Engineering Proposals: Free Template + 12 Proposal Writing Tips
- Digital Asset Management
- Marketing Technology
Posted by: Cinthya Soto
An engineering service proposal is a standardized document pivotal in guiding the selection of consultants. The engineering proposal is more than just a document; it’s your opportunity to showcase expertise, understanding, and value among the piles of proposals.
Whether you’re a seasoned engineering consultant or a firm stepping into the arena of important projects, your ability to craft a compelling proposal can make all the difference in placing your business ahead of the competition. After all, in 2023 alone companies sourced 39% of their revenue from RFPs .
However, mastering the creation of such a proposal is a complex task. For those wanting to successfully navigate this process, you must be ready to grasp the fundamental concepts of engineering proposals. But what exactly does that include?
In this blog, we’re covering everything there is to know about writing engineering proposals. From what to include in your engineering proposal and writing tips to engineering project proposal examples and a free engineering proposal template, we aim to help you create winning proposals .

How to Write an Engineering Proposal: What to Include
Engineering proposals serve as the critical document on which selections of engineering consultants are based. For consulting firms in the engineering sector, these proposals are the principal tool for winning new contracts. For clients or project owners, they are an invaluable resource to help them choose the best consultants. But what should be included in an engineering proposal format?
Here are the different sections you should include in your engineering proposal:
Cover Page
The cover page of your engineering proposal sets the first impression. It should include the project title, the name of the organization or individual presenting the proposal, the date, and any relevant project identification details. Make sure to keep it professional and clean to reflect the seriousness of your intentions.

Cover Letter
The cover letter personalizes your engineering proposal. It should briefly introduce your organization, express your enthusiasm for the project, and highlight the key points that make your proposal stand out. This is your opportunity to establish a connection with the reader and encourage them to read further.
Introduction
The proposal introduction serves as the executive summary of your proposal. It should include an overview of your organization, the purpose of the proposal, and a summary of what the proposal will cover.
Make sure to clearly define the problem or opportunity your proposal addresses. Essentially, the introduction clarifies the purpose of crafting the proposal. It should lay out the foundation for why the proposal is necessary.
Additionally, the introduction should provide a concise overview of the proposal’s content. This summary needs to be engaging and offer a glimpse of the detailed descriptions to follow. It reveals your core idea and outlines the strategy you intend to use in delivering your services. Here’s an example of what a successful proposal introduction looks like:

Project Background
This section delves into the details of the project. Describe the current situation, the specific problem or opportunity, and the objectives of the project. Providing a concise but thorough background helps the reader understand the context and the necessity of the proposed work.
You should illustrate the issue or situation that led to the creation of your proposal. In this section, it’s important to show a thorough comprehension of the problem at hand.
Qualifications
In this section, highlight your qualifications and experience relevant to the project. Detail your technical expertise, prior successful projects, and any unique skills or resources that make you stand out. This section reassures the client that you are capable of handling the project.
When writing this section, make sure to accurately highlight your skill set to emphasize your suitability for the project at hand. Consider this section as the part of your resume where you detail your skills and experiences.
While you should showcase your expertise, It’s also important to showcase, if relevant, your company’s proficiency and ability to successfully carry out the proposed task.
Project Team
Typically, an engineering proposal requires including details about each team member, their specific roles, and their professional backgrounds. The collective expertise of the project team often plays a critical role in the selection of a qualified engineering consultant, which is why the “Project Team” section is extremely important.
In this section, showcase the team that will work on the project. Ensure that every team member’s relevant experience is detailed in the proposal. Make sure to include brief employee bios in your RFP resumes that highlight each member’s qualifications and relevant experience. Just a few well-crafted sentences on such skills can make a significant difference.

The right tools can help in creating and formatting these bios to present a professional image. With a robust digital asset management (DAM) solution like OpenAsset , you can cut down on the hours spent creating resumes and employee bios for engineering proposals.
A notable feature for employee bios is Content Assist , powered by OpenAsset’s Generative AI. It’s designed to assist users in creating project descriptions and employee bios within OpenAsset. In simple terms, Content Assist will analyze the existing data in your OpenAsset system to create original project descriptions and employee bios.
OpenAsset and the Employee Module enhance productivity within your organization by automating the creation of employee resume documents . This helps you present your team in the best light possible and quickest way possible.
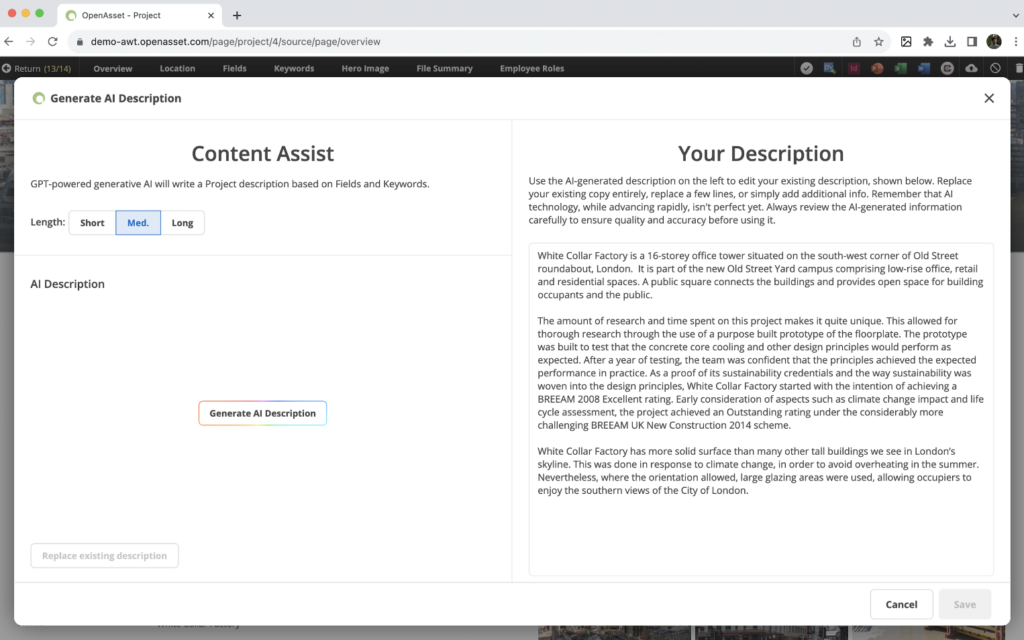
Remember, the strength of your team and how you present your team can be a significant deciding factor in winning the proposal.
Scope of Work
In the scope of work , you’ll want to detail the specific activities, deliverables, and timelines involved in the project. It’s crucial for an engineering proposal to precisely outline the project scope. Given that misunderstandings about project scope are a primary cause of project issues or failures, defining the scope with as much clarity is essential to prevent and more easily resolve problems.
Clearly outline the work that will be done, the methodologies used, and the expected outcomes. This section should align expectations and minimize misunderstandings about the project’s scope. When the scope is clearly defined, everyone involved understands the extent of work expected within the project’s framework.
Work Schedule
The work schedule section of the proposal does precisely what its name suggests: it monitors your work schedule.
Provide a detailed schedule of the project, including key milestones, deadlines, and dependencies. This section maps out the timeline for completing the project and is crucial as it informs your audience about the expected timelines and milestones.
The work schedule should be realistic and allow for some flexibility. You can enhance clarity by incorporating well-organized tables and specific time allocations. It’s also crucial to demonstrate your understanding of project management and your ability to complete the project on time.
Including a work schedule provides a professional touch to your proposal. Should you find yourself unable to stick to this schedule once the project has begun, it’s crucial to communicate any changes as soon as possible with the relevant parties.
Project Cost
Undoubtedly, the cost of engineering services holds significant weight in the decision-making process. The potential consultant is expected to define costs for each team member based on suitable hourly rates and the estimated hours needed for each stage of the project, along with a summary. While engineering associations recommend choosing consultants based on qualifications above cost, the reality is that pricing remains a key determinant.
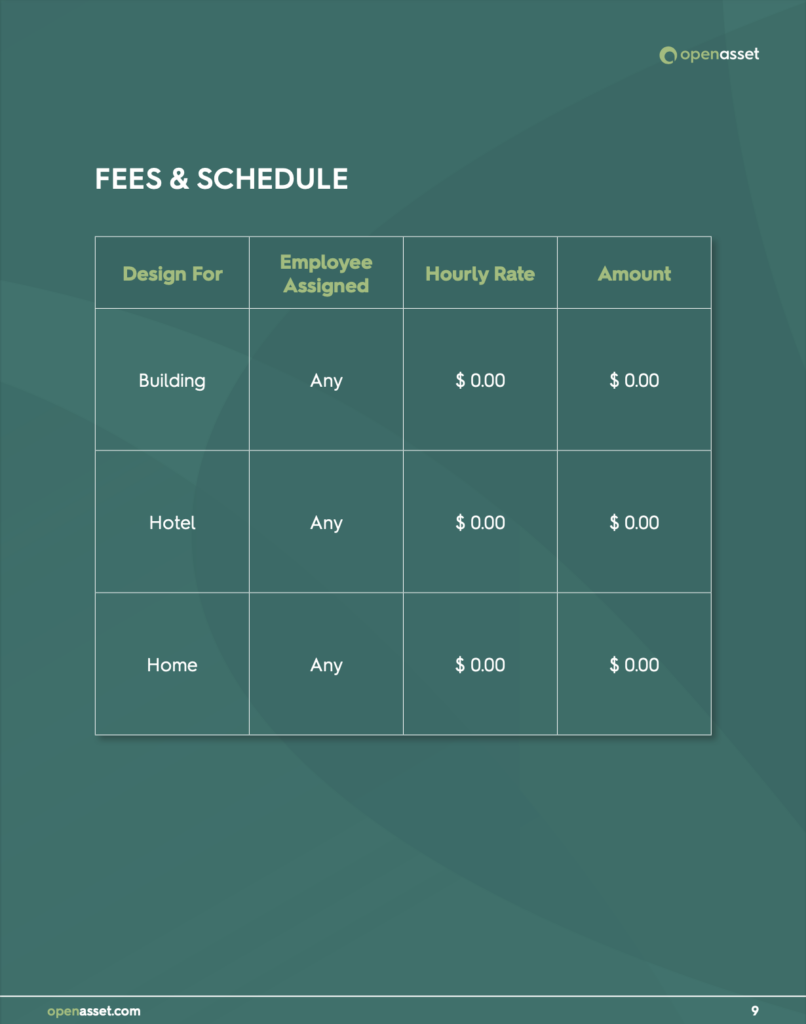
In this section, detail the expected expenses for your project by itemizing them and assigning monetary values to each category. Break down the costs into distinct groups, such as individual labor charges per employee, material costs, and so on. Summing up these figures will provide the total cost, offering the reader a clear financial overview.
This facilitates an informed decision-making process, allowing for a thorough assessment of different factors before committing funds.
Write a Strong Proposal Conclusion
The conclusion of the proposal mirrors the concluding section of a cover letter. Here, you should explain the reasons for considering you or your team as the ideal choice for the project and provide your contact information. It’s also an opportunity to reaffirm why you or your team is the most suitable candidate for the project.
Conclude your proposal by summarizing the main points, reiterating the benefits of choosing your organization, and expressing your eagerness to work on the project. End on a positive note, inviting further discussion or questions. You want to write a compelling conclusion that will leave a lasting impression on the reader.
| now. |
Expert Engineering Project Proposal Tips
To maximize your chances of winning projects with your engineering proposals, here are 12 proposal writing tips to keep in mind when crafting your next engineering proposal:
1. Read the RFP Multiple Times
Simply reading the Request for Proposal (RFP) is not enough; a deep understanding of the evaluation criteria is crucial. It’s essential to review the RFP carefully, taking in every detail beyond the basic requirements such as submission dates, formatting guidelines, and required signatures.
This thorough examination ensures you are aligned with all the requirements, conditions, and expectations outlined in the RFP. Such attentiveness not only aids in crafting a tailored response that aligns with the issuer’s needs but also minimizes the risk of non-compliance with the RFP’s requirements.
Moreover, upon reading a new RFP, it’s smart to draft a checklist detailing all essential criteria. This approach allows a good amount of time for you to make sure everything is included in your RFP response and allows you to request any necessary clarifications well in advance of the deadline.
2. Do Your Research
Undertaking comprehensive research is a cornerstone in the development of a compelling engineering proposal. This process involves gathering data, understanding industry standards, exploring the project’s context, and analyzing the potential impact of your work.
Research allows you to approach the project with a depth of knowledge that will reflect the feasibility, innovation, and planning of your proposal. It also provides a foundation for making informed decisions, identifying potential risks, and proposing effective solutions.
In essence, the research you conduct forms the backbone of a proposal that’s both convincing and achievable.
3. Create a Clear Proposal Format
If you’re wondering how to draft a proposal, starting with a clear format is a great start. Maintaining a clear engineering proposal format is fundamental to creating a structured and professional document. A standardized format ensures that the information is presented in an organized manner, making it easy for the reviewers to follow and evaluate. The format typically includes a well-defined table of contents, sections with clear headings, and a logical flow of information.
This structured approach helps display your message with precision and prevents critical elements from being overlooked. Consistency in format across various sections, such as the project background, scope, schedule, and qualifications, reinforces the overall flow of the proposal.
A well-formatted proposal not only reflects your professionalism but also helps in communicating the seriousness and preparedness of your team for the project.
4. Introduce Your Company’s Background
Introducing your company with a concise background in your engineering proposal is a critical step in setting the stage for a strong pitch. This section should provide a snapshot of your company’s history, core competencies, successes, and mission as they relate to the project in question. It’s an opportunity to establish credibility and build trust with the proposal’s reviewers.
This introduction should show the essence of your company’s identity, values, and the journey that has led to its current standing in the industry. Highlighting notable achievements, experience in similar projects, and the overarching vision can create a compelling narrative that resonates with the potential client.
A well-articulated company background serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the proposal is built, underlining why your firm is uniquely suited for the project.

5. Feature Your Team’s Talent
In an engineering proposal, it’s important to select the best employees for your RFP response . Make sure to illustrate the unique skill sets, qualifications, and experiences that each member brings to the table. You can use this section to delve into the specific talents that differentiate your team from competitors.
Detailing individual roles and how they will contribute to the success of the project not only showcases the depth of your collective proficiency but also helps build confidence in your team’s ability to deliver results. Remember to align these talents with the project requirements, demonstrating a perfect fit between your team’s capabilities and the project’s needs.
If you’re looking to generate employee resumes in minutes that demonstrate your team’s talent, a robust DAM can help you store and manage employee profiles. A DAM for engineering like OpenAsset saves you time and resources in managing your resumes. Through the use of Generative AI, you can create project descriptions and employee RFP bios.
6. Include Images and Graphics
Incorporating images and proposal graphics into your engineering proposal can significantly enhance its impact. Civil engineering projects typically require various diagrams, illustrations, and maps. This is because the essence of designs is best conveyed through visual representation for complete clarity. The same principle applies to proposals, where visual elements are crucial for demonstrating complex information clearly and effectively.
Moreover, using images to communicate visually will save reading time for the client. The reader will also appreciate the amount of effort put into preparing the engineering proposal.
Use tools like OpenAsset to seamlessly find and present visuals of projects that align closely with the prospective client’s needs or showcase your team’s qualifications. This tailored visual approach not only shows your past successes but also provides a compelling, concrete visual narrative of what you can deliver.
Moreover, AI in DAM saves you time and resources in managing your images through AI-suggested keywords, image similarity search, AI Content Assist, and more. These features:
- Reduce the time it takes to manually tag images
- Helps you build and expand taxonomies
- Gives you additional images to select from and use.
- Enables you to leverage Generative AI for project descriptions and employee RFP bios
Images are not just embellishments; they can be powerful testimonials of your work’s relevance and quality, speaking volumes more than words alone.
7. Use Clear Language
Using clear and concise language is crucial when crafting an engineering proposal. The ability to demonstrate complex ideas effectively without resorting to overly technical jargon or unnecessarily complicated explanations is a skill that cannot be overstated.
Likewise, it’s important not to assume that the readers will be familiar with the specialized jargon of your field. Take time to research the client and the reviewing committee to grasp their expertise and knowledge base. When delving into detailed technical matters, ensure you offer sufficient background to maintain inclusivity and prevent any misunderstandings.
Proposals should be accessible, ensuring that stakeholders, regardless of their technical background, can grasp the proposed concepts and see the value in them.
Your team might possess attributes such as “remarkable efficiency, strong motivation, and outstanding qualifications,” yet, it’s likely that your competitors claim the same. Such language is often so overused in proposals that they become clichéd and lose their impact.
Rather than relying on generic adjectives, prove your capabilities with concrete examples of past projects or situations that illustrate your skills in action. Even more compelling would be citing testimonials or endorsements from previous clients who can vouch for your expertise. Here’s what that could look like in your proposal:

Additionally, avoiding excessive language not only helps in maintaining the reader’s attention but also demonstrates your ability to communicate efficiently. The proposal should be as concise as possible without sacrificing completeness. Every sentence should serve a purpose, whether it’s to inform, persuade, or clarify.
8. Keep It Short
Coming across an RFP with a large page limit or no page limit might give you the impression that you should create a significantly lengthy proposal. However, it’s best to resist this urge to write a 200-page proposal.
Keep in mind, your potential client will be comparing your proposal with several others. A concise submission allows them to quickly discern the essential details. Overloading your proposal with text increases the likelihood of them skimming over key points — steer clear of dense paragraphs.
A concise proposal not only respects the reviewer’s time but also enhances readability and comprehension. It’s essential to spread your message and value proposition without unnecessary elaboration. Precision in language, clarity in presenting solutions, and conciseness in your descriptions can make a powerful impact.
Moreover, a proposal that is straight to the point is often a sign of a well-thought-out project plan and a capable, organized team that knows how to communicate. A compact and well-structured proposal often speaks volumes about your project management skills and your respect for the client’s resources and time constraints.
9. Practice Teamwork
A collaborative approach ensures that diverse expertise and perspectives contribute to a more robust and comprehensive document. It’s the teamwork among team members, with their unique skill sets and experiences, that can elevate the quality of a proposal.
Working together with your team in the proposal process can lead to innovative solutions that might not surface in a siloed work environment. Teamwork facilitates thorough cross-checking, brainstorming, and problem-solving, which are essential to addressing the complex challenges typically presented in engineering projects.
Remember, surrounding yourself with an effective team is the key to success. A collaborative culture could be what makes you stand out from the competition.
Moreover, highlighting the collaborative nature of your team within the proposal can also serve as a testament to your capability to work together, a quality often wanted by clients. It’s not just about the final product but also about demonstrating the process of how your team works together to achieve excellence.
10. Proofread and Double-Check
Proofreading and carefully double-checking your proposal is as essential as the content itself. This step ensures that your document is free from errors, which could otherwise affect the credibility of your proposal. It’s not only about catching typos or grammatical mistakes; it’s about ensuring that every figure, fact, and statement aligns with the RFP requirements and your research findings.
A proposal that is well-edited and error-free communicates attention to detail and a commitment to excellence. It’s recommended to have multiple team members review the proposal to provide fresh perspectives and catch issues that you might have overlooked.
Remember, a single mistake could raise doubts about the professionalism of your work and the quality of the project delivery. Therefore, rigorous proofreading and double-checking are necessary to validate the integrity and professionalism of your engineering proposal.
11. Meet Deadlines
Meeting deadlines is important in the context of engineering proposals. The ability to deliver on time reflects your professionalism and reliability. It’s a non-negotiable element of project management that sets the stage for how potential clients view your commitment to the project’s success.
Planning is essential to ensure deadlines are not just met, but comfortably, allowing planning for any unexpected circumstances that might arise. Missing a deadline can have significant repercussions, from damaging your reputation to disqualification from the bidding process.
However, it’s not just about avoiding the negative. Following deadlines can also enhance your standing with clients, as it demonstrates respect for their time and trust in your ability to manage the project effectively from the start.
12. Submit the Proposal on Time
Part of meeting deadlines includes submitting your proposal on time. Every RFP specifies a submission deadline that must be met. Contrary to project deadlines, which may be subject to change during a project, the cut-off date for proposal submission is non-negotiable.
Physical submissions of hard copy proposals are often marked with an actual time stamp upon receipt. If that timestamp shows your submission arrived even one second past the deadline, it will unfortunately be too late.
With the rise in digital submissions, the strict adherence to deadlines continues. Considering potential issues like slow upload speeds or internet disruptions, it’s wise to plan additional time when submitting proposals electronically.
Make sure it’s clear how the proposal will be submitted so there are no surprises. You should also ask for help when it’s needed, especially if you are facing roadblocks and don’t have much time left.
Moreover, building buffer time for reviews and potential revisions is a wise strategy. Proposal writing often shows that tasks tend to extend beyond anticipated time frames. Whether you run out of printing paper or a team member makes a last-minute change, you need to be prepared. Therefore, allowing yourself a generous timeline for the preparation and submission of the final documents can mitigate the risk of missing the deadline.
Meeting deadlines reflect your professionalism and reliability, which are critical factors in the selection process. It demonstrates your commitment to the project timeline and sets the stage for the timely execution of the work ahead. Engineering proposals are also an investment of time and money and if you miss the deadline, this investment is wasted.
Additionally, a punctual proposal suggests that your project management and organizational skills are well-tuned, giving potential clients confidence in your ability to deliver results within the specified timeframe.
Free Engineering Proposal Template
At OpenAsset, we want to provide you with valuable resources to help pave the way toward success. That’s why we’re providing a free engineering project proposal template to inspire your proposal writing journey.

Use OpenAsset for Your Engineering Services Proposal
Leveraging a robust DAM, like OpenAsset , in your engineering proposals is a game-changer. OpenAsset streamlines the process of incorporating high-quality images and project data that represent your team’s past achievements and expertise.
By using OpenAsset, you can create a visually impactful and content-rich proposal that stands out. It not only saves valuable time by organizing your assets efficiently but also ensures that you present a polished, professional, and tailored proposal to your potential clients.
OpenAsset’s DAM solution makes AEC proposals simpler, faster, and more successful. That’s why 99% of customers renew. Leverage OpenAsset to elevate your proposals and effectively demonstrate why your team is the ideal choice for any AEC project.
Ready to start creating engineering proposals that will set you apart?
Get OpenAsset DAM Insights

How to Create Winning Proposals
What to read next.

Civil Engineering Marketing & Sales Strategies to Win More Deals
As the civil engineering industry evolves, so must firms’ strategies to attract and retain clients. Civil engineering marketing and sa...

Answers to the Top 20 IT Questions About DAM Software
As an architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) firm, managing a growing library of digital assets efficiently is crucial for firms ...

Proposal Writing Skills: Top 18 Characteristics, Traits, and Qualities
A proposal writer is a skilled professional responsible for creating detailed, persuasive documents that outline a company’s offerings...
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies
AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Engineering Project Proposal Examples with Templates and Samples

Kavesh Malhotra
Engineering projects are the bedrock of innovation and progress in our world. From designing complex infrastructure to developing cutting-edge technology, engineering projects shape the future. But behind every successful project is a well-crafted proposal. A project proposal is like a roadmap, charting the course from idea to reality. It's a critical document that conveys your vision, strategies, and plans to stakeholders.
In this blog, we'll embark on a journey through engineering project proposals. We understand that you're not looking for a lecture on what they are but rather how to create them efficiently and effectively. Whether you're in the realm of civil engineering, IT engineering, or network engineering, SlideTeam templates are your secret weapons for crafting compelling proposals.
Learn how to create a compelling engineering company profile with valuable insights and tips, ensuring your engineering firm makes a lasting impression.
The Power of Engineering Project Proposals
An engineering project proposal is more than just a formal request for resources. It's a persuasive document that must convey a clear vision, scope, and strategy. It sets the foundation for a project's success. Effective engineering project proposals serve several critical functions:
- Site Preparation: Like preparing a canvas before a painting, an engineering project proposal readies the ground for your project's execution.
- Project Implementation Timeline: It's the backbone of your proposal. This project implementation timeline outlines the project's phases, milestones, and deadlines.
- Release and Evolution Process: How will your project evolve over time? This process ensures your project remains adaptable in an ever-changing landscape.
- Prototyping: Especially crucial in IT engineering, prototypes provide a glimpse into your project's potential.
- IP Addressing Scheme: In the world of network engineering, IP addresses are the lifeblood of communication. This scheme lays the groundwork for connectivity.
- Proposed Design: This blueprint helps stakeholders visualize your vision. It's the difference between mere words and a compelling narrative.
Get ready to embark on a journey through a treasure trove of Engineering Project Proposal Templates designed to transform your projects into resounding successes. These templates are your golden ticket to hassle-free proposal creation, offering not just a head start but also the freedom to craft a captivating presentation tailored to your exact needs.
Imagine all the time and energy you'll save, no longer laboring over creating presentations from scratch. Instead, you'll be equipped with powerful templates that ensure your proposals are not just good but exceptional.
Discover a selection of the best engineering project report template s to help you craft informative and compelling project reports.
Let us now present our top 10 engineering project proposal templates:
Template 1: Cover letter for Engineering Project Proposal Template
This is the colloquial first impression. It sets the tone for your proposal and serves as a gateway to your project. A well-written introduction and prototyping ensures your proposal starts on a positive note. Use it to promote your company's services and attract more clients. Highlight your key offerings, such as skilled workforce, global consultancy, effective management, and infrastructure maintenance. You can also showcase your past project certifications to establish credibility in the construction industry. Download this well-crafted introduction that is vital to engage your audience right from the start, as it is the face of your project.

DOWNLOAD NOW
Template 2: Scope of Engineering Project Proposal Template
Defining the project's scope is critical. This slide offers a clear and detailed delineation of your project's boundaries. It defines the services the company will offer to meet the requirements like proposed design, drafting, site survey, complete planning and engineering, etc. It presents the deliverables, ensuring everyone involved knows the project's exact parameters. Download this slide that helps in clearly stating the project's boundaries and deliverables.

Template 3: Activity Schedule for Engineering Project Proposal Template
A project is only as good as its execution. For successful project execution, a comprehensive activity schedule is crucial. This layout outlines the project's activities like site survey, preparation, construction, etc. It also outlines the status and project implementation timeline of these tasks, ensuring a well-organized and efficient implementation process. Download this slide that offers a structured, organized approach to project implementation.

Template 4: Your Investment for Engineering Project Proposal Template
The financial aspect is often a key concern for stakeholders. This section deals with the financial aspects of your engineering project proposal. It helps in explaining the budget, making it transparent, straightforward, and easily understandable. It includes the cost of planning and budgeting, site surveying, building proposed design , construction materials, and labor charges. Download this slide that will be an essential component for securing necessary resources.

Template 5: Cover letter for Network Engineering Project Design Proposal
In the realm of network engineering, communication is vital. A well-crafted introduction and prototyping set the stage for your project and introduces the project to stakeholders. It lets you showcase the clients' needs and proposed solutions. The experience in cable installation and their applications for a secure network is also highlighted. Further, the proposal cover letter provides assurance of achieving the desired goals in a short period of time, making it a highly effective solution for the client's needs. Effective communication is crucial in network engineering projects, and downloading this introduction sets the tone for effective collaboration.

Template 6: Cabling and Connectivity for Network Engineering Project Design Proposal
Network projects rely on seamless connectivity, and this template is a blueprint for ensuring the project's cabling and connectivity are robust and efficient. It provides crucial information in a tabular format on the types of cables the sender will use to meet the customer's requirements. It covers information like the category of cables, data rate, distance, and application. Download this presentation that plays a crucial role in a robust network infrastructure design.

Template 7: Our Team Structure for Network Engineering Project Design Proposal
The right team is essential for any project's success, and a thriving network engineering project requires a well-organized team. This slide outlines the structure of the team, defining roles and responsibilities, and key members responsible for meeting the customer's requirements along with their departments. Download this chart to ensure an efficient project management process.

Template 8: Cover Letter for IT Engineering Project Proposal
In IT engineering, innovation and clarity are paramount. A compelling introduction and prototyping sparks interest and sets the tone for a dynamic project. This web app development cover letter introduces your company name and introduction and lets you showcase the project context with details of the client's requirements and proposed deliverables. Additionally, the cover letter covers the experience and approach to meet the client's requirement for an app for customizing nutrition plans. Download this introductory slide that grabs stakeholders' attention and outlines the project's key elements.

Template 9: Work Breakdown Structure for IT Engineering Project Proposal
Understanding the components and tasks in an IT project is crucial. This template helps break down the project into manageable parts, making the project more comprehensible and manageable. It covers the details of the task name, its duration, start date, finish date, and project implementation timeline . Download this template for understanding an IT engineering project.

Template 10: Company Overview for IT Engineering Project Proposal
A project doesn't exist in isolation. A company's background and context are integral to an IT engineering project proposal. This slide offers information about the computer science project management company, covering details about its vision, mission, and achievements. Download this preset to provide an overview of your company, conveying its identity and ethos to stakeholders, which is essential for trust and credibility.

A Journey Worth Taking
An engineering project is an intricate dance of proposed design , execution, and management. It is about turning visions into reality and requires a well-structured proposal that communicates your ideas coherently. However, crafting an engineering project proposal is more than just a task; it's a journey. It's about creating a compelling narrative that captures the essence of your project and excites your stakeholders. The above templates are the tools that will transform your proposals into powerful, persuasive documents that lead your projects to success.
Also, explore a collection of top engineering proposal templates with real samples and examples to assist you in creating effective engineering proposals.
Now, it's your turn to take your project to new heights. Download these templates and embark on your journey to engineering success.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Agriculture Project Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Research Paper Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Hospitality Management System Project Proposal Templates with Examples and Samples
- 7 WordPress Web Design Proposal PowerPoint Templates to Showcase Your Portfolio
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 7 Solar Power PowerPoint Templates with Samples and Examples
Top 7 Investment Tracking Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


Engineering Project Proposal
Proposal maker.
Engineering project proposals are written for a variety of reasons. There are some engineering project proposals that are made to persuade potential sponsors, funding agencies, and/or creditors. There are also some engineering project proposals that allow the plans of engineers to be considered and approved by the management of the firm where they work for or the clients who would like to get their services. With these being said, an engineering project proposal is actually like a concept proposal in a way that it reflects and presents the specific ideas of an engineer for a particular engineering project.
An engineering project proposal must be aligned with the kind of engineering project that you would like to be a part of. It should also be the result of either a request or an existing issue, concern, or problem. To guide you in developing a clear and goal-derived engineering project proposal , we have listed several downloadable examples of engineering project proposals that are used in various activities and programs.
15+ Engineering Project Proposal Examples
Engineering proposal example.

- Google Docs
Size: A4, US
Engineering Project Proposal Template

Engineering Student Project Proposal Template

- Apple Pages
Size: 115 KB
Engineering Project Execution Plan Template

Size: 26 KB
Engineering Project Scope Template

Size: 162 KB
Free Engineering Project Roadmap Template

- Apple Keynote
- Google Slides
Size: 66 KB
Civil Engineering Project Manager Resume Template

Size: 98 KB
Agricultural Engineering Project Proposal Example

Size: 44 KB
Software Engineering Project Proposal Example

Size: 133 MB
Engineering Research Project Proposal Example

Industrial and Systems Engineering Project Proposal Example

Size: 201 KB
Chemical Engineering Project Proposal Example

Size: 601 KB
Computer Engineering Project Proposal Example

Size: 551 KB
Mechanical Engineering Project Proposal Report Example

Size: 350 KB
Engineering Project Proposal Format Example

Size: 187 KB
Mechanical Engineering Project Proposal Example

Engineering Project Proposal Example

How to Impress the Target Audience of Your Engineering Project Proposal
If you think that only consulting engineers are bound to develop an engineering project proposal, then you may want to think again. There are different engineering positions that are also required or tasked to come up with an engineering project proposal may they be in their own fields of engineering expertise or in the fields of education, advanced research, and academics.You may also see project proposal outlines .
Since there are a lot of engineering project proposals that you can create, expect that there are also different types of audiences that you need consider whenever you plan to develop this document. Here are some of the ways on how you can impress the target audience of your engineering project proposal:
1. Make sure that you will properly define the entities who support the project that you are proposing. Knowing how your audience is can give you more idea on how you can properly present the engineering project proposal in a more appealing manner. You may also see short proposals .
2. You can rely on templates and references when making an engineering project proposal but make sure that the content and discussion presentation that you will come up with must be aligned with the needs, requirements, and expectations of your audience. With this, you can identify the set quality standards that you need to meet or even exceed for the engineering project proposal to be approved. You may also see non-profit proposals .
3. Know the scope and limitations of the information that you will include in the engineering project proposal based on the type of audience for your presentation. As an example, there is a big difference with the way you present engineering project proposals to external entities and the company that you work for. External entities like clients and investors need more information about your services and offers, while your company requires the proper budgeting for raw materials and engineering workforce. You may also see fundraising proposal .
4. Be aware of the background of your clients. This will help you know the information that are essential to be included in the specific engineering project proposal that you will make. In comparison to a management plan, your engineering project proposal must also be based on how you would like your target audience to perceive the potential of your recommendations for development.
Engineering Project Proposal Content
An engineering project proposal may be the result of a proposal request from clients or the management. It can also be a direct proposition from an engineer presenting potential solutions to problems or current conditions. No matter what the purpose of the proposal writing or the creation of an engineering project proposal is, you have to keep in mind that it is important for you to ensure that you will create a comprehensive, well-detailed, and organized document. Here are some necessary information that are commonly found in an engineering project proposal:
1. Have a proposal statement that can define the scope and limitations of the engineering project proposal. You have to develop a limit to what you are proposing so that project expectations can be set. Minimum requirements can also be expected to all stakeholders of the potential engineering project if this will be done. You may also see budget proposals .
2. Write an introduction for the engineering project proposal. A brief discussion of the proposal’s description can present the need for the engineering project. This part of the engineering project proposal can also help you to present the purpose not only of the project but the usage of the proposal document as well.
3. Present the situation that made you decide to write the engineering project proposal. Are you required by the management of the business? Are you presenting the proposal to a client or another organization? Are you trying to recommend or suggest an engineering project that can benefit a target community? Knowing the purpose of the engineering project proposal can make it easier for the audience to understand the need for the proposed project to be implemented. You may also see research proposal .
4. Have a representation of the methodology that you will follow should the proposal be approved. List down all the processes that the project team and other stakeholders will undergo so that your target audience can be aware of these activities.
5. Create a work schedule for the engineering team. Present the specific time frame that you would like to execute so that you can make sure that the project is time-bound. Proposed work processes that are within specific time schedules can make the engineering project proposal more impressive. You may also see proposal memo examples.
6. Have a financial plan for the engineering project that you are proposing. List down all the cost that the business or the clients need to prepare for so that the project can be implemented. Before creating the proposal, you can already ask for the budget range of entities so that you can have a guide when selecting suppliers, contractors, and workforce providers. You may also see security proposal .
7. It is highly recommended for you to write a few information about your credentials or the milestones of your company. This is a great way to present your credibility and trustworthiness. Moreover, it can reflect your ability to provide all the deliverable that can make the project be created with quality standards.
8. Be particular with the discussion of your desired results. You have to stick with the purpose of the engineering project. Moreover, you always have to be specific when discussing this part of the engineering project proposal as this is a big factor when considering the approval of your proposal. You can also come up with a conclusion that can summarize the entire engineering project proposal discussion. You may also see development project proposals .
Suggestions, Tips, and Recommendations in Making an Engineering Proposal Project
Engineers create project proposals to present the professional work that they would like to propose so that the particular needs of different stakeholders can be provided. With the range of engineering processes that have varying practices and natures of circumstances, there are different engineering project proposals that can be created. For you to come up with a concise and comprehensive engineering project proposal, listed below are some of the suggestions, tips, and recommendations that you can refer to. You may also policy proposals .
1. Maintain organization when presenting the discussion within the engineering project proposal. You have to ensure that your audience is aware of what they can expect from you especially when it comes to work processes, quality metrics, deliverable, and timetable attainability. You may also see service proposals .
2. Use proposal examples and templates as references especially those that are aligned with the exact kind of engineering proposal project that you need to make. Always remember that you should not just look into the content of the document but the proper presentation of these information as well.
3. Know the tone of the discussion that you will incorporate in the engineering project proposal. Do you want the engineering proposal project to be engaging and persuasive? Would you like it to be business-oriented? Different writing approaches can be done depending on the kind of engineering project proposal that you are bound to make. You may also see professional proposals .
Having the right mind-set and the goal to finish an outstanding engineering proposal project can help you a lot when it comes to preparing the document. Again, feel free to refer to downloadable examples, tips, and guidelines so that you can be more efficient in using your time and effort when creating an engineering proposal project.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a proposal for a new school recycling program
Compose a proposal for a school field trip to a science museum.
| Before an article, report, or brief is accepted into the the author must first submit a proposal that specifies the importance of the research, the scope and limitations of the research, and the methods for the research. Submitters should read the journal's before submitting. |
Engineering Proposals
Consulting engineers aren't the only engineers who write proposals. For instance, in academia, engineers write proposals to receive funding for their research or even to initiate a project. Some engineers produce proposals to be read and approved by management while others send proposals to specific funding agencies or clients.
Definition of Proposals
A proposal is a description of the work you will complete on a project. The details included in a proposal depend on the project's scope and who will read the document. Typically, organizations advertise a need for proposalsand consulting engineers respond to the need. However, as an engineer, you may determine that a problem exists, and therefore, propose solutions to an organization. In this case, you must first convince the agency that the problem exists before proposing your solutions.
Types of Proposals
Different types of proposals are necessary for different projects. In academia, engineers produce grant proposals or research proposals in order to receive funding from government agencies and non-profit organizations. In industry, engineers, especially consultants, write proposals or "bids." Engineers produce these proposals for the company where they are working or for other organizations.
A proposal's audience is those supporting the proposed project. The details you provide in a proposal may change, depending on your audience. For instance, if you submit a Proposal to your company's management, you may not have to include project costs or other background information. On the other hand, if you produce a proposal for an organization outside your company, you may need to provide more details. These details might include a rationale for why they should fund your project, as well as the necessary materials and costs. Before writing a proposal, you should always research your audience's background. This way, you will have a better idea about what information to include in your proposal.
General Format
You can submit a proposal in several ways, depending on your audience. For example, proposing a project to your supervisor may require a phone call or a quick e-mail. Or, you may write a short memo, outlining your ideas. On the other hand, you may have to produce a lengthy proposal that provides project background and completely describes the proposed work. Typically, you will know which format to use based on the proposal's context.
When you write a lengthy proposal, you will have to spend time conducting research before you begin writing. This research might include locating other designs and theories to refer to as examples or to critique. A proposal might also include graphics to help an audience visualize your ideas. You might incorporate other data, such as dollar figures and time schedules, so your audience knows exactly how long the project will take to complete and much it will cost them To read more, choose any of the items below:
Introduction
In the proposal's Introduction, you should provide information about the need for a proposal. In other words, here is where you state why you are writing the proposal in the first place. You should also provide an overview of what the rest of the proposal includes.
Qualifications
In the Qualifications section, you should show that you and your organization (if applicable) are skilled and capable of completing the proposed work successfully. You should view this section as a "resume" since in it, you will depict your skills and experiences. If your audience is your supervisor or other managing decision-makers, then you may not need to include this section.
In the Background section, you should depict the problem/situation that lead to your writing a proposal. Here, you should show that you thoroughly understand the problem. If your audience already knows the Background, you may not need to include this section. For example, your supervisor or other managing decision-makers may already be familiar with the specific problem. Therefore, you don't need to tell them what they already know.
Work Schedule
The Work Schedule section does exactly what its name implies: It presents the time frame in which you will complete the proposed work. This section informs your audience of what to expect from you and when. It also helps to keep you organized. If, after you begin working, you are unable to keep this schedule, you should always communicate changes in deadlines to the appropriate people.
Proposal Statement
In the Proposal Statement section, you should inform your audience of exactly what you are proposing. You should also include what you aren't proposing. For example, if you are proposing partial work on a project, state this and then verify what your work will not include.
In the Cost section, you should present what costs you anticipate your project will involve. To do this, divide your expenses into categories and provide dollar figures. For example, labor costs for each worker, materials, etc. Then, you might provide a total cost.
In the Results section, you should discuss the outcome of your proposal. The types of outcomes resulting from a proposal cover a wide range. For example, you may be creating a design, building an actual construction, or even producing a lengthy report. Be sure to state exactly what the Results will be.
The Conclusion section is similar to the ending of a cover letter. Here, you should summarize why you should be considered and how you can be contacted. You might also reiterate why you are the best person or group for the project.
Methodology
In the Methodology section, you should present how you will complete the project's work. This is similar to a Lab Report's Procedures section in that you have to discuss the steps you will have taken to reach a final goal.
Perspectives on Proposals
Dave alciatore, mechanical engineering.
Internal Proposals
"You're likely to write internal proposals if you work with a product development group in a big company. For example, you might conduct research on possible new product lines. Then, you would write a proposal to communicate that you want to pursue this product, but that it will involve testing and development. In other words, it's going to cost money. In order to get financial support, you have to write a proposal that presents your plans. This includes the benefits of the product in terms of profit."
Tom Siller, Civil Engineering
Consulting Engineers
"If you are a consulting engineer, you will work in a very competitive environment because you have to sell your services. In order to get work on a project, you have to submit a proposal or give a presentation. To do this successfully, you have to know who your client is and what that client expects."
John Mahan, Electrical Engineering
Proposal Types
"Engineers write many different types of proposals. Sometimes, a proposal has to be powerful and business-oriented. Many companies don't want to look too far into the future, not even past two years. So, you have to be very specific and down to earth. You have to tell them when exactly you will complete the work. In Phase One, you'll do x. In Phase Two, you'll do y. You should also include the benefits gained during each phase."
Citation Information
Dawn Kowalski. (1994-2024). Engineering Proposals. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.
Visit the Health Advisories website for the latest vaccination and mask information and to Report a Case.
Mechanical Engineering
How to Write a Project Proposal
Contents of proposal.
A recommended template for an MS project or thesis proposal is provided at the following link, from which you can make a Google Docs copy or download a Microsoft Word file:
ME 295 and ME 299 Proposal Template
Proposal Approval Process
The project proposal must be written so that it provides a strong evidence of a student’s thorough understanding of the topic and the capabilities to carry out the work successfully. There are three levels of approvals and signatures required to ascertain that the student in fact has the understanding and capabilities to complete the project successfully. First, the proposal is reviewed, evaluated, and signed by the advisory committee. Next, the signed Proposal Evaluation Form is attached to the proposal, along with the completed Proposal Cover Sheet and submitted to the ME office for approval and signatures of the Graduate Advisor and the Department Chair. Refer to the Projects and Thesis tab for proposal deadline.
See our detailed instructions [pdf] for submitting the project proposal in DocuSign to help guide you through the process.
Proposal Deadline
The proposal must be approved by the advisory committee, the Graduate Advisor, and the Department Chair prior to the university deadline for adding a course, usually the second week of February for the Spring semester and the second week of September for the Fall semester. The add-code for the first term project is issued by the ME office only after the approved project proposal has been received. Failure to meet the deadlines can delay your graduation.
Sample Proposals
The following are some representative examples of project proposals. Your proposal may have additional requirements depending on your project committee chair.
- Sample 1 (Bicycle brake)
- Sample 2 (Collapsible cup)
- Sample 3 (Object detection)
- Sample 4 (Metamaterial)
- Sample 5 (Battery)

Written Thesis Proposal
Introduction
The goal of this article is to help you to streamline your writing process and help convey your ideas in a concise, coherent, and clear way. The purpose of your proposal is to introduce, motivate, and justify the need for your research contributions. You want to communicate to your audience what your research will do ( vision ), why it is needed ( motivation ), how you will do it ( feasibility ).
Return to ToC
Before you start writing your proposal
A thesis proposal is different than most documents you have written. In a journal article, your narrative can be post-constructed based on your final data, whereas in a thesis proposal, you are envisioning a scientific story and anticipating your impact and results. Because of this, it requires a different approach to unravel your narration. Before you begin your actual writing process, it is a good idea to have (a) a perspective of the background and significance of your research, (b) a set of aims that you want to explore, and (c) a plan to approach your aims. However, the formation of your thesis proposal is often a nonlinear process. Going back and forth to revise your ideas and plans is not uncommon. In fact, this is a segue to approaching your very own thesis proposal, although a lot of time it feels quite the opposite.
Refer to “Where do I begin” article when in doubt. If you have a vague or little idea of the purpose and motivation of your work, one way is to remind yourself the aspects of the project that got you excited initially. You could refer to the “Where do I begin?” article to explore other ways of identifying the significance of your project.
Begin with an outline. It might be daunting to think about finishing a complete and coherent thesis proposal. Alternatively, if you choose to start with an outline first, you are going to have a stronger strategic perspective of the structure and content of your thesis proposal. An outline can serve as the skeleton of your proposal, where you can express the vision of your work, goals that you set for yourself to accomplish your thesis, your current status, and your future plan to explore the rest. If you don’t like the idea of an outline, you could remind yourself what strategy worked best for you in the past and adapt it to fit your needs.
Structure Diagram

Structure your thesis proposal
While some variation is acceptable, don’t stray too far from the following structure (supported by the Graduate Student Handbook). See also the Structure Diagram above.
- Cover Page. The cover page contains any relevant contact information for the committee and your project title. Try to make it look clean and professional.
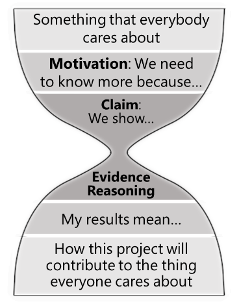
- Specific Aims . The specific aims are the overview of the problem(s) that you plan to solve. Consider this as your one-minute elevator pitch on your vision for your research. It should succinctly (< 1 page) state your vision (the What), emphasize the purpose of your work (the Why), and provide a high-level summary of your research plans (the How).
- You don’t need to review everything! The point of the background is not to educate your audience, but rather to provide them with the tools needed to understand your proposal. A common pitfall is to explain all the research that you did to understand your topic and to demonstrate that you really know your information. Instead, provide enough evidence to show that you have done your reading. Cut out extraneous information. Be succinct.
- Start by motivating your project. Your background begins by addressing the motivation for your project. If you are having a hard time brainstorming the beginning of your background, try to organize your thoughts by writing down a list of bullet points about your research visions and the gap between current literature and your vision. They do not need to be in any order as they only serve to your needs. If you are unsure of how to motivate your audience, you can refer to the introductions of the key literatures where your proposal is based on, and see how your proposal fits in or extends their envisioned pictures. Another exercise to consider is to imagine: “What might happen if your work is successful?” This will motivate your audience to understand your intent. Specifically, detailed contributions to help advance your field more manageable to undertake than vague high-level outcomes. For example, “Development of the proposed model will enable high-fidelity simulation of shear-induced crystallization” is a more specific and convincing motivation, compared to, “The field of crystallization modeling must be revolutionized in order to move forward.”
- Break down aims into tractable goals. The goal of your research plan is to explain your plans to approach the problem that you have identified. Here, you are extending your specific aims into a set of actionable plans. You can break down your aims into smaller, more tractable goals whose union can answer the lager scientific question you proposed. These smaller aims, or sub-aims, can appear in the form of individual sub-sections under each of your research aims.
- Reiterate your motivations. While you have already explained the purpose of your work in previous sections, it is still a good practice to reiterate them in the context of each sub-aim that you are proposing. This will inform your audience the motivation of each sub-aim and help them stay engaged.
- Describe a timely, actionable plan. Sometimes you might be tempted to write down every area that needs improvement. It is great to identify them; at the same time, you also need to decide on what set of tasks can you complete timely to make a measurable impact during your PhD. A timely plan now can save a lot of work a few years down the road. Plan some specific reflection points when you’ll revisit the scope of your project and evaluate if changes are needed. Some pre-determined “off-ramps” and “retooling” ideas will be very helpful as well, e.g., “Development of the model will rely on the experimental data of Reynold’s, however, modifications of existing correlations based on the validated data of von Karman can be useful as well.”
- Point your data to your plans. The preliminary data you have, data that others in your lab have collected, or even literature data can serve as initial steps you have taken. Your committee should not judge you based on how much or how perfect your data is. More important is to relate how your data have informed you to decide on your plans. Decide upon what data to include and point them towards your future plans.
- Name your backup plans. Make sure to consider back-up plans if everything doesn’t go as planned, because often it won’t. Try to consider which part of your plans are likely to fail and its consequence on the project trajectory. In addition, think about what alternative plans you can consider to “retune” your project. It is unlikely to predict exactly what hurdles you will encounter; however, thinking about alternatives early on will help you feel much better when you do.
- Safety. Provide a description of any relevant safety concerns with your project and how you will address them. This can include general and project-specific lab safety, PPE, and even workspace ergonomics and staying physical healthy if you are spending long days sitting at a desk or bending your back for a long time at your experimental workbench.
- Create the details of your timeline. The timeline can be broken down in the units of semester. Think about your plans to distribute your time in each sub-aims, and balance your research with classes, TA, and practice school. A common way to construct a timeline is called the Gantt Chart. There are templates that are available online where you can tailor them to fit your needs.
- References. This is a standard section listing references in the appropriate format, such as ACS format. The reference tool management software (e.g., Zotero, Endnote, Mendeley) that you are using should have prebuilt templates to convert any document you are citing to styles like ACS. If you do not already have a software tool, now is a good time to start.
Authentic, annotated, examples (AAEs)
These thesis proposals enabled the authors to successfully pass the qualifying exam during the 2017-2018 academic year.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Thesis proposal example 1, thesis proposal example 2.
IEEE Account
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
All Formats
Proposal Templates
16+ engineering project proposal templates – pdf, word, pages.
A proposal takes a while to make, and sometimes it is not approved. While some have written it many times, others may still find the writing process a tricky part. If you tried working on a research project proposal during your student days, building a project proposal for an electrical, civil, mechanical, technical, computer, software, and business engineering project can be a challenge to your career.

Proposal Template Bundle

- Google Docs
Construction Project Template Bundle

Construction Request for Proposal Template Bundle

Engineering Student Project Proposal Template

- Apple Pages
Engineering Project Proposal Sample

Free Engineering Brief Project Proposal Template

Electrical Engineering Project Proposal Outline Example

Civil Engineering Project Proposal Presentation Letter Example

Structure of an Engineering Project Proposal
1. executive summary, 2. introduction, 3. project description or program, free engineering design project proposal guideline.


Free Example of Project Research Proposal for Engineering

Government Engineering Project Business Proposal Sample

Free Mechanical Student Engineering Design Project Proposal

4. Timeline and Milestones
6. qualifications, mechanical engineering one page project proposal guideline.

Simple Software Engineering Economic Project Proposal

Free Mechanical Redesign Plan Project Proposal Sample

Project Executive Summary Proposal Sample for Engineering

Free Engineering Design Services Project Description Proposal
Free Engineering Project introduction Proposal

Geotechnical Engineering Construction Project Proposal

Free Computer Engineering Design Project Proposal

Finishing Your Engineering Project Proposal
1. proofread, 2. let others proofread, 3. reduce words; retain font size, 4. take extra care in writing the summary, more in proposal templates.
Construction Technology Instagram Post Template
Construction humor instagram post template, construction equipment instagram ad template, construction management instagram ad template, construction company instagram ad template, residential construction instagram ad template, construction technology linkedin post template, construction industry news linkedin post template, sustainable construction linkedin post template, construction safety awareness linkedin post template.
- Proposal Templates – 170+ Free Word, PDF, Format Download!
- 57+ Training Proposal Templates in PDF | Google Docs | MS Word | Pages
- 7+ Logistics Proposal Templates in PDF
- 13+ Recruitment Proposal Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF | MS Excel
- 12+ Logistics Business Proposal Templates in PDF
- 67+ Project Proposal in PDF , Docs
- 39+ Sponsorship Proposal Templates – Free Word, Excel, PDF Format Download!
- 23+ Funding Proposal Templates – DOC, PDF, Excel, Apple Pages, Google Docs
- 22+ Bid Proposal Templates – Word, PDF, Google Docs, Apple Pages
- 16+ School Project Proposal Templates – Word, PDF
- 11+ Product Business Proposal Templates – Sample, Example
- 10+ Travel Insurance Document Templates in Google Docs | Google Sheets | Excel | Word | Numbers | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Auto Insurance Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Homeowners Insurance Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 25+ Small Business Proposal Templates – Word, PDF
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.

Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia
Research Proposal Examples for Every Science Field
Looking for research funding can be a daunting task, especially when you are starting out. A great way to improve grant-writing skills is to get inspired by winning research proposal examples.
To assist you in writing a competitive proposal, I have curated a collection of real-life research proposal examples from various scientific disciplines. These examples will allow you to gain inspiration about the way research proposals are structured and written.
Structure of a Research Proposal
A research proposal serves as a road-map for a project, outlining the objectives, methodology, resources, and expected outcomes. The main goal of writing a research proposal is to convince funding agency of the value and feasibility of a research project. But a proposal also helps scientists themselves to clarify their planned approach.
While the exact structure may vary depending on the science field and institutional guidelines, a research proposal typically includes the following sections: Problem, Objectives, Methodology, Resources, Participants, Results&Impact, Dissemination, Timeline, and Budget. I will use this structure for the example research proposals in this article.

Here is a brief description of what each of the nine proposal sections should hold.
A concise and informative title that captures the essence of the research proposal. Sometimes an abstract is required that briefly summarizes the proposed project.

Clearly define the research problem or gap in knowledge that the study aims to address. Present relevant background information and cite existing literature to support the need for further investigation.

State the specific objectives and research questions that the study seeks to answer. These objectives should be clear, measurable, and aligned with the problem statement.

Methodology
Describe the research design, methodology, and techniques that will be employed to collect and analyze data. Justify your chosen approach and discuss its strengths and limitations.

Outline the resources required for the successful execution of the research project, such as equipment, facilities, software, and access to specific datasets or archives.

Participants
Describe the research team’s qualification for implementing the research methodology and their complementary value

Results and Impact
Describe the expected results, outcomes, and potential impact of the research. Discuss how the findings will contribute to the field and address the research gap identified earlier.

Dissemination
Explain how the research results will be disseminated to the academic community and wider audiences. This may include publications, conference presentations, workshops, data sharing or collaborations with industry partners.

Develop a realistic timeline that outlines the major milestones and activities of the research project. Consider potential challenges or delays and incorporate contingency plans.
Provide a detailed budget estimate, including anticipated expenses for research materials, equipment, participant compensation, travel, and other relevant costs. Justify the budget based on the project’s scope and requirements.
Consider that the above-mentioned proposal headings can be called differently depending on the funder’s requirements. However, you can be sure in one proposal’s section or another each of the mentioned sections will be included. Whenever provided, always use the proposal structure as required by the funding agency.
Research Proposal template download
This research proposal template includes the nine headings that we just discussed. For each heading, a key sentence skeleton is provided to help you to kick-start the proposal writing process.

Real-Life Research Proposal Examples
Proposals can vary from field to field so I will provide you with research proposal examples proposals in four main branches of science: social sciences, life sciences, physical sciences, and engineering and technology. For each science field, you will be able to download real-life winning research proposal examples.
To illustrate the principle of writing a scientific proposal while adhering to the nine sections I outlined earlier, for each discipline I will also provide you with a sample hypothetical research proposal. These examples are formulated using the key sentence structure that is included in the download template .
In case the research proposal examples I provide do not hold exactly what you are looking for, use the Open Grants database. It holds approved research proposals from various funding agencies in many countries. When looking for research proposals examples in the database, use the filer to search for specific keywords and organize the results to view proposals that have been funded.
Research Proposals Examples in Social Sciences
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded projects in social sciences.
| (Cultural Anthropology) | |
Here is an outline of a hypothetical Social Sciences research proposal that is structured using the nine proposal sections we discussed earlier. This proposal example is produced using the key sentence skeleton that you will access in the proposal template .
The Influence of Social Media on Political Participation among Young Adults

Social media platforms have become prominent spaces for political discussions and information sharing. However, the impact of social media on political participation among young adults remains a topic of debate.

With the project, we aim to establish the relationship between social media usage and political engagement among young adults. To achieve this aim, we have three specific objectives:
- Examine the association between social media usage patterns and various forms of political participation, such as voting, attending political rallies, and engaging in political discussions.
- Investigate the role of social media in shaping political attitudes, opinions, and behaviors among young adults.
- Provide evidence-based recommendations for utilizing social media platforms to enhance youth political participation.

During the project, a mixed methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews will be used to determine the impact of social media use on youth political engagement. In particular, surveys will collect data on social media usage, political participation, and attitudes. Interviews will provide in-depth insights into participants’ experiences and perceptions.

The project will use survey software, transcription tools, and statistical analysis software to statistically evaluate the gathered results. The project will also use project funding for participant compensation.

Principal investigator, Jane Goodrich will lead a multidisciplinary research team comprising social scientists, political scientists, and communication experts with expertise in political science and social media research.

The project will contribute to a better understanding of the influence of social media on political participation among young adults, including:
- inform about the association between social media usage and political participation among youth.
- determine the relationship between social media content and political preferences among youth.
- provide guidelines for enhancing youth engagement in democratic processes through social media use.

We will disseminate the research results within policymakers and NGOs through academic publications in peer-reviewed journals, presentations at relevant conferences, and policy briefs.

The project will start will be completed within two years and for the first two objectives a periodic report will be submitted in months 12 and 18.
The total eligible project costs are 58,800 USD, where 15% covers participant recruitment and compensation, 5% covers survey software licenses, 55% are dedicated for salaries, and 25% are intended for dissemination activities.
Research Proposal Examples in Life Sciences
Here are real-life research project examples in life sciences.
| | |
| | |
| (postdoctoral fellowship) | |
| (National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences) |
Here is a hypothetical research proposal example in Life Sciences. Just like the previous example, it consists of the nine discussed proposal sections and it is structured using the key sentence skeleton that you will access in the proposal template .
Investigating the Role of Gut Microbiota in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome (GUT-MET)
Obesity and metabolic syndrome pose significant health challenges worldwide, leading to numerous chronic diseases and increasing healthcare costs. Despite extensive research, the precise mechanisms underlying these conditions remain incompletely understood. A critical knowledge gap exists regarding the role of gut microbiota in the development and progression of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
With the GUT-MET project, we aim to unravel the complex interactions between gut microbiota and obesity/metabolic syndrome. To achieve this aim, we have the following specific objectives:
- Investigate the composition and diversity of gut microbiota in individuals with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Determine the functional role of specific gut microbial species and their metabolites in the pathogenesis of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
During the project, we will employ the following key methodologies:
- Perform comprehensive metagenomic and metabolomic analyses to characterize the gut microbiota and associated metabolic pathways.
- Conduct animal studies to investigate the causal relationship between gut microbiota alterations and the development of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
The project will benefit from state-of-the-art laboratory facilities, including advanced sequencing and analytical equipment, as well as access to a well-established cohort of participants with obesity and metabolic syndrome.

Dr. Emma Johnson, a renowned expert in gut microbiota research and Professor of Molecular Biology at the University of PeerRecognized, will lead the project. Dr. Johnson has published extensively in high-impact journals and has received multiple research grants focused on the gut microbiota and metabolic health.
The project will deliver crucial insights into the role of gut microbiota in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Specifically, it will:
- Identify microbial signatures associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome for potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
- Uncover key microbial metabolites and pathways implicated in disease development, enabling the development of targeted interventions.
We will actively disseminate the project results within the scientific community, healthcare professionals, and relevant stakeholders through publications in peer-reviewed journals, presentations at international conferences, and engagement with patient advocacy groups.
The project will be executed over a period of 36 months. Key milestones include data collection and analysis, animal studies, manuscript preparation, and knowledge transfer activities.
The total eligible project costs are $1,500,000, with the budget allocated for 55% personnel, 25% laboratory supplies, 5% data analysis, and 15% knowledge dissemination activities as specified in the research call guidelines.
Research Proposals Examples in Natural Sciences
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded projects in natural sciences.
| (FNU) | |
| (USGS) (Mendenhall Research Fellowship Program) | |
| (Earth Venture Mission – 3 NNH21ZDA002O) |
Here is a Natural Sciences research proposal example that is structured using the same nine sections. I created this proposal example using the key sentence skeleton that you will access in the proposal template .
Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity Dynamics in Fragile Ecosystems (CLIM-BIODIV)
Climate change poses a significant threat to global biodiversity, particularly in fragile ecosystems such as tropical rainforests and coral reefs. Understanding the specific impacts of climate change on biodiversity dynamics within these ecosystems is crucial for effective conservation and management strategies. However, there is a knowledge gap regarding the precise mechanisms through which climate change influences species composition, population dynamics, and ecosystem functioning in these vulnerable habitats.
With the CLIM-BIODIV project, we aim to assess the impact of climate change on biodiversity dynamics in fragile ecosystems. To achieve this aim, we have the following specific objectives:
- Investigate how changes in temperature and precipitation patterns influence species distributions and community composition in tropical rainforests.
- Assess the effects of ocean warming and acidification on coral reef ecosystems, including changes in coral bleaching events, species diversity, and ecosystem resilience.
- Conduct field surveys and employ remote sensing techniques to assess changes in species distributions and community composition in tropical rainforests.
- Utilize experimental approaches and long-term monitoring data to evaluate the response of coral reefs to varying temperature and pH conditions.
The project will benefit from access to field sites in ecologically sensitive regions, advanced remote sensing technology, and collaboration with local conservation organizations to facilitate data collection and knowledge sharing.
Dr. Alexander Chen, an established researcher in climate change and biodiversity conservation, will lead the project. Dr. Chen is a Professor of Ecology at the University of Peer Recognized, with a track record of three Nature publications and successful grant applications exceeding 25 million dollars.
The project will provide valuable insights into the impacts of climate change on biodiversity dynamics in fragile ecosystems. It will:
- Enhance our understanding of how tropical rainforest communities respond to climate change, informing targeted conservation strategies.
- Contribute to the identification of vulnerable coral reef ecosystems and guide management practices for their protection and resilience.
We will disseminate the project results to the scientific community, conservation practitioners, and policymakers through publications in reputable journals, participation in international conferences, and engagement with local communities and relevant stakeholders.
The project will commence on March 1, 2024, and will be implemented over a period of 48 months. Key milestones include data collection and analysis, modeling exercises, stakeholder engagement, and knowledge transfer activities. These are summarized in the Gantt chart.
The total eligible project costs are $2,000,000, with budget allocation for research personnel, fieldwork expenses, laboratory analyses, modeling software, data management, and dissemination activities.
Research Proposal Examples in Engineering and Technology
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded research projects in the field of science and technology.
| (USGS) (Mendenhall Postdoctoral Research Fellowship) | |
| (ROSES E.7 (Support for Open Source Tools, Frameworks, and Libraries)) |
Here is a hypothetical Engineering and Technology research proposal example that is structured using the same nine proposal sections we discussed earlier. I used the key sentence skeleton available in the proposal template to produce this example.
Developing Sustainable Materials for Energy-Efficient Buildings (SUST-BUILD)
The construction industry is a major contributor to global energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Addressing this issue requires the development of sustainable materials that promote energy efficiency in buildings. However, there is a need for innovative engineering solutions to overcome existing challenges related to the performance, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of such materials.
With the SUST-BUILD project, we aim to develop sustainable materials for energy-efficient buildings. Our specific objectives are as follows:
- Design and optimize novel insulating materials with enhanced thermal properties and reduced environmental impact.
- Develop advanced coatings and surface treatments to improve the energy efficiency and durability of building envelopes.
- Conduct extensive material characterization and simulation studies to guide the design and optimization of insulating materials.
- Utilize advanced coating techniques and perform full-scale testing to evaluate the performance and durability of building envelope treatments.
The project will benefit from access to state-of-the-art laboratory facilities, including material testing equipment, thermal analysis tools, and coating application setups. Collaboration with industry partners will facilitate the translation of research findings into practical applications.
Dr. Maria Rodriguez, an experienced researcher in sustainable materials and building technologies, will lead the project. Dr. Rodriguez holds a position as Associate Professor in the Department of Engineering at Peer Recognized University and has a strong publication record and expertise in the field.
The project will deliver tangible outcomes for energy-efficient buildings. It will:
- Develop sustainable insulating materials with superior thermal performance, contributing to reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in buildings.
- Introduce advanced coatings and surface treatments developed from sustainable materials that enhance the durability and energy efficiency of building envelopes, thereby improving long-term building performance.
We will disseminate project results to relevant stakeholders, including industry professionals, architects, and policymakers. This will be accomplished through publications in scientific journals, presentations at conferences and seminars, and engagement with industry associations.

The project will commence on September 1, 2024, and will be implemented over a period of 36 months. Key milestones include material development and optimization, performance testing, prototype fabrication, and knowledge transfer activities. The milestones are summarized in the Gantt chart.
The total eligible project costs are $1,800,000. The budget will cover personnel salaries (60%), materials and equipment (10%), laboratory testing (5%), prototyping (15%), data analysis (5%), and dissemination activities (5%) as specified in the research call guidelines.
Final Tips for Writing an Winning Research Proposal
Come up with a good research idea.
Ideas are the currency of research world. I have prepared a 3 step approach that will help you to come up with a research idea that is worth turning into a proposal. You can download the Research Idea Generation Toolkit in this article.
Start with a strong research outline
Before even writing one sentence of the research proposal, I suggest you use the Research Project Canvas . It will help you to first come up with different research ideas and then choose the best one for writing a full research proposal.
Tailor to the requirements of the project funder
Treat the submission guide like a Monk treats the Bible and follow its strict requirements to the last detail. The funder might set requirements for the topic, your experience, employment conditions, host institution, the research team, funding amount, and so forth.
What you would like to do in the research is irrelevant unless it falls within the boundaries defined by the funder.
Make the reviewer’s job of finding flaws in your proposal difficult by ensuring that you have addressed each requirement clearly. If applicable, you can even use a table with requirements versus your approach. This will make your proposed approach absolutely evident for the reviewers.
Before submitting, assess your proposal using the criteria reviewers have to follow.
Conduct thorough background research
Before writing your research proposal, conduct comprehensive background research to familiarize yourself with existing literature, theories, and methodologies related to your topic. This will help you identify research gaps and formulate research questions that address these gaps. You will also establish competence in the eyes of reviewers by citing relevant literature.
Be concise and clear
Define research questions that are specific, measurable, and aligned with the problem statement.
If you think the reviewers might be from a field outside your own, avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language to help them to understand the proposal better.
Be specific in describing the research methodology. For example, include a brief description of the experimental methods you will rely upon, add a summary of the materials that you are going to use, attach samples of questionnaires that you will use, and include any other proof that demonstrates the thoroughness you have put into developing the research plan. Adding a flowchart is a great way to present the methodology.
Create a realistic timeline and budget
Develop a realistic project timeline that includes key milestones and activities, allowing for potential challenges or delays. Similarly, create a detailed budget estimate that covers all anticipated expenses, ensuring that it aligns with the scope and requirements of your research project. Be transparent and justify your budget allocations.
Demonstrate the significance and potential impact of the research
Clearly articulate the significance of your research and its potential impact on the field. Discuss how your findings can contribute to theory development, practical applications, policy-making, or other relevant areas.
Pay attention to formatting and style guidelines
Follow the formatting and style guidelines provided by your institution or funding agency. Pay attention to details such as font size, margins, referencing style, and section headings. Adhering to these guidelines demonstrates professionalism and attention to detail.
Take a break before editing
After preparing the first draft, set it aside for at least a week. Then thoroughly check it for logic and revise, revise, revise. Use the proposal submission guide to review your proposal against the requirements. Remember to use grammar checking tools to check for errors.
Finally, read the proposal out loud. This will help to ensure good readability.
Seek feedback
Share your proposal with mentors, colleagues, or members of your research community to receive constructive feedback and suggestions for improvement. Take these seriously since they provide a third party view of what is written (instead of what you think you have written).
Reviewing good examples is one of the best ways to learn a new skill. I hope that the research proposal examples in this article will be useful for you to get going with writing your own research proposal.
Have fun with the writing process and I hope your project gets approved!
Learning from research proposal examples alone is not enough
The research proposal examples I provided will help you to improve your grant writing skills. But learning from example proposals alone will take you a rather long time to master writing winning proposals.
To write a winning research proposal, you have to know how to add that elusive X-Factor that convinces the reviewers to move your proposal from the category “good” to the category “support”. This includes creating self-explanatory figures, creating a budget, collaborating with co-authors, and presenting a convincing story.
To write a research proposal that maximizes your chances of receiving research funding, read my book “ Write a Winning Research Proposal “.

This isn’t just a book. It’s a complete research proposal writing toolkit that includes a project ideation canvas, budget spreadsheet, project rating scorecard, virtual collaboration whiteboard, proposal pitch formula, graphics creation cheat sheet, review checklist and other valuable resources that will help you succeed.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:

One comment
Hi Martins, I’ve recently discovered your content and it is great. I will be implementing much of it into my workflow, as well as using it to teach some graduate courses! I noticed that a materials science-focused proposal could be a very helpful addition.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on September 5, 2024.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2024, September 05). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

Research Proposal Example/Sample

In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Ace Your Research Proposal

How To Choose A Research Topic: 5 Key Criteria
How To Choose A Research Topic Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + Free Topic...

Writing A Research Proposal: 4 Hacks To Fast-Track The Process
🎙️ PODCAST: Writing A Research Proposal 4 Time-Saving Tips To Fast-Track Your...

Research Proposal Essentials: 5 Critical Dos & Don’ts
Learn about 5 critically important things that you need to do (or avoid doing) when writing a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis.

How To Find A Research Gap: Step-By-Step Process
How To Find A Research Gap, Quickly A step-by-step guide for new researchersBy: Derek...

The Research Problem & Problem Statement
The Research Problem & Statement What they are & how to write them (with...
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
14 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the effectiveness of junior call on prevention of theft
kindly assist me in writing the proposal in psychology education
Please,Kindly assist my in my phd thesis writing on personal and socio cultural factors as determinate of family planning adoption
I’m interested to apply for a mhil program in crop production. Please need assistance in proposal format.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- Menu Close
- Search
Research Proposal Guidelines
Doctor of Engineering applicants are required to submit a Research Proposal as part of their application. The research laid out in the proposal needs to be of importance to the applicant’s employer as it forms the basis for the collaboration between Johns Hopkins Engineering and your company/agency.
The research proposals are evaluated both by your prospective advisor (who will have expertise in your subject) as well as the Doctor of Engineering Oversight Committee (who have backgrounds spanning many different areas). You need to write a proposal that is appropriate for both audiences. That is, you need to provide an overview of your research goals that is broadly understandable to someone who is not knowledgeable in your field and also a deeper discussion for someone with the appropriate expertise.
Please use this Research Proposal Template for your application.
The project you propose should require depth and creativity. The results you plan to obtain should have impact beyond a narrowly focused problem. We recommend that you use the questions articulated in the Heilmeier Catechism as a guide to creating an engaging, successful proposal.
- What are you trying to do? Articulate your objectives using absolutely no jargon.
- How is it done today, and what are the limits of current practice?
- What’s new in your approach and why do you think it will be successful?
- If you’re successful, what difference will it make?
- What are the risks and the payoffs?
- How much will it cost?
- How long will it take?
- What are the midterm and final “exams” to check for success
Please note that you need not address all of these questions, but they provide a helpful framework for preparing your proposal.
Finally, we want to know about prior research experience and including that as an appendix to your proposal is most welcome.

Proposal Templates > Engineering Proposal Template
Engineering Proposal Template
If you work as an engineer, you know how important a professional and persuasive engineering proposal can be when it comes to securing new contracts. We’ve taken the guesswork out of putting together impressive looking proposals with our free and fillable engineering proposal template that can be customized to your needs in minutes. Edit, deliver, and track your proposal, then get approval with built-in eSignatures.

Best proposal software ever!
I’ve tried soooo many proposal softwares and I’ll never try another one after Proposable. It’s so easy to use and it looks good, which all the others don’t.
Account Executive , Grow.com
Smart, reliable, and constantly improving.
Proposable just works. I can make visually interesting sales presentations, dynamically insert content, and execute agreements. Proposable powers our entire sales process.
CEO , Periodic

In all of the examples so far, we’ve discussed using templates to help draft job proposals. A sales proposal template is not only a great timesaver, as it keeps you from needing to figure out formatting and structure, but it also ensures you don’t miss any important pieces when putting together business proposal ideas. It’s a little like having a blueprint for building a house – having a plan up front makes the project come together much more smoothly.
There are a number of formats that can be used to create proposals – while you can find a contract proposal template or a pricing proposal template in InDesign, Microsoft Word is the most common and usually the simplest way to build a proposal. Either of these formats will then allow you to save a project proposal PDF, which keeps it from being altered by someone else.
Whatever kind of proposal template you need, Proposable can help you. Visit our template page and take a look at what we have to offer – we have templates for many fields besides engineering.
To find the right template for your specific project, simply do a search for the exact project you need, as well as the format – for example, search for “free proposal template Word,” “free training proposal template Word,” “free website proposal template Word” or “proposal template PDF.” Whether you need a sample cover letter for a grant proposal or a service proposal template, Proposable has you covered.
- Business Templates
- Sample Proposals
FREE 11+ Engineering Project Proposal Samples in PDF | MS Word
Proposals are created to introduce something new to get approval or to attract investors. It is also created as a response to a request for proposal , which usually solves the problem that the requester is seeking when requesting for a proposal. Proposals are common in business defined as a written offer from a seller to its prospective buyer. Even if it is common in business, it is not limited to the act of selling and buying. Introducing engineering projects require the use of a proposal. The project could be for business, school, research, or wholly just to disseminate information to the public. Here are project proposal samples that will help you learn and understand more about this useful document.
Engineering Project Proposal Samples
1. engineering project proposal sample pdf, 2. engineering project proposal example, 3. engineering design project proposal format, 4. engineering research proposal example pdf, what is a proposal in engineering, 5. mechanical engineering project proposal sample pdf, 6. engineering project proposal template, 7. chemical engineering project proposal template, 8. engineering project proposal, 9. civil engineering proposal example pdf, 10. engineering design proposal example, 11. software engineering project proposal sample pdf, 12. engineering services proposal template, how to write a project proposal, what are the 4 types of project proposal, what is project proposal pdf, what is format in project proposal, how to write a good project, how do you write a project final report, how do i start a project file.
- Google Docs

Engineers don’t just solve problems and make calculations as what we actually know of. Part of their jobs is to design certain things and ensure that their functionality matches that of their product’s design. This engineering design project proposal format sample is intended to be used by students, specifically the electrical and computer engineering senior students. The format serves as a guide on how the project proposal should look like and what contents must be written in each section or part of the proposal. With the appropriate changes, this format sample can be used on other project proposals.

Size: 543 KB
Making an engineering research proposal can be made easier and more convenient if you have the right tools that will help you get started and and finish the job. And if you are looking for that kind of tool, then you can count on this sample to help you. The sample is simple and easy to follow. It provides guide questions that will help you write relevant and appropriate content for your proposal. The structure used for your research proposal is also provided and every part or section has a brief description to it so that your content will be of quality.
In engineering, a proposal is a formal document outlining a plan for a specific project or solution. It provides a detailed description of the project’s objectives, scope, methodology, timeline, and budget. The proposal aims to persuade stakeholders, clients, or decision-makers that the proposed engineering solution is viable, effective, and aligns with the project requirements. It often includes technical specifications, cost estimates, and potential benefits, serving as a comprehensive guide for initiating and implementing engineering projects. The clarity and persuasiveness of the proposal are crucial for obtaining approval and support for the proposed engineering endeavor.

Mechanical engineering is one of the oldest engineering disciplines that incorporates the construction, design, and the use of machines. It is a course in college that is taken up by students who find interest in such discipline and those who want to work in the field. The sample project proposal shown above is taken from the Mechanical Engineering Department from a particular university. The sample proposal is all about designing a hovercraft. It is no doubt a detailed and comprehensive project proposal that uses a total of 18 pages. You will find this a good source of ideas and other related information.

Using this project proposal template will help you prepare and write an efficient and reliable project proposal for your engineering project. There are six sections in this proposal template and each section is described in detail so that you can write high-quality content throughout your proposal. These sections include details to be written on your project cover sheet; organizational history, mission, vision, and structure; background and analysis of the problem to be addressed; proposed goal, objectives, target population, and implementation sample plan ; annual project budget; attachments; and a sample project budget outline.

Size: 602 KB
If mechanical engineering works more on the use of machines, chemical engineering focuses on the use of principles of chemistry, physics, mathematics, biology, and economics. Just like all other engineering project proposals, it is something that should not be taken lightly and could be more complicated than one expects it to be. This chemical engineering project proposal sample would make a reliable tool where one can get help and ideas for their own work analysis .

Size: 145 KB
Before buildings and other infrastructures are built, a proposal is first created to introduce and detail what the said infrastructure is for, its benefits, and what it can contribute to the public or to a community. An engineering infrastructure proposal template is the perfect template to use if you need to write such a proposal. It will also increase the chances of your proposal getting approved. So if you need a persuasive template for your engineering project work, then this one is good for you.

Size: 341 KB
A request for proposal is not the actual proposal itself but is a document that calls on prospective individuals or organizations who are ready to take on a certain challenge. It is a document that provides detailed instructions on how a proposal should be written and what the proposal should be all about. This sample is calling on to professional civil engineers to take on a bridge replacement project. If you need to writing proposal that is similar to the sample above, then you will enjoy browsing through the pages of this sample.

Size: 44 KB
In need of a proposal template for your design proposal? Why not check out this customizable and really cool design proposal template. This template will definitely be worth your while. Everything about it and all of the sections in different pages are detailed to ensure that you are well guided throughout the proposal making process and ensures that your content is always of good quality. You may use it for your interior design proposal or graphic design proposal .

Size: 134 KB
Want to make a simple yet useful project proposal? Then you need this software engineering project proposal sample. This sample consists of four pages and will definitely be a useful sample reference material that will guide you with writing your own.

Size: 63 KB
- Introduction: Clearly define the project’s purpose and objectives.
- Project Description: Provide details on the project scope, goals, and deliverables.
- Background and Rationale: Explain why the project is necessary, including any relevant context or previous work.
- Methodology: Outline the approach, methods, and tools you’ll use to execute the project.
- Budget: Clearly present the financial aspects, detailing costs and resources required.
- Timeline: Develop a realistic project timeline with milestones.
- Expected Outcomes: Specify the anticipated results and impact.
- Evaluation Plan: Describe how you’ll measure project success.
- Formally Solicited: Responding to a specific request, follow guidelines provided.
- Informally Solicited: Developed based on discussions or informal requests.
- Unsolicited: Initiated by the proposer without a specific request, aiming to address a perceived need.
- Continuation or Non-competing: Proposing additional funding or resources for an ongoing project. Steps involve defining objectives, detailing methods and resources, presenting a budget, and demonstrating the project’s alignment with organizational goals. Each type requires tailoring to the specific circumstances and adhering to proposal writing best practices.
A Project Proposal PDF is a document presenting a project plan in Portable Document Format (PDF). It outlines project details, objectives, methodologies, timelines, and other relevant information for stakeholders’ review.
The format in a project proposal includes sections like introduction, background, objectives, methods, timeline, budget, evaluation, and team information. It provides a structured presentation of the proposed project.
Write a good project by clearly defining objectives, developing a detailed plan with milestones, allocating resources efficiently, considering potential challenges, and incorporating evaluation mechanisms for continuous improvement and success.
To write a project final report, summarize project objectives, methods, findings, and outcomes. Reflect on challenges faced, detail achievements, and provide recommendations for future improvements.
Start a project file by creating a structured folder with key sections, including an introduction, project plan, budget, resources, timelines, and evaluation. Use clear labels for easy organization.
In conclusion, this customizable engineering services proposal template is easy to use and will surely make your proposal writing experience an easy one. Download this template now to produce a high-quality and reliable proposal of your own!
Related Posts
9+ sample product proposal letters - word, pdf, sample funding proposal template - 8+ free documents in pdf ..., 8+ sample business proposal cover letters - pdf, word, 10+ sample training proposal letters - pdf, word, 12+ loan proposals - word, pdf, pages, sample informal proposal template - 5+ free documents in pdf, 18+ event proposal letters samples & templates - pdf, doc, sample salary proposal letter - 8+ examples in pdf, word, sample project proposal report - 9+ examples in pdf, word, sample job proposal letter - 7+ examples in pdf, word, 47+ proposal letter examples - word, pdf, sample project proposal template - 22+ free documents in pdf ..., 9+ sample project proposal letter - examples in word, pdf, 10+ art proposal templates - pdf, word, pages, sample loan proposal - 11+ documents in pdf, word, 16+ film proposal templates - pdf, word, sample proposal offer letter - 6+ examples in pdf, word, 10+ sample event proposal letters - pdf, word, sample business proposal letter to client - 7+ documents in pdf ....
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Active funding opportunity
Nsf 24-576: gen-4 engineering research centers, program solicitation, document information, document history.
- Posted: May 20, 2024
- Replaces: NSF 22-580
Program Solicitation NSF 24-576
|
Letter of Intent Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
September 03, 2024
Preliminary Proposal Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
September 30, 2024
Full Proposal Deadline(s) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization’s local time):
By Invitation Only
Important Information And Revision Notes
This solicitation encourages proposals addressing a broad spectrum of engineering topics, including but not limited to advanced manufacturing, advanced wireless, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, microelectronics and semiconductors, net-zero technologies, quantum engineering, and systems engineering for healthcare.
This solicitation is updated to clarify the definition of underrepresented students in STEM and to welcome proposal submissions that broaden geographic and demographic participation. More details are provided in Section IV. ELIGIBILITY INFORMATION .
Cost Sharing: Cost sharing is required. The formula for required cost sharing is described in the full text of this solicitation.
Any proposal submitted in response to this solicitation should be submitted in accordance with the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) that is in effect for the relevant due date to which the proposal is being submitted. The NSF PAPPG is regularly revised and it is the responsibility of the proposer to ensure that the proposal meets the requirements specified in this solicitation and the applicable version of the PAPPG. Submitting a proposal prior to a specified deadline does not negate this requirement.
Summary Of Program Requirements
General information.
Program Title:
Gen-4 Engineering Research Centers (ERC) Convergent Research and Innovation through Inclusive Partnerships and Workforce Development
Founded in 1984, the Engineering Research Centers (ERC) program brings technology-based industry and universities together in an effort to strengthen the competitive position of American industry in the global marketplace. These partnerships are expected to establish cross-disciplinary centers focused on advancing fundamental engineering knowledge and engineered systems technology while exposing students to the integrative aspects of engineered systems and industrial practice. The goal of the ERC program has traditionally been to integrate engineering research and education with technological innovation to transform and improve national prosperity, health, and security. Building upon this tradition, NSF is interested in supporting ERCs to develop and advance engineered systems, which if successful, will have a high Societal Impact. The ERC program supports convergent research (CR) that will lead to strong societal impact. Each ERC has interacting foundational components that go beyond the research project, including engineering workforce development (EWD) at all participant stages, where all participants gain mutual benefit, and value creation within an innovation ecosystem (IE) that will outlast the lifetime of the ERC. These foundational elements are integrated throughout ERC activities and in alignment with the Center's vision and targeted societal impact. The overall impact of the ERC program is expected within the Engineering Community, the Scientific Enterprise, and Society.
Cognizant Program Officer(s):
Please note that the following information is current at the time of publishing. See program website for any updates to the points of contact.
Sandra Cruz-Pol, telephone: (703) 292-2928, email: [email protected]
Dana L. Denick, telephone: (703) 292-8866, email: [email protected]
Randy Duran, telephone: (703) 292-5326, email: [email protected]
Nadia A. El-Masry, telephone: (703) 292-4975, email: [email protected]
Paul Torrens, telephone: (703) 292-2473, email: [email protected]
Lan Wang, telephone: (703) 292-5098, email: [email protected]
- 47.041 --- Engineering
Award Information
Anticipated Type of Award: Cooperative Agreement
Up to 4 depending on the quality of the proposals and the availability of funds. ERCs are generally funded for ten years, with an initial award for the first five years and second award based on performance and review of a renewal proposal. This solicitation seeks to make awards for the first five years for new ERCs.
See Section III of this solicitation for additional information about the allowable maximum annual budget for years one through five.
NSF expects to make the ERC awards in the summer of 2026. The budget distribution among the lead and core partners should be appropriate for the scope of work and activities planned for each foundational component.
Note that ERCs will not be granted no-cost extensions (NCE).
Co-funding:
NSF is currently in negotiations with other government agencies to form partnerships in support of ERC awards. These partnerships have the potential to expand the total number of awards. This is contingent upon realization of these partnerships, and budgets provided to these organizations by Congress for FY 2026 and 2027.
Eligibility Information
Who May Submit Proposals:
Proposals may only be submitted by the following:
Only U.S. Institutions of Higher Education (IHEs), also referred to in this solicitation as universities and academic institutions, accredited in, and having a campus located in the US, that grant engineering degrees at the undergraduate, masters, and doctoral engineering level may submit proposals as the lead university. The Lead university submits the proposal, and the award is made to the lead university. Support is provided to core partner universities and any affiliated faculty from other partner institutions through subawards. NSF welcomes proposal submissions that broaden geographic and demographic participation. Proposals from STEM-minority-serving institutions (STEM-MSI*), non-R1 schools, emerging research institutions, and IHEs in EPSCoR-eligible jurisdictions, as lead or core partners, as well as IHEs that primarily serve populations of students with disabilities or women in engineering interested in STEM, are encouraged.
Invited full proposals must meet all the following organizational requirements or they will be returned without review:
- The Lead must be an Institution of Higher Education per the Carnegie Foundational Attribute: https://carnegieclassifications.acenet.edu/
- A proposed ERC must be multi-institutional, with a lead university and additional domestic university core partners. There is no maximum number of partner institutions.
- To qualify as a core partner institution, there must be financial support for a minimum of three faculty participating in the ERC along with financial support for a minimum of three students (Postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students).
- The lead or at least one of the core partner universities must be a STEM-MSI* university.
- Commitments from lead and core partner universities for cost sharing must be in place.
*For this solicitation STEM-MSI is defined by the Department of Education as institutions of higher education enrolling populations with significant percentages of undergraduate minority students, or that serve certain populations of minority students under various programs created by Congress.
Eligibility may be determined by reference to the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) of the US Department of Education National Center for Education Statistics ( https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/ ).
Who May Serve as PI:
The Lead PI must be a faculty member at the Lead university. Non-Lead PIs are the co-PIs listed on the Cover Sheet after the Lead PI and may be from institutions other than the lead university. In order to provide more flexibility for the Center's management, the Lead PI and the ERC Director are not required to be the same person, however, both must be affiliated with the lead institution.
Limit on Number of Proposals per Organization:
If an institution has two active ERC awards, it does not qualify to submit an ERC preliminary proposal as a lead institution. There are no other restrictions or limits on the number of preliminary proposals submitted by a Lead institution. Full Proposals may be submitted only by invitation and only by the lead institution designated in the preliminary proposal.
Limit on Number of Proposals per PI or co-PI:
There are no restrictions or limits.
Proposal Preparation and Submission Instructions
A. proposal preparation instructions.
Letters of Intent: Submission of Letters of Intent is required. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Preliminary Proposals: Submission of Preliminary Proposals is required. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Full Proposals:
- Full Proposals submitted via Research.gov: NSF Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide (PAPPG) guidelines apply. The complete text of the PAPPG is available electronically on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg .
- Full Proposals submitted via Grants.gov: NSF Grants.gov Application Guide: A Guide for the Preparation and Submission of NSF Applications via Grants.gov guidelines apply (Note: The NSF Grants.gov Application Guide is available on the Grants.gov website and on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=grantsgovguide ).
B. Budgetary Information
Cost Sharing Requirements:
Cost Sharing is required. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Indirect Cost (F&A) Limitations:
Not Applicable
Other Budgetary Limitations:
Other budgetary limitations apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
C. Due Dates
Letter of Intent Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization's local time):
Preliminary Proposal Due Date(s) (required) (due by 5 p.m. submitting organization's local time):
Proposal Review Information Criteria
Merit Review Criteria:
National Science Board approved criteria. Additional merit review criteria apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Award Administration Information
Award Conditions:
Additional award conditions apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
Reporting Requirements:
Additional reporting requirements apply. Please see the full text of this solicitation for further information.
I. Introduction
The National Science Foundation (NSF) created the Engineering Research Centers (ERC) program in 1984 to bring technology-based industry and universities together in an effort to strengthen the competitive position of American industry in the global marketplace. These partnerships established cross-disciplinary centers focused on advancing fundamental engineering knowledge and engineered systems technology while exposing students to the integrative aspects of engineered systems and industrial practice. As a result, ERCs have produced a wide range of new fundamental knowledge, engineered systems and other technologies aimed at spawning whole new fields or industries or radically transforming the product lines, processes, and practices of current industries. At the same time, they have produced a new generation of engineering graduates who are highly innovative, diverse, globally engaged, and effective as technology leaders in academia and industry.
NSF has continually refined the goals and purposes of the ERC program to meet shifting needs. The NSF-requested 2017 study from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) "A New Vision for Center-Based Engineering Research" ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/24767/a-new-vision-for-center-based-engineering-research ) recommends that NSF places a greater emphasis on forming research centers focused on convergent research and education approaches that address challenges with significant societal impact. Complex societal problems require a convergent approach for the deep integration of knowledge, tools, and ways of thinking across disciplinary boundaries. A detailed explanation of the convergence concept can be found in a 2014 National Academies report, "Convergence: Facilitating Transdisciplinary Integration of Life Sciences, Physical Sciences, Engineering and Beyond" ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18722/convergence-facilitating-transdisciplinary-integration-of-life-sciences-physical-sciences-engineering ).
This current iteration of the ERC program reflects the recommendations from the NASEM study as well as other sources. The program continues to focus on advancing an engineered system through inclusive cross-disciplinary and cross-sector partnerships, while placing greater emphasis on research with high- risk/high-payoff ideas that lead to societal impact through convergent approaches, engaging broader stakeholder communities, and using team science concepts for their team formation.
II. Program Description
A. ERC Program Model
The ERC program is grounded by the four foundational components of the ERC: Convergent Research (CR), Engineering Workforce Development (EWD), Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI), and the Innovation Ecosystem (IE) (Figure 1). These foundational components are connected by an integrated, holistic ERC vision and strategic plan. The whole of the ERC has added value and synergies that require a center or institute-like approach as opposed to individual projects.
Convergent Research (CR): High-risk/high-payoff research ideas and discoveries that push the frontiers of engineering knowledge; ERC convergent research is a highly collaborative and interdisciplinary approach that leads to positive impacts on society. Convergence involves the integration of various fields in engineering and science, including all branches of science, in a coordinated and interdependent manner. This approach fosters strong collaborations that are essential for successful inquiry.
Engineering Workforce Development (EWD): In addition to training opportunities for ERC participants, the Center engages in human resource capacity development aligned with the targeted engineered system. ERC EWD strengthens a robust spectrum of engineering education pathways and technical workforce opportunities. EWD occurs at all levels of the Center and provides opportunities for engagement by all ERC members including students, faculty, and external partners as appropriate. The ERC EWD program is driven by the future education, workforce development, and labor market needs relevant to the proposed Center.
Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI): In addition to fomenting a diverse team, the culture of the ERC and teams within the ERC demonstrate an environment of inclusion in which all members feel valued and welcomed, creatively contribute, and gain mutual benefit from participating. Because of the ERC's attention to diversity and culture of inclusion, participation from members of groups traditionally underrepresented in engineering as well as diverse scientific and other perspectives is required. The ERC DCI program ensures diversity at all levels of the Center and employs an intentional and evidence-based approach to developing a culture of inclusion.
Innovation Ecosystem (IE): Trusted partners that work together to create and enhance the capacity for innovation and new ways for delivering value with positive societal impact. ERC innovation ecosystems (IE) include effective translational efforts from ideation to implementation, workforce development that creates the workforce needed for the enterprise, and deliberate efforts to attract funding and resources. ERCs articulate plans for strategic engagement of stakeholder communities while including the legal, ethical, civic, and societal acceptance frameworks needed to protect the participants.
The ERC foundational elements are carried out in concert through ERC activities and in alignment with the Center's vision and targeted societal impact. The overall impact of the ERC program is expected within the Engineering Community , the Scientific Enterprise , and Society , shown in Figure 1 (above). These may be thought of as nested regions of increasing influence, where the largest scale of impact is on society itself. Potential outcomes of ERCs are organized within each of the four ERC foundational components.
Engineering Community: ERCs not only create fundamental knowledge and technology, but also impact the engineering community, preparing students and researchers by highlighting new engineering approaches and best practices for engineering workforce development, diversity and inclusion, and academic-industrial partnerships.
Scientific Enterprise: ERCs should be exemplars of how cohesive, high-performing teams engage in convergent research and innovative approaches to create major impact that informs and inspires the scientific community, engineering and beyond.
Society: ERCs enable society to have a better quality of life, and be more resilient, productive, and safe. Each ERC is expected to have a transformational positive impact on significant societal challenges and opportunities. This is the level where the introduction of value creation and technology innovation requires an understanding of socio-technical interactions and how they might impact society at large. In response, new strategies, concepts, ideas and/or re- organizations may be needed to shore-up, extend, or strengthen society. The desired outcome is the ERC's ability to assist society in its drive to advance the national health, prosperity, welfare, and to secure the national defense.
The goal of the ERC program has traditionally been to integrate engineering research and education with technological innovation to transform and improve national prosperity, health, and security. Building upon this tradition, NSF is interested in supporting ERCs to develop and advance engineered systems, which if successful, will have a high Societal Impact .
ERCs create inclusive cultures not only to integrate scientific discovery with technological innovation through convergent engineered systems research and education, but also to include the participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in engineering. ERCs build partnerships with industry, practitioners, and other key stakeholders to strengthen the innovative capacity of the United States in a global context. In addition to building capacity for research, innovation, and a diverse workforce, ERCs are expected to produce significant outcomes within the 10-year timeframe of NSF support and beyond.
ERCs should realize a vision of advancing an engineered system driven by clearly articulated societal impact and should have strong synergies or value-added rationale that justifies a center or institute-like approach. As part of creating sustainable positive impacts on society and communities, ERCs should focus on positive outcomes that can be seen within engineering communities and build and empower human resource capacity for their targeted engineering challenges. Beyond this, ERCs should contribute to the scientific enterprise by advancing research, science, engineering fundamentals, and research communities. This should be demonstrated with benchmarks against the state-of-the-art. ERCs should build knowledge, prepare students and researchers that respect and flourish in an environment with diverse perspectives, impact how engineering research is conducted and provide value for society. The ERC program encourages proposals addressing a broad spectrum of engineering topics, including but not limited to advanced manufacturing, advanced wireless, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, microelectronics and semiconductors, net zero technologies, quantum engineering, and systems engineering for healthcare.
C. Key Elements of an ERC
Vision: The ERC vision guides discovery and technology to uniquely transform US prosperity, health, and/or security in 10 years. The vision describes the compelling new idea, explains how it relates to national needs, and makes the connection to engineering.
Strategic Plan: The ERC strategic plan connects and leverages research, engineering workforce development, diversity and culture of inclusion, and innovation ecosystem to address the chosen societal challenge. The overall plan should employ three strategic approaches:
Convergence : "Convergence is an approach to problem solving that cuts across disciplinary boundaries. It integrates knowledge, tools, and ways of thinking across disciplinary boundaries in STEM fields to form a comprehensive synthetic framework for tackling scientific and societal challenges that exist at the interfaces of multiple fields." ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18722/convergence-facilitating-transdisciplinary-integration-of-life-sciences-physical-sciences-engineering ). This is also stated in another report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) from the Committee on a Vision for the Future of Center-based Multidisciplinary Engineering Research, which defined convergent engineering as a deeply collaborative, team-based engineering approach for defining and solving important and complex societal problems ( https://www.nap.edu/catalog/24767/a-new-vision-for-center-based-engineering-research ). Hence, convergent research blends scientific disciplines in a coordinated, reciprocal way and fosters the robust collaboration needed for successful inquiry and has the strong potential to lead to transformative solutions and new fields of study. The research thrusts, testbeds, team formation, and other major aspects of the research plan should support a convergent approach.
Stakeholder Engagement : The intentional and early-stage engagement of all parties who may contribute to the ERC or may be impacted by the ERC along its capacity-building and value creation responsibilities. Stakeholders can include, but are not limited to, relevant researchers across partner institutions with complementary research and education expertise; undergraduate and graduate students, postdoctoral researchers; industry leaders who can guide the innovation effort; partners for innovation, education, workforce development, and diversity and culture of inclusion of all participants; and beneficiaries of the ERC outcomes (e.g., community members, users, customers, patients, and watchdog organizations).
Team Formation : The process by which all necessary disciplines, skills, perspectives, and capabilities are brought together. Successful teams are interdependent, multidisciplinary, and diverse and can work and communicate effectively even when geographically dispersed. Team formation includes evidence-based strategies and team science training to overcome barriers to effective, collaborative teaming, including the integration of members with different areas of expertise, different vocabularies and core values and ways of approaching problems, different understanding of the problems to be addressed, different values, and different working styles. This is especially needed during the early stages of the Center.
Organization and Management Structure:
Effective Leadership: ERC leaders have intellectual vision, demonstrable leadership, successful entrepreneurial experience, a track record of delivering results, and the ability to communicate clearly and effectively with diverse audiences such as team members, sponsors, partners, host institutions, stakeholders, press and media, and the public. Below are some example practices desired for effective ERC leadership and management teams:
- Empowers all team members to contribute;
- Builds consensus around goals and problem definition;
- Facilitates communication to ensure a common understanding among all stakeholders; and resolves conflicts and builds trust.
It is rare that a single individual will have all of these attributes; thus, a strong leader will need to assemble an executive team that covers this broad spectrum of skills. The Center Director should understand their strengths and limitations, should be effective in assembling an executive leadership team that fills in the gaps of their limitations, and should be supported by an effective Council of Deans (See Section II.C. for details of the formation of the Council of Deans).The Director does not need to be a faculty member.
Organization and Management: An effective management structure begins with a clear understanding of the goals of the ERC and how the structure (including the ERC four foundational components) will support those goals. The structure should have the flexibility to adapt as the needs of the ERC change, as key people transition into or out of the ERC, or change roles, and to handle other changes as the ERC matures.
It is critical to have one person or team that has clear responsibility for each foundational component of the ERC. However, each ERC participant and each of the core participants should also understand the importance of each foundational component and be engaged in their role in carrying it out. Core partner institutions must meet the eligibility requirements of at least 3 faculty and 3 students participating in the ERC; postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students. Proposing teams will determine the funding source(s) of student support and nature of participation, whether graduate or undergraduate. Typically, ERC’s have many more fully/partly funded graduate and undergraduate students engaged in the ERC, in addition to faculty or postdocs.
ERC program experience has shown that an important role in the ERC structure is that of an administrative director, as described below. This remains a mandatory piece of the management structure.
Administrative Director: An experienced staff member at the lead university who is responsible for operational management, financial management, data collection, publicity, and reporting, etc. for the ERC. Post-award NSF training is available for this position given the ERC reporting complexities.
Lead Institution: The lead institution effectively guides the multiple elements of the ERC. The ERC headquarters are located at the lead institution, and the lead institution is the NSF recipient and is ultimately responsible for the financial and reporting obligations of the ERC award.
Core Partners: To qualify as a core partner university, there must be a minimum of three faculty participating in the ERC along with a minimum of three students; postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students. Core partners are included in the Cost Sharing requirements and in the Council of Deans (See Section II.C. for details of the formation of the Council of Deans.)
Other potential partners may include universities contributing affiliated faculty, federal laboratories, private-sector or non-profit organizations, educational partners, and/or foreign collaborators' universities or institutions. While not considered core partners, the involvement of such partners can be valuable.
Industrial/Practitioner Member: An organization that satisfies all requirements for membership according to the Center's membership agreement which may include financial support (cash or in-kind).
ERCs should engage industrial/practitioner members from sectors such as the Federal Government, State government, local government, quasi-government research, industry, industry association, policy organization, regulatory agency, medical facility, private foundation, nonprofit, venture capitalists, community organizations, professional/trade union, and other stakeholders as appropriate for the center's mission.
Affiliated Faculty Member: The ERC may include affiliated faculty members, which are faculty members who are contributing to the ERC from institutions other than the lead or core partner universities and are included in the budget.
Institutional Commitment: The lead and all core partner institutions must augment support for the ERC through cost-sharing and other allowed means and sustain the ERC once NSF's support ceases. Lead, core, and other partner academic institutions must commit to:
- Joining in partnership to support the ERC's vision, strategic plans, and activities in CR, EWD, DCI, IE and their integration across the institutions.
- Assuring cross-university industrial membership and intellectual property (IP) policies that recognize shared rights for joint work.
- Adopting institutional policies to reward faculty, particularly those in the promotion and tenure process, for participating in convergent research and innovation, technological advance, mentoring, university and pre-college education activity, and delivering on the ERC's plans for workforce development and creating an inclusive and diverse culture. NSF strongly encourages the full spectrum of diverse talent that society has to offer.
- Official recognition for university students engaged in mentoring of other university students and in pre-college outreach. This recognition is crucial to acknowledge their efforts and motivate them to continue their valuable work
Community Feedback: Broad-based stakeholder feedback to the ERCs is one of the important mechanisms used by the ERC to provide continual monitoring of the Center's health.
Advisory Boards: Advisory boards are formed to reinforce and support the proper functioning of the ERC's foundational components which are CR, EWD, DCI, and IE, as described above. Careful consideration must be given to defining each advisory board's functional role and selecting quality board members capable of overseeing that role. An example of a generic ERC feedback loop structure is illustrated in Figure 2. As part of the NSF Management/Oversight, the NSF Program Director and the NSF Site Visit Team (SVT) typically interact with the ERC and give feedback to the ERC once a year at a minimum. The advisory boards provide feedback at least twice a year; usually more often on an as needed basis. It may occasionally be necessary to form additional special committees to support special needs of the Center's vision. The staffing of these committees may be either internal or external. The Council of Deans and Student Leadership Council, as defined below, are mandatory advisory groups; however, the ERC is expected to propose appropriate advisory groups beyond these two.
Student Leadership Council (SLC): Undergraduate and graduate students from all partner universities responsible for coordinating their various activities in support of the ERC. A student president and a student co-president lead the SLC. The SLC will prepare a written Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis and present the SWOT findings during the annual visit of the NSF Site Visit Team (SVT).
Council of Deans: Led by the Dean of Engineering from the Lead university, this Council includes the Deans from the lead and each core partner institution. They meet collectively to provide administrative support of the ERC and to help facilitate multiple ERC elements across the lead and core partner universities. The Dean may not designate an alternate unless a PI, Co-PI, Director, or any senior personnel is also a Dean at the Institution. The two roles cannot be performed by the same person.
III. Award Information
Estimated program budget, number of awards, and average award size/duration are subject to the availability of funds. The maximum annual budget allowed is shown in the table below.
|
|
1 | $3,500,000 |
2 | $4,500,000 |
3 | $6,000,000 |
4 | $6,000,000 |
5 | $6,000,000 |
Year 1 budget will be committed upon award, and subsequent year budgets are subject to satisfactory annual review of accomplishments and availability of funds. After a gradual ramp up, years three through five are projected to level off at $6,000,000 in each of those years. Pending performance and outcome of a renewal review in the fourth year, support for years six to eight will continue at $6,000,000 per year until the eighth year. Support for years nine and ten will be phased down, with $4,000,000 in year 9 and $2,600,000 in year 10. No-cost extensions (NCEs) will not be granted.
IV. Eligibility Information
Proposals may only be submitted by the following: Only U.S. Institutions of Higher Education (IHEs), also referred to in this solicitation as universities and academic institutions, accredited in, and having a campus located in the US, that grant engineering degrees at the undergraduate, masters, and doctoral engineering level may submit proposals as the lead university. The Lead university submits the proposal, and the award is made to the lead university. Support is provided to core partner universities and any affiliated faculty from other partner institutions through subawards. NSF welcomes proposal submissions that broaden geographic and demographic participation. Proposals from STEM-minority-serving institutions (STEM-MSI*), non-R1 schools, emerging research institutions, and IHEs in EPSCoR-eligible jurisdictions, as lead or core partners, as well as IHEs that primarily serve populations of students with disabilities or women in engineering interested in STEM, are encouraged. Invited full proposals must meet all the following organizational requirements or they will be returned without review: The Lead must be an Institution of Higher Education per the Carnegie Foundational Attribute: https://carnegieclassifications.acenet.edu/ A proposed ERC must be multi-institutional, with a lead university and additional domestic university core partners. There is no maximum number of partner institutions. To qualify as a core partner institution, there must be financial support for a minimum of three faculty participating in the ERC along with financial support for a minimum of three students (Postdoctoral scholars may not be included as students). The lead or at least one of the core partner universities must be a STEM-MSI* university. Commitments from lead and core partner universities for cost sharing must be in place. *For this solicitation STEM-MSI is defined by the Department of Education as institutions of higher education enrolling populations with significant percentages of undergraduate minority students, or that serve certain populations of minority students under various programs created by Congress. Eligibility may be determined by reference to the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) of the US Department of Education National Center for Education Statistics (https://nces.ed.gov/ipeds/).
V. Proposal Preparation And Submission Instructions
Letters of Intent (required) :
1. LETTER OF INTENT
A Letter of Intent (LOI) is required to facilitate the NSF review process. The LOI must be submitted via Research.gov no later than the LOI deadline date. Please note the following conditions:
- LOIs must be submitted through Research.gov (not Grants.gov). A Minimum of one PI and up to four co-PIs are allowed.
- A list of all anticipated Core Partner Universities is required.
- The lead university cannot change after submission of the Letter of Intent.
Title: The title should begin with "NSF Engineering Research Center for ( insert the rest of the title and the Center's acronym )". The title should reflect the engineered system of the proposed ERC.
Lead PI and/or Center Director: The Lead PI's information is automatically included when the LOI is created. If the Lead PI and the Center Director are different individuals, please include the Center Director's name, university, department, phone number, and e-mail address at the beginning of the Synopsis section.
Anticipated ERC Non-Lead PIs (co-PIs): Identify up to four co-PIs. For the LOI, the participating team (Senior/Key Personnel) will be limited to the lead PI and up to four co-PIs who may come from any or all the domestic core partner universities.
Anticipated Core Partner Universities: The Lead university (not PI) is binding throughout the process. Other partners may change. The anticipated core partner universities should be included in the Manage Participating Organizations section of the LOI.
Synopsis (not to exceed one page): Upload brief statements of the vision and goals of the ERC, its potential for societal impact, and an integrated plan for the Center. Include an overview of the research program, such as research thrust titles, goals, and fundamental gaps or barriers in knowledge/technology that it meets. Although the EWD, DCI, and the IE are also critical foundational components of an ERC, they do not need to be described in detail in the LOI.
Other Comments (an additional max 2,500 characters including any blank spaces): Continue Synopsis as needed in this section.
Keywords: In order of decreasing emphasis, list up to ten keywords that represent the scientific interdisciplinary content in the proposal.
Letter of Intent Preparation Instructions :
When submitting a Letter of Intent through Research.gov in response to this Program Solicitation please note the conditions outlined below:
Submission by an Authorized Organizational Representative (AOR) is not required when submitting Letters of Intent.
A Minimum of 0 and Maximum of 4 Other Senior Project Personnel are permitted
A Minimum of 0 and Maximum of 6 Other Participating Organizations are permitted
- Keywords is required when submitting Letters of Intent
- Submission of multiple Letters of Intent is permitted
Preliminary Proposals (required) : Preliminary proposals are required and must be submitted via Research.gov, even if full proposals will be submitted via Grants.gov.
2. PRELIMINARY PROPOSAL
Submission of a Preliminary Proposal is required to be eligible for an invitation to submit a Full Proposal.
Preliminary Proposal Preparation Instructions:
Preliminary proposals must explicitly address the following questions in the project description:
- What are the compelling new ideas and what is the potential for high societal impact?
- What is the ERC engineered system? Is it high-risk but high payoff? Is the 3-plane chart well-conceived and justified?
- Why is an ERC necessary to tackle the idea?
- What is the proposed management structure for the ERC? How will the ERC's organization and management structure integrate and implement the four foundational components (CR, EWD, DCI, and IE) and foster the desired team formation?
- What are the proposed strategies for engaging and developing the appropriate stakeholder community?
- Does the proposed ERC create an inclusive environment where all the ERC participants learn to work in a team towards a common goal?
Preliminary Proposal Set-Up: Select "Prepare New Preliminary Proposal" in Research.gov. Search for and select this solicitation title in Step One of the Preliminary Proposal wizard. The information in Step 2 is pre-populated by the system. In Step 3 select "Single proposal (with or without subawards). Separately submitted collaborative preliminary proposals will be returned without review.
Title: The title should begin with "NSF Engineering Research Center for ( insert the rest of the title and the Center's acronym )". The rest of the title and acronym can change from the LOI to the submitted preliminary proposal as long as it is in the same topic area. The title should reflect the system focus of the proposed ERC.
The required components of the preliminary proposal are given below. Page limitations given here will be strictly enforced. Proposers should review the most current PAPPG for specific information and format for the required sections. No other sections are required or may be included in the preliminary proposal.
Cover Sheet: Select the proposed start date and proposed duration.
Project Summary (1 page): The Project Summary must have three separate section headers entitled "Overview", "Intellectual Merit", and "Broader Impacts"; each heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line. Within the Overview section, include a separate sub-section entitled "Proposed Vision". The summary should be informative to those working in the same or related fields and understandable to a scientifically or technically literate reader.
Project Description: Maximum 10 pages, total, containing the following sections, not necessarily in this order. All figures and tables must be included within the 10-page limit.
The proposing team (Participant Table) should be submitted as a supplementary document.
The Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts of the ERC must be addressed and described throughout the narrative as an integral part of the Project Description. Between Sections IV and V, include a separate header for Broader Impacts, as specified below. In addition, Results from Prior Support is not a required section for the preliminary proposal.
Outline for the Preliminary Proposal Project Description (up to 10 pages)
II. Strategic Plan
III. Organization and Management Structure
IV. Convergent Research
BROADER IMPACTS ( Please note: The Project Description must include a separate section header labeled Broader Impacts and the heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line. )
V. Engineering Workforce Development
VI. Diversity and Culture of Inclusion
VII. Innovation Ecosystem
I. Vision: The proposed vision for the ERC must be explained, with a discussion of the convergent engineering research theme and the anticipated societal impact. Explain the proposed transformative engineered system and the potential for impact on society, the engineering community and the greater scientific community.
II. Strategic Plan: The plan must define the engineered system and describe how the features of the ERC will be integrated to achieve the vision, in particular the cohesive plan for involving participants at all levels in the four foundational components:
- Convergent Research (CR)
- Engineering Workforce Development (EWD)
- Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI)
- Innovation Ecosystem (IE)
III. Organization and Management Structure: Describe the proposed management, including the functions of key personnel and the role of any advisory committee (including the required Student Leadership Council and the Council of Deans), executive committee, program committee, or their equivalent. Note that there is no recommendation for how ERCs should be managed. This solicitation provides for flexibility on organization structure and management and is part of the review criteria – as such the proposal should clearly justify the proposed structure.
IV. Convergent Research (CR): The role of convergence and team formation in the proposed research must be described. Research activities must address any gaps and barriers to achieve the proposed vision. Research must advance fundamental knowledge and support the development of technology that is proven through proof-of-concept testbeds as part of a well-defined engineered system. Integration of research activities must be graphically depicted on a clearly legible version of the ERC Program's 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart ( http://erc-assoc.org/content/three-plane-diagram ) that is tailored to the proposed ERC. The chart should be at least half a page, but a full page is recommended for legibility, as this chart is used at several stages of the NSF review process. This section should clearly state what new knowledge is expected that would advance the state of the art in key research areas.
V. Engineering Workforce Development (EWD): A proposed evidence-based program for human capacity development for the future engineering and technical workforce must be described. The program goals and expected outcomes must be described. Proposed activities should logically lead to targeted outcomes and support diverse pathways and experiences for participants. Existing programs and partnerships may be leveraged to support the ERC EWD program and provide opportunities to engage with potential participants.
VI. Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI): Preliminary ideas to create and nurture a culture of inclusion to foster the engagement of all ERC participants. This section should include evidence-based and intentional programming approach.
VII. Innovation Ecosystem (IE): An innovation ecosystem development effort must be proposed. However, DO NOT list potential or committed industrial or other supporters.
In addition, the preliminary proposal must also include these documents and information.
References Cited (required): See PAPPG for format guidelines.
Senior/Key Personnel Documents: The Lead PI, Center Director (if different from the Lead PI) and up to four co-PIs) must be designated as Senior/Key Personnel and must provide the following documents in accordance with the guidance contained in PAPPG Chapter II.D.2.h.
- Biographical Sketches
- Collaborators & Other Affiliations (COA)Information
Supplementary Documents:
A letter of commitment from the Dean of Engineering of the lead institution must be submitted which describes the support for and commitment to the ERC (including space for the ERC headquarters) should it be funded. While the Lead PI does not need to be from the School of Engineering, this letter must be from the Dean of Engineering to demonstrate the Engineering Dean's support for the proposed impact of the ERC on the engineering community.
The Dean should NOT include any financial commitments. Instead, the Dean should make a statement as to how the proposed ERC will align with the strategic directions of the college or the university. Proposals submitted without a letter of commitment from the Dean of Engineering will be returned without review. No letters of collaboration are allowed.
Participant Table (one page maximum): Provide a participant table that includes all committed ERC personnel: (1) Name of the Lead PI (and ERC Director, if different from the Lead PI) and Non-Lead PIs, (2) Institution(s), (3) Department(s), and (4) Most Relevant Field(s) of Expertise. In addition, please list all committed senior/key personnel. Do not identify members of advisory boards. The team table should include only those personnel who would receive NSF funds. This table is used by NSF in the merit review process to manage reviewer selection.
Single Copy Documents:
Collaborators & Other Affiliations Information: Information regarding collaborators and other affiliations (COA) must be separately provided for all members of the ERC Leadership Team and key faculty who are not designated as Senior/Key Personnel. Proposers must follow the guidance contained in PAPPG Chapter II.D.2.h. and include the COA information in the Additional Single Copy Documents section of the preliminary proposal. The accuracy of this section is very important to the integrity of the ERC review process. Please be accurate, up to date, and complete with the entries, including professional email addresses.
Institutional Affiliations: Beyond the affiliations captured on the COA form for individual ERC participants, the ERC Lead University must report any institutional affiliations arising from partnerships including any government agencies, international partners, industry partners or other non-academic institutional partners. The institutional affiliation information must be entered into the ERC Preliminary Proposal Institutional Conflict template (See bullet #2 on http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 ) and uploaded into the Additional Single Copy Documents section.
DO NOT SUBMIT other documents, including letters of commitment or collaboration from the domestic partner universities, prospective industrial members, or other future partners. The only allowed item is the required letter of commitment from the Dean of Engineering at the Lead Institution.
RELIMINARY PROPOSAL REQUIREMENTS
(Note: This is NOT a total list of the ERC preliminary proposal requirements. Refer to the ERC Solicitation and the PAPPG for complete requirements).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Full Proposal Preparation Instructions : Proposers may opt to submit proposals in response to this Program Solicitation via Research.gov or Grants.gov.
- Full Proposals submitted via Research.gov: Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation should be prepared and submitted in accordance with the general guidelines contained in the NSF Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide (PAPPG). The complete text of the PAPPG is available electronically on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg . Paper copies of the PAPPG may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from [email protected] . The Prepare New Proposal setup will prompt you for the program solicitation number.
- Full proposals submitted via Grants.gov: Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation via Grants.gov should be prepared and submitted in accordance with the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide: A Guide for the Preparation and Submission of NSF Applications via Grants.gov . The complete text of the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide is available on the Grants.gov website and on the NSF website at: ( https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=grantsgovguide ). To obtain copies of the Application Guide and Application Forms Package, click on the Apply tab on the Grants.gov site, then click on the Apply Step 1: Download a Grant Application Package and Application Instructions link and enter the funding opportunity number, (the program solicitation number without the NSF prefix) and press the Download Package button. Paper copies of the Grants.gov Application Guide also may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from [email protected] .
See PAPPG Chapter II.D.2 for guidance on the required sections of a full research proposal submitted to NSF. Please note that the proposal preparation instructions provided in this program solicitation may deviate from the PAPPG instructions.
3. FULL PROPOSAL
Full Proposal Preparation Instructions :
As a multi-university ERC, the proposal must be submitted as a single integrated proposal by the Lead university, with proposed subawards to the other partner institutions. Separately submitted collaborative proposals from each partner will not be accepted.
Select "Prepare New Full Proposal" in Research.gov. Search for and select this solicitation title in Step One of the Full Proposal wizard. Select "Center" as the proposal type. In the proposal details section, select "Single proposal (with or without subawards)." Separately submitted collaborative proposals will be returned without review.
Title: Research.gov will pre-pend the title with "Center." The remainder of the title should begin with "NSF Engineering Research Center for ( insert the rest of the title and the Center's acronym )". The title should reflect the engineering system of the proposed ERC.
Cover Sheet: For planning purposes, September 1, 2026 should be shown as the requested start date. The award duration should be 60 months.
Project Summary (1 page): The Project Summary must have three separate section headers entitled "Overview", "Intellectual Merit", and "Broader Impacts"; each heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line. Within the Overview section, include a separate sub-section entitled "Proposed Vision".
The summary should be informative to those working in the same or related fields and understandable to a scientifically or technically literate reader. Full proposals that do not contain the Project Summary as described above will be returned without review.
Project Description: Maximum 26 pages, total, containing the following sections, not necessarily in this order. Figures and tables must be included within the 26-page limit.
Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts: The intellectual merit and broader impacts of the ERC must be addressed and described throughout the narrative as an integral part of the Project Description. Between Sections IV and V, include a separate header for Broader Impacts, as specified below.
Outline for the Full Proposal Project Description (up to 26 pages)
BROADER IMPACTS ( Please note: The Project Description must include a separate section header labeled Broader Impacts and the heading must be on its own line with no other text on that line .)
VIII. Evaluation Plan
IX. Financial Support and Functional Allocation of Resources
X. Results from Prior NSF Support
The proposed vision for the ERC must be explained, with a discussion of the convergent engineering research theme and the anticipated societal impact. Explain the proposed transformative engineered system and the potential for impact on society, the engineering community and the greater scientific community.
Rationale: Make the case for why the proposed ERC is appropriate and why a convergent approach is needed for the targeted societal impact. Articulate why this vision cannot be realized with a series of individual investigators awards, the additional value of the proposed ERC compared with the sum of its parts.
The plan must clearly define the engineered system and describe how the features of the ERC will be integrated to achieve the vision, in particular the cohesive plan for involving participants at all levels in the four foundational components:
The Strategic Plan should include the high-level goals within each of these foundational components that will be described in more detail in later sections and the interrelationships among those goals, as well as the strategic role of partner institutions in integrating the foundation components and achieving these goals. The plan should also include the high-level expected progress of the ERC efforts across the 10-years of support in these four fundamental components, including ERC growth. The plan should further include discussions on the overarching convergent approach, the engagement of the stakeholder community, and the plans for convergent team formation. The ERC Strategic Plan should provide a roadmap with major milestones and describe how the ERC will know when it has been successful in meeting its goals. Finally, the ERC Strategic Plan should also articulate the logical reasoning that connects the proposed activities to the identified goals as well as the connections between the goals and the desired impacts expressed in the ERC Vision. The overall strategy must have the flexibility and the agility to evolve over time. An ERC needs to continually refine its vision based on a reliable feedback mechanism to focus on core advances, prune less compelling ERC elements, and refine as necessary the level of detail of its strategic plan over time.
Leadership Team: To properly address the four foundational components of the ERC, among the ERC Leadership Team, there must be identified individuals with: (a) deep expertise in the fundamental science/engineering areas envisioned by the ERC; (b) strategic leadership in innovation including intellectual property; (c) expertise in engineering workforce development and (d) experience in diversity and inclusion. Provide a chart summarizing the composition and expertise of the leadership team. Justify how each of the disciplines in this spectrum is needed for the convergent approach.
Management Plan: Proposals must include a management plan that describes the administration of the Center, including the functions of the leadership team, key personnel, and the role of any advisory committees, including the required Student Leadership Council and the Council of Deans, executive committee(s), and/or program committees or their equivalent. While the details of the structure are left to the proposers, the management structure should be designed to facilitate and integrate the ERC's critical and foundational components (CR, EWD, DCI, and IE). In addition, the proposed management plan should address the roles, authorities, and accountability for the leadership team that will ensure no bottlenecks in decision making.
Specifically, the successful proposal will delineate:
- The overall management and reporting structure of the ERC.
- Which personnel or groups will be responsible for CR, EWD, DCI, and IE. Please explain the relevant experience and expertise of these individuals and how they fit their assigned roles.
- These individuals should be included in the leadership team.
- An organizational chart, including advisory boards and the reporting/feedback loops involved.
The accompanying narrative for the organization chart should define the functional roles and responsibilities of each leadership position, and how these positions support the integrated strategic plan described earlier. It should also define the functional purpose of any additional advisory bodies that are deemed necessary to support the four foundational components, accomplish the proposed ERC vision, and achieve the desired long-term societal impact. Note that the functional roles of the two mandated ERC Advisory Bodies, the Council of Deans and the Student Leadership Council, are defined earlier in the section on Community Feedback. Since the quality of team member interaction is critical to team effectiveness, describe the managerial processes overlaying the organization chart that will be used to integrate the team. Please provide sufficient detail to allow critical evaluation.
Institutional Configuration: Describe the institutional configuration given the proposed vision for the ERC. Discuss the value added by each core partner university in meeting the goals of the four foundational components. Discuss the value added by any partnerships as described in the Key Elements of an ERC – Partners section.
IV. Convergent Research (CR)
ERCs are expected to have center-scale convergent engineering research that will support the ERC's overall potential for societal impact. The research program is the core of the ERC from which all ERC activities evolve.
Research Strategy: Clearly describe the proposed engineered system (a combination of components and elements that work together to perform a useful function) for the ERC. This section must include detailed research strategies, such as the 3-plane diagram (described below), research thrusts, and testbeds. A 10-year roadmap must illustrate the critical path, milestones, contributions from research projects, interdependence of research activities, short- and long-term deliverables, and overarching objectives in knowledge, technology, and proof of principle testbeds included in the ERC's vision. Impacts of the proposed research and technology outcomes on society, stakeholders, and the scientific and engineering communities must be included. Discuss how the research strategy will support the proposed societal impact of the ERC, including any potential negative consequences that would arise from the development of new technologies. Include risk mitigation strategies if appropriate. This section should also include strategies for building and maintaining teams appropriate for the proposed convergent approach and the process for starting, managing, and potentially ending research projects throughout the lifetime of the ERC. This section should clearly state what fundamental knowledge is expected within each thrust to advance the state of the art, including engineering as a whole discipline.
ERC 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart: Identify and characterize interdependent research thrusts and activities at fundamental knowledge, enabling technology, and systems-level testbed(s) scales. Integration of research activities must be graphically depicted on a clearly legible version of the ERC Program's 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart ( https://erc-assoc.org/content/strategic-planning-research-3-plane-chart ) that is tailored to the proposed ERC. The chart should be at least half a page, but a full page is recommended for legibility, as this chart is used at several stages of the NSF review process.
Research Thrusts: Each thrust description should start with a table that lists the thrust leader and other faculty/research participants by name, department, and institution. International partners, if any, who may be involved in the early stages of the thrust efforts must also be listed. Discuss the goals and objectives of the thrust vis-à-vis the goals of the ERC and the convergent research strategic plan and how these thrusts will support each other. Provide information on fundamental knowledge and technology deliverables. Identify the gaps and barriers the thrust will address in the context of the ERC's strategic plan. Discuss the convergent cross-disciplinary mix of expertise needed to achieve the goals of the thrust, as well as how the proposed team fulfills that need. Describe how future team building will support the convergent approach. Benchmark the research proposed for the thrust with respect to the state-of-the-art. Discuss the role of the thrust's research relative to the ERC's 3- Plane Strategic Planning Chart.
Project-level descriptions of specific research activities for each thrust must describe the proposed research and link it to the thrust goals. Describe a few exemplar projects in depth to allow judgment of the quality of the effort proposed, rather than superficially describing all projects. For these projects, provide examples of fundamental barriers the research will address, the need for a convergent approach, and project-level methods to address the barriers.
Demonstrate that the desired results constitute breakthroughs and are attainable in ten years. Discuss how projects support and integrate with other thrusts, enabling technologies, and systems-level testbeds in an overall convergent research approach.
Testbeds: Enabling- and systems-level testbeds must include a description of proposed proof-of-concept demonstration(s) in each testbed and personnel needed to construct and implement each proposed testbed. The research program budget should support technical staff to work with students and faculty to build these testbeds.
Note: NSF funds may not be used to support clinical trials. If the research involves vertebrate animals or includes human subjects, PAPPG requirements must be followed for the full proposal.
V. Engineering Workforce Development (EWD)
The ERC EWD program is driven by the future education, workforce development, and labor market needs relevant to the proposed Center. A proposed evidence-based program for building human capacity for the future engineering and technical workforce must be described. The proposed program should provide strategic goals for the ERC as well as targeted and specific outcomes related to workforce development and education.
Workforce Development occurs at all levels of the Center and provides opportunities for all ERC members including students, faculty, and external partners as appropriate. Proposed activities should logically lead to targeted outcomes and support diverse pathways and experiences for participants. Engineering workforce activities should contribute to a diverse, globally competitive, and team-oriented engineering workforce that has experience in convergent research, technology advancement, industrial practice, and innovation. Rather than a comprehensive set of training opportunities (general public, faculty, professional, vocational, graduate students, undergraduate students, and K-12), EWD programs should include a strategic selection of targeted activities that logically connect to each other and that will enable the long-term vision of the Center ERCs should leverage team and institutional expertise and resources to maximize impact with targeted activities.
At least 6 non-ERC students must enroll in a Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) program budgeted at a minimum of $80K per year from the ERC base budget, as well as at least 6 participants must be engaged in a Research Experiences for Teachers (RET) program budgeted at a minimum of $60K per year from the ERC base budget. Awarded ERCs are encouraged to submit proposals to the annual Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) Site and Research Experiences for Teachers (RET) Site competitions to expand the Center's workforce development impact. Partnerships with inner city, rural, or other high needs schools are especially encouraged, as is participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM. Suitable metrics to assess progress towards meeting the ERC's goals should be described, and feedback loops should be in place for continuous program improvement.
Describe how the leadership team will effectively support workforce development and educational programming and their growth. This section should also clearly describe how the proposed workforce development program will interact with existing educational or training systems at all partner institutions. Include a description of plans for engaging with partners, recruiting participants, and anticipated participant experiences. Educational partnerships may be leveraged to support the program and provide opportunities to engage with potential participants. All Engineering Workforce Development program participants, whether internal or external to the ERC, should have opportunities that are unique and would otherwise not be possible without the ERC.
VI. Diversity and Culture of Inclusion (DCI)
Describe the vision and plans for nurturing a culture that ensures participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM. A culture of inclusion has many important aspects that are essential for deep collaboration, including the participation of members from diverse scientific backgrounds and training which is necessary for true convergent research and innovation. A culture of inclusion must also foster participation of a diversity of partner institutions, including industry and practitioners, that will bring different perspectives to bear on the goals of the ERC. At least one core partner institution that enrolls and graduates a high percentage of underrepresented students in engineering and STEM fields must be included.
Describe preliminary ideas to create and nurture a culture that fosters the engagement of all ERC participants, including those from a diverse range of scientific backgrounds. This section should include evidence-based and intentional programming to support the inclusion of all talent that integrates and strengthen convergent research efforts across all institutions. Suitable metrics to assess the ERC's goals should be described, and feedback loops should be in place for independent assessment and continuous improvement in all dimensions of ERC operation.
In this section, describe how the leadership team will effectively create an inclusive culture for the ERC in which all members feel valued and welcomed, creatively contribute, and gain mutual benefit from participating. Include a description of plans for recruiting, mentoring, and retaining undergraduates, graduate students, and members of the research and leadership team from full spectrum of diverse talent in engineering. Describe the role of all partners, including plans to connect with ERC’s research and innovation goals in meaningful way, benefiting the students and faculty in the Center.
The ERC program is committed to including the participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM.
VII. Innovation Ecosystem (IE)
At its core, the innovation ecosystem is a network formed among trusted partners working together towards the common goal of creating and enhancing the capacity for innovation within the ecosystem.
In this section, discuss how the ERC will foster the creation of societal value from innovations (e.g., inventions, goods, services, businesses) that benefit society in a sustainable fashion (i.e., value creation). Identify the innovation ecosystem stakeholders relevant to realizing the proposed vision and societal impact.
Describe the strategy to form relationships with stakeholders to garner support for the Center's vision. Specifically, include the ERC's plans for developing and fostering industrial/practitioner memberships and involvement; technology transfer to member and non-member firms; if included, the role of university and state and local government as facilitators of entrepreneurship, civics, economic/workforce development and innovation; or regulatory agencies as influencers of the ERC innovation , end users or customers as beneficiaries of the ERC innovation, and plans for supporting translational research when appropriate.
To maximize positive social impact, any anticipated potential negative consequences caused by the introduction of the ERC technology should be addressed. In these cases, make sure to include stakeholder(s) that will work to mitigate the negative impacts, such as through consideration of regulation and ethics.
Provide a description of how the proposed member firms (e.g., innovation partners, facilitators, influencers, and beneficiaries) align to the proposed ERC's technology area. That is, as the ERC's research program evolves, note at which points in time in the ERC development over its 10-year lifespan different types of stakeholders engage with the ERC to enable success and create societal value. Some stakeholders may be engaged for the entire 10 years, and others may be involved with focused research activities at critical points in time (e.g., testbed development).
Discuss the integration of all stakeholders into the governance and operations of the ERC. Include a letter of collaboration ( please make sure to use the template provided in the PAPPG ) from each stakeholder that identifies their commitment to work with the ERC as described in the project description. The letters should be uploaded in the Supplementary Documents section.
Legal Frameworks: The different stakeholder groups/organizations/partners operate under very different legal frameworks that can make seamless collaboration difficult. Consequently, the ERC must work within the university structure to create an environment where the frameworks can be modified so that the different entities can come together for productive interaction. In advance of anyone joining the ERC, it is important to put in place legal agreements that protect the interests of the stakeholder entities and the university partners. Therefore, at a minimum, all ERCs require two legal frameworks to handle (1) intellectual property and (2) industry/practitioner membership agreements. The specifics of the ERC vision and the nature of the stakeholder community will determine whether additional legal frameworks are necessary.
- Intellectual Property: Describe the overall Intellectual Property (IP) strategy consistent with planned value creation in the ERC, and the corresponding management of the ERC IP across the lead and partner institutions and the approaches that will enable licensing of ERC's IP and/or adopting of other ERC outcomes. This plan must discuss management of possible conflicts-of-interest of any ERC researchers and the ERC's technology transfer endeavors. If an award is made, the IP policy must be prepared and submitted within 90 days of the award.
- Industry/Practitioner Membership Agreement: Discuss the terms of the draft membership agreement including the proposed fee structure and benefits. Describe the type(s) of support to be received. A letter of commitment (one page maximum for each) from each firm/practitioner organization committed to joining the ERC as a member and providing (cash and/or in-kind) support in the event that an award is made must be uploaded in Supplementary Documents.
Based on the goals and desired outcomes of the ERC strategic plan, a proposed evaluation plan is required that includes all four foundational components as well as a risk analysis . The purpose of ERC evaluation is to provide feedback on progress towards meeting Center goals. The evaluation plan should include formative aspects that allow the Center to make evidence-based decisions about changes in its activities and summative aspects to provide evidence of impact across all elements of the ERC. This section should include the evaluation questions, as well as, a description of the type of evaluation design and methods that will be used to address each question. This section should specify the mechanisms and timeline for how the results and recommendations from evaluation and assessment will be fed back into ERC goals, objectives, and milestones to ensure continual progress and attainment of goals, targets, and impacts during the project period. It should also identify the person(s) who will lead the ERC evaluation and briefly describe their academic training and professional experience that qualifies them to serve as an evaluator. Evaluator(s) may be internal or external to ERC institutions but should be positioned to carry out the evaluation plan as objectively as possible.
Awardees may be required to participate in program-level evaluation activities by which NSF can assess implementation processes and progress toward program level outcomes. NSF, an NSF contractor, or a grantee on behalf of NSF, may periodically conduct program evaluations or special projects that necessitate access to project level staff and data. This activity may occur at any time during the award period and could occur after NSF support has ended. ERC participation includes responding to inquiries, interview and other methods of common data collection and/or aggregation across ERCs. In addition, PIs and ERC evaluators may be asked to assist in developing program evaluation activities that will mutually benefit the agency and ERC participants.
Discuss the plans for financial and in-kind support from all sources, except cost sharing. Include plans for allocation of those resources to fulfill the goals of the ERC. Include a functional budget table, showing only the estimated proportional distribution of effort across the ERC in its first 5 years without showing the support levels from any sources. The table must not show the sources of support, since the reviewers cannot have access to the level of academic support. A template of the table can be found on bullet #3: http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 .
This section of the proposal must also include a pie chart showing the allocation of resources and committed levels of support for the first five years from industrial or practitioner member firms and any additional non-member commitments from state and/or local governments for cash and/or in-kind support. A template of the table for Pie Chart Showing Allocation of Resources and Committed Levels of Support can be found on bullet #4: http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 .
Provide a pie chart showing the planned distribution of the requested NSF funds for year one between the lead, each domestic partner university, and each university contributing affiliated faculty.
If the Director and Lead PI (if different) identified on the proposal have received prior NSF support, including any award with an end date in the past five years or current funding including any no-cost extensions, the intellectual merit and broader impacts accomplished under that award should be discussed. In cases where the Director and Lead PI have received more than one award (excluding amendments to existing awards), they should only report on the award that is most closely related to the proposal (for each, if the Director and Lead PI are different people) . See PAPPG II.D.2.iii for the required format of this section. Recommended length – no more than one page.
In addition, the proposal must also include these documents and information.
References Cited: See PAPPG for format guidelines.
Budgetary Information: Travel Funds for ERC Leadership Team's Participation in Biennial Meetings: Members of the ERC Leadership Team are required to participate in the ERC Biennial Meeting (typically held in odd years) and the cross- ERC Leadership Team retreats (which are typically held annually). The purpose of biennial meeting is to share successes and failures across the ERCs, receive updates on the ERC Program, and provide input for future ERC Program improvements. The purpose of the retreats is to focus on issues and best practices specific to the different leadership team groups. The biennial meetings are held in the Washington DC area for 2.5 days. Retreats are held in various locations for 1-2 days. Travel funds must be included in each annual budget to support participation in alternating biennial and leadership retreats for each person identified.
Note: The budget justification section should only identify items that are not cost shared. A justification and explanation of cost shared items needs to be appended to the cost sharing tables that are submitted in the single-copy documents section of the proposal.
Cost sharing is mandatory and is specific to the ERC solicitation . The percentage of cost share is determined using the Cost Sharing Formula in the Budgetary Information section of this solicitation. Lead and core partner institutions are responsible for cost share on their entire portion of NSF funds, including sub-awards from their institutions to affiliate partners or other payees. Please see the Budgetary Information section of this solicitation for additional information.
Facilities, Equipment and Other Resources . In this section, please include ONLY facilities, equipment, and personnel that are directly relevant and unique to the proposed ERC. Briefly discuss such laboratories, facilities, cyberinfrastructure, personnel, and equipment, particularly those shared by the ERC team members. Distinguish existing facilities and equipment from any that will be acquired by the ERC (see PAPPG Chapter II.C.2.i). Space must be identified on the campus of the lead academic institution for the ERC headquarters. Describe the headquarters, including the size, functionality, and features. Discuss how the cyberinfrastructure, facilities, and equipment of the ERC will be used to form and sustain a collaborative ERC team with shared resources and information.
Letters of commitment should be included in the supplementary documents for facilities, equipment, etc. that are being provided by institutions or collaborators which are not from the lead institution or the core partners.
Senior/Key Personnel Documents
In accordance with the guidance in the PAPPG, the following information must be provided for all individuals designated as Senior/Key Personnel. This includes the Lead PI, Center Director if different from the Lead PI, co-PIs, all members of the ERC Leadership Team and key faculty.
- Biographical Sketch
- Current and Pending (Other) Support
- Collaborators & Other Affiliations Information
- Synergistic Activities
Supplementary Documents . In addition to the requirements contained in the PAPPG, the following items must be provided as supplementary documents.
Table of Academic/Other Participants and Industrial/Practitioner Members: The table should be created using the table format available on the ERC Association website on bullet #5 at: http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 . Download and use the Word file named " ERC Participants Table Template for Inclusion in Full Proposal. " Provide all the required information in each section of the table.
Letters of Commitment : These letters should express commitment, but should not praise or advocate for the project, and must follow the format for letters of collaboration given in the PAPPG. Submit the following required letters as indicated:
- Lead university: Senior university administrators (Dean of Engineering plus one other higher-level university official) for the lead university attesting to the institutional commitment to the goals of the ERC and a commitment to headquarters space in both letters. The letters should not mention cost sharing, as that information cannot be revealed to reviewers. The letters should indicate the institutional commitment to all major aspects of the ERC, including each of the four foundational components, and assure the development of a cross-ERC IP policy within 90 days, if an award is made.
- Each Core Partner University: A senior administrator (Dean or equivalent) attests to the partner's institutional commitment to the goals of the ERC.
- If applicable, officials from any participating federal laboratories indicating their involvement in the ERC and their commitment to provide support for their staff participating in the ERC.
- Member Organizations: A letter of commitment (one page maximum for each) from each firm/practitioner organization committed to joining the ERC as a member and providing (cash and/or in-kind) support.
Letters of Collaboration
The following Letters of Collaboration are required if applicable to the proposed ERC. These letters should state generic willingness to collaborate, but should not provide specific details on types or amounts of contributions and must follow the format for letters of collaboration given in the PAPPG:
- Officials of firms and agencies able to commit to membership.
- An administrator of each proposed pre-college or community college partners committing to their roles in the ERC as described in the Project Description.
- State or local government agencies and other organizations committed to partnership with the ERC.
- Domestic affiliated facult y if their projects are planned to be in place during years one through five. Note that no letters are required from the administrators of the universities providing affiliated faculty.
- Foreign collaborators , if any.
All letters should be addressed to:
ERC Program
Division of Engineering Education and Centers
U.S. National Science Foundation
All signed letters must be scanned and uploaded in the Other Supplementary Documents section of the proposal. Please instruct the letter writers not to mail, email, or fax copies to the NSF, as they will not be considered.
Draft Membership Agreement . Submit draft industry/practitioner membership agreement.
Data Management and Sharing Plan . Provide a Data Management and Sharing Plan according to guidance in the PAPPG. Go to ENG Data Management Plans | NSF - National Science Foundation ( https://www.nsf.gov/eng/general/dmp.jsp ) for Engineering-specific guidance.
Mentoring Plan . If applicable, provide a mentoring plan for postdoctoral scholars or graduate students who will be supported by ERC funds.
Single Copy Documents . Viewable only by NSF (also refer to the PAPPG Chapter II.C.1 on "Single-Copy Documents" for additional information):
Optional List of Suggested Reviewers or Reviewers Not to Include: Proposers may include in the single copy documents section a list of suggested reviewers who they believe are especially well qualified to review the proposal. Proposers also may designate persons they would prefer not to review the ERC proposal, indicating why. These suggestions are optional. PAPPG Exhibit II-2 contains information on conflicts of interest that may be useful in the preparation of this list. The cognizant Program Officer handling the proposal considers the suggestions and may contact the proposer for further information. However, the decision whether to use the suggestions remains with the Program Officer.
Required Cost Sharing Tables and Justification: Complete and submit the following tables: " Committed Cash and In-Kind Academic Support, Years 1-5 " and, if applicable, a table showing the " Nature of In-Kind Support " identifying any in-kind commitments and the sources of the commitments. A template of those tables can be found at (bullet #6): http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 . The tables should be uploaded into the single copy documents section of the full proposal. Appended to the cost sharing tables will be a justification/explanation of the source, nature, amount, and availability of any proposed cost sharing. The Proposers are directed not to include these tables and the cost sharing justification in any other part of the proposal, as cost sharing commitments are not provided to the reviewers. Refer to the section on Budgetary Information and Cost Sharing in this solicitation for information on cost sharing requirements and policies.
Proposal Update: If the proposed ERC is evaluated by a Site Visit Team (SVT), a 10-page reply that integrates changes in the proposed ERC based on comments from the SVT members and the Site Visit Report will be requested to facilitate the final stages of the review process.
INVITED FULL PROPOSAL REQUIREMENTS
(Note: This is NOT a total list of the ERC proposal requirements. Refer to the ERC Solicitation and the PAPPG for complete requirements).
|
|
Academic cost sharing (Lead and domestic core partner universities) | Yes, Single Copy Documents |
Identification of funded faculty/staff members from the lead and university-level partner institutions | Project Description |
Chart summarizing the leadership team | Project Description |
Organizational Chart | Project Description |
ERC 3-Plane Strategic Planning Chart | Project Description |
Research Thrusts Participant Tables | Project Description |
Functional Years 1-5 Budget Table | Project Description |
Years 1-5 Committed Industrial and Other Non-NSF, Non-Academic Support table | Project Description |
Years 1-5 Planned Distribution of NSF Funds | Project Description |
Draft membership agreement | Supplementary Documents |
Draft IP policy | Required following award |
Lead Institution: Two letters of commitment, one from the Dean of Engineering and one from a higher-level administrator, describing committed institutional resources | Yes - (but no cost sharing identified in letters) Supplementary Documents |
Core Partner Institutions: Letters of commitment from a senior administrator at the rank of Dean or equivalent from the partner institution, describing committed institutional resources | Yes - (but no cost sharing identified in letters)-Supplementary Documents |
Federal Laboratories: Letters of commitment from administrators of federal laboratories contributing support for staff in the ERC, attesting to laboratory support for that staff time | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of commitment to membership from firms / agencies / hospitals committed to joining the ERC as members and providing cash and in-kind support to the ERC | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from firms / agencies / hospitals committed to joining the ERC as members | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from pre-college partner administrators (school district or individual schools), community college administrators, or other education and outreach partners | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from state or local government agency or state governor providing non-member financial support to the ERC | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Letters of collaboration from foreign collaborators | Yes, if applicable -Supplementary Documents |
Table of "Committed Cash and In-Kind Academic Support, Years 1-5" and a table "Nature of In-Kind Support." Also, append to the tables a justification/explanation of any cost shared items | Single-Copy Documents |
| Yes, Supplementary Documents |
Post Proposal Submission to NSF: Other Required Documents
Cost Sharing:
Cost Sharing is required.
Invited full proposals will include a budget for each of the five years. Research.gov or Grants.gov will automatically provide a cumulative budget. Provide separate budgets for subawards to the domestic core partner institutions and any affiliated institutions whose faculty and students would be supported by the ERC's budget. Allowable budgets for the first five years are as follows: The budget for year one may be no more than $3,500,000, no more than $4,500,000 for year two, no more than $6,000,000 for year three, no more than $6,000,000 for year four, and for year five.
Cost Sharing: Mandatory Cost Sharing is required but inclusion of voluntary committed cost sharing is prohibited.
Mandatory Cost Sharing Requirements and Policies: Cost sharing is required of the lead university and core partner university(ies) to support and sustain the ERC. Cost sharing is not a review criterion for the ERCs; it is an eligibility criterion. Because cost sharing is not a review criterion, details on cost sharing will not be shared with the reviewers.
Upon issuance of the award, the lead university is responsible to secure, retain, manage, and certify to NSF the ERC cost sharing (cash and in-kind), at the level stated in the cooperative agreement. The total level of cost sharing proposed must be calculated using the "Cost Sharing Formula" below.
Cost sharing must not exceed the mandatory level stated in the ERC cost sharing formula. This would be considered "voluntary committed cost sharing" which is specifically prohibited according to NSF's cost sharing policies. ERC proposals that include cost sharing amounts in excess of the specified formula will be returned without review or declined.
Instructions for Disclosure and Non-Disclosure of Cost Sharing within the Proposal:
Cost Sharing and Letters of Commitment: Since cost sharing is not to be seen or considered by reviewers, any letters of commitment should not mention any cost sharing (cash or in-kind), since the reviewers will see these letters. See Section V.A for details concerning the letters of commitment.
Cost Sharing in the Budget Submission: The proposed cost sharing (including the estimated value of any in-kind cost sharing), according to the formula below, must be shown on Line M of the NSF proposal budget form. (Line M is masked from reviewers.)
Cumulative cost sharing should be entered for all 5 years on Line M of the first-year budget. Do not include the cost sharing figures on Line M of the budget for years 2-5. Do not include the justification / explanation for any cost-shared items in the budget justification section of the proposal. Only the non-cost shared items should be explained in the budget justification section, identifying the source, nature, amount and availability of non-cost shared items.
Cost Sharing Tables and Justification: The cost sharing commitment of the ERC must be documented in the proposal and the details presented in the tables of committed support. The lead institution is instructed to provide a table of "Committed Cash and In-Kind Academic Support, Years 1-5" (including any partner university providing cash for years 1-5). Proposers must also complete the table "Nature of In-Kind Support" identifying in-kind commitments and the sources of the commitments. A template of those tables can be found at (bullet #6) http://erc-assoc.org/content/templates-proposal-preparation-0 . The tables should be uploaded into the "Single Copy Documents" section of the proposal. Append to the cost sharing tables a justification / explanation of the source, nature, amount and availability of any proposed cost sharing. Do not include these tables and the cost sharing justification in any other part of the proposal, as cost sharing commitments are not to be provided to reviewers.
Cost Sharing Formula:
ERC cost sharing requirements are determined based on classification at the time of the LOI submission deadline as defined in the "Carnegie Foundation's Classification of Institutions of Higher Education." Limited financial resources at smaller colleges and universities that lack high research activity may present significant challenges to cost sharing. Therefore:
- RU/VH: Research Universities - required cost sharing level is 20% of the allocation of the NSF budget to the lead or core partner university;
- RU/H: Research Universities - required cost sharing level is 15% of the allocation of the NSF budget to the lead or core partner university;
- DRU: Doctoral/Research Universities - cost sharing level is 10% of the allocation of the NSF budget to that core partner university.
- Master's L: Master's Colleges and Universities - cost sharing level is 10% of the allocation of the NSF budget to that core partner university/college;
- Bac/Diverse: Baccalaureate Colleges--Diverse Fields - cost sharing level is 5% of the allocation of the NSF budget to that core partner college.
If the university is classified in more than one Carnegie category, it must cost share at the highest cost sharing category as described above. The Carnegie classification shall remain throughout the duration of the competition and any subsequent award. The total ERC cost share shall be 20% or less, depending upon the Carnegie classifications for each of the partners.
ERC Support Cost-Sharing Sources:
The proposed cost sharing must be shown on Line M on the proposal budget. For purposes of budget preparation, the cumulative cost sharing amount must be entered on Line M of the first year’s budget. Should an award be made, the organization’s cost sharing commitment, as specified on the first year’s approved budget, must be met prior to award expiration.
Such cost sharing will be an eligibility, rather than a review criterion. Proposers are advised not to exceed the mandatory cost sharing level or amount specified in the solicitation.
When mandatory cost sharing is included on Line M, and accepted by the Foundation, the commitment of funds becomes legally binding and is subject to audit. When applicable, the estimated value of any in-kind contributions also should be included on Line M. An explanation of the source, nature, amount and availability of any proposed cost sharing must be provided in the budget justification. Contributions may be made from any non-Federal source, including non-Federal grants or contracts, and may be cash or in-kind. 2 CFR § 200.306 describes criteria and procedures for the allowability of cash and in-kind contributions in satisfying cost sharing and matching requirements. It should be noted that contributions derived from other Federal funds or counted as cost sharing toward projects of another Federal agency must not be counted towards meeting the specific cost sharing requirements of the NSF award.
Failure to provide the level of cost sharing required by the NSF solicitation and reflected in the NSF award budget may result in termination of the NSF award, disallowance of award costs and/or refund of award funds to NSF by the awardee.
The overall ERC-level budget should be prepared to assure sufficient funding from all sources to achieve the goals of the ERC. Hence, this budget would include faculty and staff to support the research, education, diversity and culture of inclusion, industrial collaboration/innovation, and management of the ERC. Budgets should include resources for reporting, site visit costs, and travel for cross-ERC collaboration and NSF meetings. The budget submitted to NSF will include an allocation plan for the NSF funding only.
May 09, 2025
D. Research.gov/Grants.gov Requirements
For Proposals Submitted Via Research.gov:
To prepare and submit a proposal via Research.gov, see detailed technical instructions available at: https://www.research.gov/research-portal/appmanager/base/desktop?_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=research_node_display&_nodePath=/researchGov/Service/Desktop/ProposalPreparationandSubmission.html . For Research.gov user support, call the Research.gov Help Desk at 1-800-381-1532 or e-mail [email protected] . The Research.gov Help Desk answers general technical questions related to the use of the Research.gov system. Specific questions related to this program solicitation should be referred to the NSF program staff contact(s) listed in Section VIII of this funding opportunity.
For Proposals Submitted Via Grants.gov:
Before using Grants.gov for the first time, each organization must register to create an institutional profile. Once registered, the applicant's organization can then apply for any federal grant on the Grants.gov website. Comprehensive information about using Grants.gov is available on the Grants.gov Applicant Resources webpage: https://www.grants.gov/applicants . In addition, the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide (see link in Section V.A) provides instructions regarding the technical preparation of proposals via Grants.gov. For Grants.gov user support, contact the Grants.gov Contact Center at 1-800-518-4726 or by email: [email protected] . The Grants.gov Contact Center answers general technical questions related to the use of Grants.gov. Specific questions related to this program solicitation should be referred to the NSF program staff contact(s) listed in Section VIII of this solicitation.
Submitting the Proposal: Once all documents have been completed, the Authorized Organizational Representative (AOR) must submit the application to Grants.gov and verify the desired funding opportunity and agency to which the application is submitted. The AOR must then sign and submit the application to Grants.gov. The completed application will be transferred to Research.gov for further processing.
The NSF Grants.gov Proposal Processing in Research.gov informational page provides submission guidance to applicants and links to helpful resources including the NSF Grants.gov Application Guide , Grants.gov Proposal Processing in Research.gov how-to guide , and Grants.gov Submitted Proposals Frequently Asked Questions . Grants.gov proposals must pass all NSF pre-check and post-check validations in order to be accepted by Research.gov at NSF.
When submitting via Grants.gov, NSF strongly recommends applicants initiate proposal submission at least five business days in advance of a deadline to allow adequate time to address NSF compliance errors and resubmissions by 5:00 p.m. submitting organization's local time on the deadline. Please note that some errors cannot be corrected in Grants.gov. Once a proposal passes pre-checks but fails any post-check, an applicant can only correct and submit the in-progress proposal in Research.gov.
Proposers that submitted via Research.gov may use Research.gov to verify the status of their submission to NSF. For proposers that submitted via Grants.gov, until an application has been received and validated by NSF, the Authorized Organizational Representative may check the status of an application on Grants.gov. After proposers have received an e-mail notification from NSF, Research.gov should be used to check the status of an application.
VI. NSF Proposal Processing And Review Procedures
Proposals received by NSF are assigned to the appropriate NSF program for acknowledgement and, if they meet NSF requirements, for review. All proposals are carefully reviewed by a scientist, engineer, or educator serving as an NSF Program Officer, and usually by three to ten other persons outside NSF either as ad hoc reviewers, panelists, or both, who are experts in the particular fields represented by the proposal. These reviewers are selected by Program Officers charged with oversight of the review process. Proposers are invited to suggest names of persons they believe are especially well qualified to review the proposal and/or persons they would prefer not review the proposal. These suggestions may serve as one source in the reviewer selection process at the Program Officer's discretion. Submission of such names, however, is optional. Care is taken to ensure that reviewers have no conflicts of interest with the proposal. In addition, Program Officers may obtain comments from site visits before recommending final action on proposals. Senior NSF staff further review recommendations for awards. A flowchart that depicts the entire NSF proposal and award process (and associated timeline) is included in PAPPG Exhibit III-1.
A comprehensive description of the Foundation's merit review process is available on the NSF website at: https://www.nsf.gov/bfa/dias/policy/merit_review/ .
Proposers should also be aware of core strategies that are essential to the fulfillment of NSF's mission, as articulated in Leading the World in Discovery and Innovation, STEM Talent Development and the Delivery of Benefits from Research - NSF Strategic Plan for Fiscal Years (FY) 2022 - 2026 . These strategies are integrated in the program planning and implementation process, of which proposal review is one part. NSF's mission is particularly well-implemented through the integration of research and education and broadening participation in NSF programs, projects, and activities.
One of the strategic objectives in support of NSF's mission is to foster integration of research and education through the programs, projects, and activities it supports at academic and research institutions. These institutions must recruit, train, and prepare a diverse STEM workforce to advance the frontiers of science and participate in the U.S. technology-based economy. NSF's contribution to the national innovation ecosystem is to provide cutting-edge research under the guidance of the Nation's most creative scientists and engineers. NSF also supports development of a strong science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) workforce by investing in building the knowledge that informs improvements in STEM teaching and learning.
NSF's mission calls for the broadening of opportunities and expanding participation of groups, institutions, and geographic regions that are underrepresented in STEM disciplines, which is essential to the health and vitality of science and engineering. NSF is committed to this principle of diversity and deems it central to the programs, projects, and activities it considers and supports.
A. Merit Review Principles and Criteria
The National Science Foundation strives to invest in a robust and diverse portfolio of projects that creates new knowledge and enables breakthroughs in understanding across all areas of science and engineering research and education. To identify which projects to support, NSF relies on a merit review process that incorporates consideration of both the technical aspects of a proposed project and its potential to contribute more broadly to advancing NSF's mission "to promote the progress of science; to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare; to secure the national defense; and for other purposes." NSF makes every effort to conduct a fair, competitive, transparent merit review process for the selection of projects.
1. Merit Review Principles
These principles are to be given due diligence by PIs and organizations when preparing proposals and managing projects, by reviewers when reading and evaluating proposals, and by NSF program staff when determining whether or not to recommend proposals for funding and while overseeing awards. Given that NSF is the primary federal agency charged with nurturing and supporting excellence in basic research and education, the following three principles apply:
- All NSF projects should be of the highest quality and have the potential to advance, if not transform, the frontiers of knowledge.
- NSF projects, in the aggregate, should contribute more broadly to achieving societal goals. These "Broader Impacts" may be accomplished through the research itself, through activities that are directly related to specific research projects, or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project. The project activities may be based on previously established and/or innovative methods and approaches, but in either case must be well justified.
- Meaningful assessment and evaluation of NSF funded projects should be based on appropriate metrics, keeping in mind the likely correlation between the effect of broader impacts and the resources provided to implement projects. If the size of the activity is limited, evaluation of that activity in isolation is not likely to be meaningful. Thus, assessing the effectiveness of these activities may best be done at a higher, more aggregated, level than the individual project.
With respect to the third principle, even if assessment of Broader Impacts outcomes for particular projects is done at an aggregated level, PIs are expected to be accountable for carrying out the activities described in the funded project. Thus, individual projects should include clearly stated goals, specific descriptions of the activities that the PI intends to do, and a plan in place to document the outputs of those activities.
These three merit review principles provide the basis for the merit review criteria, as well as a context within which the users of the criteria can better understand their intent.
2. Merit Review Criteria
All NSF proposals are evaluated through use of the two National Science Board approved merit review criteria. In some instances, however, NSF will employ additional criteria as required to highlight the specific objectives of certain programs and activities.
The two merit review criteria are listed below. Both criteria are to be given full consideration during the review and decision-making processes; each criterion is necessary but neither, by itself, is sufficient. Therefore, proposers must fully address both criteria. (PAPPG Chapter II.C.2.d(i). contains additional information for use by proposers in development of the Project Description section of the proposal). Reviewers are strongly encouraged to review the criteria, including PAPPG Chapter II.C.2.d(i), prior to the review of a proposal.
When evaluating NSF proposals, reviewers will be asked to consider what the proposers want to do, why they want to do it, how they plan to do it, how they will know if they succeed, and what benefits could accrue if the project is successful. These issues apply both to the technical aspects of the proposal and the way in which the project may make broader contributions. To that end, reviewers will be asked to evaluate all proposals against two criteria:
- Intellectual Merit: The Intellectual Merit criterion encompasses the potential to advance knowledge; and
- Broader Impacts: The Broader Impacts criterion encompasses the potential to benefit society and contribute to the achievement of specific, desired societal outcomes.
The following elements should be considered in the review for both criteria:
- Advance knowledge and understanding within its own field or across different fields (Intellectual Merit); and
- Benefit society or advance desired societal outcomes (Broader Impacts)?
- To what extent do the proposed activities suggest and explore creative, original, or potentially transformative concepts?
- Is the plan for carrying out the proposed activities well-reasoned, well-organized, and based on a sound rationale? Does the plan incorporate a mechanism to assess success?
- How well qualified is the individual, team, or organization to conduct the proposed activities?
- Are there adequate resources available to the PI (either at the home organization or through collaborations) to carry out the proposed activities?
Broader impacts may be accomplished through the research itself, through the activities that are directly related to specific research projects, or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project. NSF values the advancement of scientific knowledge and activities that contribute to achievement of societally relevant outcomes. Such outcomes include, but are not limited to: full participation of women, persons with disabilities, and other underrepresented groups in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM); improved STEM education and educator development at any level; increased public scientific literacy and public engagement with science and technology; improved well-being of individuals in society; development of a diverse, globally competitive STEM workforce; increased partnerships between academia, industry, and others; improved national security; increased economic competitiveness of the United States; and enhanced infrastructure for research and education.
Proposers are reminded that reviewers will also be asked to review the Data Management Plan and the Postdoctoral Researcher Mentoring Plan, as appropriate.
Additional Solicitation Specific Review Criteria
PRELIMINARY Proposal Additional Review Criteria:
Reviewers should consider these high-level questions:
How well does the preliminary proposal narrative address the following in the project description?
- What is the compelling new idea and what is the potential high societal impact?
- What is the engineered system? Is it high-risk but high payoff?
- Is the 3-plane chart well-conceived and justified?
- How does the proposed Center's research benchmark against the state-of-the-art?
- What is the proposed management structure for the ERC? How will the proposed organization and management structure integrate and implement the four foundational components (CR, EWD, DCI, and IE) and foster team-formation?
- Does the proposed ERC create an inclusive environment where all the ERC participants learn to work on a team towards a common goal?
FULL Proposal Additional Review Criteria:
- What is the engineered system?
- Why is the proposed vision compelling?
- Why is the proposed research competitive when benchmarked against the state-of-the-art?
- How well does the proposed ERC justify the need for a center or institute-like approach?
High Societal Impact
- What is the potential for high societal impact?
- How realistic is the proposed plan for high societal impact?
- If the proposed strategy is high-risk does the potential payoff from anticipated impacts justify the investment?
Convergence Research
- Does the proposed research require a convergent approach and is its implementation well documented?
- How well justified is the argument that convergence is necessary for the desired impact?
- How well has the convergent approach been fully integrated into the proposal?
- What is the likelihood the research will lead to significant fundamental advances, new discoveries, and technological developments?
- How well does the proposed research use the testbeds to integrate and to advance proofs-of-concept to achieve the proposed vision?
- Are there well-defined implementation milestones for convergence research?
Stakeholder Engagement
- Are effective mechanisms to gather, engage, and implement feedback from appropriate stakeholders in place (i.e., collaborators, supporters, advisory boards, external committees)?
Team Formation
- How does the team formation and the implementation of team science support the proposed convergent research?
- How well has the ERC demonstrated strategies to overcome barriers for effective, dynamic teaming?
Strategic Plan
- How well does the Center present an integrated strategic plan for the ERC to address the key elements of each foundational component and their integration?
- How well does the proposal present an appropriate and compelling management structure and plan to carry out Center activities?
Management and Organization
- How appropriate are the qualifications of proposed leadership and management team?
- How well does the proposal present appropriate and compelling management structure and plan to carry out Center activities?
- Are effective mechanisms to gather and implement feedback from appropriate stakeholders in place, including advisory boards and external committees?
Engineering Workforce Development
- To what extent is the proposed program coherent and aligned with the overall goals and vision of the ERC?
- Do the proposed Engineering Workforce Development plans include appropriate strategies for recruiting participants and engaging with partners?
- Are the proposed Engineering Workforce Development plans evidence-based and likely to achieve the desired experiences, outcomes, and impact described?
Diversity and Culture of Inclusion
- How well does the discussion include a clear strategy to support Diversity and Culture of Inclusion?
- To what extent does the program propose evidence-based approaches for Diversity and Culture of Inclusion that are integrated with all dimensions of ERC operation?
- How well does the management plan include clear accountability for Diversity and Culture of Inclusion aspects of the ERC across all partners?
Innovation Ecosystem
- How well does the proposal describe a plan to build a network of trusted partners for innovation capacity?
- How appropriate is the proposed structure and processes for value creation to move from ideation to implementation?
Evaluation Plan
- How well has the Center developed a logic evaluation framework to guide the implementation of the strategic plan and evaluate Center performance?
- How well does the evaluation plan include formative aspects that allow the Center to make evidence-based decisions about changes in its activities and summative aspects to provide evidence of impact across all elements of the Center?
Financial Support and Resources
- Are the estimated budget allocations reasonable to achieve the proposed ERC vision?
- Does the Center have adequate capital (i.e., facilities, equipment, cyberinfrastructure) and procedural (i.e., safety, environmental) resources?
- Does the Center have a convincing plan for data sharing and management?
B. Review and Selection Process
Proposals submitted in response to this program solicitation will be reviewed by
Ad hoc Review and/or Panel Review, Site Visit Review, or Reverse Site Review.
For Additional Review Criteria (see above listing)
Reviewers will be asked to evaluate proposals using two National Science Board approved merit review criteria and, if applicable, additional program specific criteria. A summary rating and accompanying narrative will generally be completed and submitted by each reviewer and/or panel. The Program Officer assigned to manage the proposal's review will consider the advice of reviewers and will formulate a recommendation.
After scientific, technical and programmatic review and consideration of appropriate factors, the NSF Program Officer recommends to the cognizant Division Director whether the proposal should be declined or recommended for award. NSF strives to be able to tell proposers whether their proposals have been declined or recommended for funding within six months. Large or particularly complex proposals or proposals from new recipients may require additional review and processing time. The time interval begins on the deadline or target date, or receipt date, whichever is later. The interval ends when the Division Director acts upon the Program Officer's recommendation.
After programmatic approval has been obtained, the proposals recommended for funding will be forwarded to the Division of Grants and Agreements or the Division of Acquisition and Cooperative Support for review of business, financial, and policy implications. After an administrative review has occurred, Grants and Agreements Officers perform the processing and issuance of a grant or other agreement. Proposers are cautioned that only a Grants and Agreements Officer may make commitments, obligations or awards on behalf of NSF or authorize the expenditure of funds. No commitment on the part of NSF should be inferred from technical or budgetary discussions with a NSF Program Officer. A Principal Investigator or organization that makes financial or personnel commitments in the absence of a grant or cooperative agreement signed by the NSF Grants and Agreements Officer does so at their own risk.
Once an award or declination decision has been made, Principal Investigators are provided feedback about their proposals. In all cases, reviews are treated as confidential documents. Verbatim copies of reviews, excluding the names of the reviewers or any reviewer-identifying information, are sent to the Principal Investigator/Project Director by the Program Officer. In addition, the proposer will receive an explanation of the decision to award or decline funding.
VII. Award Administration Information
A. notification of the award.
Notification of the award is made to the submitting organization by an NSF Grants and Agreements Officer. Organizations whose proposals are declined will be advised as promptly as possible by the cognizant NSF Program administering the program. Verbatim copies of reviews, not including the identity of the reviewer, will be provided automatically to the Principal Investigator. (See Section VI.B. for additional information on the review process.)
B. Award Conditions
An NSF award consists of: (1) the award notice, which includes any special provisions applicable to the award and any numbered amendments thereto; (2) the budget, which indicates the amounts, by categories of expense, on which NSF has based its support (or otherwise communicates any specific approvals or disapprovals of proposed expenditures); (3) the proposal referenced in the award notice; (4) the applicable award conditions, such as Grant General Conditions (GC-1)*; or Research Terms and Conditions* and (5) any announcement or other NSF issuance that may be incorporated by reference in the award notice. Cooperative agreements also are administered in accordance with NSF Cooperative Agreement Financial and Administrative Terms and Conditions (CA-FATC) and the applicable Programmatic Terms and Conditions. NSF awards are electronically signed by an NSF Grants and Agreements Officer and transmitted electronically to the organization via e-mail.
*These documents may be accessed electronically on NSF's Website at https://www.nsf.gov/awards/managing/award_conditions.jsp?org=NSF . Paper copies may be obtained from the NSF Publications Clearinghouse, telephone (703) 292-8134 or by e-mail from [email protected] .
More comprehensive information on NSF Award Conditions and other important information on the administration of NSF awards is contained in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) Chapter VII, available electronically on the NSF Website at https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg .
Administrative and National Policy Requirements
Build America, Buy America
As expressed in Executive Order 14005, Ensuring the Future is Made in All of America by All of America’s Workers (86 FR 7475), it is the policy of the executive branch to use terms and conditions of Federal financial assistance awards to maximize, consistent with law, the use of goods, products, and materials produced in, and services offered in, the United States.
Consistent with the requirements of the Build America, Buy America Act (Pub. L. 117-58, Division G, Title IX, Subtitle A, November 15, 2021), no funding made available through this funding opportunity may be obligated for an award unless all iron, steel, manufactured products, and construction materials used in the project are produced in the United States. For additional information, visit NSF’s Build America, Buy America webpage.
Special Award Conditions:
TBD - Programmatic Terms and Conditions: TBD - Financial and Administrative Terms and Conditions:
C. Reporting Requirements
For all multi-year grants (including both standard and continuing grants), the Principal Investigator must submit an annual project report to the cognizant Program Officer no later than 90 days prior to the end of the current budget period. (Some programs or awards require submission of more frequent project reports). No later than 120 days following expiration of a grant, the PI also is required to submit a final annual project report, and a project outcomes report for the general public.
Failure to provide the required annual or final annual project reports, or the project outcomes report, will delay NSF review and processing of any future funding increments as well as any pending proposals for all identified PIs and co-PIs on a given award. PIs should examine the formats of the required reports in advance to assure availability of required data.
PIs are required to use NSF's electronic project-reporting system, available through Research.gov, for preparation and submission of annual and final annual project reports. Such reports provide information on accomplishments, project participants (individual and organizational), publications, and other specific products and impacts of the project. Submission of the report via Research.gov constitutes certification by the PI that the contents of the report are accurate and complete. The project outcomes report also must be prepared and submitted using Research.gov. This report serves as a brief summary, prepared specifically for the public, of the nature and outcomes of the project. This report will be posted on the NSF website exactly as it is submitted by the PI.
More comprehensive information on NSF Reporting Requirements and other important information on the administration of NSF awards is contained in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) Chapter VII, available electronically on the NSF Website at https://www.nsf.gov/publications/pub_summ.jsp?ods_key=pappg .
NSF requires ERCs to submit annual reports that are more extensive in scope than those required of single investigator awards. NSF provides guidelines for these reports. NSF also requires ERCs to collect and submit to NSF data on indicators of progress, outcome, impact, and financial management. NSF provides data definition guidelines and templates for the recording and submission of these data through a secure web site.
VIII. Agency Contacts
Please note that the program contact information is current at the time of publishing. See program website for any updates to the points of contact.
General inquiries regarding this program should be made to:
For questions related to the use of NSF systems contact:
- NSF Help Desk: 1-800-381-1532
- Research.gov Help Desk e-mail: [email protected]
For questions relating to Grants.gov contact:
Grants.gov Contact Center: If the Authorized Organizational Representatives (AOR) has not received a confirmation message from Grants.gov within 48 hours of submission of application, please contact via telephone: 1-800-518-4726; e-mail: [email protected] .
IX. Other Information
The NSF website provides the most comprehensive source of information on NSF Directorates (including contact information), programs and funding opportunities. Use of this website by potential proposers is strongly encouraged. In addition, "NSF Update" is an information-delivery system designed to keep potential proposers and other interested parties apprised of new NSF funding opportunities and publications, important changes in proposal and award policies and procedures, and upcoming NSF Grants Conferences . Subscribers are informed through e-mail or the user's Web browser each time new publications are issued that match their identified interests. "NSF Update" also is available on NSF's website .
Grants.gov provides an additional electronic capability to search for Federal government-wide grant opportunities. NSF funding opportunities may be accessed via this mechanism. Further information on Grants.gov may be obtained at https://www.grants.gov .
About The National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent Federal agency created by the National Science Foundation Act of 1950, as amended (42 USC 1861-75). The Act states the purpose of the NSF is "to promote the progress of science; [and] to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare by supporting research and education in all fields of science and engineering."
NSF funds research and education in most fields of science and engineering. It does this through grants and cooperative agreements to more than 2,000 colleges, universities, K-12 school systems, businesses, informal science organizations and other research organizations throughout the US. The Foundation accounts for about one-fourth of Federal support to academic institutions for basic research.
NSF receives approximately 55,000 proposals each year for research, education and training projects, of which approximately 11,000 are funded. In addition, the Foundation receives several thousand applications for graduate and postdoctoral fellowships. The agency operates no laboratories itself but does support National Research Centers, user facilities, certain oceanographic vessels and Arctic and Antarctic research stations. The Foundation also supports cooperative research between universities and industry, US participation in international scientific and engineering efforts, and educational activities at every academic level.
Facilitation Awards for Scientists and Engineers with Disabilities (FASED) provide funding for special assistance or equipment to enable persons with disabilities to work on NSF-supported projects. See the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide Chapter II.F.7 for instructions regarding preparation of these types of proposals.
The National Science Foundation has Telephonic Device for the Deaf (TDD) and Federal Information Relay Service (FIRS) capabilities that enable individuals with hearing impairments to communicate with the Foundation about NSF programs, employment or general information. TDD may be accessed at (703) 292-5090 and (800) 281-8749, FIRS at (800) 877-8339.
The National Science Foundation Information Center may be reached at (703) 292-5111.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Purpose. The purpose of your thesis proposal is to introduce your research plan to your thesis committee. You want the committee members to come away understanding what your research will accomplish, why it is needed (motivation), how you will do it (feasibility & approach), and most importantly, why it is worthy of a PhD (significance).
From what to include in your engineering proposal and writing tips to engineering project proposal examples and a free engineering proposal template, we aim to help you create winning proposals. Contents hide. 1 How to Write an ... Do Your Research . Undertaking comprehensive research is a cornerstone in the development of a compelling ...
Template 5: Cover letter for Network Engineering Project Design Proposal. In the realm of network engineering, communication is vital. A well-crafted introduction and prototyping set the stage for your project and introduces the project to stakeholders. It lets you showcase the clients' needs and proposed solutions.
PDF | On Jan 31, 2023, Precious Eberechi Azubuike - Zubi published SAMPLE RESEARCH PROPOSAL | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate ... Engineering Research and Advanced ...
Stay focused on your topic and make sure to fully answer the questions that are asked. Neglecting to answer or not focusing on the questions at hand will hurt your proposal. Guideline 2: Follow directions. Word and character limits, as well as format requirements, are given for a reason.
2. Write an introduction for the engineering project proposal. A brief discussion of the proposal's description can present the need for the engineering project. This part of the engineering project proposal can also help you to present the purpose not only of the project but the usage of the proposal document as well. 3.
Sample Proposals. Before an article, report, or brief is accepted into the Undergraduate Engineering Review, the author must first submit a proposal that specifies the importance of the research, the scope and limitations of the research, and the methods for the research. Submitters should read the journal's Request for Proposals before submitting.
In academia, engineers produce grant proposals or research proposals in order to receive funding from government agencies and non-profit organizations. In industry, engineers, especially consultants, write proposals or "bids." Engineers produce these proposals for the company where they are working or for other organizations.
Your proposal may have additional requirements depending on your project committee chair. Sample 1 (Bicycle brake) Sample 2 (Collapsible cup) Sample 3 (Object detection) Sample 4 (Metamaterial) Sample 5 (Battery) A detailed rundown of how graduate students should go about generating their project proposals for a MS in Mechanical Engineering at ...
SCOPE. Following tasks will be undertaken as a part of the proposed research-. Task 1. Task 2. Task 3, etc. METHODOLOGY AND APPROACH. This section needs to answer self-imposed questions and should reflect that the student has good understanding of the problem and of the barriers in the path.
Before you begin your actual writing process, it is a good idea to have (a) a perspective of the background and significance of your research, (b) a set of aims that you want to explore, and (c) a plan to approach your aims. However, the formation of your thesis proposal is often a nonlinear process. Going back and forth to revise your ideas ...
A research proposal is an obvious and essential part of a Ph.D. application in most parts of the world. It is an outline of your proposed project, whose aim is to present and justify your research idea and explain the practical ways in which you think this research should be implemented. It is often the first opportunity for you to communicate your ideas to attract interest from faculty ...
Masters Research Proposal Guidelines - General Information. This document provides guidelines for writing the research proposal at the master's level (Minor / full dissertation). Please take note of the following before you work carefully through it: Length of the detailed proposal for masters candidates: approximately 3 000 words.
Use our engineering project proposal templates to let you write an introduction, executive summary, description, and design outline with ease. Each proposal template contains a brief free format for a multi or one page engineering plan. With our samples, you can have time to write a proposal letter, presentation, and other economic and business ...
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded research projects in the field of science and technology. Funder. Title. US Geological Survey (USGS) (Mendenhall Postdoctoral Research Fellowship) Using Integrated Population Modelling in Decision-support Tools to Connect Science and Decision Makers.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...
Ecological Engineering (EEE) graduate degree program. This program will provide a leadership role in Indiana's economic and social development by preparing EEE graduates to join a high. uality educated workforce in an area of national need. The creation of graduate degrees in Environmental and Ecological Engineering will contribute to meeting ...
Doctor of Engineering applicants are required to submit a Research Proposal as part of their application. The research laid out in the proposal needs to be of importance to the applicant's employer as it forms the basis for the collaboration between Johns Hopkins Engineering and your company/agency. The research proposals are evaluated both ...
An engineering bid proposal sample can take many forms, and templates exist for all of them, whether an InDesign free proposal template or a civil engineering project proposal sample PDF. ... a Word research proposal template, or an electronics project proposal sample. Again, finding the right format is also just a matter of searching - look ...
proposal, you should always research your audience's background. This way, you will have a better idea about what information to include in your proposal. General Format You can submit a proposal in several ways, depending on your audience. For example, proposing a project to your supervisor may require a phone call or a quick e-mail.
Thesis/Project Proposal Format Thesis Proposal Prior to taking ECE 600 Master's Thesis, a proposal for the thesis research must be prepared by the student in consultation with the Graduate Advisor. The proposal must be approved by the student's ... EGR 500 Engineering Internship: name, signature, date of student's Graduate Advisor.
Engineering Research Proposal Example PDF. lo.unisa.edu.au. Details. File Format. PDF; Size: 543 KB. Download. Making an engineering research proposal can be made easier and more convenient if you have the right tools that will help you get started and and finish the job. And if you are looking for that kind of tool, then you can count on this ...
Founded in 1984, the Engineering Research Centers (ERC) program brings technology-based industry and universities together in an effort to strengthen the competitive position of American industry in the global marketplace. ... Download and use the Word file named "ERC Participants Table Template for Inclusion in Full Proposal." Provide all the ...