhelming for your student, it’s possible they might be struggling with a learning or neurological difference or disorder that makes completing homework harder than it is for their unaffected peers. These are the most common:
ADHD & Homework Refusal
One of the most common ones to consider is Attentive-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), which generally makes it harder to do difficult or boring tasks because of differences in the ADHD brain’s reward circuit. As a result, those with ADHD struggle with self-management abilities like task initiation , organization, planning & prioritizing, and emotional regulation. You can learn more about ADHD specifically here.
Dyslexia & Autism Spectrum Disorder Impact and Schoolwork Struggles
Two other common learning differences to consider include dyslexia, which involves difficulty reading due to problems identifying speech sounds and learning how they relate to letters, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). ASD is a developmental disorder that impairs the ability to communicate and interact with the world. If you suspect that any of these examples could be relevant to your child, then we encourage you to have them evaluated by a neuropsychologist or other qualified clinician. Identifying the core struggle is a critical step in conquering the issues surrounding homework. Most importantly, remember that a learning difference can make work feel impossible and overwhelming, so the more parents can do to reduce that stress around homework, the more likely they'll be able to actually help their student - which leads perfectly into our next cause...
Micromanaging
When students refuse to do homework, caregivers find themselves with a difficult choice - either directly intervene to make sure homework is completed or disengage and let them suffer the academic consequences that come with missing homework assignments. Both options are unappealing, yet it can be easy to rationalize direct involvement as the best course of action. After all, you want your kid to succeed, right? If you see that a child has trouble staying motivated, organized, and on top of things, shouldn’t caregivers be willing to do whatever it takes to help them overcome that?
Not necessarily! This approach has two big problems: first, it keeps our kids dependent on us instead of helping them learn to do things for themselves. Second, in the context of homework refusal, you have to remember that a student’s avoidance is often a coping mechanism to avoid the stress of homework. When parents start micromanaging homework time by nagging them to start, hovering over them while they work, checking for completion, and enforcing their attention on the task at hand, it's actually making homework more stressful for them. As a result, our noble intention can suddenly have unforeseen consequences. If you’ve found your direct involvement with your child’s work has resulted in more conflict, more stress around school work, and continued avoidance of homework, then the evidence indicates that that approach is likely making the problem worse. Luckily, there are other options parents can do to support this issue that we’ll be covering later on in this article.
Anxiety
Although homework can feel stressful (even for the most successful students), it needn’t be at a debilitating level. If your student has developed high emotional responses to homework that involve crying, shaking, hyperventilating, or tantrums surrounding homework, then anxiety may be the core issue at play. If anxiety is the core issue fueling homework refusal , then micromanaging will likely make it worse. Instead, it's important to seek out mental health support for the anxiety specifically and work through the underlying beliefs around homework that are reinforcing your student’s avoidance.
Perfectionism
Some students set unrealistically high expectations for themselves and their work, which can make it overwhelming to finish or even get started in the first place. This phenomenon is called perfectionism , and it’s often misunderstood as only applying to the highest performing students. In reality, perfectionism does not mean your work is actually perfect. In fact, that initial expectation can significantly decrease the quality of work as students may feel they can’t reach the ideal they’ve set for themselves and decide there’s no point in trying at all. Breaking down this core belief is central to overcoming the larger issue of homework refusal and can be done with the support of a coach or mental health professional.
Untreated Executive Dysfunction
Executive Function skills enable us to plan, focus attention, remember instructions, get started on work, and manage multiple tasks. When an individual struggles with these types of tasks on a regular basis, they're experiencing Executive Dysfunction - a catch-all term for the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral difficulties that impact one's ability to succeed in their academic, professional, and personal lives. These include issues with time management, organization, task initiation, emotional regulation, planning & prioritizing, and impulse control. Up to 90% of those with ADHD struggle with Executive Dysfunction, which impairs goal-directed behavior such as completing homework. However, you don’t need to have a diagnosis of ADHD to struggle with these skills. Many other issues, including the ones we covered so far, can cause issues in those areas. Regardless of the cause, strengthening Executive Function skills can make homework much more manageable.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) is a type of behavior disorder defined by children being uncooperative, defiant, and hostile toward peers, parents, teachers, and other authority figures. If the issue of refusal extends beyond homework, this may be a core cause to consider. Seek out a clinician who specializes in this issue, as it’s not an easy one to navigate alone as a parent. Treatment for ODD often includes psychotherapy, parent training, and could involve medication to treat underlying conditions such as depression, anxiety, or ADHD, as well.
3. How do you overcome homework refusal?
Now that we’ve covered the most common causes of homework refusal, let’s explore some of the most practical solutions available to overcome it.
If your ADHD child refuses to do schoolwork or has trouble finding motivation, simple methods like dividing homework into smaller tasks, rewarding little achievements, scheduling breaks, and modeling behavior can make a big difference in their motivation to complete assignments. It can also prove helpful to seek outside help from professionals like therapists, coaches and counselors.
We’ll break these solutions up into three categories: parenting strategies, Executive Function strategies, and seeking outside support. Let’s start with parenting solutions first.
5 Parenting Solutions for Homework Refusal
1. reconsider what your parenting role could look like .
As we explored earlier, there are a number of reasons why caregivers ideally shouldn’t be deeply involved in their student’s daily homework routine if that student is working through homework refusal. So that leaves an important question: what might the most useful caregiver role be?
Answering this question starts with talking to your student about what they think is a fair level of involvement with their homework. Is it simply checking in to make sure they know what needs to get done or are they okay with a more involved role that includes setting the environment up for success? The answer will depend on the student, but the important thing is to involve your student in the conversation. If you can speak to them at their level and involve them in the process of establishing your role, you’re already showing them that you’re their ally - not their enemy. Over time, you can evaluate that role in action night-to-night and see how it impacts their ability to get homework done. If something isn’t working or needs to change, return to the initial conversation to come up with a new plan to experiment with. If this doesn’t work or the refusal is still extreme, then you’ll know it’s time to look for outside support, which we’ll cover near the end of this article.
2. Set Clear Homework Expectations (and get your child’s buy-in!)
On the opposite end of micromanaging, there’s also the potential for enabling bad habits. This is why it’s important to set clear expectations around homework but also involve your child in creating those expectations. Talk through what seems reasonable and what happens if work isn’t done - and make it clear that you simply want them to succeed. Also, understand that each kid is different regarding how they feel about and approach their school work. Some may find English to be easy but have no patience at all for algebra, some may love math but get frustrated even just thinking about writing an essay. Whatever the case may be for your child, it’s important to know your child’s strengths and challenges, and what conditions allow them to learn best. This includes considering the frequency of breaks while working, how they can transition into work time, what environment allows them to be most productive, and which assignments give them the most trouble. After a month or two, you should have a clearer indication of what’s working, what’s not, and whether your child needs additional support beyond what you can provide.
3. Celebrate Small Wins
Completing all their homework may look like a typical night for some students, but for a student with homework refusal, it’s a big deal to even take out their materials to get started - or to have a conversation about what needs to be done. Celebrating these types of small wins with rewards or encouragement can be a great way to motivate students by reminding them that homework time doesn’t have to be such an excruciating experience. Small wins can include trying out a new tool or strategy, sitting down to focus for a given time, or starting homework without a fight. Whatever the wins might be, be sure to acknowledge them so your student knows you see the changes they're making, no matter how small. It reminds them that progress happens often a little bit at a time and even those small increments can feel really great when you shine a light on them.
4. Model What You’d Like to See
If your child gets upset at the idea of homework, then simply staying calm through their emotional outbursts and demonstrating a solution-oriented attitude can go a long way. When kids see that their caregivers are calm, collected, and ready to find solutions, it can lay the groundwork to help them regulate themselves and mirror that calmer approach. At the very least, this technique helps caregivers be mindful of keeping their own emotions on a even keel during a challenging interaction with their child.
5. Connect with Your Child’s Teacher
As you’re working through these changes, work on building a good relationship with your child’s teacher and involve them in the process of change. Start off at the beginning of the school year by sharing your goals and worries with them, and stay in touch as the year progresses to share what you’ve been working on at home and where they can help in the classroom. Your relationship with your child’s teachers will pay off during the good times, but even more so during the challenging ones.
6 Executive Function Strategies for Homework Refusal
Executive Function strategies are helpful for all students regardless of whether they’re a child with ADHD that refuses to do school work or any other core reason for refusing homework. We know they’re effective because our coaches use them in video sessions with the students they work with and they’ve seen how transformative they can be for all areas of a student's life, including homework. One reason that they’re so effective is that they rely on the belief that when there’s a way there’s a will . In other words, when students know how to get their homework done (the way), they’ll be more motivated to actually do it in the first place (the will). Hopefully, these strategies will help pave that road for your student’s own transformation, too.
5-Minute Goals
Sometimes big tasks are just too overwhelming to even start. To reduce the burden and motivate students out of inaction, have them choose the first assignment to do and spend just 5 minutes on a timer seeing what they can get done.

When we’re given permission to stop after 5 minutes of work, starting may not seem so overwhelming. We’ve seen this tactic become a springboard to more extended periods of work simply due to the fact that it eliminates the fear of getting started. You may find that the 5 minutes lead your student into becoming immersed in the work at hand and continuing to work past that stopping point. If not, then try pairing this tactic with our next strategy…
Scheduled Breaks
Every homework assignment is its own task to conquer and may deserve its own scheduled break, too. Maintaining constant focus over a few hours and many assignments is challenging, even for adults. After a while, your student may lose steam and not want to do more. This is where structured breaks come in. When your student makes substantial progress or finishes one assignment, encourage them to take a timed 5 or 10-minute break to transition to their next assignment. Scheduling this into the homework session can make the burden seem less overwhelming overall and the individual assignments easier to start, knowing that there will be breaks in between. This strategy works best when the student has a say in how long the break should be relative to the assignment and what the break should consist of. Activities like listening to a favorite song, shooting a dozen freethrows, or grabbing a healthy snack can recharge a student without deraling their progress entirely
Cognitive Pairing
Homework time doesn’t always have to be just doom and gloom. One effective way to make homework time less scary is by pairing work with something fun and rewarding. This could be a pet curled up by your child’s side, their favorite treat waiting for them before they start, or a playlist of music they can enjoy listening to while they work (instrumental tends to be best!) Whatever it might be, pairing homework time with something they enjoy can greatly reduce the urge to avoid whatever assignment needs to get done.
Body doubling
One of the most challenging parts of starting homework is simply the feeling of having to tackle it alone. The chances that your student has a friend or someone from their class they can do homework with is likely high - so why not buddy up with them to get work done? This technique is also called body doubling and can be done with a friend, sibling, or even a caregiver who also needs to get work done, too. On top of making homework time less intimidating, it also can put kids on their best behavior if they’re with a friend that they’re not comfortable melting down in front of. This can be a great way for them to learn firsthand that homework doesn’t have to feel like such an unbearable burden.
The Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a method of working in pre-determined chunks of time. It’s essentially a combination of short, productive intervals (like 5-minute goals) and short breaks. For example, your student could work for 25 minutes, take a 5-minute break, and then go back to work. Coach and podcast host, Hannah Choi, encourages her clients to pay attention to diminishing returns when using the Pomodoro Technique. In this context, diminishing returns means that the effort being put in doesn’t necessarily yield the same results as it did when first starting the activity. Finding out when your student is most productive can be an effective bit of insight to have when deciding the sequence of the work they have to do. There are a number of apps that have Pomodoro Timers that can be used to set the working and break periods ahead of time ( like this one ).
Soften the blow
Transitioning from something fun or relaxing to a dreaded non-preferred task like homework is often going to pose a challenge. "Softening the blow" is one way to ease into these types of tasks or responsibilities. Some examples of this could be eating a snack, calling a friend, or even just stepping outside for a quick walk before sitting down to start homework. These all can work well as structured transitions. Best of all? In addition to reducing homework refusal, this approach also builds cognitive flexibility and task initiation - two critical Executive Function skills.
4. What Outside Support Can Help with Homework Refusal?
If you’ve read through all this and at any point said to yourself “this is too much for me to do alone,” then it might be worth looking for outside support. For homework refusal, one of these three options might be the best choice, depending on your student’s core challenge area.
Executive Function Coaching
Executive Function coaches work on strengthening the core self-management skills of time management, task initiation, organization, emotional regulation, and planning & prioritizing. Since challenges in these areas can make homework much more difficult to approach (let alone finish), working with a coach 1:1 to apply strategies in their week to strengthen these key areas can prove to be the missing ingredient for overcoming homework refusal. Best of all, coaches provide a different perspective from a parent or teacher and can be viewed as an ally in a student's journey rather than another person telling them what they need to do. You can learn about our approach to Executive Function coaching here.
Behavioral Therapy
If your child has more involved core issues such as anxiety, Oppositional Defiant Disorder, or other neuropsychological profiles, it’s worth researching occupational or behavioral therapists near you who specialize in those particular areas. Once those support links are in place, parents, coaches, and tutors all have a much higher likelihood of success at empowering kids to overcome their homework refusal.
Tutoring
If every Executive Function and behavioral factor are accounted for and homework is still a battle, then a tutor in the subject area your student is struggling in may be the best support option. A good tutor can fill in gaps that are holding a student back in a particular subject and give them a new teaching perspective to make the information really stick.
The Takeaway
Your student's homework refusal can feel like an exhausting problem with no solutions, but there are a number of approaches you can use to improve the situation at home. A good combination of understanding why your child is refusing homework, what role your parenting plays in the equation, and what strategies and supports you can lean on all provide the foundation your student needs for a lasting transformation. Above all, know that change is possible!
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
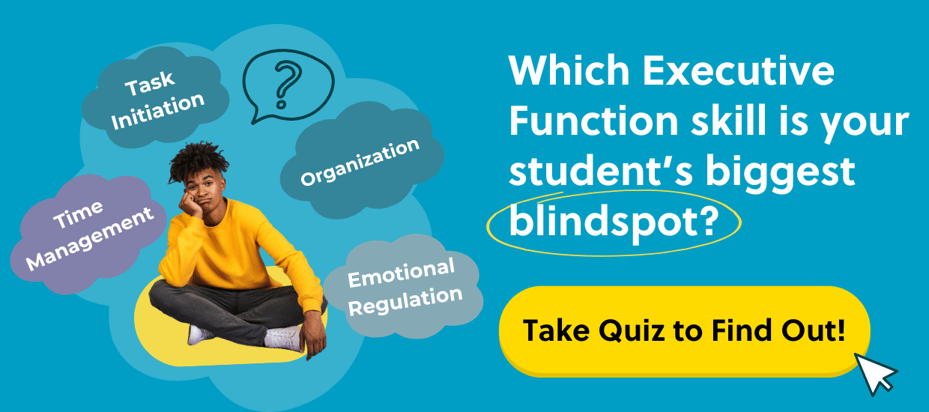
About the Author
Sean potts and jackie hebert.
Sean Potts is the Marketing Specialist at Beyond BookSmart and a recent graduate of Ithaca College’s Integrated Marketing Communications program. As a former coaching client and intern at BBS, Sean has spent the better part of the last ten years witnessing firsthand the positive impact Beyond BookSmart's mission has on transforming students’ lives. Jackie Hebert is the Director of Marketing for Beyond BookSmart. Whether it's managing our websites, overseeing our social media content, authoring and editing blog articles, or hosting webinars, Jackie oversees all Marketing activities at Beyond BookSmart. Before joining Beyond BookSmart in 2010, Jackie was a Speech-Language Pathologist at Needham High School. She earned her Master's degree in Speech-Language Pathology from Boston University, and her Bachelor’s Degree in Psychology from the University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
Previous Post
Is Online Executive Function Coaching Effective?
Is Executive Function the Missing Link to Your Kid's Success?
Latest Post
How to help a child who can't sit still in school, how to help your child avoid burnout in school, 13 symptoms that may indicate adhd in elementary-aged children, related post, 7 self-regulation tips to reduce homework battles with your child.
Editor's note: This week, we feature guest blogger Hanna Bogen, a Speech-Language Pathologist and...
From Homework Battles to Self-Management: 4 Tips for Parents
Editor's note: This week, our guest blogger is Dr. Timothy Davis, a psychologist and a child and...
How to Convince Your Child to Stop Multitasking When Doing Homework
You feel like a broken record. How many times have you mentioned/suggested/demanded that your child...
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Dear Life Kit
- Life Skills
Snuggles, pep talks and love notes: 10 ways to calm your kid’s back-to-school jitters

Becky Harlan

The transition back to school can be overwhelming for kids. Explaining the changes and setting expectations can help them feel more prepared to take on the year. Urbazon/Getty Images hide caption
New teachers, classmates, routines and expectations -- a new school year almost always means change for both kids and their caregivers. And that can be nerve-wracking for everyone.
To help families ease into the transition, Life Kit asked teachers, pediatricians and child development experts for their best back-to-school advice. These tips have been edited for length and clarity.
😴 Adjust your child's summer sleep schedule to a school schedule . At least one or two weeks before school starts, move bedtime and wake-up time up by 15-minute increments every few days until the desired schedule is reached. — Dr. Nilong Vyas , pediatrician and sleep consultant
📚 Gradually reintroduce structure into a child’s daily routine to help them prepare for school. Add a 15-minute block of educational content to your kid’s routine, such as a read-aloud, math puzzle or science experiment . — Keisha Siriboe , early childhood literacy consultant
🗯 Remind kids that almost everyone feels a little nervous on the first day of school. Naming and describing an emotion and letting children know you understand how they feel can help them feel more in control over their feelings instead of feeling overwhelmed by them. — Leah Orchinik , pediatric psychologist, Nemours Children's Health

6 ways grown-ups can recreate that fresh, buzzy feeling of a new school year
🗓 To ease a child’s anxiety about going back to school, help them understand what to expect. As Daniel Tiger sings, “When we do something new, let’s talk about what we’ll do.” Remind them that “grown-ups come back” [at the end of the school day] — and they can share their new experiences at school with their loved ones. – Mallory Mbalia , director of learning and education at Fred Rogers Productions , producers of the TV show Daniel Tiger’s Neighborhood
❓Talk to your child about how they might handle challenging situations, even if they are not likely to happen. For example, if your son is worried about getting lost in a new school, help him problem solve by creating a plan about what he would do if that did happen so he feels more prepared and confident. —Leah Orchinik, pediatric psychologist, Nemours Children's Health

These Back To School Tips Can Help Parents Support Their Kids This School Year
👋 Make up a special goodbye ritual together. Morning goodbyes can be challenging. But you can create daily memories your child will cherish for years to come. Say, “See you later, alligator! In a while, crocodile!”, do a special handshake or enjoy an extra-long hug. You can also kiss your child’s palm and then hold each other’s hands tightly to “seal it in.” Tell your child to remember they’ll carry your kiss with them all day long, and they can do the same for you! — Jeanette Betancourt , senior vice president of U.S. social impact, Sesame Workshop
☕️ Fill their connection cup before and after school. Even if you're tired in the morning, set that alarm for 15 minutes earlier so you can have a snuggle session with your child. Read a book together. Have breakfast together. When you pick them up from school, be aware they will need another connection cup top-up. Sometimes they will present with this after-school meltdown because they're so depleted. — Vanessa Lapointe , author of Discipline without Damage
🧭 Make sure your child knows how to navigate their world in tech-free ways . Even if your child has a smartphone, make sure they know what to do if they’re approached by a stranger, how to get help for an injury and other street smarts. Help isn’t always a button away. — Leah Plunkett , author of Sharenthood
💡 Discuss family or classroom conflicts with your child. Have a daily conversation topic such as, “What’s been a good or hard part about your day?” or “What rules do we need to help everyone feel loved and respected?” Then have a weekly discussion to keep things on track and make kids part of problem-solving. — Thomas Lickona , author of How to Raise Kind Kids
📣 Pour positive words of affirmation into your children on a daily basis. For example, “I love you. I’m proud of you. It’s going to be a great day. It's OK to make mistakes.” Parents can leave notes inside their child's lunch boxes. Or I've had parents ask me to write a sticky note on their child's desk for them. These messages allow a kid to feel powerful and confident throughout the day. —Jarod Renford, first grade teacher in Washington, D.C.
The digital story was edited by Malaka Gharib. The visual editor is Beck Harlan. We'd love to hear from you. Leave us a voicemail at (202) 216-9823, or email us at [email protected].
Listen to Life Kit on Apple Podcasts and Spotify , and sign up for our newsletter .
Teaching Students with ADHD
- ADHD Parenting Tips: How to Help a Child with ADHD
- ADHD in Children: Signs, Symptoms, and Help for ADHD in Kids
- ADHD in Adults: Symptoms, Effects, and Self-Help
Tips for Managing Adult ADHD
- ADHD Medications for Children and Adults
Adult ADHD and Relationships
Adhd tests and diagnosis.
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
Setting up a child with ADHD for school success
Tips for working with teachers, tips for managing adhd symptoms at school, tips for making learning fun for a child with adhd, tips for mastering homework, adhd and school how to help a child with adhd in school.
School can be a challenge for students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)—but there are ways you can help your child or teen succeed in the classroom.

The classroom environment can pose challenges for a child with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD or ADD). The very tasks these students find the most difficult—sitting still, listening quietly, concentrating—are the ones they are required to do all day long. Perhaps most frustrating of all is that most of these children want to be able to learn and behave like their unaffected peers. Neurological deficits, not unwillingness, keep kids with attention deficit disorder from learning in traditional ways.
As a parent, you can help your child cope with these deficits and overcome the challenges school creates. You can work with your child to implement practical strategies for learning both inside and out of the classroom and communicate with teachers about how your child prefers to learn. With consistent support, the following strategies can help your child enjoy learning, meet educational challenges—and experience success at school and beyond.
Remember that your child’s teacher has a full plate: in addition to managing a group of children with distinct personalities and preferences, they can also expect to be teaching students with ADHD . Teachers may try their best to help your child with attention deficit disorder learn effectively, but parental involvement can dramatically improve your child’s education. You have the power to optimize your child’s chances for success by supporting the steps taken in the classroom. If you can work with and support your child’s teacher, you can directly affect the experience of your child with ADHD at school.
There are a number of ways you can work with teachers to keep your child on track at school. Together you can help your child learn to find their feet in the classroom and work effectively through the challenges of the school day. As a parent, you are your child’s advocate. For your child to succeed in the classroom, it is vital that you communicate their needs to the adults at school. It is equally important for you to listen to what the teachers and other school officials have to say.
You can ensure that communication with your child’s school is constructive and productive. Try to keep in mind that your mutual purpose is finding out how to best help your child succeed in school. Whether you talk over the phone, email, or meet in person, make an effort to be calm, specific, and above all positive—a good attitude can go a long way when communicating with the school.
Plan ahead. You can arrange to speak with school officials or teachers before the school year even begins. If the year has started, plan to speak with a teacher or counselor on at least a monthly basis.
Make meetings happen. Agree on a time that works for both you and your child’s teacher and stick to it. If it’s convenient, meet in your child’s classroom so you can get a sense of their physical learning environment.
Create goals together. Discuss your hopes for your child’s school success. Together, write down specific and realistic goals and talk about how to help your child reach them.
Listen carefully. Like you, your child’s teacher wants to see them succeed at school. Listen to what they have to say—even if it is sometimes hard to hear. Understanding your child’s challenges in school is the key to finding solutions that work.
Share information. You know your child’s history, and your child’s teacher sees them every day: together you have a lot of information that can lead to better understanding of your child’s hardships. Share your observations freely, and encourage your child’s teachers to do the same.
Ask the hard questions and give a complete picture. Be sure to list any medications your child takes and explain any other treatments. Share with the teacher which tactics work well—and which don’t—for your child at home. Ask if your child is having any problems in school, including on the playground. Find out if they are eligible for any special services to help with learning.
Developing and using a behavior plan
Children with ADD/ADHD are capable of appropriate classroom behavior, but they need structure and clear expectations in order to keep their symptoms in check. As a parent, you can help by developing a behavior plan for your child—and sticking to it. Whatever type of behavior plan you decide to implement, create it in close collaboration with your child and their teacher.
Kids with ADHD respond best to specific goals and daily positive reinforcement—as well as worthwhile rewards. Yes, you may have to hang a carrot on a stick to motivate your child to behave better in class. Create a plan that incorporates small rewards for small victories and larger rewards for bigger accomplishments.
Find a behavior plan that works
The Daily Report Card is a downloadable behavior plan, which can be adjusted for elementary, middle, and even high school students with ADHD.
Source: Center for Children and Families
Developing an individualized education program (IEP)
An IEP is a free service in the United States that outlines unique accommodations to help your child with ADHD reach set goals in the classroom. For example, an IEP might include:
- Extra time for your child to spend on quizzes and tests.
- Learning plan tailored to their specific needs.
- Relocation to a classroom environment with fewer distractions.
An IEP will also include specific, measurable goals so you can keep track of what’s working best for your child.
As a parent, you can refer your child for an IEP. However, to be eligible, your child may need to undergo an evaluation that involves a review of their performance in classwork and observations of their behavior. A team of professionals—which might include teachers and healthcare providers—will conduct the assessment and then work with you to come up with a plan.
ADHD impacts each child’s brain differently, so each case can look quite different in the classroom. Children with ADHD exhibit a range of symptoms: some seem to bounce off the walls, some daydream constantly, and others just can’t seem to follow the rules.
As a parent, you can help your child reduce any or all of these types of behaviors. It is important to understand how attention deficit disorder affects different children’s behavior so that you can choose the appropriate strategies for tackling the problem. There are a variety of fairly straightforward approaches you and your child’s teacher can take to best manage the symptoms of ADHD—and put your child on the road to school success.
Managing distractibility
Students with ADHD may become so easily distracted by noises, passersby, or their own thoughts that they often miss vital classroom information. These children have trouble staying focused on tasks that require sustained mental effort. They may seem as if they’re listening to you, but something gets in the way of their ability to retain the information.
Helping kids who distract easily involves physical placement, increased movement, and breaking long stretches of work into shorter chunks.
- Seat the child with ADHD away from doors and windows. Put pets in another room or a corner while the student is working.
- Alternate seated activities with those that allow the child to move their body around the room. Whenever possible, incorporate physical movement into lessons.
- Write important information down where the child can easily read and reference it. Remind the student where the information is located.
- Divide big assignments into smaller ones, and allow children frequent breaks.
Reducing interrupting
Kids with attention deficit disorder may struggle with controlling their impulses, so they often speak out of turn. In the classroom or at home, they call out or comment while others are speaking. Their outbursts may come across as aggressive or even rude, creating social problems as well. The self-esteem of children with ADHD is often quite fragile, so pointing this issue out in class or in front of family members doesn’t help the problem—and may even make matters worse.
Correcting the interruptions of children with ADHD should be done carefully so that the child’s self-esteem is maintained, especially in front of others. Develop a “secret language” with the child with ADHD. You can use discreet gestures or words you have previously agreed upon to let the child know they are interrupting. Praise the child for interruption-free conversations.
Managing impulsivity
Children with ADHD may act before thinking, creating difficult social situations in addition to problems in the classroom. Kids who have trouble with impulse control may come off as aggressive or unruly. This is perhaps the most disruptive symptom of ADHD, particularly at school.
Methods for managing impulsivity include behavior plans, immediate discipline for infractions, and a plan for giving children with ADHD a sense of control over their day.
Make sure a written behavior plan is near the student. You can even tape it to the wall or the child’s desk.
Give consequences immediately following misbehavior. Be specific in your explanation, making sure the child knows how they misbehaved.
Recognize good behavior out loud. Be specific in your praise, making sure the child knows what they did right.
Write the schedule for the day on the board or on a piece of paper and cross off each item as it is completed. Children with impulse problems may gain a sense of control and feel calmer when they know what to expect.
Managing fidgeting and hyperactivity
Students with ADHD are often in constant physical motion. It may seem like a struggle for these children to stay in their seats. Kids with ADD/ADHD may jump, kick, twist, fidget and otherwise move in ways that make them difficult to teach.
Strategies for combating hyperactivity consist of creative ways to allow the child with ADHD to move in appropriate ways at appropriate times. Releasing energy this way may make it easier for the child to keep their body calmer during work time.
Ask children with ADHD to run an errand or complete a task for you, even if it just means walking across the room to sharpen pencils or put dishes away.
Encourage a child with ADHD to play a sport —or at least run around before and after school—and make sure the child never misses recess or P.E.
Provide a stress ball , small toy, or another object for the child to squeeze or play with discreetly at their seat.
Limit screen time in favor of time for movement.
Dealing with trouble following directions
Difficulty following directions is a hallmark problem for many children with ADHD. These kids may look like they understand and might even write down directions, but then aren’t able to follow them as asked. Sometimes these students miss steps and turn in incomplete work, or misunderstand an assignment altogether and wind up doing something else entirely.
Helping children with ADHD follow directions means taking measures to break down and reinforce the steps involved in your instructions, and redirecting when necessary. Try keeping your instructions extremely brief, allowing the child to complete one step and then come back to find out what they should do next. If the child gets off track, give a calm reminder, redirecting in a calm but firm voice. Whenever possible, write directions down in a bold marker or in colored chalk on a blackboard.
One positive way to keep a child’s attention focused on learning is to make the process fun. Using physical motion in a lesson, connecting dry facts to interesting trivia, or inventing silly songs that make details easier to remember can help your child enjoy learning and even reduce the symptoms of ADHD.
Helping children with ADHD enjoy math
Children who have attention deficit disorder tend to think in a “concrete” manner. They often like to hold, touch, or take part in an experience to learn something new. By using games and objects to demonstrate mathematical concepts, you can show your child that math can be meaningful—and fun.
Play games. Use memory cards, dice, or dominoes to make numbers fun. Or simply use your fingers and toes, tucking them in or wiggling them when you add or subtract.
Draw pictures. Especially for word problems, illustrations can help kids better understand mathematical concepts. If the word problem says there are twelve cars, help your child draw them from steering wheel to trunk.
Invent silly acronyms . In order to remember the order of operations, for example, make up a song or phrase that uses the first letter of each operation in the correct order.
Helping children with ADHD enjoy reading
There are many ways to make reading exciting, even if the skill itself tends to pose a struggle for children with ADHD. Keep in mind that reading at its most basic level involves stories and interesting information—which all children enjoy.
Read to children. Make reading cozy, quality time with you.
Make predictions or “bets.” Constantly ask the child what they think might happen next. Model prediction: “The girl in the story seems pretty brave—I bet she’s going to try to save her family.”
Act out the story. Let the child choose their character and assign you one, too. Use funny voices and costumes to bring it to life.
How does your kid prefer to learn?
When children are given information in different ways it can make it easy for them to absorb. While many children have a learning preference, it’s often best to use multiple types of teaching to keep kids with ADHD engaged.
- Auditory teaching involves talking and listening. Your child could recite facts to a favorite song, for example, or pretend they are on a radio show.
- Visual teaching uses reading or observation. Let them have fun with different fonts on the computer and use colored flash cards to study. Allow them to write or draw their ideas on paper.
- Tactile teaching uses physical touch or movement as part of a lesson. You could provide jellybeans for counters, for example, or costumes for acting out parts of literature or history. Let them use clay and make collages.
Speak to a Licensed Therapist
BetterHelp is an online therapy service that matches you to licensed, accredited therapists who can help with depression, anxiety, relationships, and more. Take the assessment and get matched with a therapist in as little as 48 hours.
Sure, kids may universally dread it—but for a parent of a child with ADHD, homework is a golden opportunity. Academic work done outside the classroom provides you as the parent with a chance to directly support your child. It’s a time you can help your child succeed at school where you both feel most comfortable: your own living room.
With your support, kids with ADHD can use homework time not only for math problems or writing essays, but also for practicing the organizational and study skills they need to thrive in the classroom.
Helping a child with ADHD get organized
When it comes to organization, it can help to get a fresh start. Even if it’s not the start of the academic year, go shopping with your child and pick out school supplies that include folders, a three-ring binder, and color-coded dividers. Help the child file their papers into this new system.
- Establish a homework folder for finished homework and organize loose papers by color-coding folders. Show your child how to file appropriately.
- Help your child organize their belongings on a daily basis, including backpack, folders, and even pockets.
- If possible, keep an extra set of textbooks and other materials at home.
- Help your child learn to make and use checklists, crossing items off as they accomplish them.
Helping a child with ADHD get homework done on time
Understanding concepts and getting organized are two steps in the right direction, but homework also has to be completed in a single evening—and turned in on time. Help a child with ADHD to the finish line with strategies that provide consistent structure.
- Pick a specific time and place for homework that is as free as possible of clutter, pets, and television.
- Allow the child breaks as often as every ten to twenty minutes.
- Teach a better understanding of the passage of time: use an analog clock and timers to monitor homework efficiency.
- Set up a homework procedure at school: establish a place where the student can easily find their finished homework and pick a consistent time to hand in work to the teacher.
Other ways to help your child with homework
Encourage exercise and sleep. Physical activity improves concentration and promotes brain growth. Importantly for children with ADHD, it also leads to better sleep , which in turn can reduce the ADHD symptoms.
Help your child eat right. Scheduling regular nutritious meals and snacks while cutting back on junk and sugary foods can help manage symptoms of ADHD.
Take care of yourself so you’re better able to care for your child. Don’t neglect your own needs. Try to eat right, exercise, get enough sleep, manage stress , and seek face-to-face support from family and friends.
More Information
- Homework Help - Tips for children with ADHD. (National Resource Center on ADHD)
- Supporting School Success - Including how to get your child organized, enlisting the school’s help, and seeking evaluation. (American Academy of Child Adolescent Psychiatry)
- Motivating the Child - How ADHD symptoms interfere with classroom expectations and how to realistically motivate your child. (LD Online)
- Step-by-Step Guide for Securing Accommodations at School - Meeting your child’s educational needs with ADHD accommodations at school. (ADDitude)
- Contents of the IEP - Guide to developing an Individualized Education Program (IEP) with school staff to address your child’s educational needs. (Center for Parent Information and Resources)
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders. (2013). In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . American Psychiatric Association. Link
- AACAP. Supporting School Success. (n.d.). American Academy of Adolescent & Child Psychiatry. Retrieved August 12, 2021, from Link
- Teaching Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Instructional Strategies and Practices– Pg 1. (2008). [Reference Materials; Instructional Materials]. US Department of Education. Link
- Gaastra, G. F., Groen, Y., Tucha, L., & Tucha, O. (2016). The Effects of Classroom Interventions on Off-Task and Disruptive Classroom Behavior in Children with Symptoms of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Meta-Analytic Review. PLOS ONE, 11(2), e0148841. Link
- CDC. (2019, November 7). ADHD in the Classroom . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Link
- “Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) (for Parents) – Nemours KidsHealth.” Accessed February 15, 2024. Link
More in ADHD
What teachers can do to help kids in the classroom

ADHD Parenting Tips
Learn what you can do to help your child thrive

ADHD in Children
What Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder looks like in kids

ADHD in Adults
Recognizing the signs and symptoms, and what you can do about it

Tips for dealing with symptoms, and being more focused and organized

ADHD Medications
Are ADHD drugs right for you or your child?

Dealing with symptoms together and developing a solid partnership

Learn how ADHD is diagnosed in kids and adults

Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.
- Latest News
- Emergencies
- Environment
- Ask the Law
- Visa+Immigration
- Phone+Internet
- Reader Queries
- Safety+Security
- Banking & Insurance
- Corporate Tax
- Travel & Tourism
- Corporate News
- Electronics
- Home and Kitchen
- Consumables
- Saving and Investment
- Budget Living
- Expert Columns
- Community Tips
- Cryptocurrency
- Cooking and Cuisines
- Guide to Cooking
- Art & People
- Friday Partner
- Daily Crossword
- Word Search
- Philippines
- Australia-New Zealand
- Corrections
- Special Reports
- Pregnancy & Baby
- Learning & Play
- Child Health
- For Mums & Dads
- UAE Success Stories
- Photos & Videos
- Course Reviews
- Learn to Play
- Schedule | Medal Tally
- South Indian
- Health+Fitness
- Best Of Bollywood
- Entertainment
- Special Features
- Gratuity Calculator
- Notifications
- Prayer Times
Back to school: Parents in the UAE master the balancing act
How professionals are creatively managing career demands and family responsibilities

As the school year swings into full gear, working parents find themselves balancing on a tightrope, caught between the demands of their careers and the myriad responsibilities of their children’s education. From crafting meticulous schedules to making spontaneous adjustments, these parents juggle job commitments with school activities and homework, striving to maintain harmony and support in their family lives. The challenges they face reveal a common thread of dedication, adaptability, and a tireless commitment to nurturing their children’s development.
For many parents, the school year signifies a fresh set of challenges. It’s not merely about getting the kids to school on time or ensuring their homework is completed; it’s about creating an environment where both work and family life can coexist harmoniously. Balancing these demands often involves a delicate dance of scheduling, communication, and flexibility, where every move can have a ripple effect on the overall family dynamic.
Structure meets flexibility

For parents such as Eliane Chalhoub, an Account Manager, managing this transition involves a finely tuned strategy. Chalhoub’s approach centres around creating a supportive environment through careful planning and organisation. “Balancing work commitments with supporting my children’s homework and school activities can be challenging,” she admits, “but with some planning, it’s definitely manageable.” Chalhoub’s method involves setting up a dedicated homework station and adhering to a structured daily routine. “I create a weekly schedule that allocates specific times for my children’s homework after my workday ends,” she explains. This approach is designed to ensure that all aspects of her family’s life—from school assignments to extracurricular activities—are seamlessly integrated into their daily routine.
Her meticulous planning extends to a shared calendar that details everything from school assignments to playdates, minimising the risk of overlooked responsibilities. Chalhoub also uses to-do lists to keep track of daily tasks, while encouraging her children to start their homework independently. “Not everything always goes as planned,” she acknowledges, “but I try to adjust my schedule or priorities as needed to stay on track.” This balance of structure and flexibility enables Chalhoub to maintain a productive and supportive home environment, despite the unpredictable nature of balancing work and family life.
Quality time over quantity
In contrast, journalist Mahmoud Ghazayel and his data engineer wife, navigate a different set of challenges. With a child still in nursery, Ghazayel’s balancing act involves a more focused approach to time management. “My child requires constant attention and care,” he admits, “which has impacted my ability to work beyond regular hours.” The high cost and limited availability of afternoon nursery care add another layer of complexity to his routine.
Yet, Ghazayel manages to find stability through quality time spent with his child. “We prioritise playing games and eating together,” he says. This focus on bonding not only helps create a sense of stability for his child but also provides him with some much-needed time in the evenings to handle house chores or catch up on emails. Despite the inherent challenges, Ghazayel’s emphasis on quality over quantity highlights the importance of meaningful interactions in maintaining family cohesion.
Integrating learning and fun

Sumit Augustine, a communications and PR professional, faces her own set of hurdles, with long working hours that often overlap with her son’s bedtime. “By the time I reach home, it is almost my son’s bedtime,” she says. Despite this, Augustine has developed creative ways to integrate learning into his daily routine. “We use our daily chores as opportunities for learning,” she explains. For example, she asks her son to make sentences with new words learned in English literature. “This helps him understand the meaning of the words and use them in the right context.”
Augustine also incorporates educational activities into their evening routine, such as playing word games and listening to audiobooks. “My son has developed a liking for languages and self-taught himself how to read Russian letters and play the piano through YouTube,” she says. Weekends are dedicated to hands-on learning experiences, such as creating models of different types of roofs. Augustine believes that these activities not only enhance her son’s understanding of concepts but also teach him valuable strategies for learning. “Investing time in teaching strategies is crucial for long-term learning,” she says. “As a parent, you have to invest in your child, whether it’s with your time or resources.”
Collaboration and family unity

For Inass Msaidi, head of public relations and communications in a real estate company, and mother of three, the balancing act is a nuanced dance of collaboration and family unity. “Managing the balance between work and family life is a delicate act,” she says. With over a decade of experience juggling a demanding career and raising a 13-year-old daughter alongside 8-year-old twins, Msaidi’s perspective is both insightful and practical. She transitioned from journalism to corporate communications in part to gain more structured timing and improve family life. “Creating meaningful connections with my kids is what truly matters,” Msaidi asserts. Her approach involves fostering a sense of teamwork within her family. “My elder daughter helps support her younger siblings,” she explains, “which creates a sense of teamwork and shared responsibility.”
Msaidi’s weekends are carefully planned to ensure a balance between personal time, family activities, and academic support. Fridays are reserved for personal time to recharge, while Saturdays are dedicated to family activities and Sundays focus on homework and meal preparation. “This routine not only promotes balance but also strengthens family connections,” she says. “It ensures that each member of the family feels valued and supported throughout the school year.” This structured approach to family life underscores Msaidi’s belief in the importance of collaboration and shared responsibility in creating a supportive home environment.
Routine and health

Valentina Brogan, an office administrator, brings her own structured approach to balancing work and family responsibilities. “I always establish a routine that includes dedicated time for work, helping my kids with homework, and school activities,” she explains. Brogan’s strategy involves prioritising tasks and delegating household responsibilities to her children, which helps her maintain focus on what’s most important. “I encourage my elder daughter to take responsibility for her homework and school activities,” she notes. Staying organised with a calendar ensures that she keeps track of important dates and deadlines, while also prioritising her children’s health and well-being. “We follow a structured schedule for homework, play, and bedtime during school days,” she says, adding that weekends are reserved for breaks and relaxation.
Brogan also emphasises the importance of regular communication with teachers and limiting screen time. “My kids focus better because they play outdoors and engage in activities like reading and art,” she explains. Her approach to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, with adequate sleep, nutritious meals, and physical activity, underscores the significance of balance in fostering both academic success and overall well-being.
More From GN Focus

AI and VR reshaping the classroom

Ensuring children’s well-being with Burjeel

How to juggle work and school with expertise

Get your kids ready for school with Skechers
Thailand’s political transition and new leadership, uae closely following case of telegram chief durov, canada to allow fewer temporary foreign workers, un humanitarian operations in gaza forced to halt, us election debate in the balance as trump cries foul.

Get Breaking News Alerts From Gulf News
We’ll send you latest news updates through the day. You can manage them any time by clicking on the notification icon.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- U.S. Open Tennis
- College football
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
FACT FOCUS: A look at claims made during the second night of the Democratic National Convention
Sen. Chuck Schumer, D-NY., speaking during the Democratic National Convention Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024, in Chicago. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham speaking during the Democratic National Convention Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024, in Chicago. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
Illinois Gov. JB Pritzker speaks during the Democratic National Convention Tuesday, Aug. 20, 2024, in Chicago. (AP Photo/Erin Hooley)
- Copy Link copied
▶ Follow the AP’s live coverage and analysis from the 2024 Democratic National Convention.
The second night of the Democratic National Convention was filled with excitement as a celebratory roll call marked Vice President Kamala Harris’ nomination to be the party’s candidate for president. As speaker after speaker addressed the convention extolling her qualities to lead the country, they also spelled out differences with her opponents, former President Donald Trump and Ohio Sen. JD Vance, at times misrepresenting the Republicans’ stances.
Here’s a look at the facts.
Missing context on Vance and the child tax credit
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer: “Senate Republicans pretend to care about middle-class families, but they voted no on expanding the child tax credit. And JD Vance didn’t even show up to vote.”
THE FACTS: Vance did indeed skip an August vote on a bill to expand the child tax credit and restore some tax breaks for businesses.
The bill failed to advance in the Senate as Republicans largely opposed the measure, arguing that they would be in position to get a better deal next year, The Associated Press reported at the time .
But there’s more to the story.
Vance has also said he would support expanding the child tax credit , currently at $2,000, to $5,000. He said the Senate vote was a “show vote,” when bills are designed to fail but allow parties to highlight issues before voters.
The cost of Trump’s economic plan
Schumer on Trump’s plan to create tariffs: “He wants to impose what is, in effect, a national sales tax on everyday products and basic necessities that we import from other countries. It will mean higher prices on just about every one of your daily needs. Donald Trump’s plan would cost a typical family $3,900 a year.”
THE FACTS: Trump has proposed imposing a tariff of anywhere from 10% to 20% on all imports and up to 60% on imports from China.
It’s Day 3 of the DNC, and there are 75 days until Election Day. Here’s what to know:
- The parents of a 23-year-old American taken hostage by Hamas during the Oct. 7 attack on Israel gave a speech Wednesday, pleading for the release of the dozens of people who continue to be held captive in Gaza .
- Takeaways: The Democratic National Convention barreled into its third day with a lineup featuring former President Bill Clinton and Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz as the closer .
- In photos: Delegates descended on Chicago after a topsy-turvy few weeks for their party. A visual look at the 2024 DNC .
- Live updates: Follow The AP’s live coverage and analysis from the 2024 Democratic National Convention .
Economists do expect it would raise prices on many goods. The Tax Policy Center, a joint project of the Urban Institute and the Brookings Institution, estimates it would reduce average incomes in the top 60% of earners by 1.8%. And the Center for American Progress Action Fund, a progressive advocacy group, has calculated that the higher tariffs would cost households an extra $3,900 a year.
However, Trump has said the tariff revenue could be used to cut other taxes, which would reduce the overall cost of the policy.
Trump’s changing views on the Affordable Care Act
New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham: “Donald Trump and JD Vance want to dismantle our healthcare system, repeal the Affordable Care Act, and limit protections for preexisting conditions.”
THE FACTS: Trump has repeatedly promised to replace former President Barack Obama’s health care law with a plan of his own. For example, three years after a Congress fully controlled by Republicans failed to repeal “Obamacare” in 2017, Trump urged the Supreme Court to overturn it .
More recently, the Republican presidential nominee threatened to reopen the contentious fight.
“The cost of Obamacare is out of control, plus, it’s not good Healthcare,” he wrote in a November 2023 post on his Truth Social site . “I’m seriously looking at alternatives. We had a couple of Republican Senators who campaigned for 6 years against it, and then raised their hands not to terminate it. It was a low point for the Republican Party, but we should never give up!”
But Trump backed off a potential repeal in April. He said in a video posted to Truth Social that he is “not running to replace the ACA” and that he intends to make it “much better, stronger and far less expensive.”
Another misrepresentation of Trump’s bleach comment
What to know about the 2024 Election
- Today’s news: Follow live updates from the campaign trail from the AP.
- Ground Game: Sign up for AP’s weekly politics newsletter to get it in your inbox every Monday.
- AP’s Role: The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information on election night, with a history of accuracy dating to 1848. Learn more.
Illinois Gov. JB Pritzker, on Trump during the COVID-19 pandemic: “And Donald, well, Donald told us to inject bleach.”
THE FACTS: This claim was also made on the first day of the Democratic National Convention by Rep. Robert Garcia of California.
It’s an overstatement. Trump actually asked whether it would be impossible to inject disinfectant into the lungs.
“And then I see the disinfectant, where it knocks it out in one minute,” he said at an April 2020 press conference . “And is there a way we can do something like that, by injection inside or almost a cleaning, because you see it gets in the lungs and it does a tremendous number on the lungs, so it’d be interesting to check that, so that you’re going to have to use medical doctors with, but it sounds interesting to me. So, we’ll see, but the whole concept of the light, the way it kills it in one minute. That’s pretty powerful.”
Find AP Fact Checks here: https://apnews.com/APFactCheck .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Approved Secret Nuclear Strategy Refocusing on Chinese Threat
In a classified document approved in March, the president ordered U.S. forces to prepare for possible coordinated nuclear confrontations with Russia, China and North Korea.

By David E. Sanger
David E. Sanger has written about American nuclear strategy for The New York Times for nearly four decades.
President Biden approved in March a highly classified nuclear strategic plan for the United States that, for the first time, reorients America’s deterrent strategy to focus on China’s rapid expansion in its nuclear arsenal.
The shift comes as the Pentagon believes China’s stockpiles will rival the size and diversity of the United States’ and Russia’s over the next decade.
The White House never announced that Mr. Biden had approved the revised strategy, called the “Nuclear Employment Guidance,” which also newly seeks to prepare the United States for possible coordinated nuclear challenges from China, Russia and North Korea. The document, updated every four years or so, is so highly classified that there are no electronic copies, only a small number of hard copies distributed to a few national security officials and Pentagon commanders.
But in recent speeches, two senior administration officials were allowed to allude to the change — in carefully constrained, single sentences — ahead of a more detailed, unclassified notification to Congress expected before Mr. Biden leaves office.
“The president recently issued updated nuclear-weapons employment guidance to account for multiple nuclear-armed adversaries,” Vipin Narang, an M.I.T. nuclear strategist who served in the Pentagon, said earlier this month before returning to academia. “And in particular,” he added, the weapons guidance accounted for “the significant increase in the size and diversity” of China’s nuclear arsenal.
In June, the National Security Council’s senior director for arms control and nonproliferation, Pranay Vaddi, also referred to the document , the first to examine in detail whether the United States is prepared to respond to nuclear crises that break out simultaneously or sequentially, with a combination of nuclear and nonnuclear weapons.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

COMMENTS
Break tasks down and keep them fun. Aim for a balance between physical and mental focus, and remember it's OK to give up if the timing isn't right. Have realistic expectations, and know that your child's focus will improve with age. Don't be scared to quit when things really are not working.
Third to fifth grades. Many children will be able to do homework independently in grades 3-5. Even then, their ability to focus and follow through may vary from day to day. "Most children are ...
If your child has trouble staying focused, try these six strategies. 1. Set a timer. Knowing there's a limit to how long they have to stay focused can make it easier for kids to hang in there. Set a timer for how long your child needs to work before having a quick snack or taking a brain break.
16 | Use a timer. A timer is a great tool to help your child keep track of how long they can stay focused. You can use it for homework or for any other tasks, and slightly increase the time set as they get better with focus and concentration. 17 | Help your child practice mindfulness.
Tip 11 - Help Your Child Practise Mindfulness. Mindfulness involves focusing your awareness on the present moment while acknowledging your thoughts and feelings. When your child is becoming distracted, encourage him or her to take a 5 minute break to sit quietly and take a moment for him or herself. Have your child use this time to think ...
Low self-confidence. 2. Make Homework Time Easier. Make study time as easy as possible for your child by providing him or her with everything needed to get work done: Quiet space: Find a quiet, distraction-free space for your child to study. Food and drink: If your child is hungry, it can be hard to focus on work.
Others need to have parents nearby to help keep them on task and to answer questions when problems arise. Ask your child where the best place is to work. Both you and your child need to discuss pros and cons of different settings to arrive at a mutually agreed upon location. Step 2. Set up a homework center.
If your child is struggling with focus at school, try having your child walk or bike to school. (One school had great success having kids take PE right before their most challenging academic class.) If homework is the problem, make sure they get some playtime after school or get them to do some physically challenging chores around the house ...
Emphasize the importance of determination, effort, and persistence in whichever example of your successes you choose to share. If your child is exhausted: Prioritize only what's really essential ...
Try creating a homework schedule and set a specific time and place for your child to get homework done. Use a timer to help your child stay on track and get a better sense of time. Learn about trouble with planning. The challenge: Studying effectively. Many kids need to be taught how to study effectively. But some may need concrete strategies.
Some kids do best by jumping into homework right after school, while others need a break and will be better focused after dinner. Set a good example. Family study time gives you the opportunity to ...
Help them make a plan. On heavy homework nights or when there's an especially hefty assignment to tackle, encourage your child break up the work into manageable chunks. Create a work schedule for the night if necessary — and take time for a 15-minute break every hour, if possible. Keep distractions to a minimum.
Stay focused on your job, which is to help your child do their job. Don't do it for them. If you feel frustrated, take a break from helping your child with homework. Your blood pressure on the rise is a no-win for everyone. Take five or ten minutes to calm down, and let your child do the same if you feel a storm brewing.
Keep the homework area quiet, with TVs and cell phones off. (Some kids actually do focus better when listening to music. If you play music, pick something instrumental, with no distracting vocals, and don't let your child crank up the volume.) If brothers or sisters are playing nearby, or other family members are talking so your child loses ...
Set up an area where your child can do their homework clutter free. For some kids, this can make a huge difference. Think about putting away loose papers, art and craft supplies, and toys to eliminate distractions. Get a special homework pen/pencil/eraser. Having a special pencil to use ONLY for homework can help some kids sit down and get it done.
This is a custom heading element. 1. Get a planner, or use a free online application. Some tool for your child easily view the daily schedule is important. This can be a physical planner or an app, but either way, it'll make sticking to a schedule much simpler. 2.
Start by telling your child that you'll set a timer for 5 minutes. All he needs to do is work for 5 straight minutes before he can take a break. And if he can't yet do 5, set the timer for 2 minutes instead. The goal is to master focused work for a set period of time and train the brain to work for longer focused periods.
The bedroom is a place for sleep, rest, and relaxation — not work and stress. 2. Create a consistent schedule. It is important for kids with ADD/ADHD to have a consistent routine. This will help your child start his or her homework and focus. Set a time each day for your child to sit down and complete his or her work. 3.
READ: 5 Tips to Help Your Kid Laser Focus on Homework. Let kids set a reward. Ask your kids to take the lead on this one. Trust me on this. Ask them to decide on something they get when homework is done. There are some guidelines to this though. Discuss the reward with your child so that you know what it is and you are able to be on board.
By Anne Kenderdine. January 27, 2014 at 12:38 p.m. EST. When my daughter began the routines of first grade and its attendant homework assignments last fall, my husband and I girded ourselves for ...
Once your child gets better at managing his time, completing his work, and getting organized, then it's time for you to back off. Let him do it on his own. Only step in if he is consistently having a problem. 5. Identify a Study Spot. Your child may need a quiet location away from brothers and sisters to study.
Turns out you were right. A Stanford study found that music engages the parts of the brain involved with attention and memory. It can really help some children focus on the task at hand. If your child is easily distracted then try playing some classical or calm music through headphones to help them concentrate. 10.
Set Clear Homework Expectations (and get your child's buy-in!) On the opposite end of micromanaging, there's also the potential for enabling bad habits. ... Small wins can include trying out a new tool or strategy, sitting down to focus for a given time, or starting homework without a fight. Whatever the wins might be, be sure to ...
📚Gradually reintroduce structure into a child's daily routine to help them prepare for school. Add a 15-minute block of educational content to your kid's routine, such as a read-aloud, math ...
Set up a homework procedure at school: establish a place where the student can easily find their finished homework and pick a consistent time to hand in work to the teacher. Other ways to help your child with homework. Encourage exercise and sleep. Physical activity improves concentration and promotes brain growth.
For many parents, the school year signifies a fresh set of challenges. It's not merely about getting the kids to school on time or ensuring their homework is completed; it's about creating an ...
THE FACTS: Vance did indeed skip an August vote on a bill to expand the child tax credit and restore some tax breaks for businesses. The bill failed to advance in the Senate as Republicans largely opposed the measure, arguing that they would be in position to get a better deal next year, The Associated Press reported at the time .
Welcome to Worship August 25th, 2024 at Claremont UCC! We're Glad You're Here! We are an open and affirming in-person and online church located in the...
President Biden approved in March a highly classified nuclear strategic plan for the United States that, for the first time, reorients America's deterrent strategy to focus on China's rapid ...
The night featured Trump introductions from Kid Rock and Ultimate Fighting Championship CEO Dana White, as well as a band blasting 1980s hits and a speech from a Trump golf course manager.