

Speechwriting 101: Writing an Effective Speech
Whether you are a communications pro or a human resources executive, the time will come when you will need to write a speech for yourself or someone else. when that time comes, your career may depend on your success..
J. Lyman MacInnis, a corporate coach, Toronto Star columnist, accounting executive and author of “ The Elements of Great Public Speaking ,” has seen careers stalled – even damaged – by a failure to communicate messages effectively before groups of people. On the flip side, solid speechwriting skills can help launch and sustain a successful career. What you need are forethought and methodical preparation.
Know Your Audience
Learn as much as possible about the audience and the event. This will help you target the insights, experience or knowledge you have that this group wants or needs:
- Why has the audience been brought together?
- What do the members of the audience have in common?
- How big an audience will it be?
- What do they know, and what do they need to know?
- Do they expect discussion about a specific subject and, if so, what?
- What is the audience’s attitude and knowledge about the subject of your talk?
- What is their attitude toward you as the speaker?
- Why are they interested in your topic?
Choose Your Core Message
If the core message is on target, you can do other things wrong. But if the message is wrong, it doesn’t matter what you put around it. To write the most effective speech, you should have significant knowledge about your topic, sincerely care about it and be eager to talk about it. Focus on a message that is relevant to the target audience, and remember: an audience wants opinion. If you offer too little substance, your audience will label you a lightweight. If you offer too many ideas, you make it difficult for them to know what’s important to you.
Research and Organize
Research until you drop. This is where you pick up the information, connect the ideas and arrive at the insights that make your talk fresh. You’ll have an easier time if you gather far more information than you need. Arrange your research and notes into general categories and leave space between them. Then go back and rearrange. Fit related pieces together like a puzzle.
Develop Structure to Deliver Your Message
First, consider whether your goal is to inform, persuade, motivate or entertain. Then outline your speech and fill in the details:
- Introduction – The early minutes of a talk are important to establish your credibility and likeability. Personal anecdotes often work well to get things started. This is also where you’ll outline your main points.
- Body – Get to the issues you’re there to address, limiting them to five points at most. Then bolster those few points with illustrations, evidence and anecdotes. Be passionate: your conviction can be as persuasive as the appeal of your ideas.
- Conclusion – Wrap up with feeling as well as fact. End with something upbeat that will inspire your listeners.
You want to leave the audience exhilarated, not drained. In our fast-paced age, 20-25 minutes is about as long as anyone will listen attentively to a speech. As you write and edit your speech, the general rule is to allow about 90 seconds for every double-spaced page of copy.
Spice it Up
Once you have the basic structure of your speech, it’s time to add variety and interest. Giving an audience exactly what it expects is like passing out sleeping pills. Remember that a speech is more like conversation than formal writing. Its phrasing is loose – but without the extremes of slang, the incomplete thoughts, the interruptions that flavor everyday speech.
- Give it rhythm. A good speech has pacing.
- Vary the sentence structure. Use short sentences. Use occasional long ones to keep the audience alert. Fragments are fine if used sparingly and for emphasis.
- Use the active voice and avoid passive sentences. Active forms of speech make your sentences more powerful.
- Repeat key words and points. Besides helping your audience remember something, repetition builds greater awareness of central points or the main theme.
- Ask rhetorical questions in a way that attracts your listeners’ attention.
- Personal experiences and anecdotes help bolster your points and help you connect with the audience.
- Use quotes. Good quotes work on several levels, forcing the audience to think. Make sure quotes are clearly attributed and said by someone your audience will probably recognize.
Be sure to use all of these devices sparingly in your speeches. If overused, the speech becomes exaggerated. Used with care, they will work well to move the speech along and help you deliver your message in an interesting, compelling way.
More News & Resources
Inside Elections Slide Deck - July 2024
July 15, 2024
Pinkham Addresses Public Affairs Leaders in Australia
July 1, 2024
Election Impact: Who’s to Blame for the Aging Presidential Options?
June 18, 2024
Takeaways from First-Year Hogans Fellows
May 15, 2024
Foundation for Public Affairs Announces 2024 Class of Hogans Fellows
April 24, 2024
Volunteer of the Year Was Integral to New Fellowship
November 16, 2023
Is the Fight for the Senate Over?
Benchmarking Reports Reveal Public Affairs’ Growing Status
New Council Chair Embraces Challenge of Changing Profession
October 25, 2023
Are We About to Have a Foreign Policy Election?
Laura Brigandi Manager of Digital and Advocacy Practice 202.787.5976 | [email protected]
Featured Event
Government relations & policy conference.
Covering emerging issues affecting local, state and federal government relations professionals, expand your network while getting answers to your toughest policy questions.
Washington, D.C. | Sept. 25-27
Previous Post Hiring Effectively With an Executive Recruiter
Next post guidance on social media policies for external audiences.
Public Affairs Council 2121 K St. N.W., Suite 900 Washington, DC 20037 (+1) 202.787.5950 [email protected]
European Office
Public Affairs Council Square Ambiorix 7 1000 Brussels [email protected]
Contact Who We Are
Stay Connected
LinkedIn X (Twitter) Instagram Facebook Mailing List
Read our Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | COPYRIGHT 2024 PUBLIC AFFAIRS COUNCIL
- Browse All Content
- Upcoming Events
- On-Demand Recordings
- Team Training with ‘Membership Plus+’
- Earn Your Certificate
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- Content Search
- Connect with Our Experts
- PAC & Political Engagement
- Grassroots & Digital Advocacy
- Communications
- Social Impact
- Government Relations
- Public Affairs Management
- Browse Research
- Legal Guidance
- Election Insights
- Benchmarking, Consulting & Training
- Where to Start
- Latest News
- Impact Monthly Newsletter
- Member Spotlight
- Membership Directory
- Recognition
- Public Affairs Glossary

What are the 10 Principles or Characteristics of Speech Writing with Examples?
Back to: Pedagogy of English- Unit 5
Definition of Speech
According to Oxford Dictionary , “ A speech is a formal talk that a person gives to an audience.”
Speech is one of the major medium of oral communication. We find different speeches in different situations but good speeches are not always found. A good speech is really enjoyable and informative. But it is very tough to deliver a speech that can entertain the audience. A good speech has many characteristics.
Speech is an oral presentation of information or delivery of messages through the use of words of spoken words delivered in front of or to an audience who have gathered in a seminar, meeting, conference, or some other event. It is a form of oral communication which is the oldest method and also the most effective method of communication. Speech is considered to be one of the most effective ways of delivering a message in any event. A speaker can present his thoughts and opinions on various matters to a large group of audience through his or her speech. Due to its efficacy, it is widely used around the world. Be it for social purposes or religious purposes, a speech can come in handy for several kinds of events.
Characteristics of Speech Writing
The 10 principles and characteristics of speech writing are as follows:
(1) Clarity
The voice of the speaker should be clear, tone should vary and pitch should be pleasant. The ideas, emotions and arguments should come straight from the heart so that audience can grasp it easily. It should register with the listeners and vibrate with their feelings and thoughts. A speech is considered to be effective when it is clear and concise. The information presented in the speech should be comprehensible to the present audience and the speech should be delivered by the speaker in a fluent and eloquent manner.
(2) Informal, personal and conversational
A good speech should be like a conversation between two good friends – personal, informal and sincere. There should be a rapport between the speaker and the audience.
(3) Concrete, vivid and imagery
A speech should help build a picture that is easy to visualize and easier to comprehend. It should be furbished by concrete examples that grasp the imagination of the listeners.
(4) Time period
It is very difficult to hold the attention of the listeners for more than 15 to 20 minutes. A good speaker should be able to convey his complete message in that period. He should come straight to the point and say what he wants by bringing three or four points to their attention.
(5) Interesting, jovial and humorous:
A speaker wins or loses the battle in the first two or three minutes. If the speaker has impressed the audience with his opening remarks, he is well on your way to winning a space in their heart. And that is the target. It has to be a heart to heart dialogue. Lace it with short humorous anecdotes – laughter lubricates learning!
Anecdotes should be short, appropriate and in good taste. Quotations, proverbs and idioms should be like arrows piercing directly in to the heart of the audience. Experienced speakers learn to master the art of reciting these statements, giving a long pause after it has been stated to let it sink in with the audience.
(6) Listener-oriented:
Audience is your customer. It is your business to know their needs and wants, their desires and their expectations. Speaker has to be very sensitive to the body language of their audience and modify the speech to fine tune with them. If the message has to gel well with the audience, speakers‟ antenna should pick up the cues from the body language of the listeners.
(7) Dynamic
Dynamism is an important quality of a good speech. There must e variation in style, tone, voice, approach depending on the situation and timing otherwise audience will lose their attention and will suffer form monotonous presentation.
(8) Free From Error
A good speech is always free from error. Error in speech can make the audience confused and loose the personality of the speaker.
(9) Authentic
The facts and figure presented in a speech must be authentic and true. False statement or information misleads the audience and hamper the acceptability of speech.
( 10) Well Organized
A good speech is always well organised and well arranged. The pats or points of a speech should be organized in logical sequence to attract and retain h attention of the audience.
(11) Use rhetorical questions
Rhetorical questions are a great way to engage your audience and make them think. By asking a question that does not require an answer, you can encourage your audience to reflect on your message and consider its implications.
(12) Use inclusive language
Inclusive language is a language that avoids stereotypes or discriminatory terms and includes everyone. Inclusive language is essential when delivering a speech, as it shows respect for your audience and makes them feel valued.
(13) Practice, practice, practice
Finally, one of the most important characteristics of speech writing is practice. Practice delivering your speech in front of a mirror or with friends or family. This will help you refine your delivery and ensure you are comfortable and confident when delivering your speech.
(14) Conciseness
Along with being clear, the message presented through the speech should also be concise so that the speech does not get tedious and does not get boring.
(15) Definiteness
The subject matter presented through the speech should be relevant and definite to the present audience.
(16) Interesting
Apart from being clear and concise, there is also a need for the speech to have an element of interest. This interest should not be limited to the subject matter but rather, the speech itself should be delivered in an engaging and interesting manner.
(17) Audience-centered
The message of the speech should be centered more around the audience rather than the speaker himself or herself.
(18) Speak Slowly
If the speaker speaks too fast, the listeners may lose track of the information being presented and hence, one must speak slowly but not too slowly so asn to put the listeners to sleep.
(19) Unbiased
The information presented in the speech should not be biased and it should be presented from a neutral point of view.
(20) Body Gestures
One should also maintain a proper posture and use appropriate body gestures to deliver the speech.
(21) Ensure Participation Of Audience
Asking questions to the listeners or the audience and involving them is necessary.
(22) Free From Emotions
The speaker should not dwell too much on his or her emotions to ensure that the speech can be delivered in an effective manner.
These are the various characteristics and principles of effective speech writing. Speech writing is a complex but rewarding skill that requires careful consideration of your purpose, audience, language, and delivery. Following these ten characteristics, you can write a powerful and effective speech that will engage your audience and leave a lasting impression. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t be afraid to rehearse your speech until you are confident and comfortable with your delivery.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1.What is speech?
2.What are the characteristics of good speech?
3.According to Author what is defination of speech?
4.Why practice is important in speech?
5.How to write good speech?

Rice Speechwriting
Beginners guide to what is a speech writing, what is a speech writing: a beginner’s guide, what is the purpose of speech writing.
The purpose of speech writing is to craft a compelling and effective speech that conveys a specific message or idea to an audience. It involves writing a script that is well-structured, engaging, and tailored to the speaker’s delivery style and the audience’s needs.
Have you ever been called upon to deliver a speech and didn’t know where to start? Or maybe you’re looking to improve your public speaking skills and wondering how speech writing can help. Whatever the case may be, this beginner’s guide on speech writing is just what you need. In this blog, we will cover everything from understanding the art of speech writing to key elements of an effective speech. We will also discuss techniques for engaging speech writing, the role of audience analysis in speech writing, time and length considerations, and how to practice and rehearse your speech. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how speech writing can improve your public speaking skills and make you feel confident when delivering your next big presentation.
Understanding the Art of Speech Writing
Crafting a speech involves melding spoken and written language. Tailoring the speech to the audience and occasion is crucial, as is captivating the audience and evoking emotion. Effective speeches utilize rhetorical devices, anecdotes, and a conversational tone. Structuring the speech with a compelling opener, clear points, and a strong conclusion is imperative. Additionally, employing persuasive language and maintaining simplicity are essential elements. The University of North Carolina’s writing center greatly emphasizes the importance of using these techniques.
The Importance of Speech Writing
Crafting a persuasive and impactful speech is essential for reaching your audience effectively. A well-crafted speech incorporates a central idea, main point, and a thesis statement to engage the audience. Whether it’s for a large audience or different ways of public speaking, good speech writing ensures that your message resonates with the audience. Incorporating engaging visual aids, an impactful introduction, and a strong start are key features of a compelling speech. Embracing these elements sets the stage for a successful speech delivery.
The Role of a Speech Writer
A speechwriter holds the responsibility of composing speeches for various occasions and specific points, employing a speechwriting process that includes audience analysis for both the United States and New York audiences. This written text is essential for delivering impactful and persuasive messages, often serving as a good start to a great speech. Utilizing NLP terms like ‘short sentences’ and ‘persuasion’ enhances the content’s quality and relevance.
Key Elements of Effective Speech Writing
Balancing shorter sentences with longer ones is essential for crafting an engaging speech. Including subordinate clauses and personal stories caters to the target audience and adds persuasion. The speechwriting process, including the thesis statement and a compelling introduction, ensures the content captures the audience’s attention. Effective speech writing involves research and the generation of new ideas. Toastmasters International and the Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill provide valuable resources for honing English and verbal skills.
Clarity and Purpose of the Speech
Achieving clarity, authenticity, and empathy defines a good speech. Whether to persuade, inform, or entertain, the purpose of a speech is crucial. It involves crafting persuasive content with rich vocabulary and clear repetition. Successful speechwriting demands a thorough understanding of the audience and a compelling introduction. Balancing short and long sentences is essential for holding the audience’s attention. This process is a fusion of linguistics, psychology, and rhetoric, making it an art form with a powerful impact.
Identifying Target Audience
Tailoring the speechwriting process hinges on identifying the target audience. Their attention is integral to the persuasive content, requiring adaptation of the speechwriting process. A speechwriter conducts audience analysis to capture the audience’s attention, employing new york audience analysis methods. Ensuring a good introduction and adapting the writing process for the target audience are key features of a great speech. Effective speechwriters prioritize the audience’s attention to craft compelling and persuasive speeches.
Structuring Your Speech
The speechwriting process relies on a well-defined structure, crucial to both the speech’s content and the writing process. It encompasses a compelling introduction, an informative body, and a strong conclusion. This process serves as a foundation for effective speeches, guiding the speaker through a series of reasons and a persuasive speechwriting definition. Furthermore, the structure, coupled with audience analysis, is integral to delivering a great speech that resonates with the intended listeners.
The Process of Writing a Speech
Crafting a speech involves composing the opening line, developing key points, and ensuring a strong start. Effective speech writing follows a structured approach, incorporating rhetorical questions and a compelling introduction. A speechwriter’s process includes formulating a thesis statement, leveraging rhetorical questions, and establishing a good start. This process entails careful consideration of the audience, persuasive language, and engaging content. The University of North Carolina’s writing center emphasizes the significance of persuasion, clarity, and concise sentences in speechwriting.
Starting with a Compelling Opener
A speechwriting process commences with a captivating opening line and a strong introduction, incorporating the right words and rhetorical questions. The opening line serves as both an introduction and a persuasive speech, laying the foundation for a great speechwriting definition. Additionally, the structure of the speechwriting process, along with audience analysis, plays a crucial role in crafting an effective opening. Considering these elements is imperative when aiming to start a speech with a compelling opener.
Developing the Body of the Speech
Crafting the body of a speech involves conveying the main points with persuasion and precision. It’s essential to outline the speechwriting process, ensuring a clear and impactful message. The body serves as a structured series of reasons, guiding the audience through the content. Through the use of short sentences and clear language, the body of the speech engages the audience, maintaining their attention. Crafting the body involves the art of persuasion, using the power of words to deliver a compelling message.
Crafting a Strong Conclusion
Crafting a strong conclusion involves reflecting the main points of the speech and summarizing key ideas, leaving the audience with a memorable statement. It’s the final chance to leave a lasting impression and challenge the audience to take action or consider new perspectives. A good conclusion can make the speech memorable and impactful, using persuasion and English language effectively to drive the desired response from the audience. Toastmasters International emphasizes the importance of a strong conclusion in speechwriting for maximum impact.
Techniques for Engaging Speech Writing
Engage the audience’s attention using rhetorical questions. Create a connection through anecdotes and personal stories. Emphasize key points with rhetorical devices to capture the audience’s attention. Maintain interest by varying sentence structure and length. Use visual aids to complement the spoken word and enhance understanding. Incorporate NLP terms such as “short sentences,” “writing center,” and “persuasion” to create engaging and informative speech writing.
Keeping the Content Engaging
Captivating the audience’s attention requires a conversational tone, alliteration, and repetition for effect. A strong introduction sets the tone, while emotional appeals evoke responses. Resonating with the target audience ensures engagement. Utilize short sentences, incorporate persuasion, and vary sentence structure to maintain interest. Infuse the speech with NLP terms like “writing center”, “University of North Carolina”, and “Toastmasters International” to enhance its appeal. Engaging content captivates the audience and compels them to listen attentively.
Maintaining Simplicity and Clarity
To ensure clarity and impact, express ideas in short sentences. Use a series of reasons and specific points to effectively convey the main idea. Enhance the speech with the right words for clarity and comprehension. Simplify complex concepts by incorporating anecdotes and personal stories. Subordinate clauses can provide structure and clarity in the speechwriting process.

The Power of Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal cues, such as body language and gestures, can add emphasis to your spoken words, enhancing the overall impact of your speech. By incorporating visual aids and handouts, you can further augment the audience’s understanding and retention of key points. Utilizing a conversational tone and appropriate body language is crucial for establishing a genuine connection with your audience. Visual aids and gestures not only aid comprehension but also help in creating a lasting impression, captivat**ing** the audience with compelling visual elements.
The Role of Audience Analysis in Speech Writing
Tailoring a speech to the audience’s needs is paramount. Demographics like age, gender, and cultural background must be considered. Understanding the audience’s interests and affiliation is crucial for delivering a resonating speech. Content should be tailored to specific audience points of interest, engaging and speaking to their concerns.
Understanding Audience Demographics
Understanding the varied demographics of the audience, including age and cultural diversity, is crucial. Adapting the speech content to resonate with a diverse audience involves tailoring it to the different ways audience members process and interpret information. This adaptation ensures that the speech can effectively engage with the audience, no matter their background or age. Recognizing the importance of understanding audience demographics is key for effective audience analysis. By considering these factors, the speech can be tailored to meet the needs and preferences of the audience, resulting in a more impactful delivery.
Considering the Audience Size and Affiliation
When tailoring a speech, consider the audience size and affiliation to influence the tone and content effectively. Adapt the speech content and delivery to resonate with a large audience and different occasions, addressing the specific points of the target audience’s affiliation. By delivering a speech tailored to the audience’s size and specific points of affiliation, you can ensure that your message is received and understood by all.
Time and Length Considerations in Speech Writing
Choosing the appropriate time for your speech and determining its ideal length are crucial factors influenced by the purpose and audience demographics. Tailoring the speech’s content and structure for different occasions ensures relevance and impact. Adapting the speech to specific points and the audience’s demographics is key to its effectiveness. Understanding these time and length considerations allows for effective persuasion and engagement, catering to the audience’s diverse processing styles.
Choosing the Right Time for Your Speech
Selecting the optimal start and opening line is crucial for capturing the audience’s attention right from the beginning. It’s essential to consider the timing and the audience’s focus to deliver a compelling and persuasive speech. The right choice of opening line and attention to the audience set the tone for the speech, influencing the emotional response. A good introduction and opening line not only captivate the audience but also establish the desired tone for the speech.
Determining the Ideal Length of Your Speech
When deciding the ideal length of your speech, it’s crucial to tailor it to your specific points and purpose. Consider the attention span of your audience and the nature of the event. Engage in audience analysis to understand the right words and structure for your speech. Ensure that the length is appropriate for the occasion and target audience. By assessing these factors, you can structure your speech effectively and deliver it with confidence and persuasion.
How to Practice and Rehearse Your Speech
Incorporating rhetorical questions and anecdotes can deeply engage your audience, evoking an emotional response that resonates. Utilize visual aids, alliteration, and repetition to enhance your speech and captivate the audience’s attention. Effective speechwriting techniques are essential for crafting a compelling introduction and persuasive main points. By practicing a conversational tone and prioritizing clarity, you establish authenticity and empathy with your audience. Develop a structured series of reasons and a solid thesis statement to ensure your speech truly resonates.
Techniques for Effective Speech Rehearsal
When practicing your speech, aim for clarity and emphasis by using purposeful repetition and shorter sentences. Connect with your audience by infusing personal stories and quotations to make your speech more relatable. Maximize the impact of your written speech when spoken by practicing subordinate clauses and shorter sentences. Focus on clarity and authenticity, rehearsing your content with a good introduction and a persuasive central idea. Employ rhetorical devices and a conversational tone, ensuring the right vocabulary and grammar.
How Can Speech Writing Improve Your Public Speaking Skills?
Enhancing your public speaking skills is possible through speech writing. By emphasizing key points and a clear thesis, you can capture the audience’s attention. Developing a strong start and central idea helps deliver effective speeches. Utilize speechwriting techniques and rhetorical devices to structure engaging speeches that connect with the audience. Focus on authenticity, empathy, and a conversational tone to improve your public speaking skills.
In conclusion, speech writing is an art that requires careful consideration of various elements such as clarity, audience analysis, and engagement. By understanding the importance of speech writing and the role of a speech writer, you can craft effective speeches that leave a lasting impact on your audience. Remember to start with a compelling opener, develop a strong body, and end with a memorable conclusion. Engaging techniques, simplicity, and nonverbal communication are key to keeping your audience captivated. Additionally, analyzing your audience demographics and considering time and length considerations are vital for a successful speech. Lastly, practicing and rehearsing your speech will help improve your public speaking skills and ensure a confident delivery.
Expert Tips for Choosing Good Speech Topics
Master the art of how to start a speech.

Popular Posts
How to write a retirement speech that wows: essential guide.
June 4, 2022
Inspiring Awards Ceremony Speech Examples
November 21, 2023
The Best Op Ed Format and Op Ed Examples: Hook, Teach, Ask (Part 2)
June 2, 2022
Short Award Acceptance Speech Examples: Inspiring Examples
Mastering the art of how to give a toast, mastering the father of the bride toast: unforgettable tips.
Oral Communication in Context Module: Principles of Speech Writing
This Self-Learning Module (SLM) is prepared so that you, our dear learners, can continue your studies and learn while at home. Activities, questions, directions, exercises, and discussions are carefully stated for you to understand each lesson.
Each SLM is composed of different parts. Each part shall guide you step-by-step as you discover and understand the lesson prepared for you.
Pre-tests are provided to measure your prior knowledge on lessons in each SLM. This will tell you if you need to proceed on completing this module or if you need to ask your facilitator or your teacher’s assistance for better understanding of the lesson.
In the previous lesson, speech was classified according to purpose: the expository or the informative speech, the persuasive speech and the entertainment speech. The manner of delivery was also discussed such as: reading or speaking from the manuscript, memorized speech, impromptu speech and extemporaneous speech. Knowing all these will lead you to be able to learn the basics of preparing a speech. But what makes the best speech. How do we deliver the speech we prepared effectively? All our questions will be answered by understanding by heart the principles of speech writing.
After going through this module, you are expected to:
1. identify the principles, techniques and process in writing;
2. set clear objectives in writing speech;
3. use the principles of effective speech writing in developing one’s speech.
Oral Communication in Context Quarter 2 Self-Learning Module: Principles of Speech Writing
Can't find what you're looking for.
We are here to help - please use the search box below.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Get in touch with us – here
- About Ginger
- About Leadership
- All programmes and courses
- Purpose-Driven Leadership
- Storytelling Mastery
- 1-2-1 training/coaching
- Elevate your Influence
- Executive Presence
- Present with Influence
- Public Speaking Foundations
- Assertive Communications
- Boosting Visibility and Confidence
- Building Your Personal Brand
- Clear & Concise Communications
- Courageous Communications
- Fearless Feedback
- High-Impact Communications
- Messages that Stand Out From the Crowd
- The Essentials of Storytelling for Business
- Virtually Brilliant for Online Communicators
- hello@gingerleadershipcomms.com
- +44 (0) 207 3888 645
Speech Writing: How to write a speech in 5 steps

Every great speech starts with an idea, be it for school or work or a TED talk about your area of speciality. We investigate how to get all those ideas from your head to a written speech and then back to your heart. Author of “ How to be Brilliant at Public Speaking “, Sarah Lloyd-Hughes explains the five steps of speech writing…
Even heads of state and other renowned orators have help in writing a speech. They often have professional speech writers to provide them with great content, but you too can learn not only how to talk but also how to write a speech like a pro.
Here are 5 steps that we take our speakers through when they’re writing a speech – and it’s the same process as we use for writing TED style talks.
Speech writing step 1: Get focused
TED talks famously focus on ‘one idea worth spreading’ and this is what helps them to retain their power. Before you write a single line, figure out what the ONE idea is that you’ll shape your talk around.
When your talk has a single focus you’ll see huge benefits:
- Clarity: For yourself and your audience.
- Easy to pass on: Popular talks, like Simon Sinek’s TED talk ‘ How great leaders inspire action ‘ or Ken Robinson’s TED favourite ‘ Do schools kill creativity? ‘ are utterly focused and easy to pass on because they have just one idea.
- Powerful: When you’re digging in one hole you get deeper, likewise with your talk you can go further with one idea.
- Memorability: Audiences these days are overwhelmed with ideas and information. You need to be much simpler than you think to stand a chance of your message being remembered.
To find your ‘idea worth spreading’ takes a little time and skill, which is why we’ve devised a complete programme for speakers who are interested in writing World Class Speeches , like the finest TED speakers.
But if you’re just looking for a place to start, these questions will help you get going:
- What do I want to say?
- What effect am I trying to have by speaking?
- If I can only put across one message in my speech, what will that be?
- What is my broader purpose in speaking?
You’re looking for one idea that is clear, interesting and hasn’t been heard before. Good luck!
Speech writing step 2: Think about your audience
Ironically, most speakers completely fail to think about their audience! Yet the best speakers are intimately aware of the needs, questions and doubts facing their audience.
Ask: To whom am I speaking? Before you start writing you first must ask yourself Who is my audience and what are they seeking ? Writing a speech for a group of human rights activists would be very different to a speech for business managers. Technology engineers might have a totally different perspective on your subject than a room full of English professors. Thinking deeply about your audience’s needs is the quality of a public speaker I call Empathy. It’s an important starting point on your speech writing journey.
Ask: Why should they listen to you? Great speech writing is grounded in purpose and message. Consider what qualifies you to speak; what you have to offer the audience that they would not be able to hear from anyone else (we all have something).
Ask: What do you want to leave your audience with? As a result of your Empathetic investigations, what would be your desired outcome as a result of the speech? Decide what your main message will be and continually return to that primary point as you compose your speech. This keeps the audience (and you) focused. As Winston Churchill said: “If you have an important point to make, don’t try to be subtle or clever. Use a pile driver. Hit the point once. Then come back and hit it again. Then hit it a third time with a tremendous whack. ”
Speech writing step 3: Build up your speech
Now you have a clear focus to your speech and an idea of how to communicate that clearly to your audience. That’s the skeleton of the speech. It’s now time to fill in that skeleton with meaty content:
- Brain Storming. Make lists of all the things you want to speak about. Once listed, it will be easier to cut or rearrange your points.
- Categorize for the win. Brainstorming should lead to a nice list with several categories. Speech writing is all about organization and finding what fits best with your audience and their needs. Think of these categories as stepping stones. Leaving a gap too large between any two stones and they will turn into stumbling blocks will sinking you and your audience. Speech writing is not very much different than writing a paper; thesis statement, support of the thesis, and a conclusion.
- Edit for the jewels . Look for the key moments in your speech that will stimulate the hearts, minds and even stomachs of your audience. Seek the most vivid experiences and stories that you can use to make your point – these are what will make your speech stand out from all the other public speaking our there.
Speech writing step 4: Create a journey
Another key skill of speech writing is to get the right information in the right order. Think of your speech like a journey up a mountain:
Get ready for the trip (introduction).
- The beginning of your speech is the place where you grab the attention of the audience and get them ready to go on a journey with you. For them to travel up your mountain with you they need to know where you’re going together, why it’s an interesting journey to go on and why you are a credible guide to lead them there.
Pass some interesting sights on the way (main body).
- Keep an audience engaged for an entire speech by raising the stakes, or raising the tension as you progress through the speech. Think about contrasts between the ‘good’ and the ‘evil’ of your subject matter and contrast the two with stories, facts, ideas or examples.
- Here you might write multiple sections to your speech, to help you stay focused. You might like to write an introduction, main body, and conclusion for each section also. All sections don’t have to be the same length. Take time to decide and write about the ones that need the most emphasis.
Reach your summit (climax).
- The climax is the moment of maximum emotional intensity that most powerfully demonstrates your key message. Think of the key ‘Ahah!’ moment that you want to take your audience to. This is the moment where you reach the top of your mountain and marvel at the view together. It’s a powerful, but underused speech writing tool.
A speedy descent (the close).
- Once you’ve hit your climax, the story is almost over. We don’t want to go all the way down the mountain with you, we’d much rather get airlifted off the top of the mountain whilst we still have the buzz of reaching our goal. This is what great speech writing manages time and again.
- Strangely enough the close can be the hardest part of speech writing. Here’s where you get to hit home your action point – the key thing you want your audience to do differently as a result of listening to your speech. Often the close is where speakers undermine the power of the rest of their speech. So, write a memorable conclusion that captures the essence of your speech, give it some punch, and stick to it!
Speech writing step 5: Test your material
Practice your speech several times so that you can feel comfortable with the material. Try the speech out on camera or to a friend to see which parts are most powerful and which you can take the red pen to.
However skilled you are (or not) at speech writing, remember that you are the magic that makes the speech work. It’s your authentic voice that will shine to the audience them and inspire them towards your message.
Follow these speech writing tips, give it some practice and you’ll be sure to be a speech writing winner.
But I’ve collected my years of experience working with world-class conference speakers and TED speakers and distilled it into a simple guidebook that you can access now for just £20 (+VAT) .
Ginger Leadership Communications
This showcase of inspiring female speakers is part of Ginger’s work with game changing leaders.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
12.5 Organizing Principles for Your Speech
Learning objective.
- Identify and understand how to use at least five different organizing principles for a speech.
There are many different ways to organize a speech, and none is “better” or “more correct” than the others. The choice of an organizing principle , or a core assumption around which everything else is arranged, depends on the subject matter, the rhetorical situation, and many other factors, including your preference as speaker.
The left column of Table 12.6 “Sample Organizing Principles for a Speech” presents seventeen different organizing principles to consider. The center column explains how the principle works, and the right column provides an applied example based on our sample speech about the First Transcontinental Railroad. For example, using a biographical organizing principle, you might describe the journey of the Lewis and Clark expedition in 1804; the signing of the Pacific Railroad Act in 1862, and the completion of the first Transcontinental Express train trip in 1876. As another example, using a spatial organizing principle, you might describe the mechanics of how a steam locomotive engine works to turn the train wheels, which move on a track to travel across distances.
As you read each organizational structure, consider how the main points and subheadings might change or be adapted to meet each pattern.
Table 12.6 Sample Organizing Principles for a Speech
| Organizing Principle | Explanation | Applied Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Time (Chronological) | Structuring your speech by time shows a series of events or steps in a process, which typically has a beginning, middle, and end. “Once upon a time stories” follow a chronological pattern. | Before the First Transcontinental Railroad, the events that led to its construction, and its impact on early America… |
| 2. Comparison | Structuring your speech by comparison focuses on the similarities and/or differences between points or concepts. | A comparison of pre– and post–First Transcontinental Railroad North America, showing how health and life expectancy remained the same. |
| 3. Contrast | Structure your speech by using contrasting points highlights the differences between items and concepts. | A contrast of pre– and post–First Transcontinental Railroad North America, by shipping times, time it took to communicate via letter, or how long it took to move out West. |
| 4. Cause and Effect | Structuring your speech by cause and effect establishes a relationship between two events or situations, making the connection clear. | The movement of people and goods out West grew considerably from 1750 to 1850. With the availability of a new and faster way to go West, people generally supported its construction. |
| Organizing Principle | Explanation | Applied Example |
|---|---|---|
| 5. Problem and Solution | Structuring your speech by problem and solution means you state the problem and detail how it was solved. This approach is effective for persuasive speeches. | Manufacturers were producing better goods for less money at the start of the Industrial Revolution, but they lack a fast, effective method of getting their goods to growing markets. The First Transcontinental Railroad gave them speed, economy, and access to new markets. |
| 6. Classification (Categorical) | Structuring your speech by classification establishes categories. | At the time the nation considered the First Transcontinental Railroad, there were three main types of transportation: by water, by horse, and by foot. |
| 7. Biographical | Structuring your speech by biography means examining specific people as they relate to the central topic. | |
| 8. Space (Spatial) | Structuring your speech by space involves the parts of something and how they fit to form the whole. | A train uses a heat source to heat water, create stream, and turn a turbine, which moves a lever that causes a wheel to move on a track. |
| 9. Ascending and Descending | Structuring your speech by ascending or descending order involves focusing on quantity and quality. One good story (quality) leads to the larger picture, or the reverse. | A day in the life of a traveler in 1800. Incremental developments in transportation to the present, expressed through statistics, graphs, maps and charts. |
| 10. Psychological | It is also called “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence” (Ayres, J. and Miller, J., 1994). Structuring your speech on the psychological aspects of the audience involves focusing on their inherent needs and wants. See Maslow and Shutz. The speaker calls to a , then focuses on the satisfaction of the need, of the solution, and ends with a proposed or historical . This is useful for a persuasive speech. | When families in the year 1800 went out West, they rarely returned to see family and friends. The country as a whole was an extension of this distended family, separated by time and distance. The railroad brought families and the country together. |
| 11. Elimination | Structuring your speech using the process of elimination involves outlining all the possibilities. | The First Transcontinental Railroad helped pave the way for the destruction of the Native American way of life in 1870. After examining treaties, relocation and reservations, loss of the buffalo, disease and war, the railroad can be accurately considered the catalyst for the end of an era. |
| 12. Ceremonial: Events, Ceremonies, or Celebrations | Structure your speech by focusing on the following: | Thanking the representatives, builders, and everyone involved with the construction of the Transcontinental Railroad. The railroad will unite America, and bring us closer in terms of trade, communication and family. Thank you for participating in today’s dedication. |
| 13. Awards | Structure your speech by focusing on the following: | >Thank everyone for coming together. The Golden Spike Award was created in honor of all the great men and women that made today possible. The person receiving this award needs no introduction. His/her tireless efforts to build partnerships, coalitions, and raise support for the railroad have been unwavering. (Name), please come and receive the Golden Spike Award. (Speech/no speech.) Thank you, everyone, for coming. |
| 14. Toast: Weddings or Similar Gatherings | Structure your speech by focusing on the following: | Thank everyone for coming together. I’ve know the groom since he played with toy trains and only now, with (partner’s name), can I see how far his involvement in our new cross-country train got him. “All the best of healthy and happiness.” Thank you everyone for joining us in this celebration of (name) and (name) (point 5 is optional). |
| 15. Speaker Introductions | Structure your speech by focusing on the following: | Thank everyone for coming together. Today’s speaker has a long history in the development of the train, including engineering technical aspects of steam locomotion. Today he/she will address the steps that lead to our very own cross-country railroad. Please help me welcome (name). (Optional after speech: Thank you, everyone. Next we have…) |
| 16. After-Dinner Speech | Structure your speech by focusing on the following: | Thank you for coming together to celebrate the driving of the Golden Spike. There have been many challenging moments along the way that I would like to share tonight (stories, anecdotes, or even a joke). While it’s been a long journey, we’ve made it. Thank you for coming tonight. |
| 17. Oral Interpretation | Structure your speech by focusing on the following: | Today I would like to share with you the proclamation that led to the railroad you see before you today. (Interpret the proclamation, using your voice to bring the written word alive.) Without the foresight, vision and leadership we can now see, this railroad might still be a dream. |
Key Takeaway
A speech may be organized according to any of many different organizing principles.
- Choose at least three different organizing principles from the left column of Table 12.6 “Sample Organizing Principles for a Speech” . Take the thesis of a speech you are preparing and write an applied example, similar to the ones provided about the First Transcontinental Railroad that shows how you would apply each of your chosen organizing principles to your speech.
- Think of one technology or application that you perceive has transformed your world. Choose two organizing principles and create two sample outlines for speeches about your topic. Share and compare with classmates.
Ayres, J., & Miller, J. (1994). Effective public speaking (4th ed., p 274). Madison, WI: Brown & Benchmark.
Maslow, A. (1970). Motivation and personality (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Harper & Row.
Shutz, W. (1966). The interpersonal underworld . Palo Alto, CA: Science and Behavior Books.
Business Communication for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- List of Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Opt-out preferences
The 7 C’s of Effective Communication – Explained with Examples
An effective communication takes place when the message sent across by the conveyer is clear and easily comprehended by the receiver and relevant response is fed back to the one who conveyed the message and the flow continues similarly.

Source: Kurhan/Adobe Stock
Although communication takes place at all times, if it is done effectively is a matter of dispute. For the most part, people don’t communicate efficiently, and this has been one of the predominant contributors to interpersonal conflicts.
Lack of proper listening, psychological conditions, poor comprehension skills, absence of mind, ambiguity in the message conveyed, and improper usage of words are some of the most frequently occurring mistakes during conversations.
So what makes communication effective? What are some of the tips and strategies that can be applied when communicating in general?
We are constantly in touch with people, texting, sending emails, creating reports, attending conferences and whatnot. So how can we scale up our communication game? What would make us stand out and seem distinctive in this world swarming with competitors?
The 7 C’s of Effective Communication
The 7 C’s of communication is an excellent strategy formulated by Scott Cutlip and Allen Center in the year 1952 in his book “Effective public relations”. This came to be utilized by people across the globe and is one of the most operative strategies used to date.
It involves the following C’s:
- Completeness
- Correctness
- Conciseness
- Consideration
- Concreteness
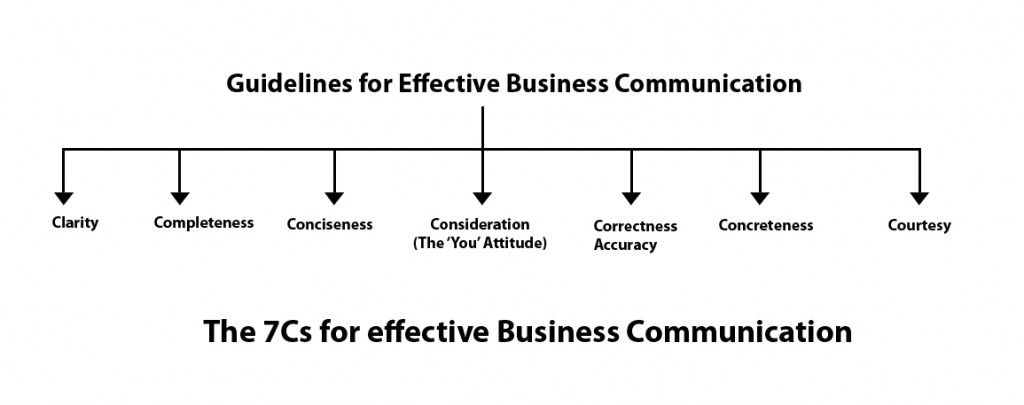
These strategies apply to both written and oral communication . The one who is aware of and makes use of these 7C’s in a sensible manner can become a good and effective communicator.
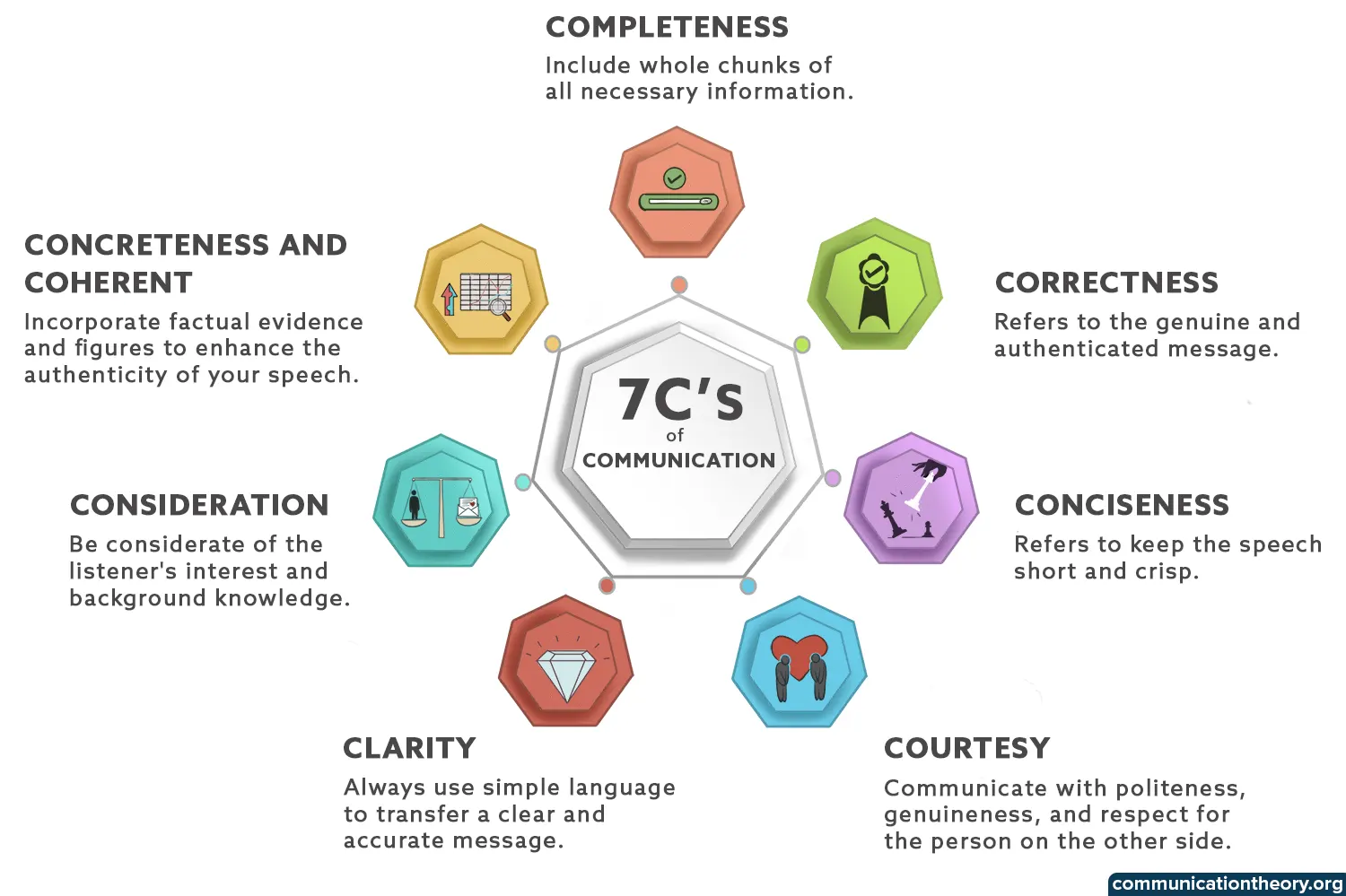
1. Completeness
This is one of the most significant aspects of effective communication . Completeness refers to giving full information about something rather than just saying it in bits and pieces. It’s the right of the recipient to receive access to the whole chunk of information to be able to follow the sender’s line of reasoning in regards to the matter being discussed.
For example, when Peter told “write a short passage on data science and send me”, Shawn couldn’t understand the context whatsoever. He had too many questions in his head about the topic, its length and the style of writing, where this piece of writing go etc.
Instead, Peter could frame his instructions as “Shawn I want you to write a 100-200 word short essay on the recent trends in data science. Submit it to me by the end of this day. I need it for our blog.”
Completeness holds much higher salience during the delegation of tasks when the subordinates need detailed instructions to pursue a task at hand.
2. Correctness
The genuineness and the value of your speech lie in its correctness and authenticity. It’s better to keep quiet rather than talk about something that you aren’t so sure of. The correctness of the speech would reflect directly on your personality and so it should be given utmost prominence.
The legitimacy of the factual information, the language used and grammar are some of the aspects of correctness amongst others.
If your audience spots any errors or blunders in your speech, it is no longer valued and they are likely to be distracted. The credibility of the speaker would also receive a massive hit and therefore the effectiveness of the communication will be compromised.
Related: Language Barriers
3. Conciseness
Conciseness is to keep the speech short and crisp. Nobody likes listening to someone who delivers long and draggy speeches because people lose interest and attention very easily. When interacting or delivering the speech, the ultimate objective is to make sure that the message is received in its intended form. Lack of conciseness will lead to the loss of essence in the content. Make sure to keep your speech brief and precise.
For example,
Intended message: “could you please receive Amanda from the airport?”
Delivered method: “Yesterday was a tiring day. Last night I couldn’t sleep properly. My wife has severe migraine and she’s down. I couldn’t have breakfast in the morning and I am tired. Amanda has taken her flight from Indonesia last night. She would reach here in some time. It would be nice if someone could pick her up from the airport.”
In this example, the message was simple. Yet, the sender makes it seem complicated and leaves the recipient feeling puzzled, irritated or exhausted. Also, he may deny the request. Such delivery of a message makes the message lose its value.
Related: Semantic Barriers
4. Courtesy
Courtesy refers to communicating with politeness, genuineness and respect for the person on the other side of the conversation. It will naturally scale up the value of communication. Courtesy is a tendency which stems out of empathy for people.
To be courteous doesn’t mean just use polite, magical phrases like “thank you”, “sorry”, “please” and “excuse me”. It also means to be honest, respectful and empathetic of people and not make sarcastic or any other form of passive-aggressive remarks.
One classic example would be from the infamous movie “Mean Girls” where Regina would tell a fellow classmate about how she loves the skirt she was wearing. As the girl leaves, Regina would tell her friend Cady how that was the ugliest skirt she has ever seen. This is an example of how you should not communicate.
In many instances, people use the power of their intellect and status to belittle the plight of others. This is so especially among those who bully the perceivably weaker ones for their timidity, racial backgrounds, gender, and color among many other aspects.
The global star Priyanka Chopra narrates in an interview about her high school days when she was severely bullied by her schoolmates. She was called names like “brownie” for her skin color and her ethnicity so much so that she was forced to have lunch inside a toilet cubicle.
Related: Assertive Communication
Clarity is to transfer accurate and easily comprehendible messages to the receiver. Before choosing to talk, be clear about your goals for the conversation. Let the other person know what your objective is for the interaction. To make your speech clear, always use simple language rather than using intricate phrases that would make comprehension difficult.
The recipient shouldn’t be made to “read between the lines”. Even if the content is complicated in nature, try to divide your ideas, distill it and make it as simple and clear as possible as that would make it easy for the receiver to grasp the information well.
6. Consideration
Consideration is quite similar to that of courtesy. It means to consider the other person and to address them putting you in their place. In other words, you talk to someone in a way you would want someone to talk to you.
For example, if you prefer someone to talk to you with respect and politeness, you would exhibit the same behaviors towards others. Just as that of courtesy, one should be inherently empathetic to be able to show consideration for the other person. When you are considerate, you sincerely regard people’s interests and benefits.
To be considerate also means to acknowledge the situational factors of the audience that you address. If you are going to give a talk on astrophysics amongst a bunch of seven-year-olds, the only response you would receive would be the sound of yawning and snoring; maybe even a giggle here and there if you’re lucky.
So when you talk to someone, remember to acknowledge their background such as their age, language proficiency, culture, literacy level, mental state, character, interests etc. so that you may be relatable to your audience and your intended message reaches them successfully.
7. Concreteness
Concrete communication denotes your message being specific, meaningful and focused. You don’t beat around the bush to get to a point. Rather it is solid and concise. You avoid vague and ambiguous messages and only strive toward making your information well received by the recipient. Your speech is crisp yet brimming with beneficial information. You incorporate factual evidence and figures to enhance the authenticity of your speech.
For example, when you say “Depression is a global issue”, you don’t just bluntly make that claim but also pitch in the statistical values and empirical evidence to support your statement.
And now, for your upcoming presentations make sure to follow these strategies and show up your confidence. These effective strategies may take you to the place of success at your workplace.
Best of luck!
Related Posts:
- Active Listening Skills - Techniques And Tips To Practice It
- Conflict Management - Skills, Styles And Models
- Most Important Social Skills - Explained With Examples
- Effective Listening Skills
- Various Types Of Communication Styles - Examples
- Non-Verbal Communication
these are the best or very good note that helps me in hawassa university while learning the business communication.
Assalamaoalikum ! Sir please give me full detail in one by one …thankyou
do you have complete intodution to 7Cs of effective bussiness communication?
I want to get detail of these seven c’s .Thank you
please whould you like to send thise cs in detail
please so the detail of 7c’s thanks …………………………………………………..
plz give me more detail
give more detail but notes is best
plz give me defination of each c’s
kindly give the explanation of these C’s.
Good post thank
I want to know more about the seven c’s
This is very very helpfull in my exam Thank you so much for all your efforts. This is best and very simple to understand.
This is very helpful, thanks for your post.
Ma sha Allah very gud and informative…
Leave a Comment
Next post: Clarity/Clearness for effective business Communication
Previous post: Features of Business Communication
- Advertising, Public relations, Marketing and Consumer Behavior
- Business Communication
- Communication / General
- Communication Barriers
- Communication in Practice
- Communication Models
- Cultural Communication
- Development Communication
- Group Communication
- Intercultural Communication
- Interpersonal Communication
- Mass Communication
- Organisational Communication
- Political Communication
- Psychology, Behavioral And Social Science
- Technical Communication
- Visual Communication
Communication Theory
Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

11th - 12th
Nature of academic texts, past tense and past perfect tense, 34.8k plays, parts of a paragraph, 3rd - 5th , cohesive devices, academic writing quiz, argumentative essay, 9th - 10th , argumentative writing.

Principles of Speech Writing
10th - 12th grade.
10 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
Which of the following principles is not included in creating an effective speech writing?
Audience Profile
Articulation
Logical Organization
Word Choice
These are specific words or phrases used by a certain individual or group which are difficult for others to understand.
It is the focal point of your speech.
Introduction
It is one of the written patterns that resent cause-effect relationship.
Problem-solution
Chronological
Biographical
Which of the following statements is not a function of a good introduction?
It serves as the core part of a speech.
It states the purpose of the speech.
It should provide reasons for the audience to listen.
It should preview the main idea of the speech.
According to Grant (2017), most experts say that the ideal length of speech is up to ______ minutes.
Which of the following purposes for writing and delivering speech is not included?
To entertain
To persuade
What writing patter is used in the following example?
"Describing the life and works of former President Magsaysay."
It restates the main idea of your speech.
True or False: The primary goal of the introduction is to get the attention of the audience.
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Vary the sentence structure. Use short sentences. Use occasional long ones to keep the audience alert. Fragments are fine if used sparingly and for emphasis. Use the active voice and avoid passive sentences. Active forms of speech make your sentences more powerful. Repeat key words and points.
The voice of the speaker should be clear, tone should vary and pitch should be pleasant. The ideas, emotions and arguments should come straight from the heart so that audience can grasp it easily. It should register with the listeners and vibrate with their feelings and thoughts. A speech is considered to be effective when it is clear and concise.
There is 1 module in this course. Fundamentals of Speechwriting is a course that enhances speechwriting skills by deepening learners' understanding of the impact of key elements on developing coherent and impactful speeches. It is aimed at learners with experience writing and speaking who wish to enhance their current skills.
We focus on the "public" at the expense of the "speaking.". To become effective at public speaking, you must do just the opposite: focus on the speaking and let go of the "public.". Think of it as a conversation between you and the audience. If you can carry on a relaxed conversation with one or two people, you can give a great speech.
What are the different parts of a written speech? How do we write an effective speech? What do we need to consider in crafting effective speeches?Credits:Cre...
The speechwriting process relies on a well-defined structure, crucial to both the speech's content and the writing process. It encompasses a compelling introduction, an informative body, and a strong conclusion. This process serves as a foundation for effective speeches, guiding the speaker through a series of reasons and a persuasive ...
5. Be authentic. Authenticity is key when it comes to delivering a powerful and effective speech. Be yourself and speak from the heart. Your audience will appreciate your honesty, which will help build a connection with them. 6. Use humor. Humor is a powerful tool that can help you connect with your audience and make your speech memorable ...
All our questions will be answered by understanding by heart the principles of speech writing. After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. identify the principles, techniques and process in writing; 2. set clear objectives in writing speech; 3. use the principles of effective speech writing in developing one's speech.
convictions, and style, can help create a speech that can be a "seamless garment" when delivered by the Member. Writing For The Spoken Word: The Distinctive Task of The Speechwriter Writing effective speeches requires a constant awareness of the distinction between the written and the spoken word: the speechwriter must learn to "write ...
Speech writing step 1: Get focused. TED talks famously focus on 'one idea worth spreading' and this is what helps them to retain their power. Before you write a single line, figure out what the ONE idea is that you'll shape your talk around. When your talk has a single focus you'll see huge benefits: Clarity: For yourself and your audience.
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Learning how to write a speech requires a keen awareness of how to tailor your rhetoric to a given issue and specific audience. Check out our essential speech-writing guidelines to learn how to craft an effective message that resonates with your audience.
This publication about speech writing and types of speeches is the second of a three-part series about developing effective public speaking skills. This series also covers an introduction to public speaking and public speaking tools. University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences Extension outreach is a partnership between ...
A successful speech is one that engages the audience and expresses a subject or set of topics clearly. Writing and delivering an effective speech could help to advance your career by developing and displaying strong communication, leadership and interpersonal skills.In this article, we explain steps and tips for how to write an effective speech that illustrates your subject and captures your ...
Table 12.6 Sample Organizing Principles for a Speech. Organizing Principle. Explanation. Applied Example. 1. Time (Chronological) Structuring your speech by time shows a series of events or steps in a process, which typically has a beginning, middle, and end. "Once upon a time stories" follow a chronological pattern.
Principles of effective speech writing | Public speaking1. Choosing a subject and topic2. Know your audience3. Sourcing information00:00 Introduction01:09 Le...
Courtesy. Clarity. Consideration. Concreteness. These strategies apply to both written and oral communication. The one who is aware of and makes use of these 7C's in a sensible manner can become a good and effective communicator. 1. Completeness. This is one of the most significant aspects of effective communication.
To develop an effective speech, you should turn to the wonderful world of rhetoric. Rhetoric is the art of increasing your effectiveness in persuasive writing, and speaking to an audience. A ...
Vary your sentence structure and length. If you write exclusively in short, punchy sentences, your prose will sound singsong. If you write exclusively in long sentences, your prose will be tiring and needlessly difficult for your readers. Aim for an elegant balance in each paragraph. Build your sentences and paragraphs around specific, concrete ...
Get a hint. 4 Principles of Speech Writing. Click the card to flip 👆. 1. Choosing a Topic 2. Analyzing the Audience 3. Sourcing the Information 4. Outlining and Organizing the Speech Contents. Click the card to flip 👆.
7. Multiple Choice. The approach that you will use in your introduction can determine the success of your speech. 8. Multiple Choice. The primary objective of speech writing is getting the right or appropriate topic. 9. Multiple Choice. The purpose of the speech will help you identify ideas that will support your main idea or message.
Principles of Speech Writing. 1. Multiple Choice. Which of the following principles is not included in creating an effective speech writing? 2. Multiple Choice. These are specific words or phrases used by a certain individual or group which are difficult for others to understand. 3. Multiple Choice.